Abstract
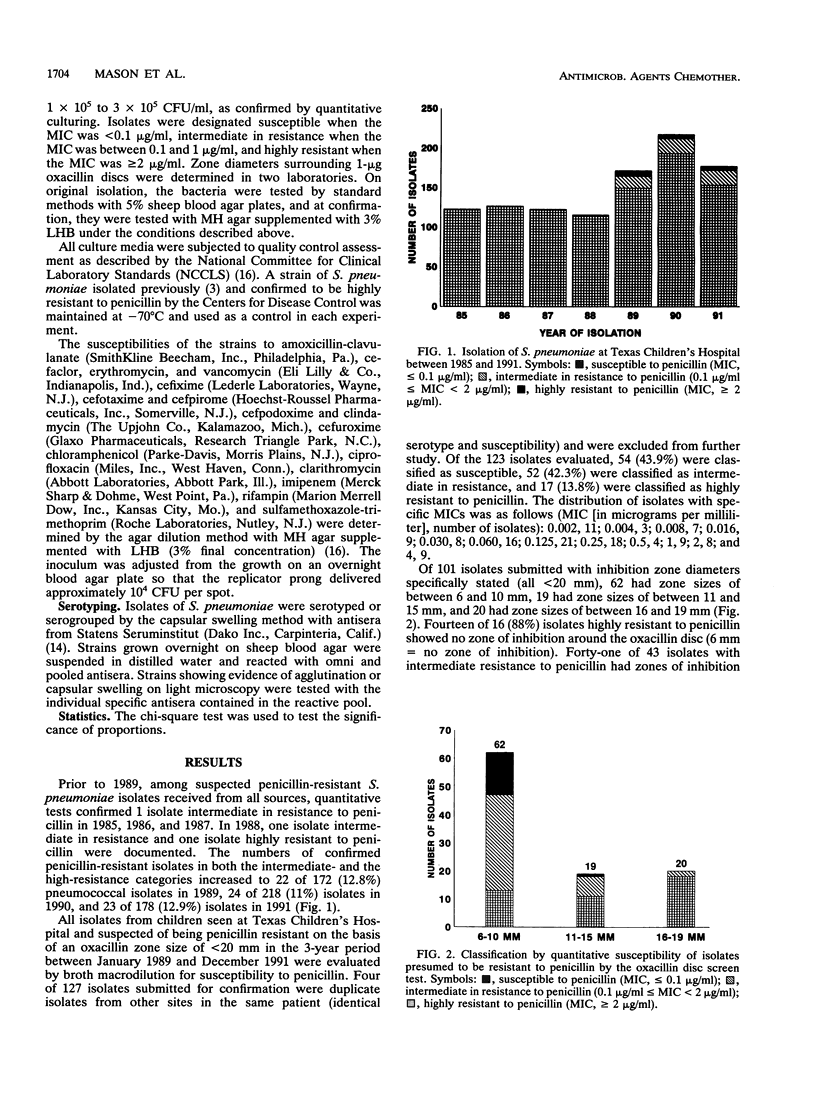
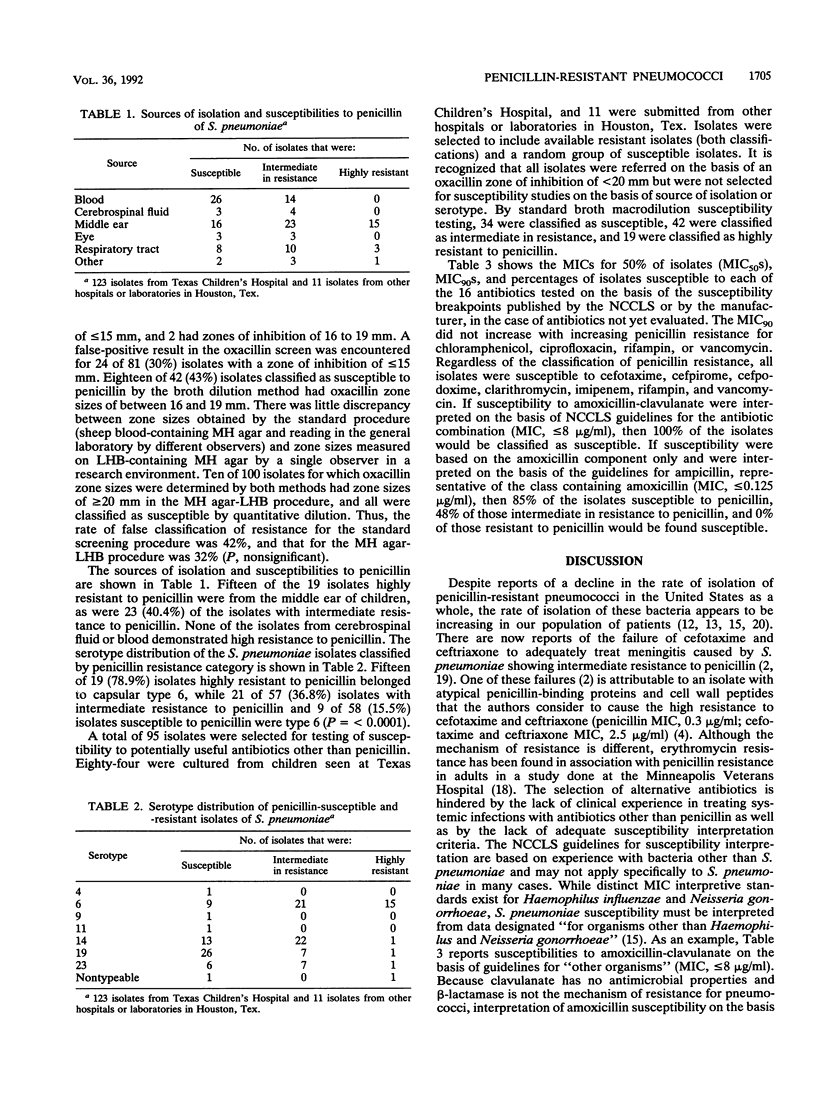
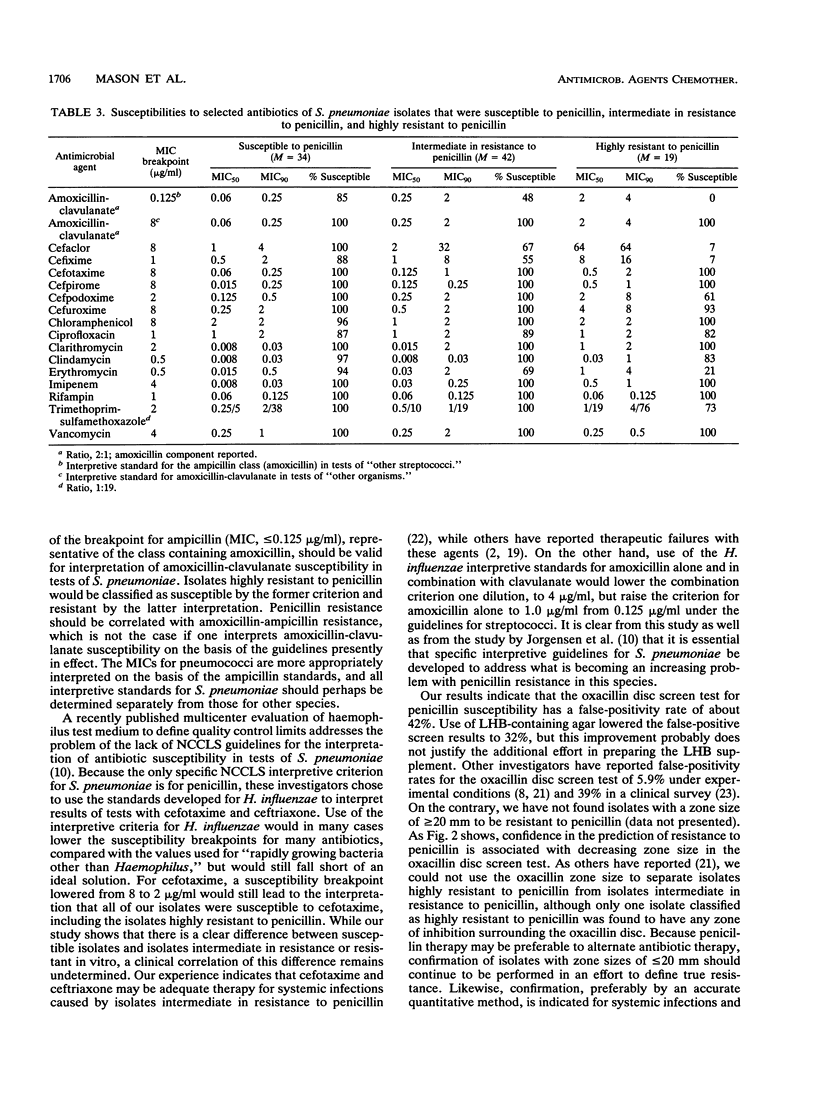
The isolation of Streptococcus pneumoniae with both high and intermediate resistance to penicillin has increased in our institution since 1989 to an average of 12.1% of all isolates. We determined the susceptibilities of 95 isolates (34 susceptible to penicillin, 42 intermediate in resistance to penicillin, and 19 resistant to penicillin) to 16 antimicrobial agents of potential use in the treatment of disease caused by S. pneumoniae. Susceptibility to penicillin was determined by broth macrodilution with Mueller-Hinton broth supplemented with 5% lysed horse blood. Isolates were classified as highly resistant when the MIC was greater than or equal to 2.0 micrograms/ml, intermediate in resistance when the MIC was between 0.1 and 1.0 microgram/ml, and susceptible when the MIC was less than 0.1 microgram/ml. Fifteen of 19 isolates found to be highly resistant to penicillin were recovered from the middle ear of children. None of the isolates recovered from cerebrospinal fluid was highly resistant to penicillin. Fifteen of these isolates highly resistant to penicillin were found to be serogroup 6. Susceptibilities to other antibiotics were determined by the agar dilution method with Mueller-Hinton agar containing 5% lysed horse blood and an inoculum of 10(4) CFU per spot delivered by a replicator device. The MIC for 90% of isolates increased with increasing penicillin resistance for all antibiotics tested, except chloramphenicol, ciprofloxacin, rifampin, and vancomycin. Regardless of the classification of penicillin resistance, all isolates were classified as susceptible to cefotaxime, cefpirome, cefpodoxime, clarithromycin, imipenem, rifampin, and vancomycin on the basis of National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards interpretive guidelines. Interpretation of susceptibilities on the basis of currently available guidelines is difficult in that susceptibility guidelines applicable specifically to S. pneumoniae are not available.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelbaum P. C. World-wide development of antibiotic resistance in pneumococci. