Abstract
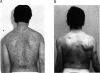
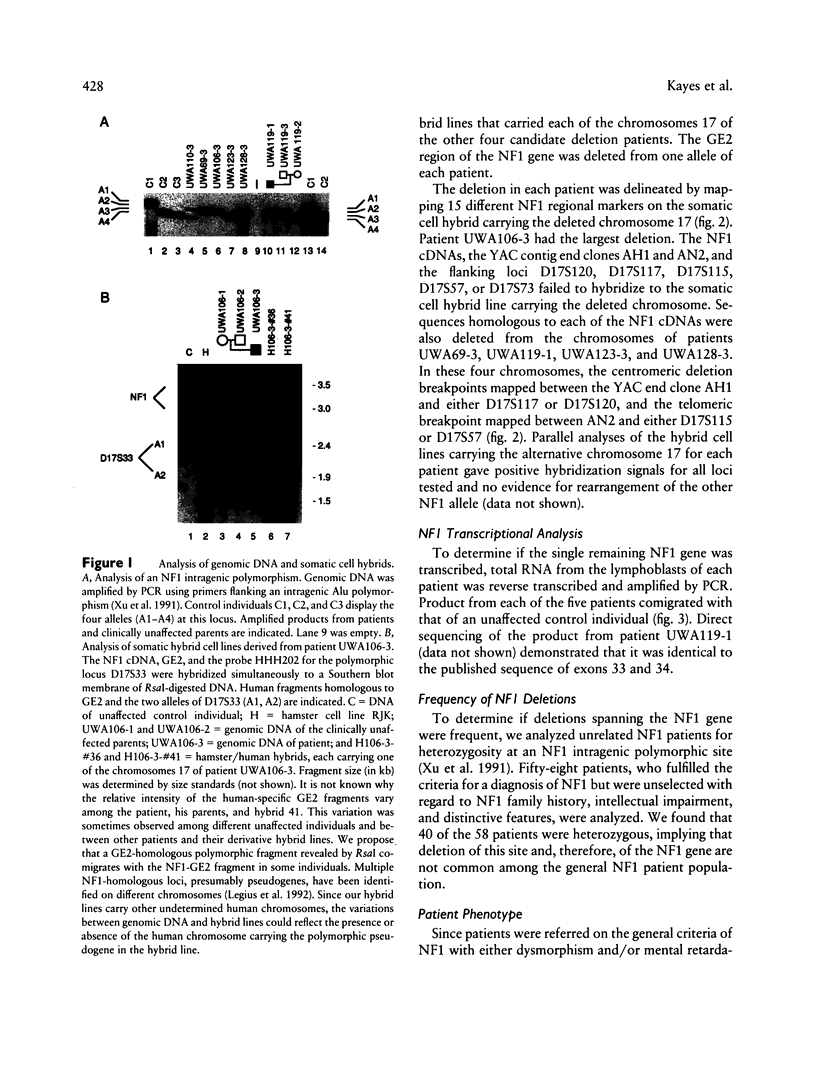
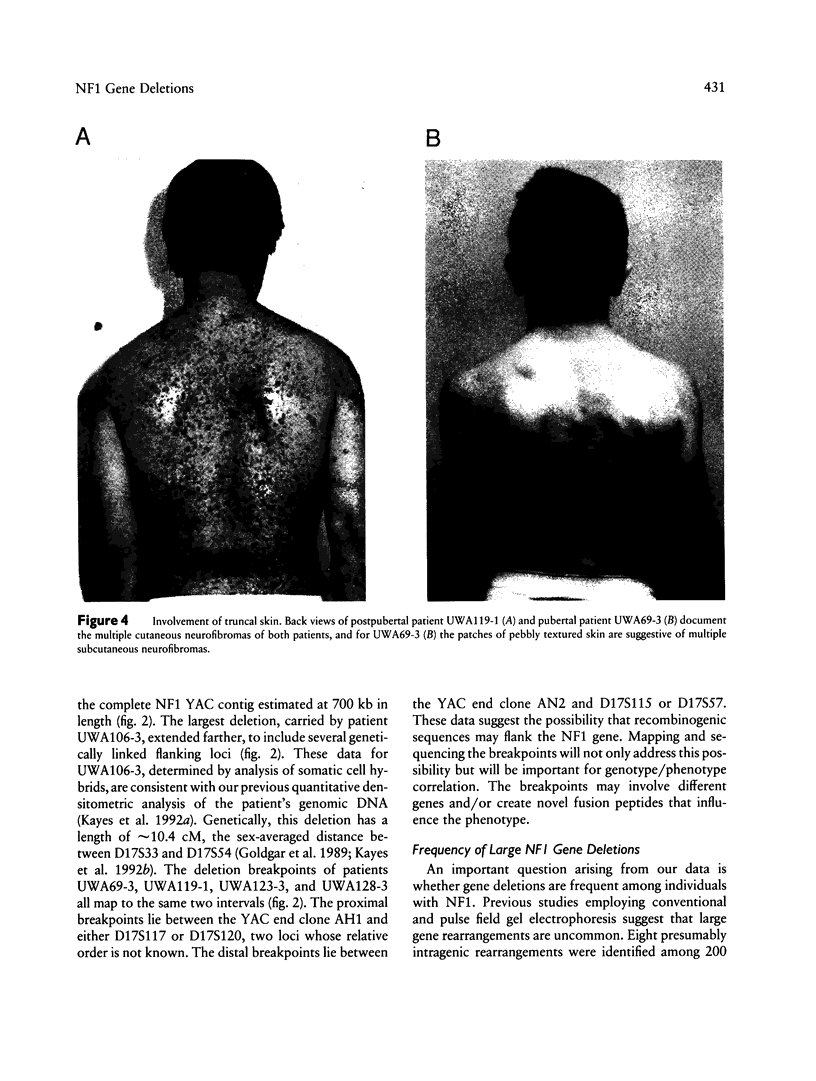
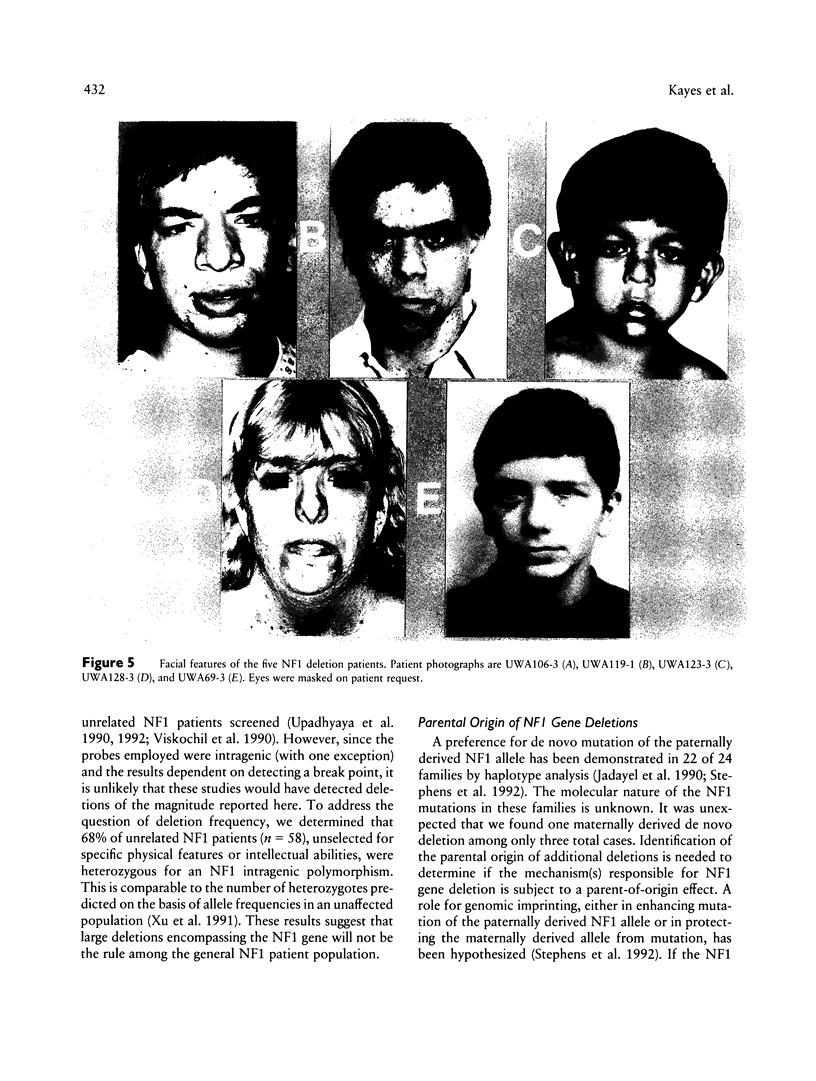
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by marked variation in clinical severity. To investigate the contribution to variability by genes either contiguous to or contained within the NF1 gene, we screened six NF1 patients with mild facial dysmorphology, mental retardation, and/or learning disabilities, for DNA rearrangement of the NF1 region. Five of the six patients had NF1 gene deletions on the basis of quantitative densitometry, locus hemizygosity, and analysis of somatic cell hybrid lines. Analyses of hybrid lines carrying each of the patient's chromosomes 17, with 15 regional DNA markers, demonstrated that each of the five patients carried a deletion > 700 kb in size. Minimally, each of the deletions involved the entire 350-kb NF1 gene; the three genes--EVI2A, EVI2B, and OMG--that are contained within an NF1 intron; and considerable flanking DNA. For four of the patients, the deletions mapped to the same interval; the deletion in the fifth patient was larger, extending farther in both directions. The remaining NF1 allele presumably produced functional neurofibromin; no gene rearrangements were detected, and RNA-PCR demonstrated that it was transcribed. These data provide compelling evidence that the NF1 disorder results from haploid insufficiency of neurofibromin. Of the three documented de novo deletion cases, two involved the paternal NF1 allele and one the maternal allele. The parental origin of the single remaining expressed NF1 allele had no dramatic effect on patient phenotype. The deletion patients exhibited a variable number of physical anomalies that were not correlated with the extent of their deletion. All five patients with deletions were remarkable for exhibiting a large number of neurofibromas for their age, suggesting that deletion of an unknown gene in the NF1 region may affect tumor initiation or development.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abuelo D. N., Meryash D. L. Neurofibromatosis with fully expressed Noonan syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Apr;29(4):937–941. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320290426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ainsworth P. J., Rodenhiser D. I. Rapid nonradioactive detection by PCR of pHHH202/RsaI RFLP linked to neurofibromatosis type I. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Nov;49(5):1098–1099. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allanson J. E., Hall J. G., Van Allen M. I. Noonan phenotype associated with neurofibromatosis. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Jul;21(3):457–462. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320210307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allanson J. E. Noonan syndrome. J Med Genet. 1987 Jan;24(1):9–13. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen L. B., Fountain J. W., Gutmann D. H., Tarlé S. A., Glover T. W., Dracopoli N. C., Housman D. E., Collins F. S. Mutations in the neurofibromatosis 1 gene in sporadic malignant melanoma cell lines. Nat Genet. 1993 Feb;3(2):118–121. doi: 10.1038/ng0293-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Wright E., Nguyen K., Cannon L., Fain P., Goldgar D., Bishop D. T., Carey J., Baty B., Kivlin J. Gene for von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis is in the pericentromeric region of chromosome 17. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1100–1102. doi: 10.1126/science.3107130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchberg A. M., Bedigian H. G., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Evi-2, a common integration site involved in murine myeloid leukemogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4658–4666. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawthon R. M., Andersen L. B., Buchberg A. M., Xu G. F., O'Connell P., Viskochil D., Weiss R. B., Wallace M. R., Marchuk D. A., Culver M. cDNA sequence and genomic structure of EV12B, a gene lying within an intron of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene. Genomics. 1991 Mar;9(3):446–460. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90410-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawthon R. M., Weiss R., Xu G. F., Viskochil D., Culver M., Stevens J., Robertson M., Dunn D., Gesteland R., O'Connell P. A major segment of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene: cDNA sequence, genomic structure, and point mutations. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90253-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clementi M., Murgia A., Anglani F., Tenconi R., Turolla L., Picci L., Zacchello F. Linkage analysis of neurofibromatosis type 1. Study of a homogeneous North Italian population with five DNA markers of chromosome 17. Hum Genet. 1991 May;87(1):91–94. doi: 10.1007/BF01213101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easton D. F., Ponder M. A., Huson S. M., Ponder B. A. An analysis of variation in expression of neurofibromatosis (NF) type 1 (NF1): evidence for modifying genes. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Aug;53(2):305–313. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estivill X., Lázaro C., Casals T., Ravella A. Recurrence of a nonsense mutation in the NF1 gene causing classical neurofibromatosis type 1. Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;88(2):185–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00206069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain P. R., Barker D. F., Goldgar D. E., Wright E., Nguyen K., Carey J., Johnson J., Kivlin J., Willard H., Mathew C. Genetic analysis of NF1: identification of close flanking markers on chromosome 17. Genomics. 1987 Dec;1(4):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain P. R., Goldgar D. E., Wallace M. R., Collins F. S., Wright E., Nguyen K., Barker D. F. Refined physical and genetic mapping of the NF1 region on chromosome 17. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Nov;45(5):721–728. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuscoe J. C., Fenwick R. G., Jr, Ledbetter D. H., Caskey C. T. Deletion and amplification of the HGPRT locus in Chinese hamster cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1086–1096. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgar D. E., Green P., Parry D. M., Mulvihill J. J. Multipoint linkage analysis in neurofibromatosis type I: an international collaboration. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;44(1):6–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huson S. M., Compston D. A., Clark P., Harper P. S. A genetic study of von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis in south east Wales. I. Prevalence, fitness, mutation rate, and effect of parental transmission on severity. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):704–711. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huson S. M., Compston D. A., Harper P. S. A genetic study of von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis in south east Wales. II. Guidelines for genetic counselling. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):712–721. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jadayel D., Fain P., Upadhyaya M., Ponder M. A., Huson S. M., Carey J., Fryer A., Mathew C. G., Barker D. F., Ponder B. A. Paternal origin of new mutations in von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):558–559. doi: 10.1038/343558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
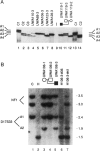
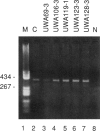
- Kayes L. M., Riccardi V. M., Burke W., Bennett R. L., Stephens K. Large de novo DNA deletion in a patient with sporadic neurofibromatosis 1, mental retardation, and dysmorphism. J Med Genet. 1992 Oct;29(10):686–690. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.10.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayes L. M., Schroeder W. T., Marchuk D. A., Collins F. S., Riccardi V. M., Duvic M., Stephens K. The gene for a novel epidermal antigen maps near the neurofibromatosis 1 gene. Genomics. 1992 Oct;14(2):369–376. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter D. H., Rich D. C., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Carey J. C. Precise localization of NF1 to 17q11.2 by balanced translocation. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;44(1):20–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legius E., Marchuk D. A., Collins F. S., Glover T. W. Somatic deletion of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene in a neurofibrosarcoma supports a tumour suppressor gene hypothesis. Nat Genet. 1993 Feb;3(2):122–126. doi: 10.1038/ng0293-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legius E., Marchuk D. A., Hall B. K., Andersen L. B., Wallace M. R., Collins F. S., Glover T. W. NF1-related locus on chromosome 15. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1316–1318. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90055-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Bollag G., Clark R., Stevens J., Conroy L., Fults D., Ward K., Friedman E., Samowitz W., Robertson M. Somatic mutations in the neurofibromatosis 1 gene in human tumors. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):275–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90408-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D. A., Saulino A. M., Tavakkol R., Swaroop M., Wallace M. R., Andersen L. B., Mitchell A. L., Gutmann D. H., Boguski M., Collins F. S. cDNA cloning of the type 1 neurofibromatosis gene: complete sequence of the NF1 gene product. Genomics. 1991 Dec;11(4):931–940. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D. A., Tavakkol R., Wallace M. R., Brownstein B. H., Taillon-Miller P., Fong C. T., Legius E., Andersen L. B., Glover T. W., Collins F. S. A yeast artificial chromosome contig encompassing the type 1 neurofibromatosis gene. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):672–680. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90140-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. A., Viskochil D., Bollag G., McCabe P. C., Crosier W. J., Haubruck H., Conroy L., Clark R., O'Connell P., Cawthon R. M. The GAP-related domain of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene product interacts with ras p21. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):843–849. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90150-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinecke P. Evidence that the "neurofibromatosis-Noonan syndrome" is a variant of von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Mar;26(3):741–745. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320260331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez H. M. The neurofibromatosis-Noonan syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Jul;21(3):471–476. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320210309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikol D. D., Gulcher J. R., Stefansson K. The oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein belongs to a distinct family of proteins and contains the HNK-1 carbohydrate. J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;110(2):471–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.2.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neitzel H. A routine method for the establishment of permanent growing lymphoblastoid cell lines. Hum Genet. 1986 Aug;73(4):320–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00279094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurofibromatosis. Conference statement. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference. Arch Neurol. 1988 May;45(5):575–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P., Viskochil D., Buchberg A. M., Fountain J., Cawthon R. M., Culver M., Stevens J., Rich D. C., Ledbetter D. H., Wallace M. The human homolog of murine Evi-2 lies between two von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis translocations. Genomics. 1990 Aug;7(4):547–554. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90198-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opitz J. M., Weaver D. D. The neurofibromatosis-Noonan syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Jul;21(3):477–490. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320210310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck J. M., Nussbaum R. L., Smead D. L., Conley M. E. X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency: localization within the region Xq13.1-q21.1 by linkage and deletion analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 May;44(5):724–730. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quattrin T., McPherson E., Putnam T. Vertical transmission of the neurofibromatosis/Noonan syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Mar;26(3):645–649. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320260320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPPORT M. M., GRAF L., ALONZO N. F. Immunochemical studies of organ and tumor lipids: VIII. Comparison of human tumor and ox spleen cytosides. J Lipid Res. 1960 Jul;1:301–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastinejad F., Blau H. M. Genetic complementation reveals a novel regulatory role for 3' untranslated regions in growth and differentiation. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):903–917. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90579-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seizinger B. R., Rouleau G. A., Ozelius L. J., Lane A. H., Faryniarz A. G., Chao M. V., Huson S., Korf B. R., Parry D. M., Pericak-Vance M. A. Genetic linkage of von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis to the nerve growth factor receptor gene. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):589–594. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90534-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard T. H., Fantel A. G. Pathogenesis of congenital defects associated with Turner's syndrome: the role of hypoalbuminemia and edema. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1986;279:440–447. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.112s440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M., Assum G., Kaufmann D., Kehrer H., Krone W. Analysis of segregation and expression of an identified mutation at the neurofibromatosis type 1 locus. Hum Genet. 1992 Dec;90(4):356–359. doi: 10.1007/BF00220458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens K., Green P., Riccardi V. M., Ng S., Rising M., Barker D., Darby J. K., Falls K. M., Collins F. S., Willard H. F. Genetic analysis of eight loci tightly linked to neurofibromatosis 1. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;44(1):13–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens K., Kayes L., Riccardi V. M., Rising M., Sybert V. P., Pagon R. A. Preferential mutation of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene in paternally derived chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1992 Jan;88(3):279–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00197259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens K., Riccardi V. M., Rising M., Ng S., Green P., Collins F. S., Rediker K. S., Powers J. A., Parker C., Donis-Keller H. Linkage studies with chromosome 17 DNA markers in 45 neurofibromatosis 1 families. Genomics. 1987 Dec;1(4):353–357. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern H. J., Saal H. M., Lee J. S., Fain P. R., Goldgar D. E., Rosenbaum K. N., Barker D. F. Clinical variability of type 1 neurofibromatosis: is there a neurofibromatosis-Noonan syndrome? J Med Genet. 1992 Mar;29(3):184–187. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.3.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassabehji M., Strachan T., Sharland M., Colley A., Donnai D., Harris R., Thakker N. Tandem duplication within a neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) gene exon in a family with features of Watson syndrome and Noonan syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):90–95. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The I., Murthy A. E., Hannigan G. E., Jacoby L. B., Menon A. G., Gusella J. F., Bernards A. Neurofibromatosis type 1 gene mutations in neuroblastoma. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):62–66. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya M., Cheryson A., Broadhead W., Fryer A., Shaw D. J., Huson S., Wallace M. R., Andersen L. B., Marchuk D. A., Viskochil D. A 90 kb DNA deletion associated with neurofibromatosis type 1. J Med Genet. 1990 Dec;27(12):738–741. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.12.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya M., Shen M., Cherryson A., Farnham J., Maynard J., Huson S. M., Harper P. S. Analysis of mutations at the neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) locus. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Dec;1(9):735–740. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.9.