Abstract
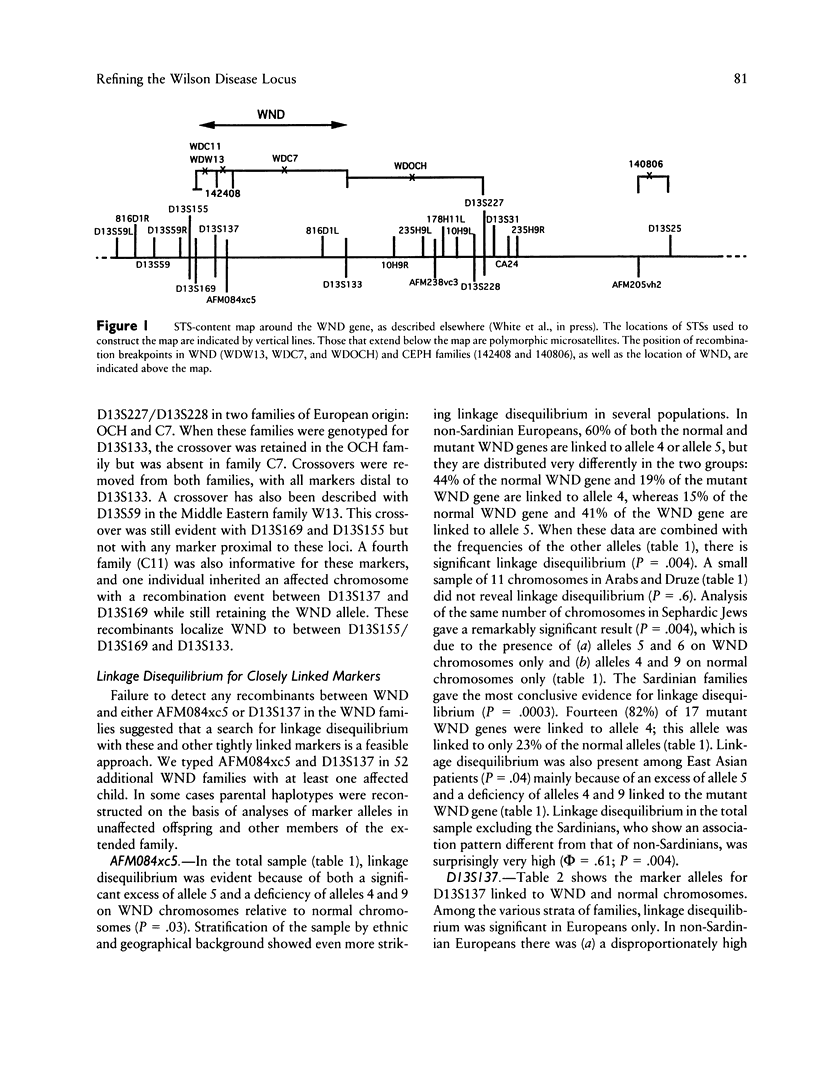
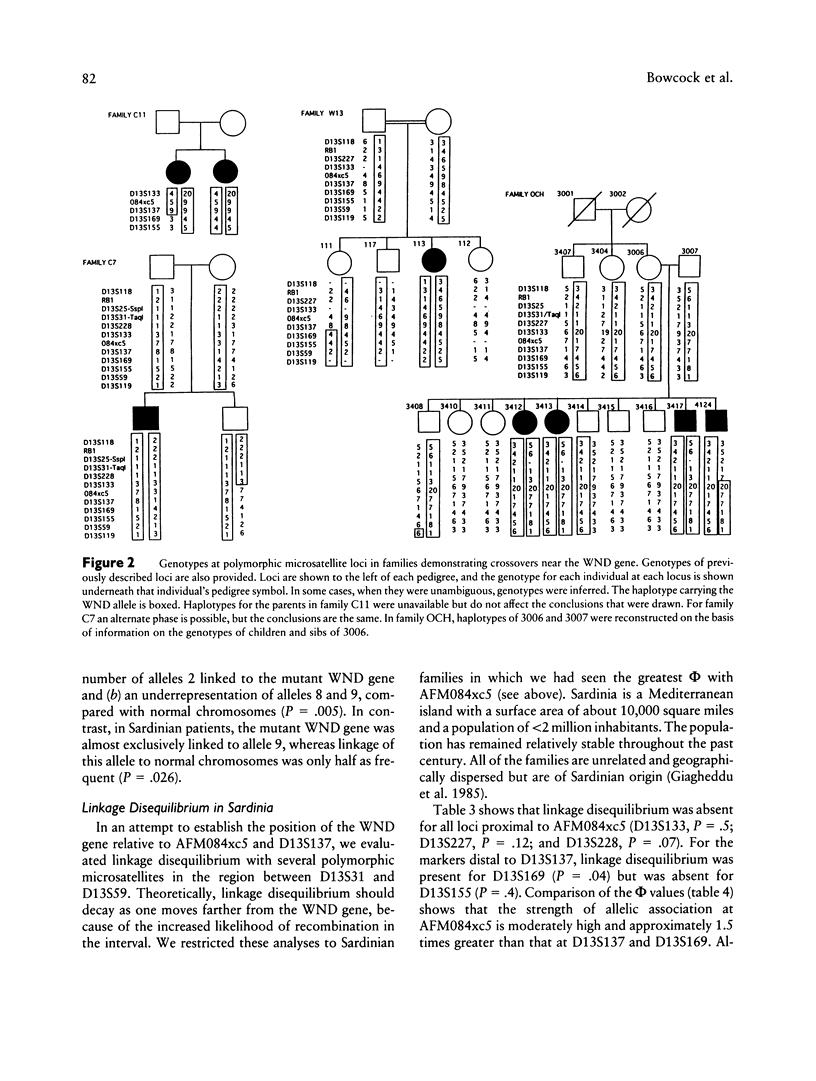
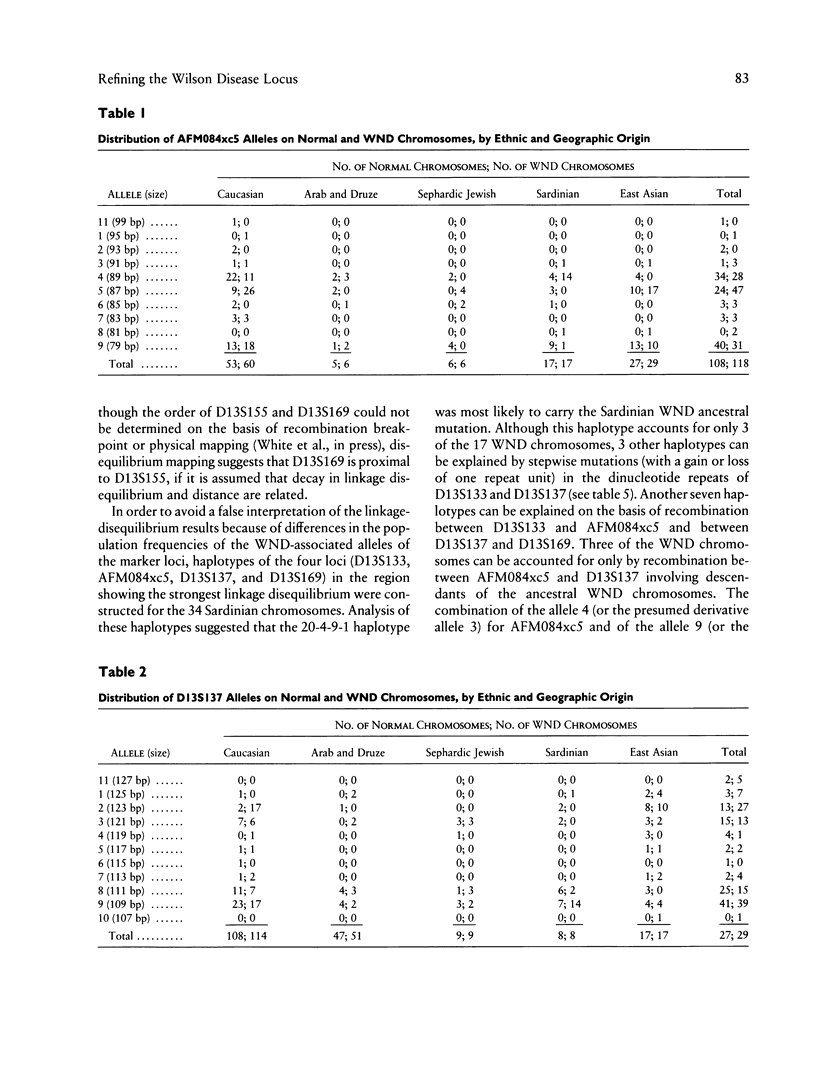
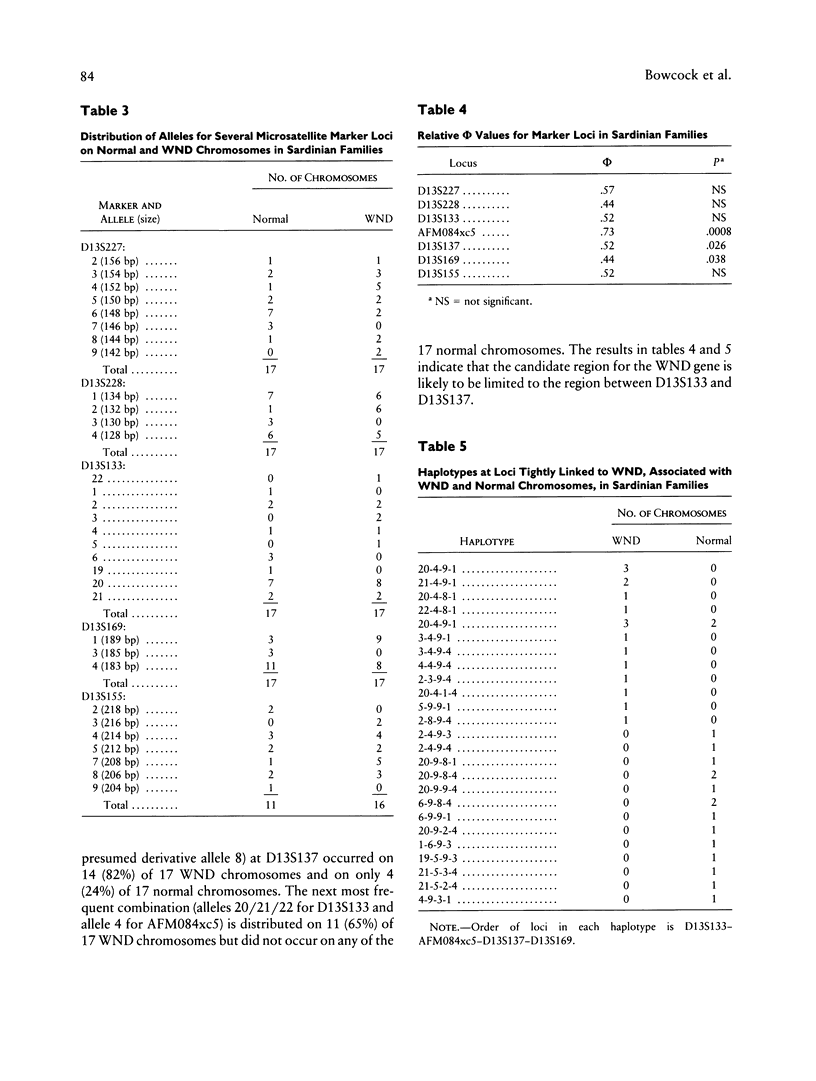
Wilson disease (WND) is an autosomal recessive disorder that is due to an inability of the liver to eliminate copper. Copper buildup in the liver, brain, kidney, and other tissues can result in liver cirrhosis, neurologic and psychiatric defects, and other problems. We have localized the disease-containing region to between D13S31 and D13S59, with > 70 multiply affected families, and have constructed a YAC contig of > 4.5 Mb that spans these loci and orders nine highly polymorphic microsatellites. Here we present an analysis of disequilibrium with markers in this interval and provide evidence for strong allelic associations between AFM084xc5 alleles and WND alleles in European, Middle Eastern, and East Asian populations. Significant but weaker allelic associations were also observed between WND alleles and alleles at D13S137 and D13S169. The strength of the association between AFM084xc5 and WND in all non-Sardinian populations combined (linkage-disequilibrium coefficient [phi] = .61) suggests that the number of mutations accounting for WND is less than expected on the basis of the variety of clinical symptoms that are observed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonné-Tamir B., Farrer L. A., Frydman M., Kanaaneh H. Evidence for linkage between Wilson disease and esterase D in three kindreds: detection of linkage for an autosomal recessive disorder by the family study method. Genet Epidemiol. 1986;3(3):201–209. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370030307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonné-Tamir B., Frydman M., Agger M. S., Bekeer R., Bowcock A. M., Hebert J. M., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Farrer L. A. Wilson's disease in Israel: a genetic and epidemiological study. Ann Hum Genet. 