Abstract
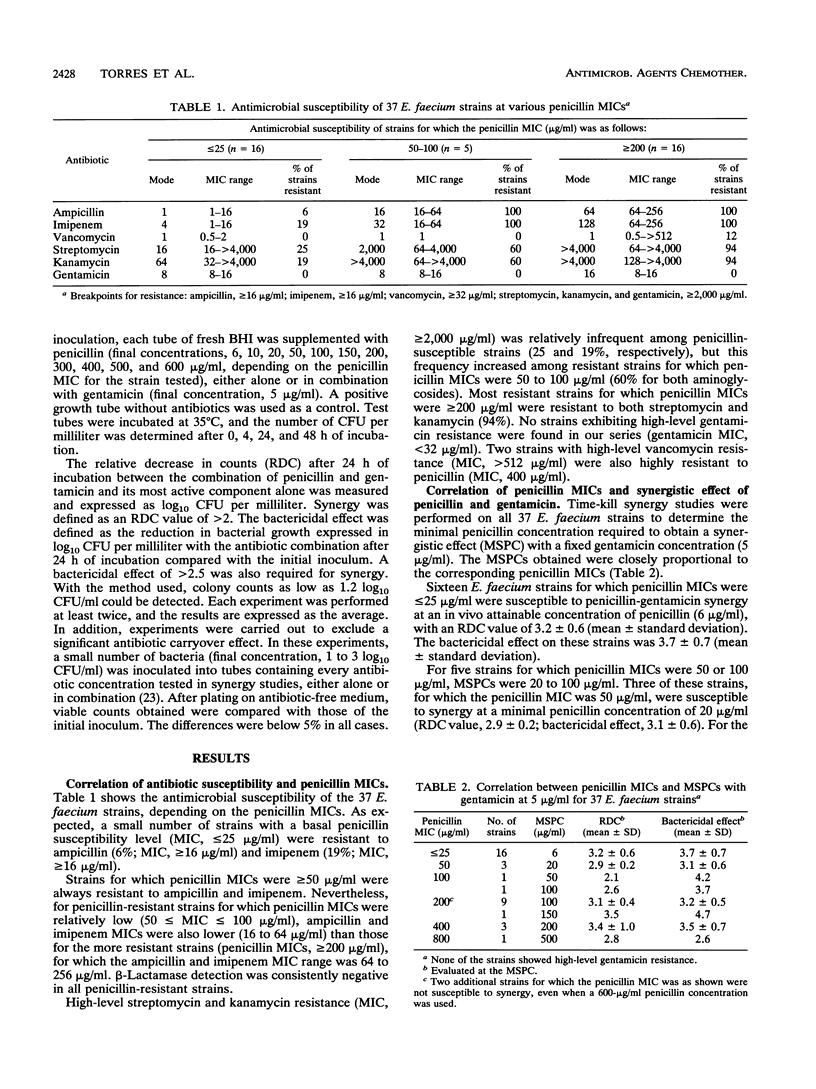
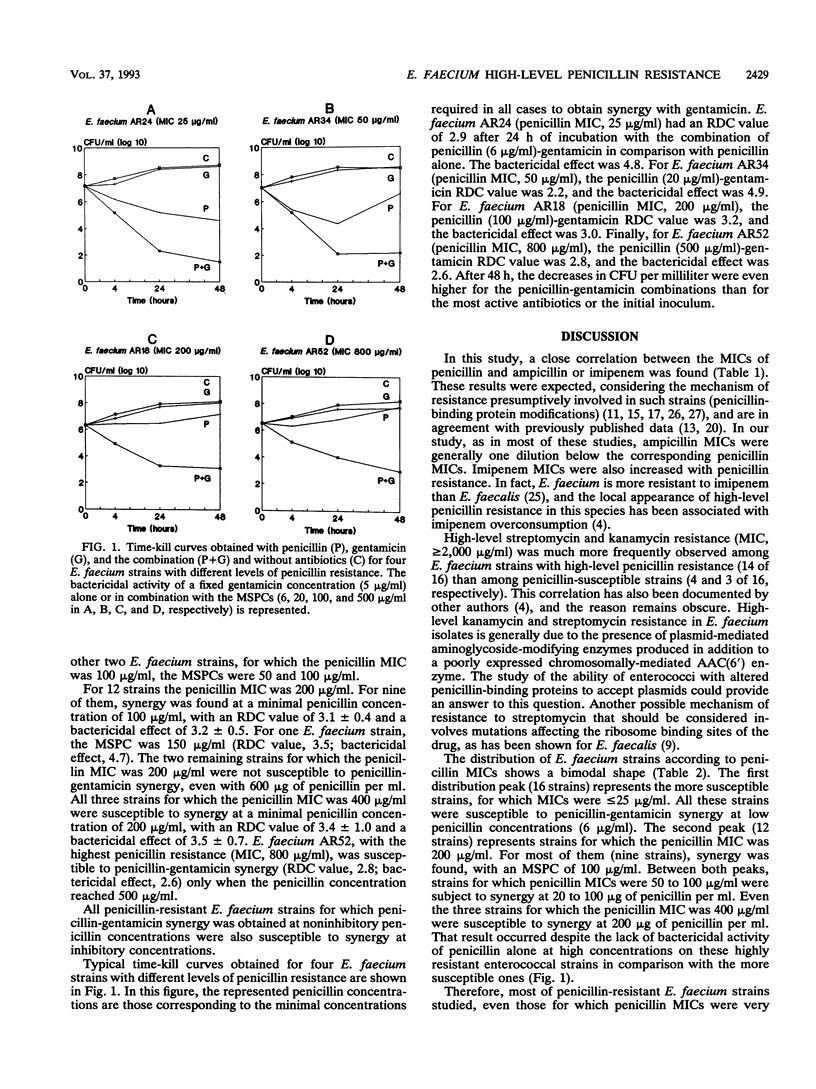
Thirty-seven Enterococcus faecium strains with different levels of penicillin susceptibility were studied in time-kill experiments with a fixed concentration (5 micrograms/ml) of gentamicin combined with different penicillin concentrations (6 to 600 micrograms/ml). Synergy was defined as a relative decrease in counts of greater than 2 log10 CFU per milliliter after 24 h of incubation when the combination of the antibiotics was compared with its most active component alone. The minimal synergistic penicillin concentrations found were 6 micrograms/ml for 16 of 16 strains for which penicillin MICs were < or = 25 micrograms/ml, 20 to 100 micrograms/ml for 14 of 17 strains for which penicillin MICs were 50 to 200 micrograms/ml, and 200 to 500 micrograms/ml for 4 of 4 strains for which MICs penicillin were > 200 micrograms/ml. Penicillin-gentamicin synergy was observed even in high-level penicillin-resistant E. faecium strains at penicillin concentrations close to one-half the penicillin MIC. The possibility of treating infections caused by high-level penicillin-resistant E. faecium strains with penicillin-gentamicin combinations in particular cases may depend on the penicillin levels attainable in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boulanger J. M., Ford-Jones E. L., Matlow A. G. Enterococcal bacteremia in a pediatric institution: a four-year review. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Sep-Oct;13(5):847–856. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.5.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce J. M., Opal S. M., Potter-Bynoe G., LaForge R. G., Zervos M. J., Furtado G., Victor G., Medeiros A. A. Emergence and nosocomial transmission of ampicillin-resistant enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 May;36(5):1032–1039. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.5.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush L. M., Calmon J., Cherney C. L., Wendeler M., Pitsakis P., Poupard J., Levison M. E., Johnson C. C. High-level penicillin resistance among isolates of enterococci. Implications for treatment of enterococcal infections. Ann Intern Med. 1989 Apr 1;110(7):515–520. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-110-7-515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cercenado E., García-Leoni M. E., Rodeño P., Rodríguez-Créixems M. Ampicillin-resistant enterococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):829–829. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.829-.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coudron P. E., Markowitz S. M., Wong E. S. Isolation of a beta-lactamase-producing, aminoglycoside-resistant strain of Enterococcus faecium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 May;36(5):1125–1126. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.5.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig W. A., Ebert S. C. Continuous infusion of beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Dec;36(12):2577–2583. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.12.2577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Farber B. F., Murray B. E., Wennersten C., Moellering R. C., Jr Ribosomal resistance of clinical enterococcal to streptomycin isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):398–399. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Collins M. D. Identification of Enterococcus species isolated from human infections by a conventional test scheme. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):731–734. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.731-734.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Grossato A., Rossi L., Cheng Y. R., Satta G. Transition from resistance to hypersusceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics associated with loss of a low-affinity penicillin-binding protein in a Streptococcus faecium mutant highly resistant to penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):678–683. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraimow H. S., Venuti E. Inconsistent bactericidal activity of triple-combination therapy with vancomycin, ampicillin, and gentamicin against vancomycin-resistant, highly ampicillin-resistant Enterococcus faecium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jul;36(7):1563–1566. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.7.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S., Swenson J. M., Hill B. C., Pigott N. E., Facklam R. R., Cooksey R. C., Thornsberry C., Jarvis W. R., Tenover F. C. Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of common and unusual species of enterococci causing infections in the United States. Enterococcal Study Group. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Sep;30(9):2373–2378. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.9.2373-2378.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. W., Stewart D., Pedler S. J. Species identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing of enterococci isolated from hospitalized patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Sep;35(9):1943–1945. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.9.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayson M. L., Eliopoulos G. M., Wennersten C. B., Ruoff K. L., De Girolami P. C., Ferraro M. J., Moellering R. C., Jr Increasing resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics among clinical isolates of Enterococcus faecium: a 22-year review at one institution. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Nov;35(11):2180–2184. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.11.2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handwerger S., Perlman D. C., Altarac D., McAuliffe V. Concomitant high-level vancomycin and penicillin resistance in clinical isolates of enterococci. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;14(3):655–661. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.3.