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viskochil D., Buchberg A. M., Xu G., Cawthon R. M., Stevens J., Wolff R. K., Culver M., Carey J. C., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Deletions and a translocation interrupt a cloned gene at the neurofibromatosis type 1 locus. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90252-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viskochil D., Cawthon R., O'Connell P., Xu G. F., Stevens J., Culver M., Carey J., White R. The gene encoding the oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein is embedded within the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):906–912. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viskochil D., White R., Cawthon R. The neurofibromatosis type 1 gene. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1993;16:183–205. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.16.030193.001151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Andersen L. B., Saulino A. M., Gregory P. E., Glover T. W., Collins F. S. A de novo Alu insertion results in neurofibromatosis type 1. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):864–866. doi: 10.1038/353864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Marchuk D. A., Andersen L. B., Letcher R., Odeh H. M., Saulino A. M., Fountain J. W., Brereton A., Nicholson J., Mitchell A. L. Type 1 neurofibromatosis gene: identification of a large transcript disrupted in three NF1 patients. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):181–186. doi: 10.1126/science.2134734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., Kwitek A. E., May P. E., Wallace M. R., Collins F. S., Ledbetter D. H. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms at the D17S250 and D17S261 loci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4640–4640. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiming X., Yu Q., Lizhi L., Ponder M., Wallace M., Gangfeng X., Ponder B. Molecular analysis of neurofibromatosis type 1 mutations. Hum Mutat. 1992;1(6):474–477. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380010604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R., Nakamura Y., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Lalouel J. M., Barker D., Goldgar D., Skolnick M., Carey J., Wallis C. E. Tightly linked markers for the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene. Genomics. 1987 Dec;1(4):364–367. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witt D. R., Hoyme H. E., Zonana J., Manchester D. K., Fryns J. P., Stevenson J. G., Curry C. J., Hall J. G. Lymphedema in Noonan syndrome: clues to pathogenesis and prenatal diagnosis and review of the literature. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Aug;27(4):841–856. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320270412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. F., Nelson L., O'Connell P., White R. An Alu polymorphism intragenic to the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene (NF1). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3764–3764. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. F., O'Connell P., Viskochil D., Cawthon R., Robertson M., Culver M., Dunn D., Stevens J., Gesteland R., White R. The neurofibromatosis type 1 gene encodes a protein related to GAP. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):599–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]