Abstract
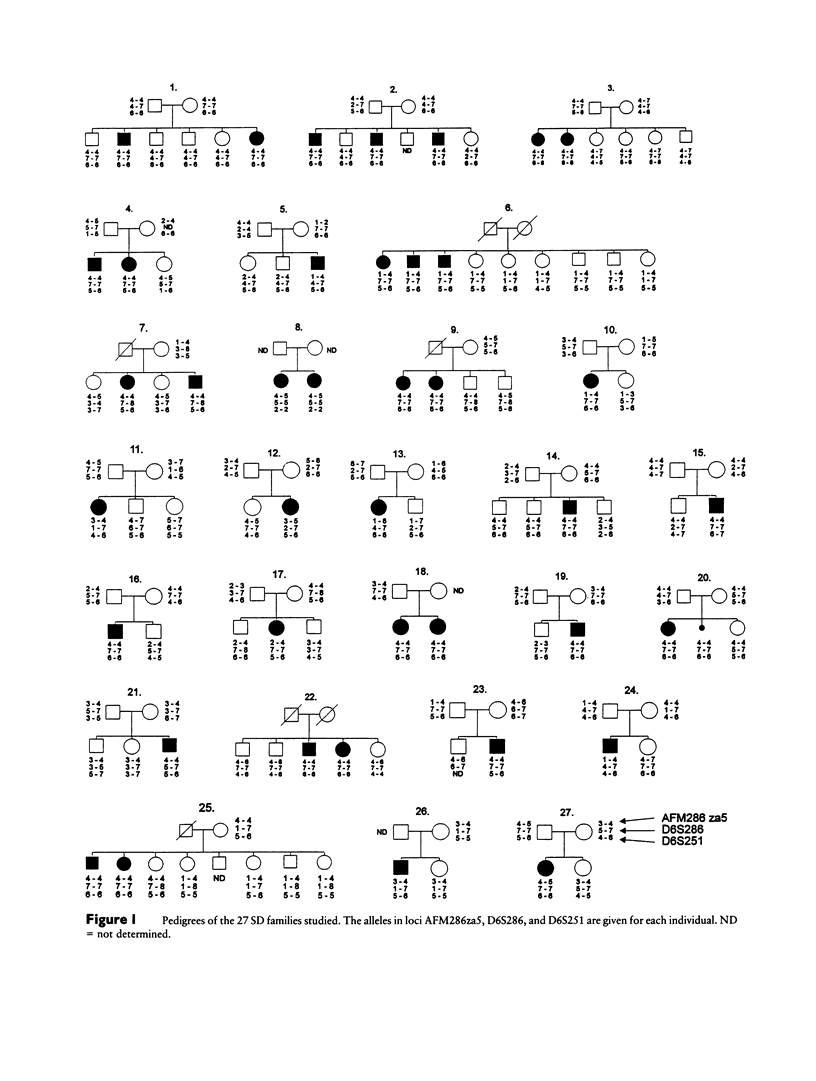
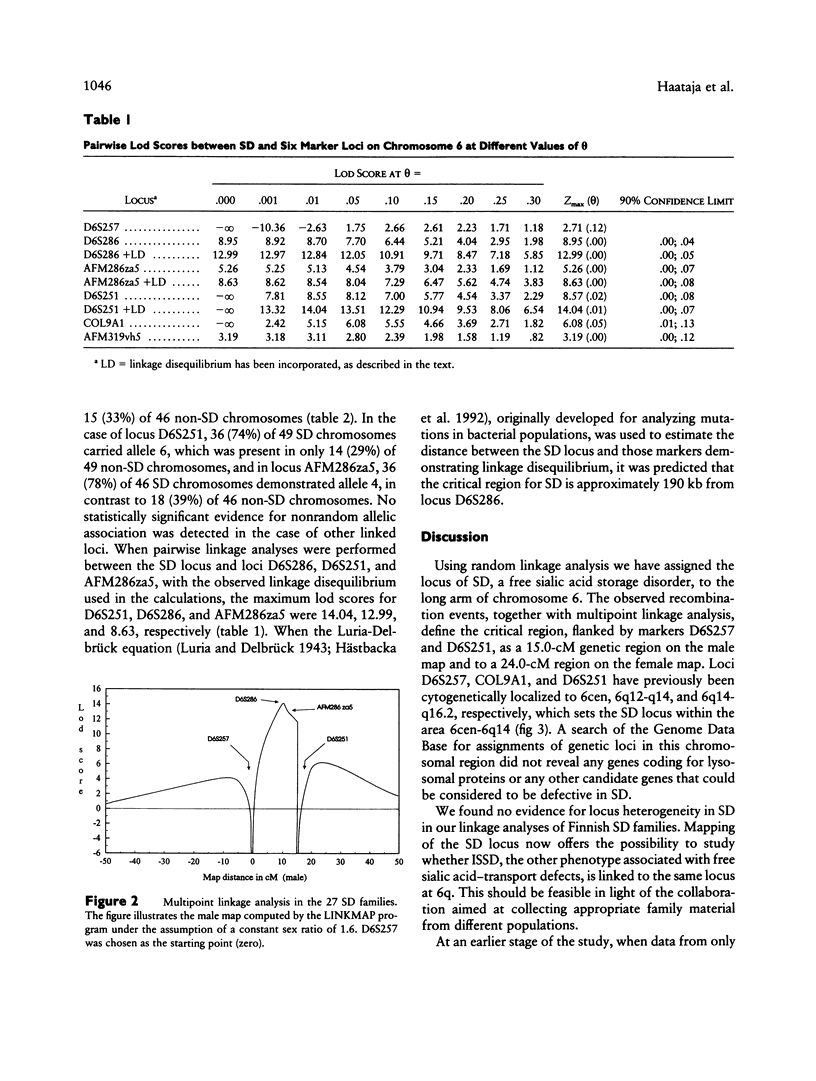
Salla disease (SD), or adult-type free sialic acid storage disease, is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder characterized by impaired transport of free sialic acid across the lysosomal membrane and severe psychomotor retardation. Random linkage analysis of a sample of 27 Finnish families allowed us to localize the SD locus to the long arm of chromosome 6. The highest lod score of 8.95 was obtained with a microsatellite marker of locus D6S286 at theta = .00. Evidence for linkage disequilibrium was observed between the SD locus and the alleles of three closely linked markers, suggesting that the length of the critical region for the SD locus is in the order of 190 kb.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aula P., Autio S., Raivio K. O., Rapola J., Thodén C. J., Koskela S. L., Yamashina I. "Salla disease": a new lysosomal storage disorder. Arch Neurol. 1979 Feb;36(2):88–94. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1979.00500380058006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Azzo A., Hoogeveen A., Reuser A. J., Robinson D., Galjaard H. Molecular defect in combined beta-galactosidase and neuraminidase deficiency in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4535–4539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. H. Exclusion mapping. J Med Genet. 1987 Sep;24(9):539–543. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.9.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haataja L., Schleutker J., Renlund M., Palotie A., Peltonen L., Aula P. Exclusion map of Salla disease: attempts to localize the disease gene using a computer program. Hum Genet. 1992 Jan;88(3):298–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00197263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock L. W., Thaler M. M., Horwitz A. L., Dawson G. Generalized N-acetylneuraminic acid storage disease: quantitation and identification of the monosaccharide accumulating in brain and other tissues. J Neurochem. 1982 Mar;38(3):803–809. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellsten E., Vesa J., Speer M. C., Mäkelä T. P., Järvelä I., Alitalo K., Ott J., Peltonen L. Refined assignment of the infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (INCL, CLN1) locus at 1p32: incorporation of linkage disequilibrium in multipoint analysis. Genomics. 1993 Jun;16(3):720–725. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., Salonen R., Laurila P., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I. Prenatal diagnosis of diastrophic dysplasia with polymorphic DNA markers. J Med Genet. 1993 Apr;30(4):265–268. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.4.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I., Sistonen P., Weaver A., Lander E. Linkage disequilibrium mapping in isolated founder populations: diastrophic dysplasia in Finland. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):204–211. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järvelä I. Infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (CLN1): linkage disequilibrium in the Finnish population and evidence that variant late infantile form (variant CLN2) represents a nonallelic locus. Genomics. 1991 Jun;10(2):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G. M., Beerens C. E., Aula P. P., Verheijen F. W. Sialic acid storage diseases. A multiple lysosomal transport defect for acidic monosaccharides. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1329–1335. doi: 10.1172/JCI115136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G. M., Beerens C. E., Galjaard H., Verheijen F. W. Functional reconstitution of the lysosomal sialic acid carrier into proteoliposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6609–6613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G. M., Verheijen F. W., Beerens C. E., Renlund M., Aula P. Sialic acid storage disorders: observations on clinical and biochemical variation. Dev Neurosci. 1991;13(4-5):327–330. doi: 10.1159/000112181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G. M., de Jonge H. R., Galjaard H., Verheijen F. W. Characterization of a proton-driven carrier for sialic acid in the lysosomal membrane. Evidence for a group-specific transport system for acidic monosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15247–15254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. S. Neuraminidase deficiency in the cherry red spot-myoclonus syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 21;79(4):1136–1141. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renlund M., Aula P. Prenatal detection of Salla disease based upon increased free sialic acid in amniocytes. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Oct;28(2):377–384. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renlund M., Aula P., Raivio K. O., Autio S., Sainio K., Rapola J., Koskela S. L. Salla disease: a new lysosomal storage disorder with disturbed sialic acid metabolism. Neurology. 1983 Jan;33(1):57–66. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renlund M. Clinical and laboratory diagnosis of Salla disease in infancy and childhood. J Pediatr. 1984 Feb;104(2):232–236. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80998-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renlund M., Tietze F., Gahl W. A. Defective sialic acid egress from isolated fibroblast lysosomes of patients with Salla disease. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):759–762. doi: 10.1126/science.3961501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleutker J., Haataja L., Renlund M., Puhakka L., Viitala J., Peltonen L., Aula P. Confirmation of the chromosomal localization of human lamp genes and their exclusion as candidate genes for Salla disease. Hum Genet. 