Abstract
A special registry of children with heart disease in the City of Toronto was set up (a) to provide for follow-up of all children with heart disease in that community, (b) to remove the “cardiac” label from children with functional murmurs, (c) to acquaint parents with facilities available for the management of children with heart disease, and (d) to record useful data regarding heart disease in children.
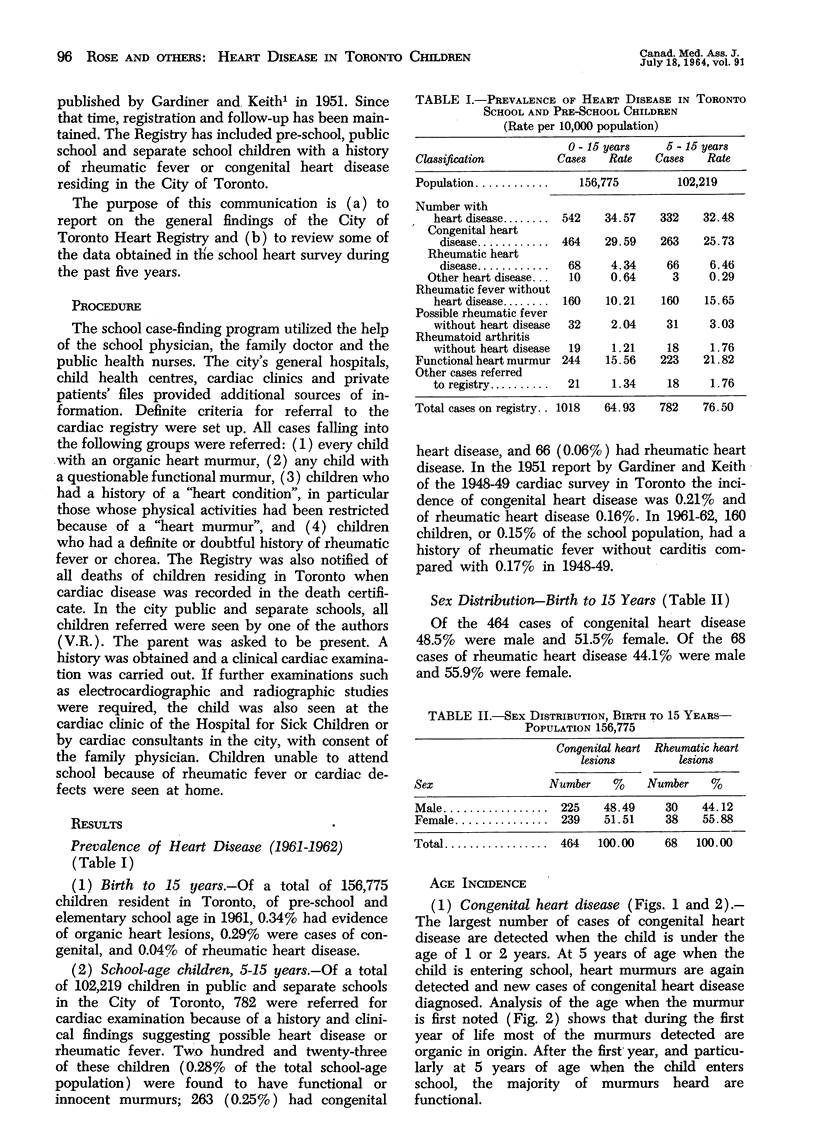
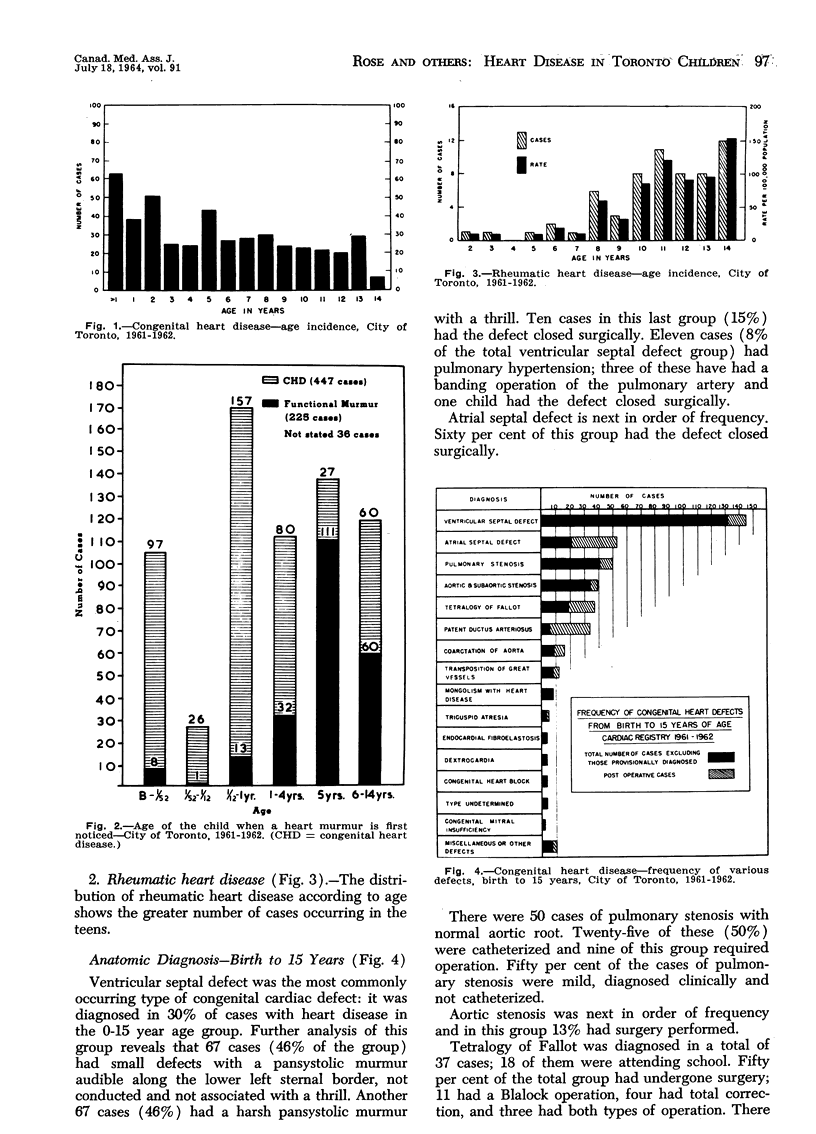
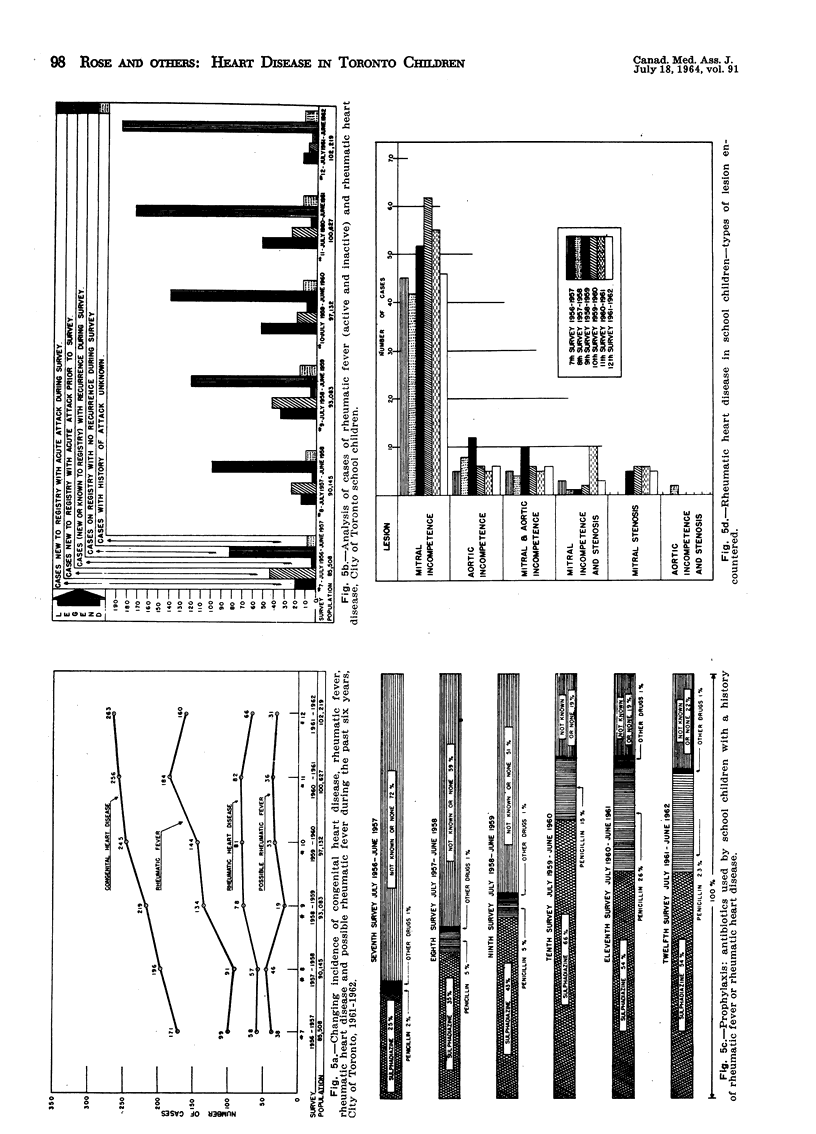
