Abstract
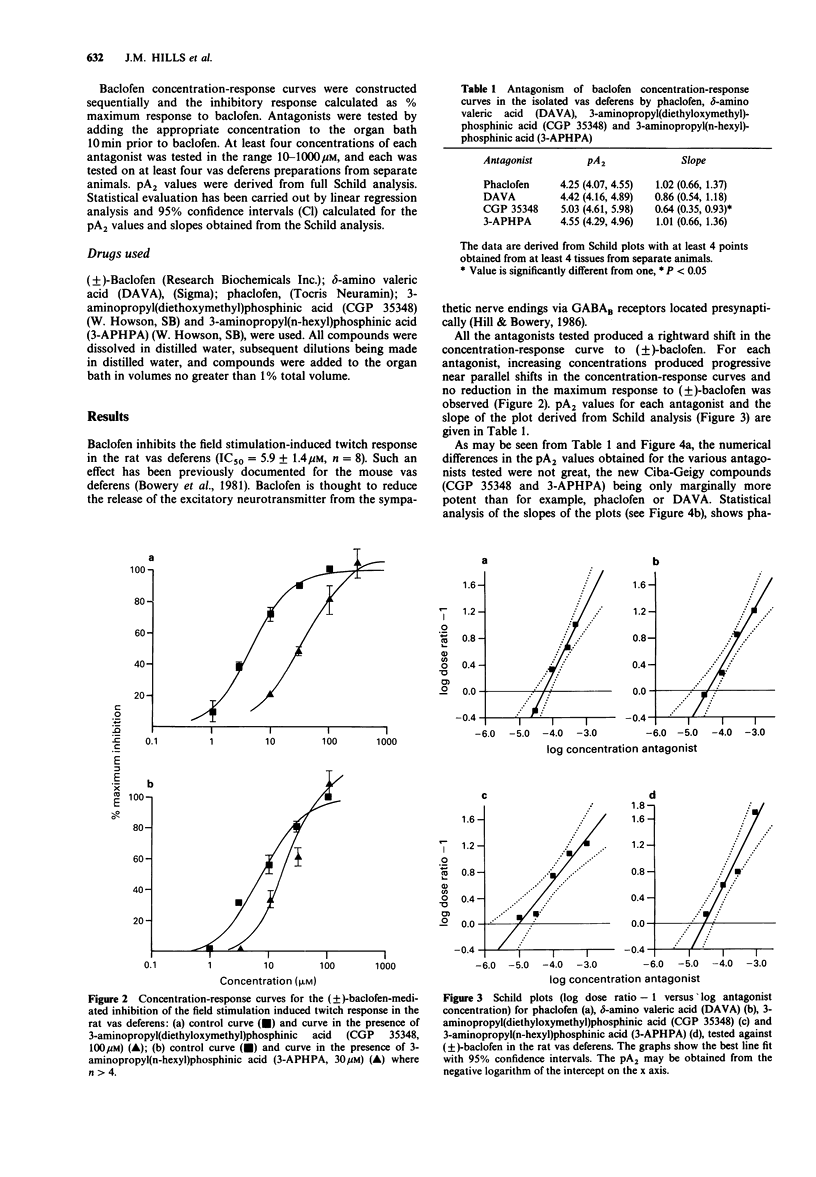
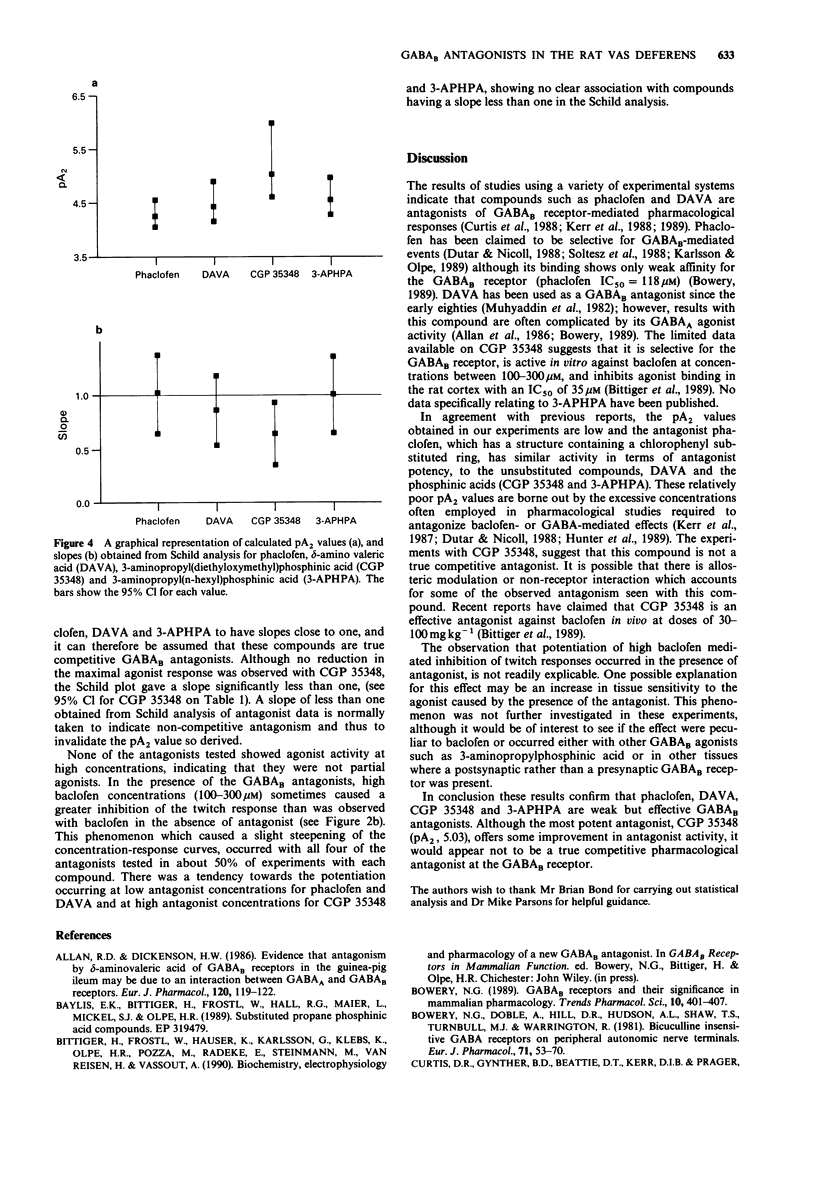
1. A series of GABAB receptor antagonists were tested against (+/-)-baclofen for activity on the presynaptic GABAB receptor in the rat vas deferens. 2. All the antagonists tested caused a rightward shift in the concentration-response curve to (+/-)-baclofen. 3. pA2 values calculated from full Schild analysis were as follows: phaclofen, pA2 = 4.3; delta-amino valeric acid, pA2 = 4.4; 3-aminopropyl(diethoxymethyl)phosphinic acid (CGP 35348), pA2 = 5.0; 3-amino-propyl(n-hexyl)phosphinic acid (3-APHPA), pA2 = 4.5. 4. These results show that none of the above compounds possess potent antagonist activity at the GABAB receptor (i.e. pA2 > 6) in this peripheral tissue. In addition, the more recently available phosphinic acid antagonists, appear to offer no great advance over the GABAB antagonists previously available.
Full text
PDF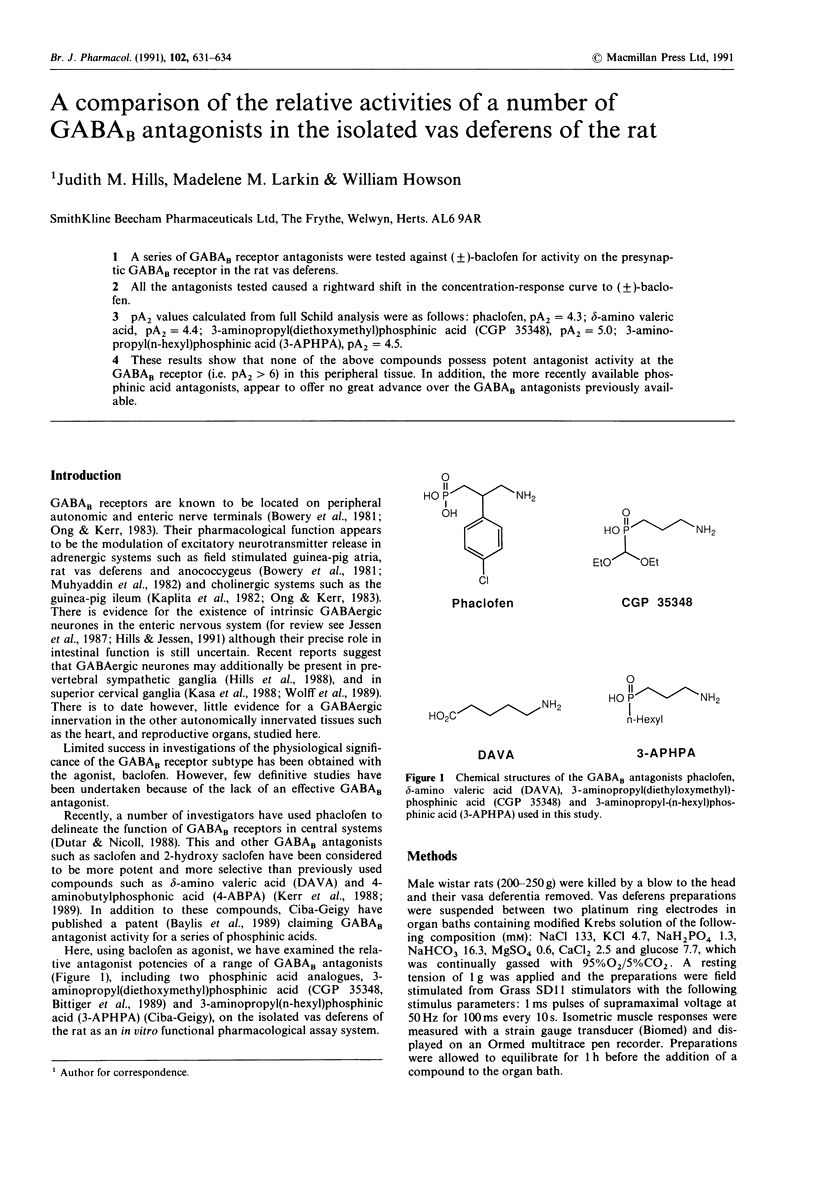

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan R. D., Dickenson H. W. Evidence that antagonism by delta-aminovaleric acid of GABAB receptors in the guinea-pig ileum may be due to an interaction between GABAA and GABAB receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan 14;120(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90650-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Doble A., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L., Shaw J. S., Turnbull M. J., Warrington R. Bicuculline-insensitive GABA receptors on peripheral autonomic nerve terminals. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 24;71(1):53–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. GABAB receptors and their significance in mammalian pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Oct;10(10):401–407. