Abstract
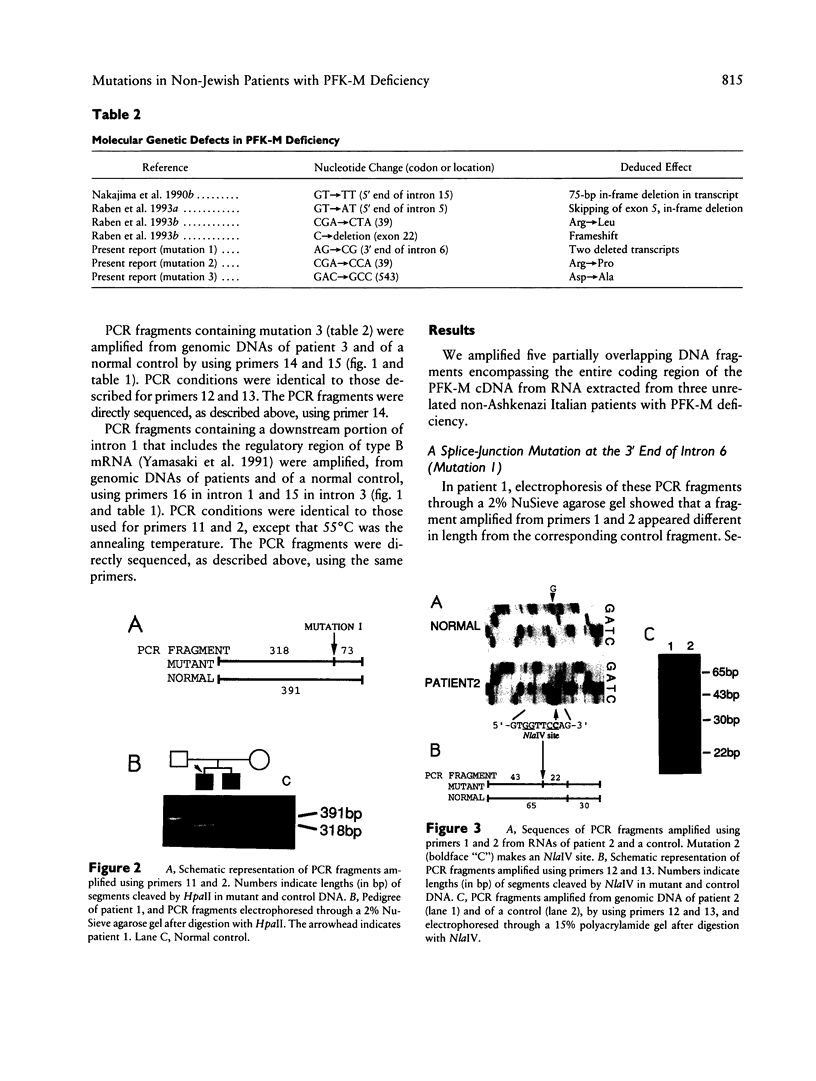
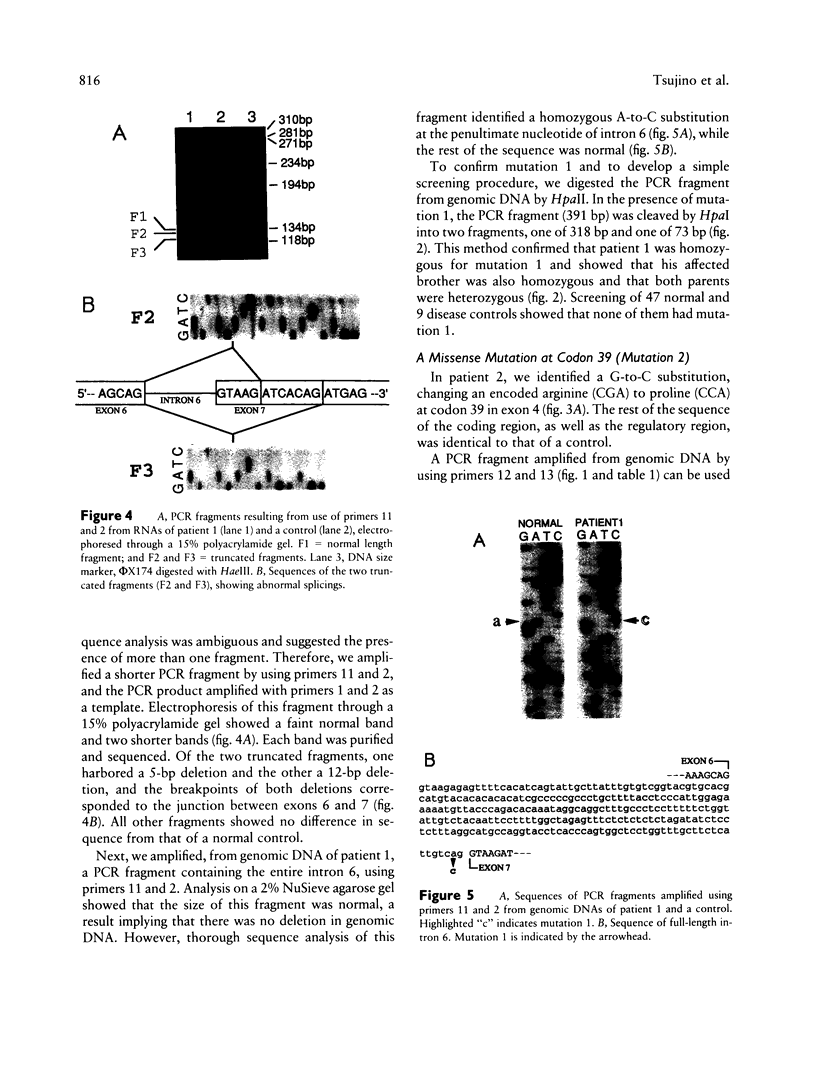
We have identified three novel mutations in four non-Ashkenazi Italian patients with muscle phosphofructokinase (PFK-M) deficiency (Tarui disease). Patient 1 was homozygous for an A-to-C substitution at the 3' end of intron 6 of the PFK-M gene, changing the consensus splice-junction sequence AG to CG. The mutation leads to activation of two cryptic splice sites in exon 7, resulting in one 5 bp- and one 12 bp-deleted transcript. An affected brother was also homozygous, and both parents were heterozygous, for the splice-junction mutation. Patient 2 was homozygous for a G-to-C substitution at codon 39, changing an encoded arginine (CGA) to proline (CCA). Patient 3 was heterozygous for an A-to-C substitution at codon 543, changing an encoded aspartate (GAC) to alanine (GCC); the PFK-M gene on the other allele was not expressed, but sequencing of the reported regulatory region of the gene did not reveal any mutation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belgrader P., Cheng J., Maquat L. E. Evidence to implicate translation by ribosomes in the mechanism by which nonsense codons reduce the nuclear level of human triosephosphate isomerase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):482–486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans P. R., Farrants G. W., Hudson P. J. Phosphofructokinase: structure and control. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Jun 26;293(1063):53–62. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehnrich S. C., Gekakis N., Sul H. S. Liver (B-type) phosphofructokinase mRNA. Cloning, structure, and expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11755–11759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotta K., Nakajima H., Yamasaki T., Hamaguchi T., Kuwajima M., Noguchi T., Tanaka T., Kono N., Tarui S. Rat-liver-type phosphofructokinase mRNA. Structure, tissue distribution and regulation. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 5;202(2):293–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono N., Mineo I., Shimizu T., Hara N., Yamada Y., Nonaka K., Tarui S. Increased plasma uric acid after exercise in muscle phosphofructokinase deficiency. Neurology. 1986 Jan;36(1):106–108. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawczak M., Reiss J., Cooper D. N. The mutational spectrum of single base-pair substitutions in mRNA splice junctions of human genes: causes and consequences. Hum Genet. 1992 Sep-Oct;90(1-2):41–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00210743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. P., Kao M. C., French B. A., Putney S. D., Chang S. H. The rabbit muscle phosphofructokinase gene. Implications for protein structure, function, and tissue specificity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4195–4199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levanon D., Danciger E., Dafni N., Bernstein Y., Elson A., Moens W., Brandeis M., Groner Y. The primary structure of human liver type phosphofructokinase and its comparison with other types of PFK. DNA. 1989 Dec;8(10):733–743. doi: 10.1089/dna.1989.8.