1991 Nov;88(1):95–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00204936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppala R., Tietze F., Krasnewich D., Weiss P., Ashwell G., Barsh G., Thomas G. H., Packman S., Gahl W. A. Sialic acid metabolism in sialuria fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7456–7461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulisalo T., Sistonen P., Hästbacka J., Wadelius C., Mäkitie O., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I. Cartilage-hair hypoplasia gene assigned to chromosome 9 by linkage analysis. Nat Genet. 1993 Apr;3(4):338–341. doi: 10.1038/ng0493-338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tondeur M., Libert J., Vamos E., Van Hoof F., Thomas G. H., Strecker G. Infantile form of sialic acid storage disorder: clinical, ultrastructural, and biochemical studies in two siblings. Eur J Pediatr. 1982 Oct;139(2):142–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00441499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vamos E., Libert J., Elkhazen N., Jauniaux E., Hustin J., Wilkin P., Baumkötter J., Mendla K., Cantz M., Strecker G. Prenatal diagnosis and confirmation of infantile sialic acid storage disease. Prenat Diagn. 1986 Nov-Dec;6(6):437–446. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970060607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenplas S., Wiid I., Grobler-Rabie A., Brebner K., Ricketts M., Wållis G., Bester A., Boyd C., Måthew C. Blot hybridisation analysis of genomic DNA. J Med Genet. 1984 Jun;21(3):164–172. doi: 10.1136/jmg.21.3.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesa J., Hellsten E., Mäkelä T. P., Järvelä I., Airaksinen T., Santavuori P., Peltonen L. A single PCR marker in strong allelic association with the infantile form of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis facilitates reliable prenatal diagnostics and disease carrier identification. Eur J Hum Genet. 1993;1(2):125–132. doi: 10.1159/000472399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilkki J., Savontaus M. L., Nikoskelainen E. K. Human mitochondrial DNA types in Finland. Hum Genet. 1988 Dec;80(4):317–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00273643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warman M. L., Tiller G. E., Polumbo P. A., Seldin M. F., Rochelle J. M., Knoll J. H., Cheng S. D., Olsen B. R. Physical and linkage mapping of the human and murine genes for the alpha 1 chain of type IX collagen (COL9A1). Genomics. 1993 Sep;17(3):694–698. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie P. J., Polymeropoulos M. H., Trent J. M., Small K. W., Weber J. L. Genetic and physical map of 11 short tandem repeat polymorphisms on human chromosome 6. Genomics. 1993 Jan;15(1):225–227. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


