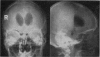
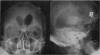
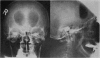
Full text
PDF





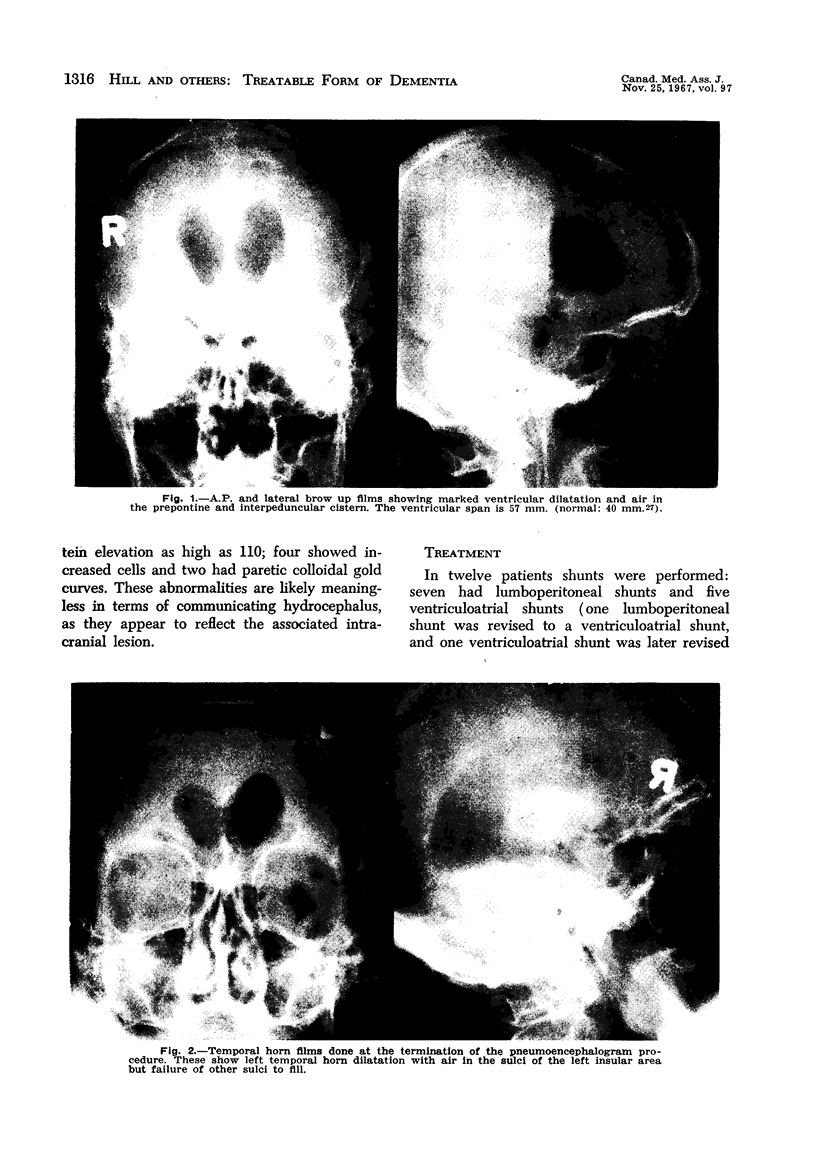
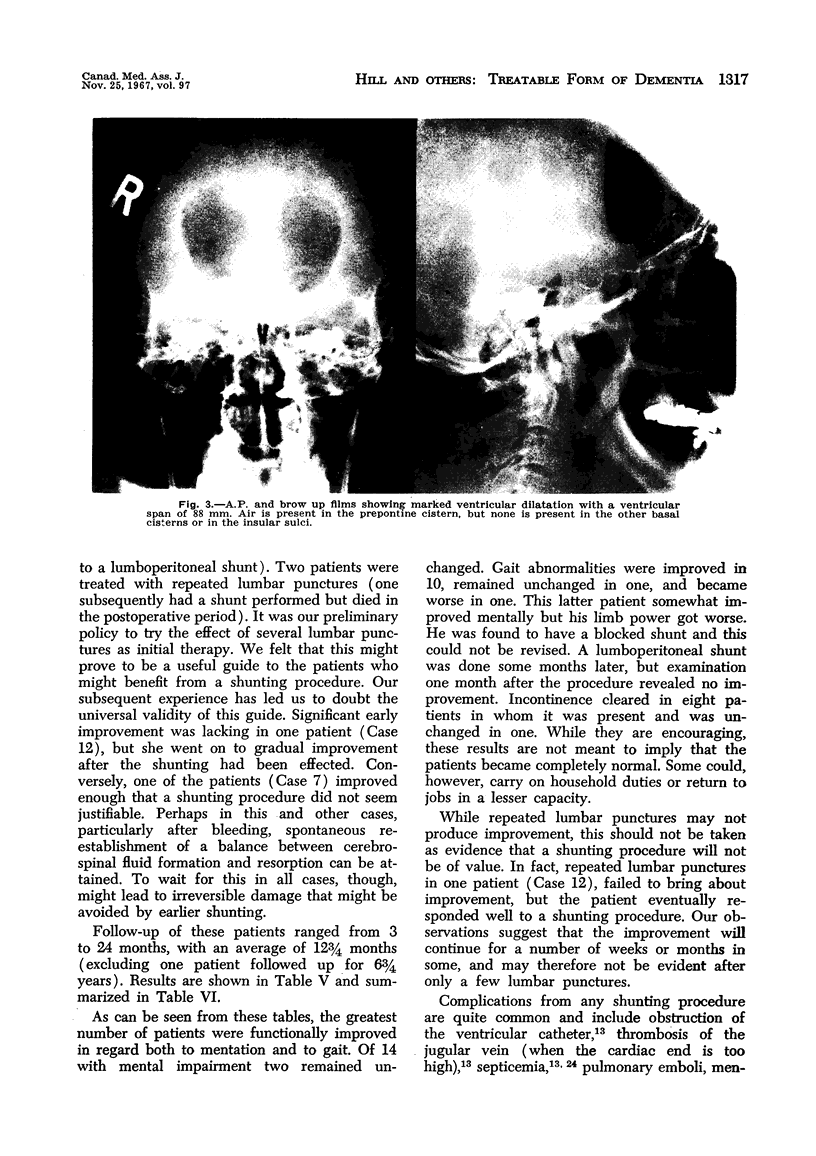
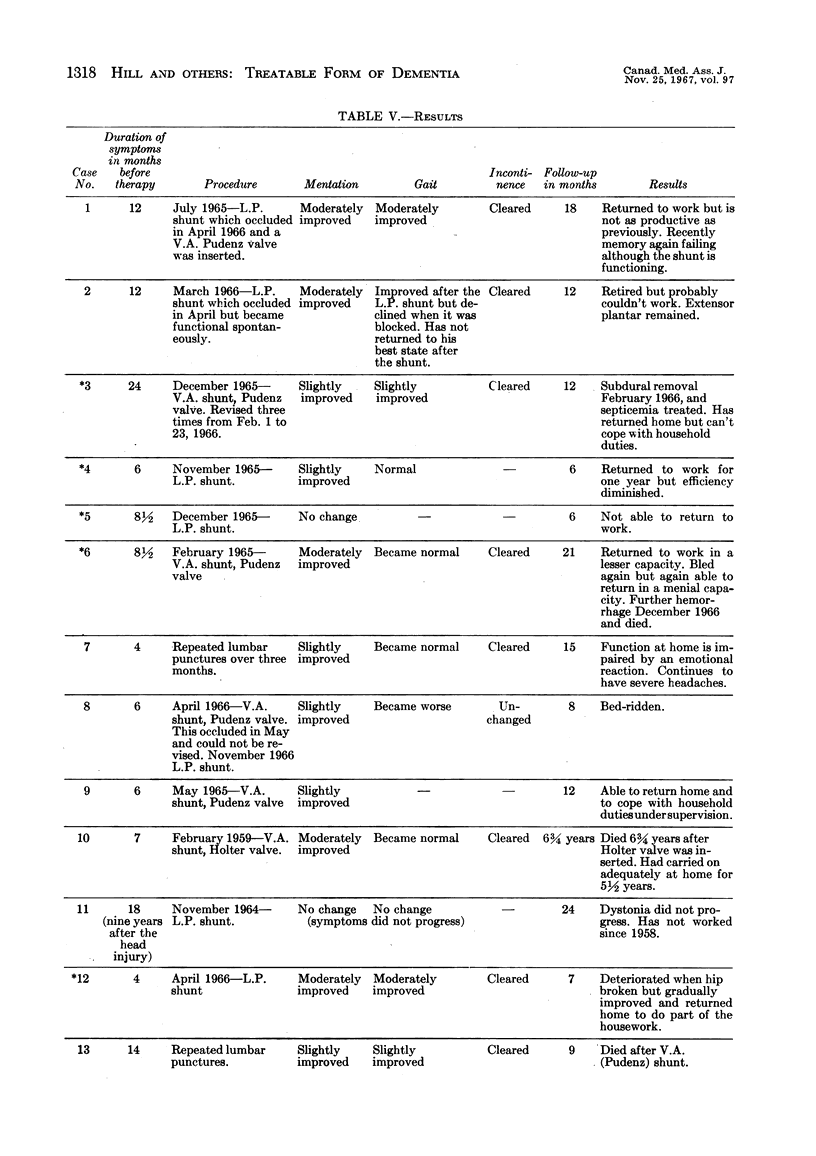


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS R. D., FISHER C. M., HAKIM S., OJEMANN R. G., SWEET W. H. SYMPTOMATIC OCCULT HYDROCEPHALUS WITH "NORMAL" CEREBROSPINAL-FLUID PRESSURE.A TREATABLE SYNDROME. N Engl J Med. 1965 Jul 15;273:117–126. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196507152730301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASKENASY H. M., HERZBERGER E. E., WIJSENBEEK H. S. Hydrocephalus with vascular malformations of the brain; a preliminary report. Neurology. 1953 Mar;3(3):213–220. doi: 10.1212/wnl.3.3.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARDENAS Y CARDENAS J. Cysticercosis of the nervous system. Pathologic and radiologic findings. J Neurosurg. 1962 Aug;19:635–640. doi: 10.3171/jns.1962.19.8.0635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. J. Persistent bacteraemia. A new syndrome due to the bacterial colonisation of the Spitz-Holter valves. