Abstract
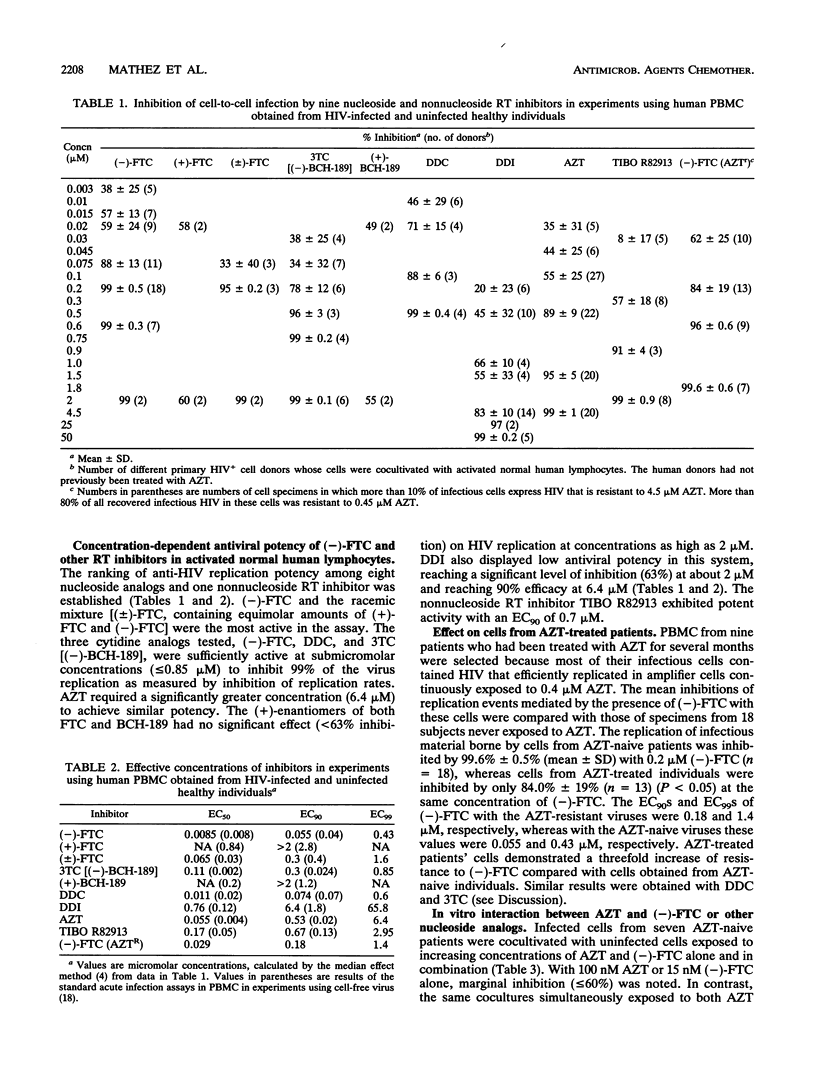
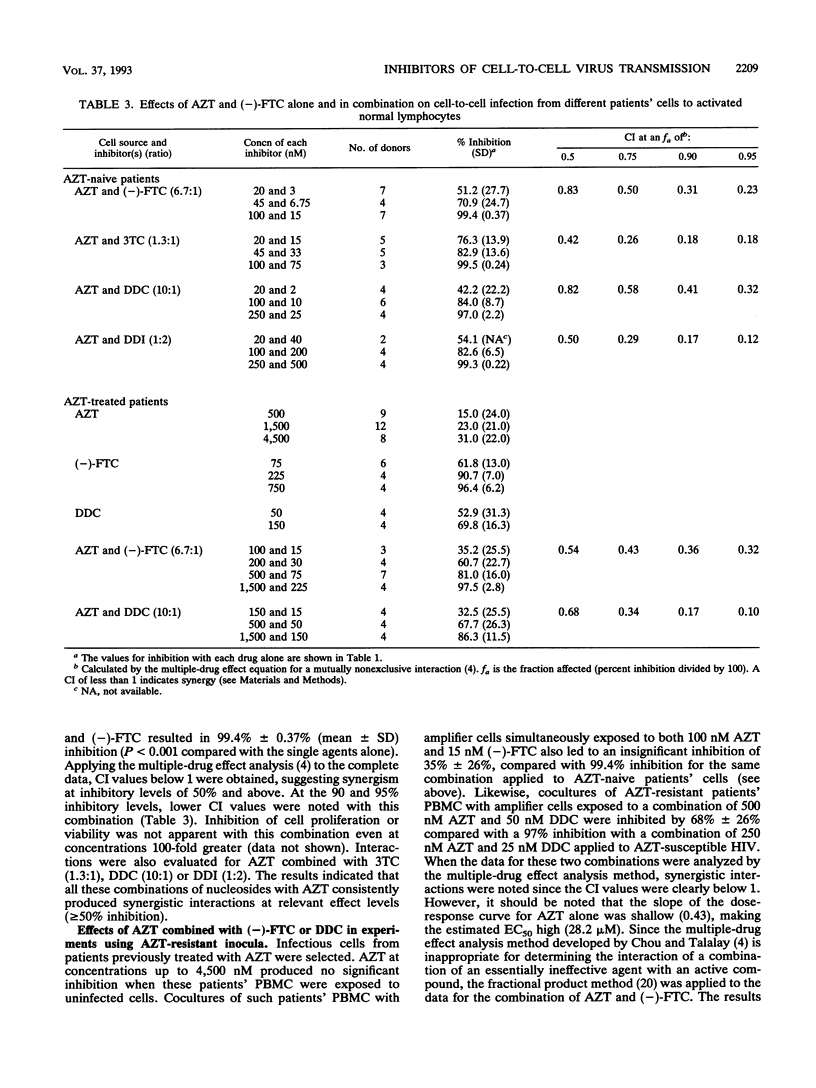
The relative in vitro potency of nine human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors was evaluated in a coculture assay which measures the frequencies of infectious primary cells from HIV-positive patients by the limiting dilution technique and measures their apparent reduction under increasing concentrations of drugs. An advantage of this assay is that it utilizes a variety of wild-type viruses not selected by in vitro propagation. Potency ranking placed the (-)-L-enantiomer of 2',3'-dideoxy-5-fluoro-3'-thiacytidine [(-)-FTC], an oxathiolane pyrimidine nucleoside analog (90% effective concentration = 55 nM), before 2',3'-dideoxycytidine (DDC) (74 nM), (-)-2',3'-dideoxy-3'-thiacytidine (3TC) (300 nM), 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT) (530 nM), TIBO R82913 (670 nM), and 2',3'-dideoxyinosine (DDI) (6,400 nM). HIV from AZT-naive patients' lymphocytes was more sensitive to the inhibitory effect of (-)-FTC, 3TC, or DDC than was highly AZT-resistant HIV obtained from AZT-treated patients' cells, indicating partial cross-resistance between thymidine and cytidine analogs. Combined inhibitory concentrations of AZT with (-)-FTC, 3TC, DDC, and DDI produced synergistic interactions as determined by the multiple-drug effect analysis. Synergistic interactions were demonstrable with AZT plus (-)-FTC or with AZT plus DDC with cells bearing AZT-resistant HIV. The inhibitory concentrations of AZT established by this cell-to-cell virus transmission assay are closer than those determined by the conventional assay system to the extracellular AZT concentrations required in patients' plasma to achieve comparable levels of HIV inhibition in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang C. N., Doong S. L., Zhou J. H., Beach J. W., Jeong L. S., Chu C. K., Tsai C. H., Cheng Y. C., Liotta D., Schinazi R. Deoxycytidine deaminase-resistant stereoisomer is the active form of (+/-)-2',3'-dideoxy-3'-thiacytidine in the inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):13938–13942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou T. C., Talalay P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1984;22:27–55. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(84)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doong S. L., Tsai C. H., Schinazi R. F., Liotta D. C., Cheng Y. C. Inhibition of the replication of hepatitis B virus in vitro by 2',3'-dideoxy-3'-thiacytidine and related analogues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8495–8499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., Davis M., Liotta D. C., Paff M., Frick L. W., Nelson D. J., Dornsife R. E., Wurster J. A., Wilson L. J., Fyfe J. A. The anti-hepatitis B virus activities, cytotoxicities, and anabolic profiles of the (-) and (+) enantiomers of cis-5-fluoro-1-[2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-oxathiolan-5-yl]cytosine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Dec;36(12):2686–2692. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.12.2686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P., Balachandran R., Ho M., Enrico A., Rinaldo C. Cell-to-cell transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in the presence of azidothymidine and neutralizing antibody. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2361–2365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2361-2365.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li P., Burrell C. J. Synthesis of human immunodeficiency virus DNA in a cell-to-cell transmission model. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Feb;8(2):253–259. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li P., Kuiper L. J., Stephenson A. J., Burrell C. J. De novo reverse transcription is a crucial event in cell-to-cell transmission of human immunodeficiency virus. J Gen Virol. 1992 Apr;73(Pt 4):955–959. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-4-955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathez D., Paul D., de Bélilovsky C., Sultan Y., Deleuze J., Gorin I., Saurin W., Decker R., Leibowitch J. Productive human immunodeficiency virus infection levels correlate with AIDS-related manifestations in the patient. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7438–7442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner M. R., Elboim H. S., Cannon T., Cavacini L., Hideshima T. Functional activity of an HIV-1 neutralizing IgG human monoclonal antibody: ADCC and complement-mediated lysis. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 May;8(5):553–558. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Orenstein J., Dimitrov D., Martin M. Cell-to-cell spread of HIV-1 occurs within minutes and may not involve the participation of virus particles. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):712–724. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90038-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., Chu C. K., Peck A., McMillan A., Mathis R., Cannon D., Jeong L. S., Beach J. W., Choi W. B., Yeola S. Activities of the four optical isomers of 2',3'-dideoxy-3'-thiacytidine (BCH-189) against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in human lymphocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Mar;36(3):672–676. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., Lloyd R. M., Jr, Nguyen M. H., Cannon D. L., McMillan A., Ilksoy N., Chu C. K., Liotta D. C., Bazmi H. Z., Mellors J. W. Characterization of human immunodeficiency viruses resistant to oxathiolane-cytosine nucleosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Apr;37(4):875–881. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.4.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., McMillan A., Cannon D., Mathis R., Lloyd R. M., Peck A., Sommadossi J. P., St Clair M., Wilson J., Furman P. A. Selective inhibition of human immunodeficiency viruses by racemates and enantiomers of cis-5-fluoro-1-[2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-oxathiolan-5-yl]cytosine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Nov;36(11):2423–2431. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.11.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., Peters J., Williams C. C., Chance D., Nahmias A. J. Effect of combinations of acyclovir with vidarabine or its 5'-monophosphate on herpes simplex viruses in cell culture and in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):499–507. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., Sommadossi J. P., Saalmann V., Cannon D. L., Xie M. Y., Hart G. C., Smith G. A., Hahn E. F. Activities of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine nucleotide dimers in primary lymphocytes infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1061–1067. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds P., Balfe P., Peutherer J. F., Ludlam C. A., Bishop J. O., Brown A. J. Human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals contain provirus in small numbers of peripheral mononuclear cells and at low copy numbers. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):864–872. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.864-872.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. S., Brian E. L., Pagano J. S. Resumption of virus production after human immunodeficiency virus infection of T lymphocytes in the presence of azidothymidine. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3769–3773. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3769-3773.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglione T. A., Collier A. C., Opheim K., Gianola F. G., Benedetti J., Corey L. Pharmacokinetic evaluations of low- and high-dose zidovudine plus high-dose acyclovir in patients with symptomatic human immunodeficiency virus infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Nov;35(11):2225–2231. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.11.2225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


