Abstract
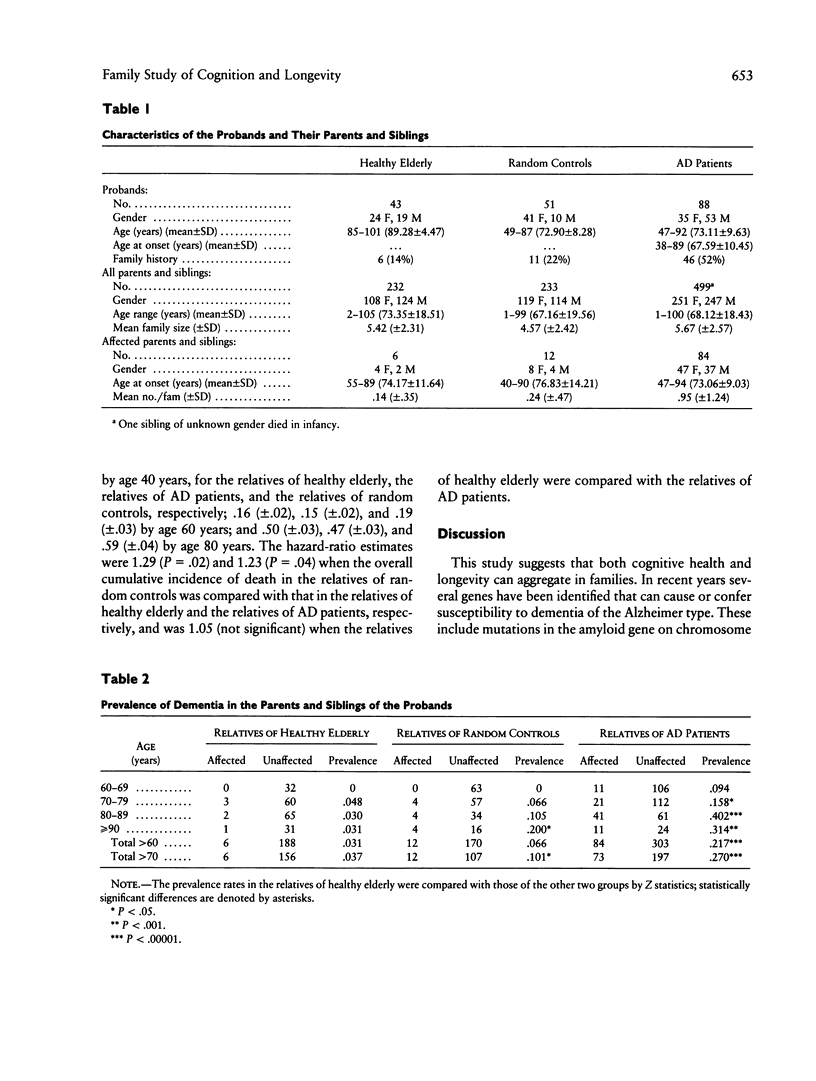
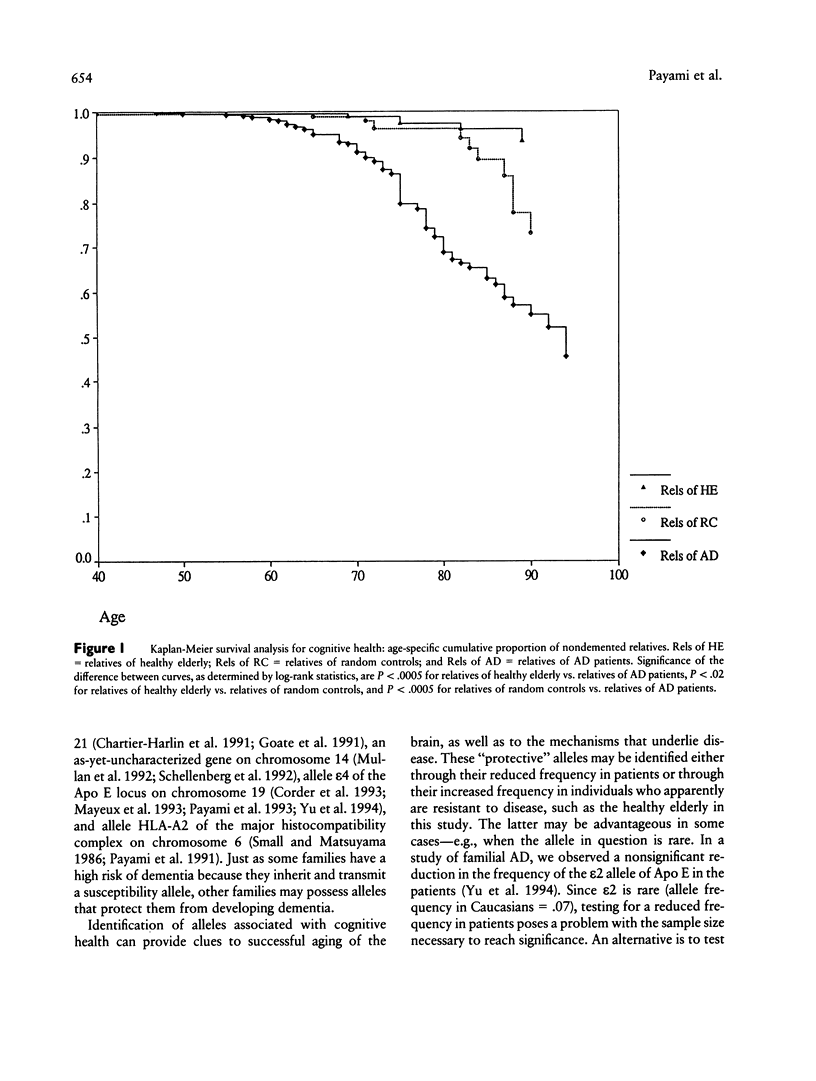
A positive family history is associated with increased risk for dementia. It is not known whether a negative family history with long-lived relatives predicts a reduced risk for dementia. We studied the survival rate and the occurrence of dementia in 232 parents and siblings of 43 optimally healthy individuals > or = 84 years of age and compared them with 233 parents and siblings of 51 random controls and 499 parents and siblings of 88 Alzheimer disease (AD) patients. Prevalence of dementia after age 60 years was .031 for the relatives of healthy elderly, .066 for the relatives of random controls, and .217 for the relatives of AD patients. The cumulative incidence of dementia by age 85 years was estimated as .041 (+/- .019) for the relatives of healthy elderly individuals, .102 (+/- .038) for the relatives of random controls, and .360 (+/- .037) for the relatives of AD patients. Hazard-ratio estimates suggest that the risk of dementia for the relatives of healthy elderly is 3 times lower than the risk for the relatives of random controls (P < .03) and is 11 times lower than the risk for the relatives of AD patients (P < .00005). An analysis of age at death indicated that the relatives of healthy elderly and the relatives of AD patients had a longer life span than did the relatives of random controls.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson M. K., Ooi W. L., Morgenstern H., Hafner A., Masur D., Crystal H., Frishman W. H., Fisher D., Katzman R. Women, myocardial infarction, and dementia in the very old. Neurology. 1990 Jul;40(7):1102–1106. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.7.1102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachman D. L., Wolf P. A., Linn R., Knoefel J. E., Cobb J., Belanger A., D'Agostino R. B., White L. R. Prevalence of dementia and probable senile dementia of the Alzheimer type in the Framingham Study. Neurology. 1992 Jan;42(1):115–119. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitner J. C. Clinical genetics and genetic counseling in Alzheimer disease. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Oct 15;115(8):601–606. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitner J. C., Silverman J. M., Mohs R. C., Davis K. L. Familial aggregation in Alzheimer's disease: comparison of risk among relatives of early-and late-onset cases, and among male and female relatives in successive generations. Neurology. 1988 Feb;38(2):207–212. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broe G. A., Henderson A. S., Creasey H., McCusker E., Korten A. E., Jorm A. F., Longley W., Anthony J. C. A case-control study of Alzheimer's disease in Australia. Neurology. 1990 Nov;40(11):1698–1707. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.11.1698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartier-Harlin M. C., Crawford F., Houlden H., Warren A., Hughes D., Fidani L., Goate A., Rossor M., Roques P., Hardy J. Early-onset Alzheimer's disease caused by mutations at codon 717 of the beta-amyloid precursor protein gene. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):844–846. doi: 10.1038/353844a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Small G. W., Roses A. D., Haines J. L., Pericak-Vance M. A. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993 Aug 13;261(5123):921–923. doi: 10.1126/science.8346443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. A., Funkenstein H. H., Albert M. S., Scherr P. A., Cook N. R., Chown M. J., Hebert L. E., Hennekens C. H., Taylor J. O. Prevalence of Alzheimer's disease in a community population of older persons. Higher than previously reported. JAMA. 1989 Nov 10;262(18):2551–2556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., Myers R. H., Cupples L. A., St George-Hyslop P. H., Bird T. D., Rossor M. N., Mullan M. J., Polinsky R., Nee L., Heston L. Transmission and age-at-onset patterns in familial Alzheimer's disease: evidence for heterogeneity. Neurology. 1990 Mar;40(3 Pt 1):395–403. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.3_part_1.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goate A., Chartier-Harlin M. C., Mullan M., Brown J., Crawford F., Fidani L., Giuffra L., Haynes A., Irving N., James L. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):704–706. doi: 10.1038/349704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrie H. C., Hall K. S., Pillay N., Rodgers D., Prince C., Norton J., Brittain H., Nath A., Blue A., Kaufert J. Alzheimer's disease is rare in Cree. Int Psychogeriatr. 1993 Spring;5(1):5–14. doi: 10.1017/s1041610293001358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howieson D. B., Holm L. A., Kaye J. A., Oken B. S., Howieson J. Neurologic function in the optimally healthy oldest old. Neuropsychological evaluation. Neurology. 1993 Oct;43(10):1882–1886. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.10.1882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff F. J., Auerbach J., Chakravarti A., Boller F. Risk of dementia in relatives of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1988 May;38(5):786–790. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.5.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman R., Aronson M., Fuld P., Kawas C., Brown T., Morgenstern H., Frishman W., Gidez L., Eder H., Ooi W. L. Development of dementing illnesses in an 80-year-old volunteer cohort. Ann Neurol. 1989 Apr;25(4):317–324. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. L., Gerteis G., Gabrielli W. F., Jr A family-genetic study of dementia of Alzheimer type. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988 Oct;45(10):894–900. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1988.01800340016002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Sano M., Chen J., Tatemichi T., Stern Y. Risk of dementia in first-degree relatives of patients with Alzheimer's disease and related disorders. Arch Neurol. 1991 Mar;48(3):269–273. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1991.00530150037014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Stern Y., Ottman R., Tatemichi T. K., Tang M. X., Maestre G., Ngai C., Tycko B., Ginsberg H. The apolipoprotein epsilon 4 allele in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1993 Nov;34(5):752–754. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohs R. C., Breitner J. C., Silverman J. M., Davis K. L. Alzheimer's disease. Morbid risk among first-degree relatives approximates 50% by 90 years of age. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1987 May;44(5):405–408. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1987.01800170019003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullan M., Houlden H., Windelspecht M., Fidani L., Lombardi C., Diaz P., Rossor M., Crook R., Hardy J., Duff K. A locus for familial early-onset Alzheimer's disease on the long arm of chromosome 14, proximal to the alpha 1-antichymotrypsin gene. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):340–342. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payami H., Kaye J., Becker W., Norman D., Wetzsteon P. HLA-A2, or a closely linked gene, confers susceptibility to early-onset sporadic Alzheimer's disease in men. Neurology. 1991 Oct;41(10):1544–1548. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.10.1544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payami H., Kaye J., Heston L. L., Bird T. D., Schellenberg G. D. Apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):738–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg G. D., Bird T. D., Wijsman E. M., Orr H. T., Anderson L., Nemens E., White J. A., Bonnycastle L., Weber J. L., Alonso M. E. Genetic linkage evidence for a familial Alzheimer's disease locus on chromosome 14. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):668–671. doi: 10.1126/science.1411576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalat S. L., Seltzer B., Pidcock C., Baker E. L., Jr Risk factors for Alzheimer's disease: a case-control study. Neurology. 1987 Oct;37(10):1630–1633. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.10.1630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small G. W., Matsuyama S. S. HLA-A2 as a possible marker for early-onset Alzheimer disease in men. Neurobiol Aging. 1986 May-Jun;7(3):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(86)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Saunders A. M., Schmechel D., Pericak-Vance M., Enghild J., Salvesen G. S., Roses A. D. Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. E., Payami H., Olson J. M., Boehnke M., Wijsman E. M., Orr H. T., Kukull W. A., Goddard K. A., Nemens E., White J. A. The apolipoprotein E/CI/CII gene cluster and late-onset Alzheimer disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Apr;54(4):631–642. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duijn C. M., Clayton D., Chandra V., Fratiglioni L., Graves A. B., Heyman A., Jorm A. F., Kokmen E., Kondo K., Mortimer J. A. Familial aggregation of Alzheimer's disease and related disorders: a collaborative re-analysis of case-control studies. Int J Epidemiol. 1991;20 (Suppl 2):S13–S20. doi: 10.1093/ije/20.supplement_2.s13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