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;6(4):367–377. doi: 10.1007/BF02013089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley J. S., Connor J. D. Ceftriaxone failure in meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae with reduced susceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991 Nov;10(11):871–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caraway N., Hawkins E., Hinds D., Mason E. Penicillin susceptibility of Streptococcus pneumoniae in a private pediatric hospital in Houston, Texas. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jul;33(7):1111–1112. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.7.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo A. M., Connor J. D., Severin A., Vaz Pato M. V., Tomasz A. A pneumococcal clinical isolate with high-level resistance to cefotaxime and ceftriaxone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Apr;36(4):886–889. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford K. L., Mason E. O., Jr, Kaplan S. L., Lamberth L. B., Tillman J. Factors associated with middle ear isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae resistant to penicillin in a children's hospital. J Pediatr. 1991 Dec;119(6):941–944. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray B. M., Converse G. M., 3rd, Dillon H. C., Jr Serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae causing disease. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):979–983. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray B. M., Dillon H. C., Jr Clinical and epidemiologic studies of pneumococcal infection in children. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;5(2):201–207. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198603000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. R., Gaspar M. N., Robins-Browne R. M., Koornhof H. J. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of pneumococci. 2. Determination of optimal disc diffusion test for detection of penicillin G resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Jan;6(1):53–64. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. R., Koornhof H. J., Robins-Browne R. M., Stevenson C. M., Vermaak Z. A., Freiman I., Miller G. B., Witcomb M. A., Isaäcson M., Ward J. I. Emergence of multiply resistant pneumococci. N Engl J Med. 1978 Oct 5;299(14):735–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197810052991402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Doern G. V., Ferraro M. J., Knapp C. C., Swenson J. M., Washington J. A. Multicenter evaluation of the use of Haemophilus test medium for broth microdilution antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Streptococcus pneumoniae and development of quality control limits. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):961–966. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.961-966.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kislak J. W., Razavi L. M., Daly A. K., Finland M. Susceptibility of pneumococci to nine antibiotics. Am J Med Sci. 1965 Sep;250(3):261–268. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196509000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klugman K. P. Pneumococcal resistance to antibiotics. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Apr;3(2):171–196. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre C., Juncosa T., Sanfeliu I. Antibiotic resistance and serotypes of 100 Streptococcus pneumoniae strains isolated in a children's hospital in Barcelona, Spain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):357–359. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marton A., Gulyas M., Munoz R., Tomasz A. Extremely high incidence of antibiotic resistance in clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae in Hungary. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):542–548. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch A. M., O'Ryan M., Van R., Pickering L. K. Invasive disease due to multiply resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in a Houston, Tex, day-care center. Am J Dis Child. 1990 Aug;144(8):923–927. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1990.02150320087033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spika J. S., Facklam R. R., Plikaytis B. D., Oxtoby M. J. Antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae in the United States, 1979-1987. The Pneumococcal Surveillance Working Group. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1273–1278. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.6.1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson J. M., Hill B. C., Thornsberry C. Screening pneumococci for penicillin resistance. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):749–752. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.749-752.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willett L. D., Dillon H. C., Jr, Gray B. M. Penicillin-intermediate pneumococci in a children's hospital. Am J Dis Child. 1985 Oct;139(10):1054–1057. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1985.02140120100037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



