Abstract
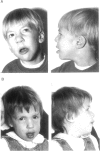
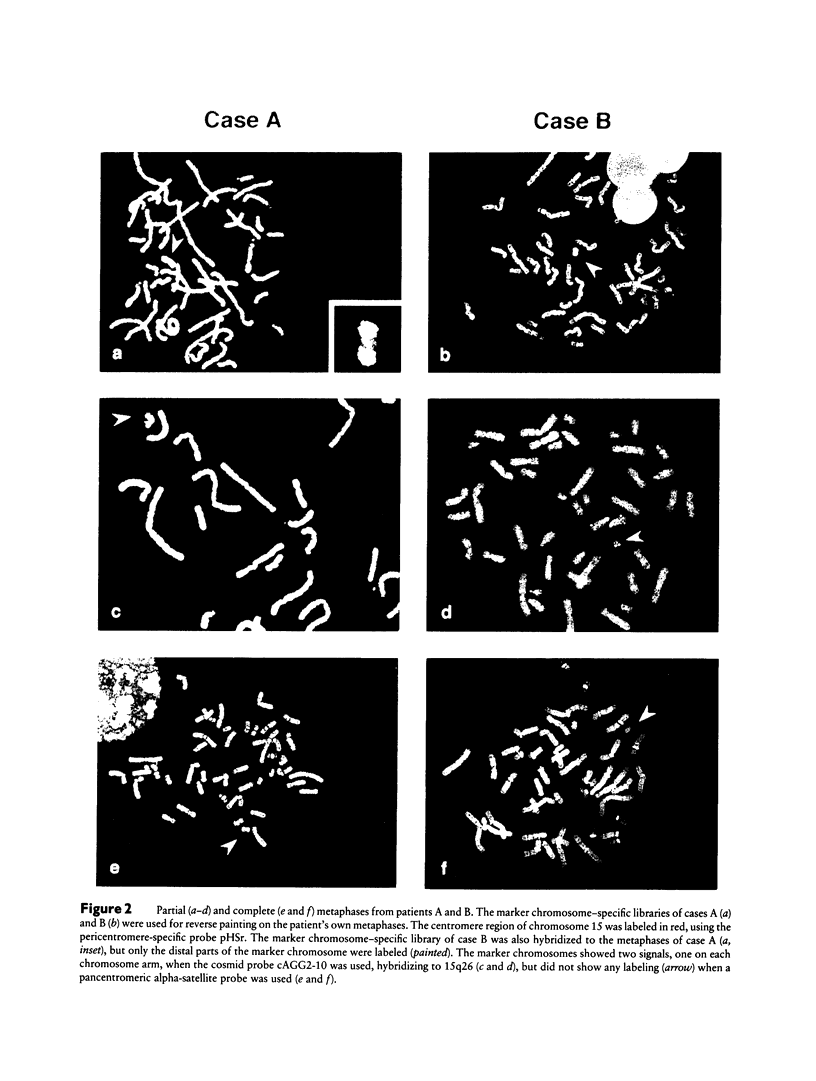
Two patients with specific and similar phenotypes were both found to have an unusual marker chromosome present in 70%-80% of their lymphocytes at routine cytogenetic examination. The marker chromosomes were isolated by flow sorting and were amplified by degenerate oligonucleotide-primed PCR. These libraries and a cosmid probe located at 15q26 were used to characterize the marker chromosomes by FISH. Both marker chromosomes were found to consist of duplicated chromosome material from the distal part of chromosome 15q and were identified as inv dup(15) (qter-->q23::q23-->qter) and inv dup(15) (qter-->q24::q24-->qter), respectively. Hence, the markers did not include any known centromere region, and no alpha-satellite DNA could be detected at the site of the primary constriction. Tetrasomy 15q may be a new syndrome, associated with a specific type of marker chromosome. In addition, further analyses of this type of marker chromosome might give new insight into the structure and function of the mammalian centromere.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blennow E., Annerén G., Bui T. H., Berggren E., Asadi E., Nordenskjöld M. Characterization of supernumerary ring marker chromosomes by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Aug;53(2):433–442. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blennow E., Telenius H., Larsson C., de Vos D., Bajalica S., Ponder B. A., Nordenskjöld M. Complete characterization of a large marker chromosome by reverse and forward chromosome painting. Hum Genet. 1992 Dec;90(4):371–374. doi: 10.1007/BF00220461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckton K. E., Spowart G., Newton M. S., Evans H. J. Forty four probands with an additional "marker" chromosome. Hum Genet. 1985;69(4):353–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00291656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callen D. F., Eyre H., Yip M. Y., Freemantle J., Haan E. A. Molecular cytogenetic and clinical studies of 42 patients with marker chromosomes. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Jul 1;43(4):709–715. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter N. P., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Perryman M. T., Telenius H., Pelmear A. H., Leversha M. A., Glancy M. T., Wood S. L., Cook K., Dyson H. M. Reverse chromosome painting: a method for the rapid analysis of aberrant chromosomes in clinical cytogenetics. J Med Genet. 1992 May;29(5):299–307. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.5.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coco R., Penchaszadeh V. B. Inherited parital duplication deficiency of chromosome 15 (p12;q22). J Genet Hum. 1978 Sep;26(3):203–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crolla J. A., Dennis N. R., Jacobs P. A. A non-isotopic in situ hybridisation study of the chromosomal origin of 15 supernumerary marker chromosomes in man. J Med Genet. 1992 Oct;29(10):699–703. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.10.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Lewis K., Rothenberg B. E. High efficiency vectors for cosmid microcloning and genomic analysis. Gene. 1989 Jun 30;79(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Wahl G. M. Cosmid vectors for genomic walking and rapid restriction mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:604–610. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., Kleczkowska A., Moerman P., Vandenberghe K., Van den Berghe H. The fetal phenotype in 15q2 duplication. Ann Genet. 1988;31(2):123–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto A., Towner J. W., Ebbin A. J., Kahlstrom E. J., Wilson M. G. Inherited partial duplication of chromosome No. 15. J Med Genet. 1974 Sep;11(3):287–291. doi: 10.1136/jmg.11.3.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Ward R. E., Nichols W. C., Palmer C. G. Familial t(8;15)(p23.3;q22.3): report of two cases with dup(15) (q22.3----qter). J Med Genet. 1987 Nov;24(11):684–687. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.11.