Abstract
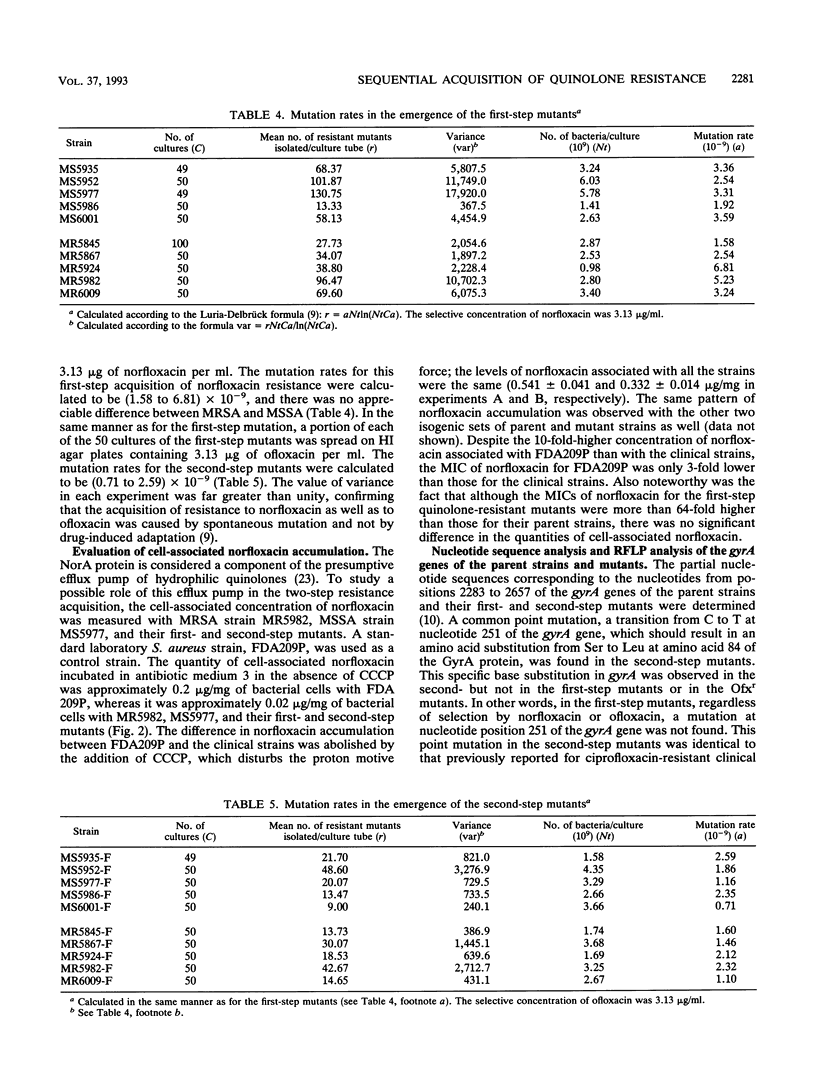
The acquisition of ofloxacin resistance by a susceptible clinical Staphylococcus aureus strain was found to be achieved in two sequential steps: the first step was accompanied by 4-fold increases in the ofloxacin MIC and 8- to 16-fold increases in the norfloxacin MIC. The second step was accompanied by further increases in both the ofloxacin and the norfloxacin MICs. A mutation of the gyrA gene resulting in an amino acid substitution was found in the second-step but not in the first-step resistant subclone. On the other hand, there was no difference in the accumulation of norfloxacin in the parent strain and the resistant subclones of each step. The rates of mutation to resistance in the steps were (1.58 to 6.81) x 10(-9) and (0.71 to 2.59) x 10(-9), respectively, and did not depend on whether the parent strain was resistant to methicillin. Some implications of these observations for clinical as well as mechanistic aspects of the prevalence of methicillin- and ofloxacin-resistant S. aureus are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg H. M., Rimland D., Carroll D. J., Terry P., Wachsmuth I. K. Rapid development of ciprofloxacin resistance in methicillin-susceptible and -resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1279–1285. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.6.1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Bedard J. Impermeability to quinolones in gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;10(4):232–239. doi: 10.1007/BF01966995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullmann W., Stieglitz M., Baars B., Opferkuch W. Comparative evaluation of recently developed quinolone compounds--with a note on the frequency of resistant mutants. Chemotherapy. 1985;31(1):19–28. doi: 10.1159/000238309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiramatsu K., Suzuki E., Takayama H., Katayama Y., Yokota T. Role of penicillinase plasmids in the stability of the mecA gene in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Apr;34(4):600–604. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.4.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S. Bacterial resistance to the quinolone antimicrobial agents. Am J Med. 1989 Dec 29;87(6C):17S–23S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S. B. Active efflux mechanisms for antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Apr;36(4):695–703. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.4.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margerrison E. E., Hopewell R., Fisher L. M. Nucleotide sequence of the Staphylococcus aureus gyrB-gyrA locus encoding the DNA gyrase A and B proteins. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1596–1603. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1596-1603.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuhashi M., Song M. D., Ishino F., Wachi M., Doi M., Inoue M., Ubukata K., Yamashita N., Konno M. Molecular cloning of the gene of a penicillin-binding protein supposed to cause high resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):975–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.975-980.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyfakh A. A. The multidrug efflux transporter of Bacillus subtilis is a structural and functional homolog of the Staphylococcus NorA protein. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Feb;36(2):484–485. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda J., Okamoto S., Takahata M., Nishino T. Inhibitory effects of ciprofloxacin and sparfloxacin on DNA gyrase purified from fluoroquinolone-resistant strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Nov;35(11):2288–2293. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.11.2288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S. Methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus resistant to quinolones. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):335–336. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.335-336.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalit I., Berger S. A., Gorea A., Frimerman H. Widespread quinolone resistance among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in a general hospital. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):593–594. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. T. Mutation rates to 4-quinolone resistance. Arzneimittelforschung. 1990 Jan;40(1):65–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreedharan S., Oram M., Jensen B., Peterson L. R., Fisher L. M. DNA gyrase gyrA mutations in ciprofloxacin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus: close similarity with quinolone resistance mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7260–7262. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7260-7262.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreedharan S., Peterson L. R., Fisher L. M. Ciprofloxacin resistance in coagulase-positive and -negative staphylococci: role of mutations at serine 84 in the DNA gyrase A protein of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Oct;35(10):2151–2154. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.10.2151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treffers H. P., Spinelli V., Belser N. O. A Factor (or Mutator Gene) Influencing Mutation Rates in Escherichia Coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1954 Nov;40(11):1064–1071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.40.11.1064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trucksis M., Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. A novel locus conferring fluoroquinolone resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5854–5860. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5854-5860.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Bogaki M., Nakamura S., Ubukata K., Konno M. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus norA gene, which confers resistance to quinolones. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6942–6949. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6942-6949.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Kojima T., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Uptake of sparfloxacin and norfloxacin by clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):368–370. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



