Abstract
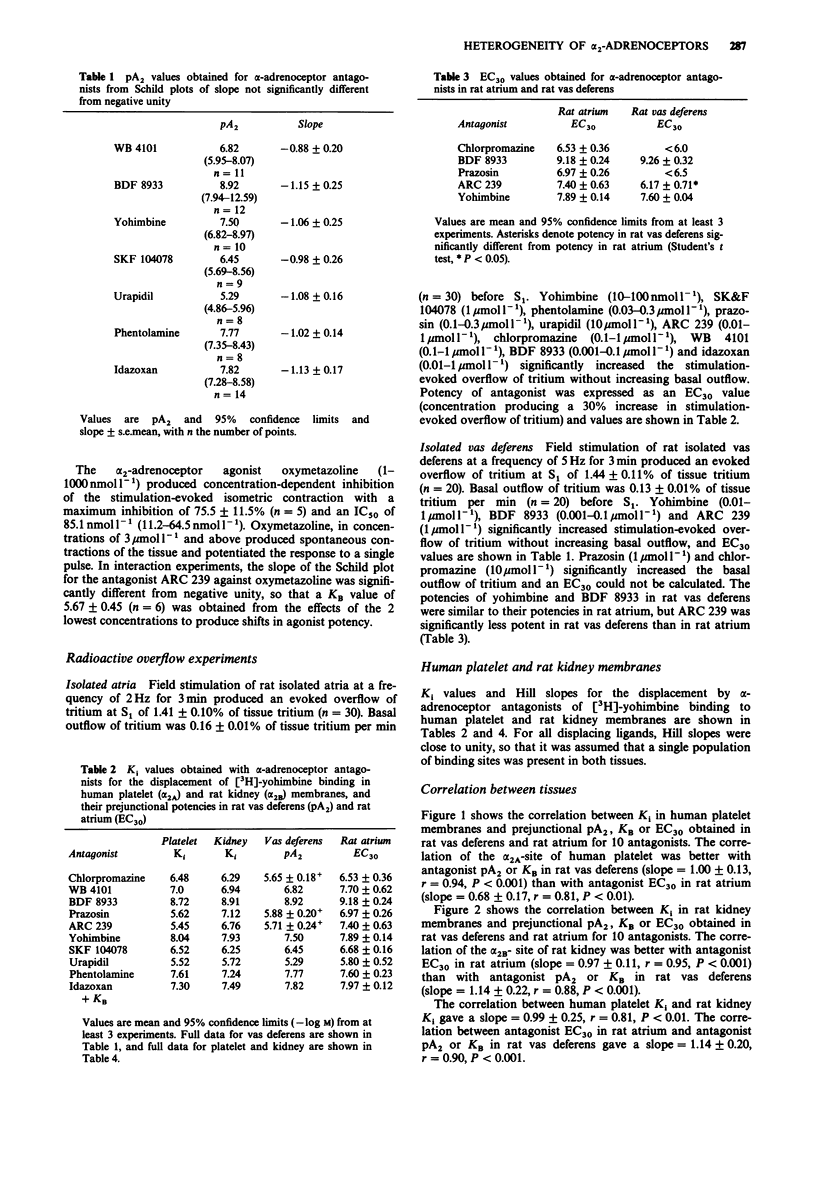
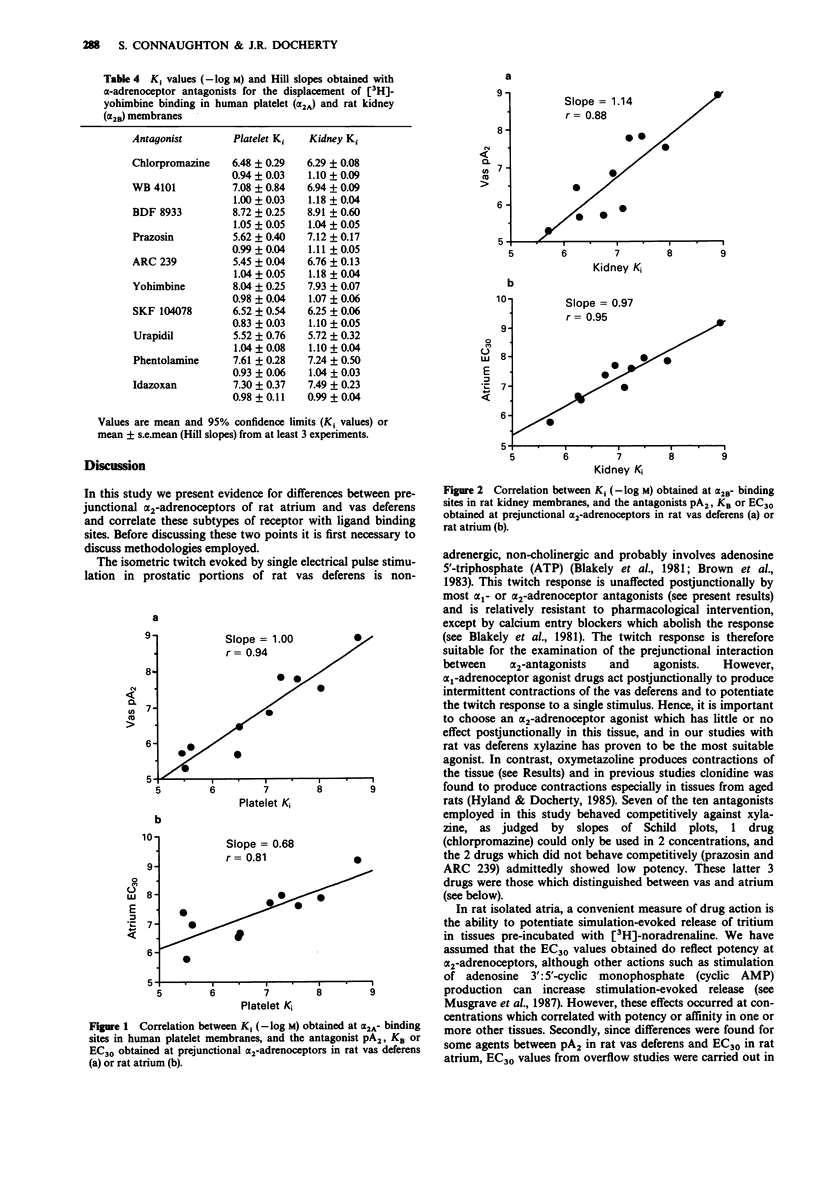
1. We have examined the potencies of a series of alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists in functional studies of prejunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rat atrium and vas deferens, and compared potencies with affinities for the alpha 2A-ligand binding site of human platelet and the alpha 2B-site of rat kidney. 2. Antagonist potency in rat atrium was expressed as an EC30 (concentration producing 30% increase in the stimulation-evoked overflow of tritium in tissues pre-incubated with [3H]-noradrenaline). Antagonist potency in rat vas deferens was expressed as a pA2 or KB at antagonizing the inhibition by the alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist xylazine of the isometric twitch to a single stimulus, or as an EC30. 3. In ligand binding studies, Ki values were obtained for the displacement by alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists of [3H]-yohimbine binding to human platelet or rat kidney membranes. 4. In functional studies, three antagonists (ARC 239, prazosin and chlorpromazine) distinguished between prejunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors of rat atrium (EC30) and rat vas deferens (pA2) and showed 49, 12 and 7 times higher potency in rat atrium, respectively. ARC 239 was also 17 times more potent in rat atrium than rat vas deferens when EC30 values were compared. 5. The correlation of affinity for the alpha 2A-site of human platelet was better with prejunctional potency in rat vas deferens than rat atrium. 6. The correlation of affinity for the alpha 2B-site of rat kidney was better with prejunctional potency in rat atrium than rat vas deferens.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeley A. G., Brown D. A., Cunnane T. C., French A. M., McGrath J. C., Scott N. C. Effects of nifedipine on electrical and mechanical responses of rat and guinea pig vas deferens. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):759–761. doi: 10.1038/294759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Docherty J. R., French A. M., MacDonald A., McGrath J. C., Scott N. C. Separation of adrenergic and non-adrenergic contractions to field stimulation in the rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):379–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11010.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley C., Curtin D., Walsh T., O'Malley K. Ageing and platelet alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;21(6):721–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb05238.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B. Heterogeneity of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1985 May;22(5):835–843. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(85)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., Ray-Prenger C., Murphy T. J. Alpha-2A and alpha-2B adrenergic receptor subtypes: antagonist binding in tissues and cell lines containing only one subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 May;245(2):600–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B. Subtypes of alpha 2-adrenoceptors: pharmacological and molecular biological evidence converge. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Oct;9(10):356–361. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung Y. D., Barnett D. B., Nahorski S. R. [3H]Rauwolscine and [3H]yohimbine binding to rat cerebral and human platelet membranes: possible heterogeneity of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Oct 15;84(1-2):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90159-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connaughton S., Docherty J. R. No evidence for differences between pre- and postjunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the periphery. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan;99(1):97–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14660.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R. The pharmacology of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptors: evidence for and against a further subdivision. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;44(2):241–284. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyland L., Docherty J. R. Further examination of the effects of ageing on the adrenoceptor responsiveness of the rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr 2;110(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90217-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapocsi J., Somogyi G. T., Ludvig N., Serfozo P., Harsing L. G., Jr, Woods R. J., Vizi E. S. Neurochemical evidence for two types of presynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Neurochem Res. 1987 Feb;12(2):141–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00979530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A. D., Loury D. N., Whiting R. L. Differences between the alpha 2-adrenoceptor in rat submaxillary gland and the alpha 2A-and alpha 2B-adrenoceptor subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):890–897. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14618.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Brodde O. E., Schnepel B., Behrendt J., Tschada R., Motulsky H. J., Insel P. A. [3H]idazoxan and some other alpha 2-adrenergic drugs also bind with high affinity to a nonadrenergic site. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;35(3):324–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. J., Bylund D. B. Characterization of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the OK cell, an opossum kidney cell line. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Feb;244(2):571–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musgrave I., Marley P., Majewski H. Pertussis toxin does not attenuate alpha 2-adrenoceptor mediated inhibition of noradrenaline release in mouse atria. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;336(3):280–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00172679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahorski S. R., Barnett D. B., Cheung Y. D. alpha-Adrenoceptor-effector coupling: affinity states or heterogeneity of the alpha 2-adrenoceptor? Clin Sci (Lond) 1985;68 (Suppl 10):39s–42s. doi: 10.1042/cs068s039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasseri A., Minneman K. P. Relationship between alpha 2-adrenergic receptor binding sites and the functional receptors inhibiting norepinephrine release in rat cerebral cortex. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;32(5):655–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neylon C. B., Summers R. J. [3H]-rauwolscine binding to alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the mammalian kidney: apparent receptor heterogeneity between species. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jun;85(2):349–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08868.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. W., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Kobilka B. K. Cloning and expression of a human kidney cDNA for an alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6301–6305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. T., Pierce D. L., Bylund D. B. Alpha-2 adrenergic regulation of norepinephrine release in the rat submandibular gland as measured by HPLC-EC. Life Sci. 1984 Sep 24;35(13):1385–1394. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90396-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