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1962 Jun;4:298–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDOFF L. M., FEIRING E. H. Subdural hematoma occurring in surgically treated hydrocephalic children, with a note on a method of handling persistent accumulations. J Neurosurg. 1953 Nov;10(6):557–563. doi: 10.3171/jns.1953.10.6.0557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLTZ E. L., SHEEHY T. F., Jr Pneumoencephalography in tuberculous meningitis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1956 Dec;74(6):835–855. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1956.74.6.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLTZ E. L., WARD A. A., Jr Communicating hydrocephalus from subarachnoid bleeding. J Neurosurg. 1956 Nov;13(6):546–566. doi: 10.3171/jns.1956.13.6.0546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foltz E. L., Shurtleff D. B. Conversion of communicating hydrocephalus to stenosis or occlusion of the aqueduct during ventricular shunt. J Neurosurg. 1966 Feb;24(2):520–529. doi: 10.3171/jns.1966.24.2.0520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakim S., Adams R. D. The special clinical problem of symptomatic hydrocephalus with normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Observations on cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics. J Neurol Sci. 1965 Jul-Aug;2(4):307–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(65)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIBLER R. F., COUCH R. S., CROMPTON M. R. Hydrocephalus in the adult following spontaneous subarachnoid haemorrhage. Brain. 1961 Mar;84:45–61. doi: 10.1093/brain/84.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LORBER J. Studies of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation in tuberculous meningitis in children. Part II. A review of 100 pneumoencephalograms. Arch Dis Child. 1951 Feb;26(125):28–44. doi: 10.1136/adc.26.125.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messert B., Baker N. H. Syndrome of progressive spastic ataxia and apraxia associated with occult hydrocephalus. Neurology. 1966 May;16(5):440–452. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.5.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penfield W., Cone W. Elementary Principles of the Treatment of Head Injuries. Can Med Assoc J. 1943 Feb;48(2):99–104. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHULMAN K., MARTIN B. F., POPOFF N., RANSOHOFF J. RECOGNITION AND TREATMENT OF HYDROCEPHALUS FOLLOWING SPONTANEOUS SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE. J Neurosurg. 1963 Dec;20:1040–1049. doi: 10.3171/jns.1963.20.12.1040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]