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashima Y., Murakami A., Weleber R. G., Kennaway N. G., Clarke L., Shiono T., Inana G. Nonsense-codon mutations of the ornithine aminotransferase gene with decreased levels of mutant mRNA in gyrate atrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jul;51(1):81–91. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H., Kono N., Yamasaki T., Hamaguchi T., Hotta K., Kuwajima M., Noguchi T., Tanaka T., Tarui S. Tissue specificity in expression and alternative RNA splicing of human phosphofructokinase-M and -L genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):1317–1321. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80931-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H., Kono N., Yamasaki T., Hotta K., Kawachi M., Kuwajima M., Noguchi T., Tanaka T., Tarui S. Genetic defect in muscle phosphofructokinase deficiency. Abnormal splicing of the muscle phosphofructokinase gene due to a point mutation at the 5'-splice site. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9392–9395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H., Noguchi T., Yamasaki T., Kono N., Tanaka T., Tarui S. Cloning of human muscle phosphofructokinase cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 19;223(1):113–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80519-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H., Yamasaki T., Noguchi T., Tanaka T., Kono N., Tarui S. Evidence for alternative RNA splicing and possible alternative promoters in the human muscle phosphofructokinase gene at the 5' untranslated region. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 30;166(2):637–641. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90856-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poorman R. A., Randolph A., Kemp R. G., Heinrikson R. L. Evolution of phosphofructokinase--gene duplication and creation of new effector sites. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):467–469. doi: 10.1038/309467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raben N., Sherman J., Miller F., Mena H., Plotz P. A 5' splice junction mutation leading to exon deletion in an Ashkenazic Jewish family with phosphofructokinase deficiency (Tarui disease). J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4963–4967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servidei S., Bonilla E., Diedrich R. G., Kornfeld M., Oates J. D., Davidson M., Vora S., DiMauro S. Fatal infantile form of muscle phosphofructokinase deficiency. Neurology. 1986 Nov;36(11):1465–1470. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.11.1465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanske S., Sakoda S., Hermodson M. A., DiMauro S., Schon E. A. Isolation of a cDNA encoding the muscle-specific subunit of human phosphoglycerate mutase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14612–14617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma P. M., Reddy G. R., Babior B. M., McLachlan A. Alternative splicing of the transcript encoding the human muscle isoenzyme of phosphofructokinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9006–9010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma P. M., Reddy G. R., Vora S., Babior B. M., McLachlan A. Cloning and expression of a human muscle phosphofructokinase cDNA. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson C. J., Fothergill-Gilmore L. A. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA encoding human platelet phosphofructokinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 15;180(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81276-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TARUI S., OKUNO G., IKURA Y., TANAKA T., SUDA M., NISHIKAWA M. PHOSPHOFRUCTOKINASE DEFICIENCY IN SKELETAL MUSCLE. A NEW TYPE OF GLYCOGENOSIS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 3;19:517–523. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujino S., Shanske S., DiMauro S. Molecular genetic heterogeneity of myophosphorylase deficiency (McArdle's disease). N Engl J Med. 1993 Jul 22;329(4):241–245. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199307223290404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujino S., Shanske S., Nonaka I., Eto Y., Mendell J. R., Fenichel G. M., DiMauro S. Three new mutations in patients with myophosphorylase deficiency (McArdle disease). Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Jan;54(1):44–52. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda K. Phosphofructokinase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1979;48:193–244. doi: 10.1002/9780470122938.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vora S., DiMauro S., Spear D., Harker D., Danon M. J. Characterization of the enzymatic defect in late-onset muscle phosphofructokinase deficiency. New subtype of glycogen storage disease type VII. J Clin Invest. 1987 Nov;80(5):1479–1485. doi: 10.1172/JCI113229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vora S., Durham S., de Martinville B., George D. L., Francke U. Assignment of the human gene for muscle-type phosphofructokinase (PFKM) to chromosome 1 (region cen leads to q32) using somatic cell hybrids and monoclonal anti-M antibody. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 Jan;8(1):95–104. doi: 10.1007/BF01538653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vora S. Isozymes of phosphofructokinase. Isozymes Curr Top Biol Med Res. 1982;6:119–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki T., Nakajima H., Kono N., Hotta K., Yamada K., Imai E., Kuwajima M., Noguchi T., Tanaka T., Tarui S. Structure of the entire human muscle phosphofructokinase-encoding gene: a two-promoter system. Gene. 1991 Aug 15;104(2):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90262-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