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoire M. J., Boue J., Junien C., Pernot C., Gilgenkrantz S., Zergollern L. Duplication 15q22 to 15qter and its phenotypic expression. Hum Genet. 1981;59(4):429–433. doi: 10.1007/BF00295485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. B., Cross P. K. Extra structurally abnormal chromosomes (ESAC) detected at amniocentesis: frequency in approximately 75,000 prenatal cytogenetic diagnoses and associations with maternal and paternal age. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Feb;40(2):83–101. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Chen X. N., Doege K., Grover J., Roughley P. J. Assignment of the human aggrecan gene (AGC1) to 15q26 using fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis. Genomics. 1993 May;16(2):546–548. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristoffersson U., Bergwall B. Partial trisomy 15(q25qter) in two brothers. Hereditas. 1984;100(1):7–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1984.tb00097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristoffersson U., Heim S., Mandahl N., Sundkvist L., Szelest J., Hägerstrand I. Monosomy and trisomy of 15q24----qter in a family with a translocation t(6;15)(p25;q24). Clin Genet. 1987 Sep;32(3):169–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1987.tb03348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacro R. V., Jones K. L., Mascarello J. T., Jones O. W., Wilson N., Jones M. C. Duplication of distal 15q: report of five new cases from two different translocation kindreds. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Mar;26(3):719–728. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320260327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Straume T., Gray J. W. Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2934–2938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluta A. F., Cooke C. A., Earnshaw W. C. Structure of the human centromere at metaphase. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 May;15(5):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch A., Pfeiffer R. A., Trautmann U., Liehr T., Rott H. D., Ulmer R. A study of ten small supernumerary (marker) chromosomes identified by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Clin Genet. 1992 Aug;42(2):84–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1992.tb03145.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R. R., Breg W. R., Erlanger B. F., Miller O. J. Preferential derivation of abnormal human G-group-like chromosomes from chromosome 15. Hum Genet. 1977 Apr 7;36(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00390430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voullaire L. E., Slater H. R., Petrovic V., Choo K. H. A functional marker centromere with no detectable alpha-satellite, satellite III, or CENP-B protein: activation of a latent centromere? Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jun;52(6):1153–1163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburton D. De novo balanced chromosome rearrangements and extra marker chromosomes identified at prenatal diagnosis: clinical significance and distribution of breakpoints. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Nov;49(5):995–1013. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wik Sjöstedt A., Alatalo M., Wahlström J., von Döbeln U., Olegård R. Replication error, a new hypothesis to explain the origin of a supernumerary marker chromosome in a mentally retarded boy. Hereditas. 1989;111(2):115–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1989.tb00385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F. Centromeres of mammalian chromosomes. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):410–416. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90302-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski L., Hassold T., Heffelfinger J., Higgins J. V. Cytogenetic and clinical studies in five cases of inv dup(15). Hum Genet. 1979 Sep;50(3):259–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00399391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip M. Y., Parsons A., Hultén M. A de novo tandem duplication 15(q21 leads to qter) mosaic. Clin Genet. 1982 Jul;22(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]