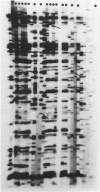
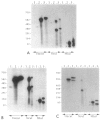
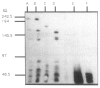
Abstract
Childhood-onset proximal spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a heritable neurological disorder, which has been mapped by genetic linkage analysis to chromosome 5q13, in the interval between markers D5S435 and D5S557. Here, we present gene sequences that have been isolated from this interval, several of which show sequence homologies to exons of beta-glucuronidase. These gene sequences are repeated several times across the candidate region and are also present on chromosome 5p. The arrangement of these repetitive gene motifs is polymorphic between individuals. The high degree of variability observed may have some influence on the expression of the genes in the region. Since SMA is not inherited as a classical autosomal recessive disease, novel genomic rearrangements arising from aberrant recombination events between the complex repeats may be associated with the phenotype observed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand R., Villasante A., Tyler-Smith C. Construction of yeast artificial chromosome libraries with large inserts using fractionation by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3425–3433. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzustowicz L. M., Lehner T., Castilla L. H., Penchaszadeh G. K., Wilhelmsen K. C., Daniels R., Davies K. E., Leppert M., Ziter F., Wood D. Genetic mapping of chronic childhood-onset spinal muscular atrophy to chromosome 5q11.2-13.3. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):540–541. doi: 10.1038/344540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundey S., Lovelace R. E. A clinical and genetic study of chronic proximal spinal muscular atrophy. Brain. 1975 Sep;98(3):455–472. doi: 10.1093/brain/98.3.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghes A. H., Ingraham S. E., Kóte-Jarai Z., Rosenfeld S., Herta N., Nadkarni N., DiDonato C. J., Carpten J., Hurko O., Florence J. Linkage mapping of the spinal muscular atrophy gene. Hum Genet. 1994 Mar;93(3):305–312. doi: 10.1007/BF00212028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghes A. H., Ingraham S. E., McLean M., Thompson T. G., McPherson J. D., Kote-Jarai Z., Carpten J. D., DiDonato C. J., Ikeda J. E., Surh L. A multicopy dinucleotide marker that maps close to the spinal muscular atrophy gene. Genomics. 1994 May 15;21(2):394–402. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clermont O., Burlet P., Burglen L., Lefebvre S., Pascal F., McPherson J., Wasmuth J. J., Cohen D., Le Paslier D., Weissenbach J. Use of genetic and physical mapping to locate the spinal muscular atrophy locus between two new highly polymorphic DNA markers. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Apr;54(4):687–694. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Parker P. J., Rhee L., Yang-Feng T. L., Chen E., Waterfield M. D., Francke U., Ullrich A. Multiple, distinct forms of bovine and human protein kinase C suggest diversity in cellular signaling pathways. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):859–866. doi: 10.1126/science.3755548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels R. J., Suthers G. K., Morrison K. E., Thomas N. H., Francis M. J., Mathew C. G., Loughlin S., Heiberg A., Wood D., Dubowitz V. Prenatal prediction of spinal muscular atrophy. J Med Genet. 1992 Mar;29(3):165–170. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.3.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery A. E. Clinical and genetic heterogeneity in spinal muscular atrophy--the multiple allele model. Neuromuscul Disord. 1991;1(4):307–308. doi: 10.1016/0960-8966(91)90106-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis M. J., Morrison K. E., Campbell L., Grewal P. K., Christodoulou Z., Daniels R. J., Monaco A. P., Frischauf A. M., McPherson J., Wasmuth J. A contig of non-chimaeric YACs containing the spinal muscular atrophy gene in 5q13. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1161–1167. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam T. C., Brzustowicz L. M., Castilla L. H., Lehner T., Penchaszadeh G. K., Daniels R. J., Byth B. C., Knowles J., Hislop J. E., Shapira Y. Genetic homogeneity between acute and chronic forms of spinal muscular atrophy. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):823–825. doi: 10.1038/345823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I., Zaremba J., Borkowska J. Chronic proximal spinal muscular atrophy of childhood and adolescence: problems of classification and genetic counselling. J Med Genet. 1985 Oct;22(5):350–353. doi: 10.1136/jmg.22.5.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I., Zaremba J., Borkowska J., Szirkowiec W. Chronic proximal spinal muscular atrophy of childhood and adolescence: sex influence. J Med Genet. 1984 Dec;21(6):447–450. doi: 10.1136/jmg.21.6.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleyn P. W., Wang C. H., Lien L. L., Vitale E., Pan J., Ross B. M., Grunn A., Palmer D. A., Warburton D., Brzustowicz L. M. Construction of a yeast artificial chromosome contig spanning the spinal muscular atrophy disease gene region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6801–6805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund S. D., Gallagher P. M., Wang B., Porter S. C., Ganschow R. E. Androgen responsiveness of the murine beta-glucuronidase gene is associated with nuclease hypersensitivity, protein binding, and haplotype-specific sequence diversity within intron 9. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5426–5434. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melki J., Abdelhak S., Sheth P., Bachelot M. F., Burlet P., Marcadet A., Aicardi J., Barois A., Carriere J. P., Fardeau M. Gene for chronic proximal spinal muscular atrophies maps to chromosome 5q. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):767–768. doi: 10.1038/344767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melki J., Burlet P., Clermont O., Pascal F., Paul B., Abdelhak S., Sherrington R., Gurling H., Nakamura Y., Weissenbach J. Refined linkage map of chromosome 5 in the region of the spinal muscular atrophy gene. Genomics. 1993 Mar;15(3):521–524. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melki J., Lefebvre S., Burglen L., Burlet P., Clermont O., Millasseau P., Reboullet S., Bénichou B., Zeviani M., Le Paslier D. De novo and inherited deletions of the 5q13 region in spinal muscular atrophies. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1474–1477. doi: 10.1126/science.7910982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melki J., Sheth P., Abdelhak S., Burlet P., Bachelot M. F., Lathrop M. G., Frezal J., Munnich A. Mapping of acute (type I) spinal muscular atrophy to chromosome 5q12-q14. The French Spinal Muscular Atrophy Investigators. Lancet. 1990 Aug 4;336(8710):271–273. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91803-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison K. E., Daniels R. J., Campbell L., McPherson J., Davies K. E. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism proximal to the spinal muscular atrophy region at D5S681. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Oct;2(10):1753–1753. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.10.1753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison K. E., Daniels R. J., Suthers G. K., Flynn G. A., Francis M. J., Buckle V. J., Davies K. E. High-resolution genetic map around the spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) locus on chromosome 5. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;50(3):520–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison K. E., Daniels R. J., Suthers G. K., Flynn G. A., Francis M. J., Grewal P. K., Dennis C., Buckle V., Ignatius J., Dubowitz V. Two novel microsatellite markers for prenatal prediction of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). Hum Genet. 1993 Sep;92(2):133–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00219680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munsat T. L., Woods R., Fowler W., Pearson C. M. Neurogenic muscular atrophy of infancy with prolonged survival. The variable course of Werdnig-Hoffmann Disease. Brain. 1969 Mar;92(1):9–24. doi: 10.1093/brain/92.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller B., Melki J., Burlet P., Clerget-Darpoux F. Proximal spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) types II and III in the same sibship are not caused by different alleles at the SMA locus on 5q. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 May;50(5):892–895. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima A., Kyle J. W., Miller R. D., Hoffmann J. W., Powell P. P., Grubb J. H., Sly W. S., Tropak M., Guise K. S., Gravel R. A. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of cDNA for human beta-glucuronidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):685–689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheth P., Abdelhak S., Bachelot M. F., Burlet P., Masset M., Hillaire D., Clerget-Darpoux F., Frézal J., Lathrop G. M., Munnich A. Linkage analysis in spinal muscular atrophy, by six closely flanking markers on chromosome 5. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Apr;48(4):764–768. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley J. M., Klinkenberg M., Wu B. M., Bachinsky D. R., Grubb J. H., Sly W. S. Mutational analysis of a patient with mucopolysaccharidosis type VII, and identification of pseudogenes. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Mar;52(3):517–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simard L. R., Prescott G., Rochette C., Morgan K., Lemieux B., Mathieu J., Melançon S. B., Vanasse M. Linkage disequilibrium analysis of childhood-onset spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) in the French-Canadian population. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Mar;3(3):459–463. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.3.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinnott P., Collier S., Costigan C., Dyer P. A., Harris R., Strachan T. Genesis by meiotic unequal crossover of a de novo deletion that contributes to steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2107–2111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares V. M., Brzustowicz L. M., Kleyn P. W., Knowles J. A., Palmer D. A., Asokan S., Penchaszadeh G. K., Munsat T. L., Gilliam T. C. Refinement of the spinal muscular atrophy locus to the interval between D5S435 and MAP1B. Genomics. 1993 Feb;15(2):365–371. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson T. G., Morrison K. E., Kleyn P., Bengtsson U., Gilliam T. C., Davies K. E., Wasmuth J. J., McPherson J. D. High resolution physical map of the region surrounding the spinal muscular atrophy gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1169–1176. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomatsu S., Fukuda S., Sukegawa K., Ikedo Y., Yamada S., Yamada Y., Sasaki T., Okamoto H., Kuwahara T., Yamaguchi S. Mucopolysaccharidosis type VII: characterization of mutations and molecular heterogeneity. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;48(1):89–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomatsu S., Sukegawa K., Ikedo Y., Fukuda S., Yamada Y., Sasaki T., Okamoto H., Kuwabara T., Orii T. Molecular basis of mucopolysaccharidosis type VII: replacement of Ala619 in beta-glucuronidase with Val. Gene. 1990 May 14;89(2):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90019-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth B., Pick E., Leutner A., Dadze A., Voosen B., Knapp M., Piechaczek-Wappenschmidt B., Rudnik-Schöneborn S., Schönling J., Cox S. Large linkage analysis in 100 families with autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) and 11 CEPH families using 15 polymorphic loci in the region 5q11.2-q13.3. Genomics. 1994 Mar 1;20(1):84–93. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]