1990 May;54(Pt 2):155–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1990.tb00372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowcock A. M., Farrer L. A., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Hebert J. M., Kidd K. K., Frydman M., Bonne-Tamir B. Mapping the Wilson disease locus to a cluster of linked polymorphic markers on chromosome 13. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Jul;41(1):27–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowcock A. M., Farrer L. A., Hebert J. M., Agger M., Sternlieb I., Scheinberg I. H., Buys C. H., Scheffer H., Frydman M., Chajek-Saul T. Eight closely linked loci place the Wilson disease locus within 13q14-q21. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):664–674. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang L. M., Tai T. Y., Wang T. R., Chang Y. C., Chen K. H., Lin R. S., Lin B. J. Esterase D and retinoblastoma gene loci are tightly linked to Wilson's disease in Chinese pedigrees from Taiwan. Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;87(4):465–468. doi: 10.1007/BF00197170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. W., Fraser F. C., Sass-Kortsak A. A genetic study of Wilson's disease: evidence for heterogeneity. Am J Hum Genet. 1972 Nov;24(6 Pt 1):646–666. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrall M., Estivill X., Williamson R. Indirect cystic fibrosis carrier detection. Lancet. 1987 Jul 18;2(8551):156–157. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92354-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., Bowcock A. M., Hebert J. M., Bonné-Tamir B., Sternlieb I., Giagheddu M., St George-Hyslop P., Frydman M., Lössner J., Demelia L. Predictive testing for Wilson's disease using tightly linked and flanking DNA markers. Neurology. 1991 Jul;41(7):992–999. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.7.992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figus A., Lampis R., Devoto M., Ristaldi M. S., Ideo A., de Virgilis S., Nurchi A. M., Corrias A., Corda R., Lai M. E. Carrier detection and early diagnosis of Wilson's disease by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. J Med Genet. 1989 Feb;26(2):78–82. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.2.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydman M., Bonné-Tamir B., Farrer L. A., Conneally P. M., Magazanik A., Ashbel S., Goldwitch Z. Assignment of the gene for Wilson disease to chromosome 13: linkage to the esterase D locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1819–1821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giagheddu A., Demelia L., Puggioni G., Nurchi A. M., Contu L., Pirari G., Deplano A., Rachele M. G. Epidemiologic study of hepatolenticular degeneration (Wilson's disease) in Sardinia (1902-1983). Acta Neurol Scand. 1985 Jul;72(1):43–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1985.tb01546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill G. M., Brewer G. J., Juni J. E., Prasad A. S., Dick R. D. Treatment of Wilson's disease with zinc. II. Validation of oral 64copper with copper balance. Am J Med Sci. 1986 Dec;292(6):344–349. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198612000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I., Sistonen P., Weaver A., Lander E. Linkage disequilibrium mapping in isolated founder populations: diastrophic dysplasia in Finland. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):204–211. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerem B., Rommens J. M., Buchanan J. A., Markiewicz D., Cox T. K., Chakravarti A., Buchwald M., Tsui L. C. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1073–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.2570460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Novelletto A., Lin C., Tagle D., Barnes G., Bates G., Taylor S., Allitto B., Altherr M., Myers R. The Huntington's disease candidate region exhibits many different haplotypes. Nat Genet. 