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutar P., Nicoll R. A. A physiological role for GABAB receptors in the central nervous system. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):156–158. doi: 10.1038/332156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hills J. M., King B. F., Mirsky R., Jessen K. R. Immunohistochemical localisation and electrophysiological actions of GABA in prevertebral ganglia in guinea-pig. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1988 Mar;22(2):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(88)90086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplita P. V., Waters D. H., Triggle D. J. gamma-Aminobutyric acid action in guinea-pig ileal myenteric plexus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Apr 8;79(1-2):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90573-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson G., Olpe H. R. Late inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in rat prefrontal cortex may be mediated by GABAB receptors. Experientia. 1989 Feb 15;45(2):157–158. doi: 10.1007/BF01954857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr D. I., Ong J., Johnston G. A., Abbenante J., Prager R. H. 2-Hydroxy-saclofen: an improved antagonist at central and peripheral GABAB receptors. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Sep 23;92(1):92–96. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90748-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr D. I., Ong J., Johnston G. A., Prager R. H. GABAB-receptor-mediated actions of baclofen in rat isolated neocortical slice preparations: antagonism by phosphono-analogues of GABA. Brain Res. 1989 Feb 20;480(1-2):312–316. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90198-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr D. I., Ong J., Prager R. H., Gynther B. D., Curtis D. R. Phaclofen: a peripheral and central baclofen antagonist. Brain Res. 1987 Mar 3;405(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90999-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kása P., Joó F., Dobó E., Wenthold R. J., Ottersen O. P., Storm-Mathisen J., Wolff J. R. Heterogeneous distribution of GABA-immunoreactive nerve fibers and axon terminals in the superior cervical ganglion of adult rat. Neuroscience. 1988 Aug;26(2):635–644. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhyaddin M., Roberts P. J., Woodruff G. N. Presynaptic gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors in the rat anococcygeus muscle and their antagonism by 5-aminovaleric acid. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;77(1):163–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong J., Kerr D. I. GABAA- and GABAB-receptor-mediated modification of intestinal motility. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 17;86(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltesz I., Haby M., Leresche N., Crunelli V. The GABAB antagonist phaclofen inhibits the late K+-dependent IPSP in cat and rat thalamic and hippocampal neurones. Brain Res. 1988 May 17;448(2):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91275-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J. R., Kasa P., Dobo E., Wenthold R. J., Joo F. Quantitative analysis of the number and distribution of neurons richly innervated by GABA-immunoreactive axons in the rat superior cervical ganglion. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Apr 8;282(2):264–273. doi: 10.1002/cne.902820208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


