Abstract
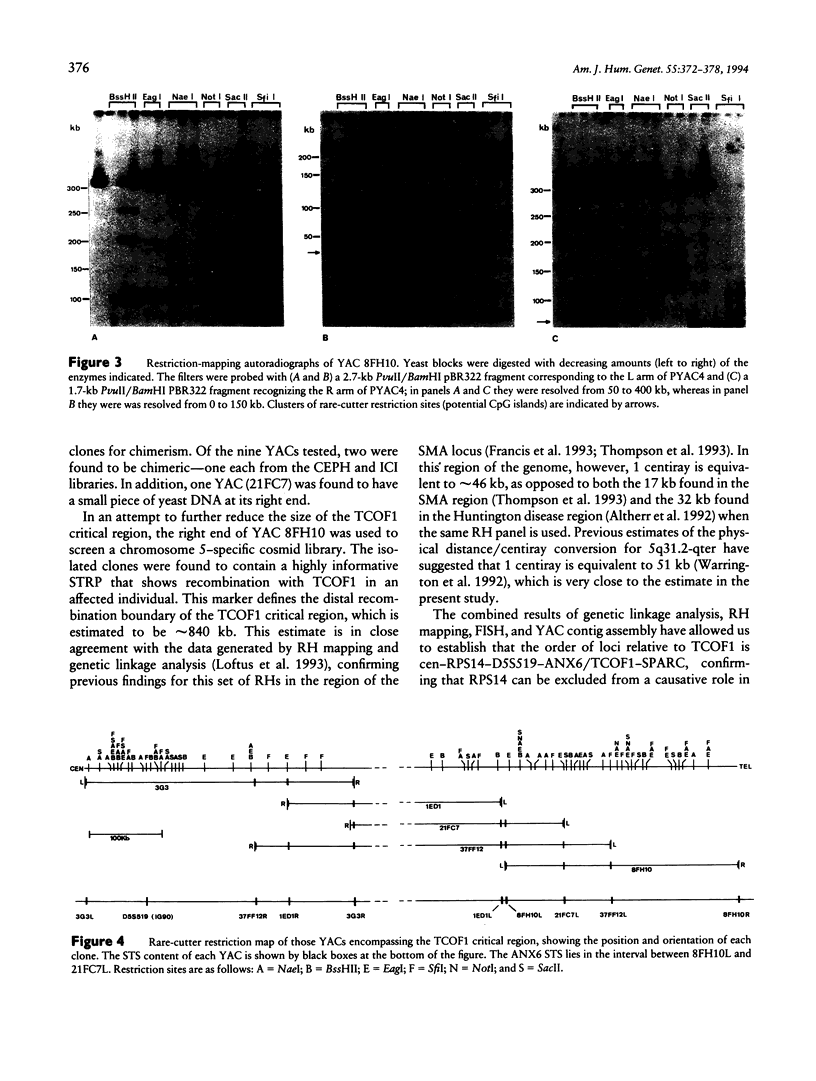
Treacher Collins syndrome (TCOF1) is an autosomal dominant disorder of craniofacial development the features of which include conductive hearing loss and cleft palate. Previous studies have localized the TCOF1 locus between D5S519 (proximal) and SPARC (distal), a region of 22 centirays as estimated by radiation hybrid mapping. In the current investigation we have created a contig across the TCOF1 critical region, using YAC clones. Isolation of a novel short tandem repeat polymorphism corresponding to the end of one of the YACs has allowed us to reduce the size of the critical region to approximately 840 kb, which has been covered with three nonchimeric YACs. Restriction mapping has revealed that the region contains a high density of clustered rare-cutter restriction sites, suggesting that it may contain a number of different genes. The results of the present investigation have further allowed us to confirm that the RPS14 locus lies proximal to the critical region and can thereby be excluded from a role in the pathogenesis of TCOF1, while ANX6 lies within the TCOF1 critical region and remains a potential candidate for the mutated gene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertsen H. M., Abderrahim H., Cann H. M., Dausset J., Le Paslier D., Cohen D. Construction and characterization of a yeast artificial chromosome library containing seven haploid human genome equivalents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4256–4260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altherr M. R., Plummer S., Bates G., MacDonald M., Taylor S., Lehrach H., Frischauf A. M., Gusella J. F., Boehnke M., Wasmuth J. J. Radiation hybrid map spanning the Huntington disease gene region of chromosome 4. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1040–1046. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90017-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anand R., Riley J. H., Butler R., Smith J. C., Markham A. F. A 3.5 genome equivalent multi access YAC library: construction, characterisation, screening and storage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):1951–1956. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler A. J., Chang D. D., Graw S. L., Brook J. D., Haber D. A., Sharp P. A., Housman D. E. Exon amplification: a strategy to isolate mammalian genes based on RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):4005–4009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.4005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler R., Ogilvie D. J., Elvin P., Riley J. H., Finniear R. S., Slynn G., Morten J. E., Markham A. F., Anand R. Walking, cloning, and mapping with yeast artificial chromosomes: a contig encompassing D21S13 and D21S16. Genomics. 1992 Jan;12(1):42–51. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90404-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon M. J., Dixon J., Houseal T., Bhatt M., Ward D. C., Klinger K., Landes G. M. Narrowing the position of the Treacher Collins syndrome locus to a small interval between three new microsatellite markers at 5q32-33.1. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 May;52(5):907–914. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon M. J., Dixon J., Raskova D., Le Beau M. M., Williamson R., Klinger K., Landes G. M. Genetic and physical mapping of the Treacher Collins syndrome locus: refinement of the localization to chromosome 5q32-33.2. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):249–253. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.4.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon M. J., Marres H. A., Edwards S. J., Dixon J., Cremers C. W. Treacher Collins syndrome: correlation between clinical and genetic linkage studies. Clin Dysmorphol. 1994 Apr;3(2):96–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon M. J., Read A. P., Donnai D., Colley A., Dixon J., Williamson R. The gene for Treacher Collins syndrome maps to the long arm of chromosome 5. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jul;49(1):17–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elvin P., Slynn G., Black D., Graham A., Butler R., Riley J., Anand R., Markham A. F. Isolation of cDNA clones using yeast artificial chromosome probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3913–3917. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazen L. E., Elmore J., Nadler H. L. Mandibulo-facial dysostosis. (Treacher-Collins syndrome). Am J Dis Child. 1967 Apr;113(4):405–410. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1967.02090190051001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis M. J., Morrison K. E., Campbell L., Grewal P. K., Christodoulou Z., Daniels R. J., Monaco A. P., Frischauf A. M., McPherson J., Wasmuth J. A contig of non-chimaeric YACs containing the spinal muscular atrophy gene in 5q13. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1161–1167. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Li X., Coss C. A., Taylor E. W., Meyers D. A., Weber J. L. Mapping the Treacher Collins syndrome locus to 5q31.3----q33.3. Genomics. 1991 Sep;11(1):193–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loftus S. K., Edwards S. J., Scherpbier-Heddema T., Buetow K. H., Wasmuth J. J., Dixon M. J. A combined genetic and radiation hybrid map surrounding the Treacher Collins syndrome locus on chromosome 5q. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Nov;2(11):1785–1792. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.11.1785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett M., Kere J., Hinton L. M. Direct selection: a method for the isolation of cDNAs encoded by large genomic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9628–9632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parimoo S., Patanjali S. R., Shukla H., Chaplin D. D., Weissman S. M. cDNA selection: efficient PCR approach for the selection of cDNAs encoded in large chromosomal DNA fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9623–9627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poswillo D. The pathogenesis of the Treacher Collins syndrome (mandibulofacial dysostosis). Br J Oral Surg. 1975 Jul;13(1):1–26. doi: 10.1016/0007-117x(75)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROVIN S., DACHI S. F., BORENSTEIN D. B., COTTER W. B. MANDIBULOFACIAL DYSOSTOSIS, A FAMILIAL STUDY OF FIVE GENERATIONS. J Pediatr. 1964 Aug;65:215–221. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(64)80522-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley J., Butler R., Ogilvie D., Finniear R., Jenner D., Powell S., Anand R., Smith J. C., Markham A. F. A novel, rapid method for the isolation of terminal sequences from yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2887–2890. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman G. A., Ye R. D., Pollock K. M., Sadler J. E., Korsmeyer S. J. Use of yeast artificial chromosome clones for mapping and walking within human chromosome segment 18q21.3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7485–7489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson T. G., Morrison K. E., Kleyn P., Bengtsson U., Gilliam T. C., Davies K. E., Wasmuth J. J., McPherson J. D. High resolution physical map of the region surrounding the spinal muscular atrophy gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1169–1176. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrington J. A., Bailey S. K., Armstrong E., Aprelikova O., Alitalo K., Dolganov G. M., Wilcox A. S., Sikela J. M., Wolfe S. F., Lovett M. A radiation hybrid map of 18 growth factor, growth factor receptor, hormone receptor, or neurotransmitter receptor genes on the distal region of the long arm of chromosome 5. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):803–808. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90156-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrington J. A., Hall L. V., Hinton L. M., Miller J. N., Wasmuth J. J., Lovett M. Radiation hybrid map of 13 loci on the long arm of chromosome 5. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):701–708. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90078-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L. Informativeness of human (dC-dA)n.(dG-dT)n polymorphisms. Genomics. 1990 Aug;7(4):524–530. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90195-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]