1992 May;1(2):99–103. doi: 10.1038/ng0592-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migone N., de Lange G., Piazza A., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Genetic analysis of eight linked polymorphisms within the human immunoglobulin heavy-chain region. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Nov;37(6):1146–1163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrukhin K. E., Speer M. C., Cayanis E., Bonaldo M. F., Tantravahi U., Soares M. B., Fischer S. G., Warburton D., Gilliam T. C., Ott J. A microsatellite genetic linkage map of human chromosome 13. Genomics. 1993 Jan;15(1):76–85. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer H., Houwen R. H., Te Meerman G. J., Loessner J., Bachmann B., Kunert E., Verlind E., Buys C. H. Identification of crossovers in Wilson disease families as reference points for a genetic localization of the gene. Hum Genet. 1992 Aug;89(6):607–611. doi: 10.1007/BF00221947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinberg I. H., Jaffe M. E., Sternlieb I. The use of trientine in preventing the effects of interrupting penicillamine therapy in Wilson's disease. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 23;317(4):209–213. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707233170405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart E. A., White A., Tomfohrde J., Osborne-Lawrence S., Prestridge L., Bonne-Tamir B., Scheinberg I. H., St George-Hyslop P., Giagheddu M., Kim J. W. Polymorphic microsatellites and Wilson disease (WD). Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Oct;53(4):864–873. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuzbasiyan-Gurkan V., Brewer G. J., Boerwinkle E., Venta P. J. Linkage of the Wilson disease gene to chromosome 13 in North-American pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jun;42(6):825–829. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