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klare I., Rodloff A. C., Wagner J., Witte W., Hakenbeck R. Overproduction of a penicillin-binding protein is not the only mechanism of penicillin resistance in Enterococcus faecium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Apr;36(4):783–787. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.4.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louie M., Simor A. E., Szeto S., Patel M., Kreiswirth B., Low D. E. Susceptibility testing of clinical isolates of Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):41–45. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.41-45.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E. The life and times of the Enterococcus. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jan;3(1):46–65. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oster S. E., Chirurgi V. A., Goldberg A. A., Aiken S., McCabe R. E. Ampicillin-resistant enterococcal species in an acute-care hospital. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1821–1823. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Steigbigel R. T., Davis H. T., Chapman S. W. Method of reliable determination of minimal lethal antibiotic concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):699–708. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahm D. F., Torres C. Effects of medium and inoculum variations on screening for high-level aminoglycoside resistance in Enterococcus faecalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):250–256. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.250-256.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapico F. L., Canawati H. N., Ginunas V. J., Gilmore D. S., Montgomerie J. Z., Tuddenham W. J., Facklam R. R. Enterococci highly resistant to penicillin and ampicillin: an emerging clinical problem? J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2091–2095. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2091-2095.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Calderwood S. B., Moellering R. C., Jr, Tomasz A. Studies on the mechanism of intrinsic resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in group D streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Mar;129(3):813–822. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-3-813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., le Bouguénec C., Gutmann L., Horaud T. One or two low affinity penicillin-binding proteins may be responsible for the range of susceptibility of Enterococcus faecium to benzylpenicillin. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Aug;131(8):1933–1940. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-8-1933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Obeid S., Gutmann L., Williamson R. Modification of penicillin-binding proteins of penicillin-resistant mutants of different species of enterococci. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Nov;26(5):613–618. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.5.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