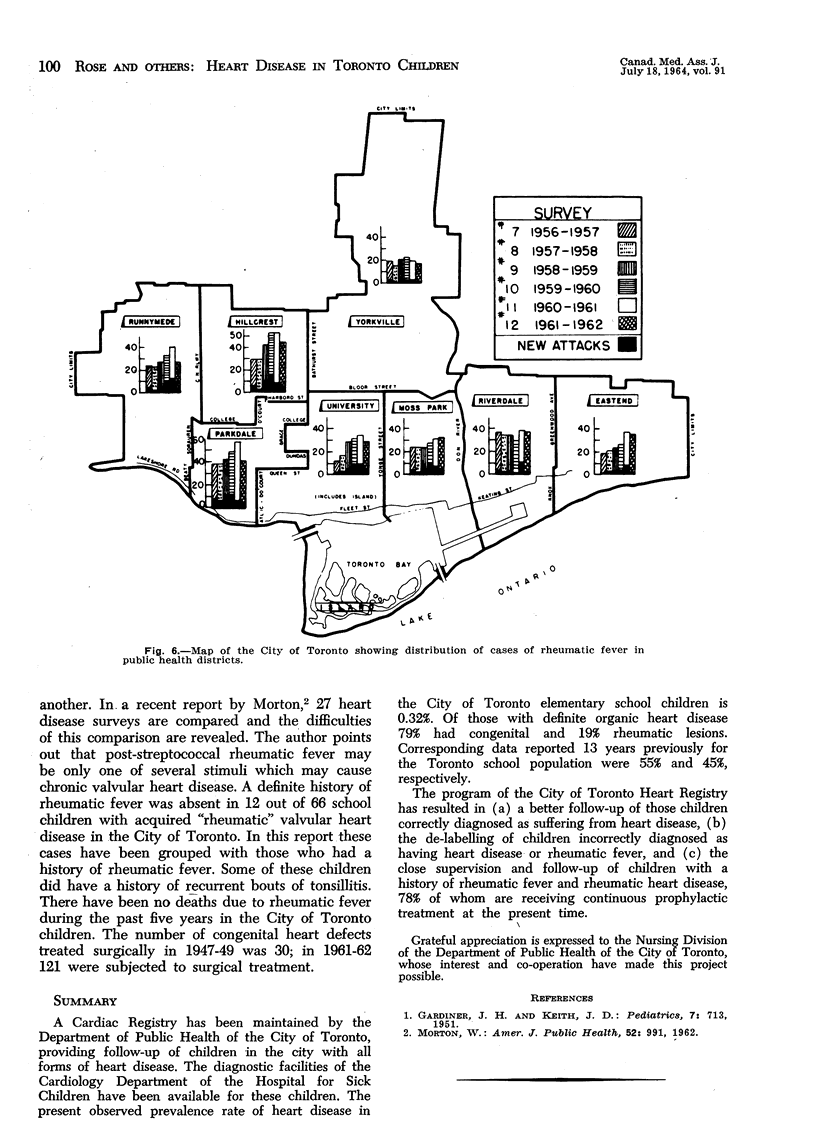
The 1961-62 Cardiac Registry showed that 542 of 156,775 pre-school and school children had evidence of heart disease; 464 were congenital and 68 rheumatic in origin: 121 children with congenital heart defects had been treated surgically. Congenital cardiac disease ranked fifth in frequency among the causes of death in children. There was a diminution of acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease in children in 1961-62 when compared with data for previous years. Seventy-eight per cent of children in this series with a history of rheumatic fever were receiving continuous prophylaxis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GARDINER J. H., KEITH J. D. Prevalence of heart disease in Toronto children; 1948-1949 cardiac registry. Pediatrics. 1951 May;7(5):713–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON W. Heart disease prevalence in school children in two Colorado communities. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1962 Jun;52:991–1001. doi: 10.2105/ajph.52.6.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


