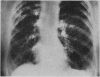
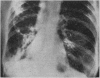
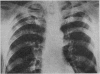
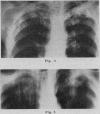
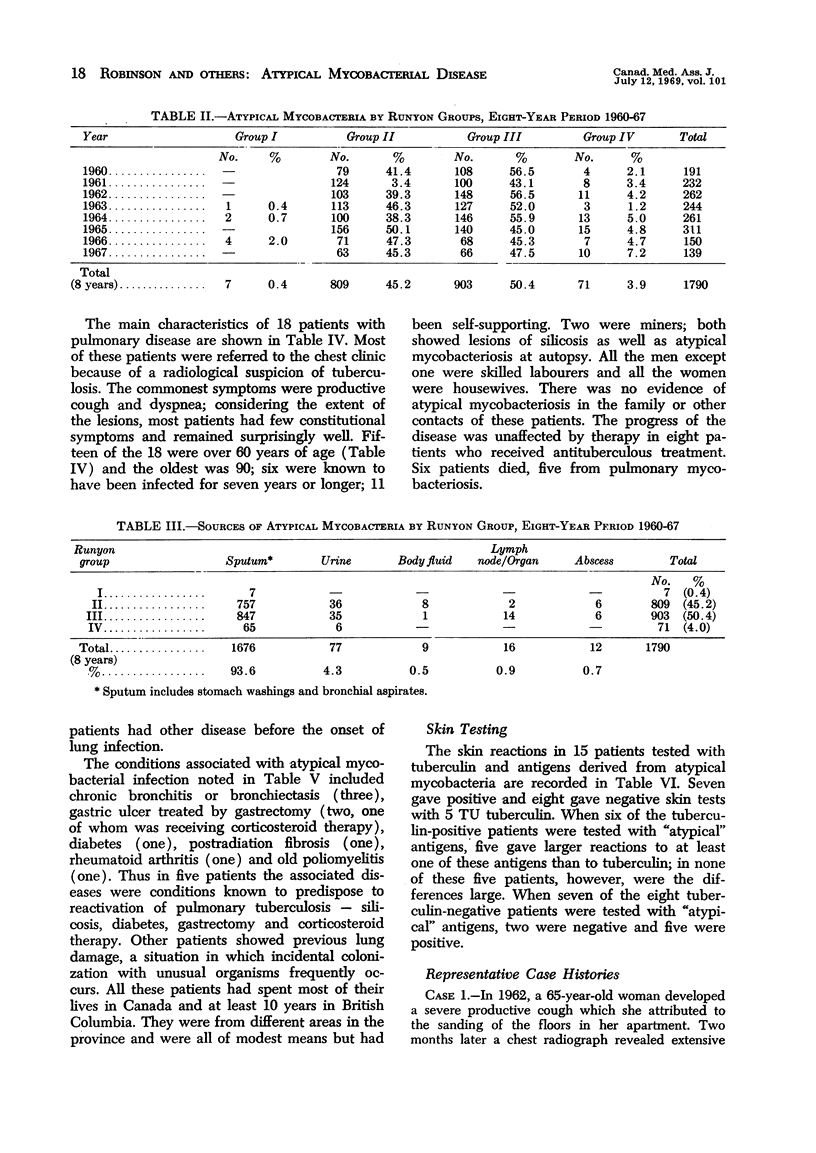
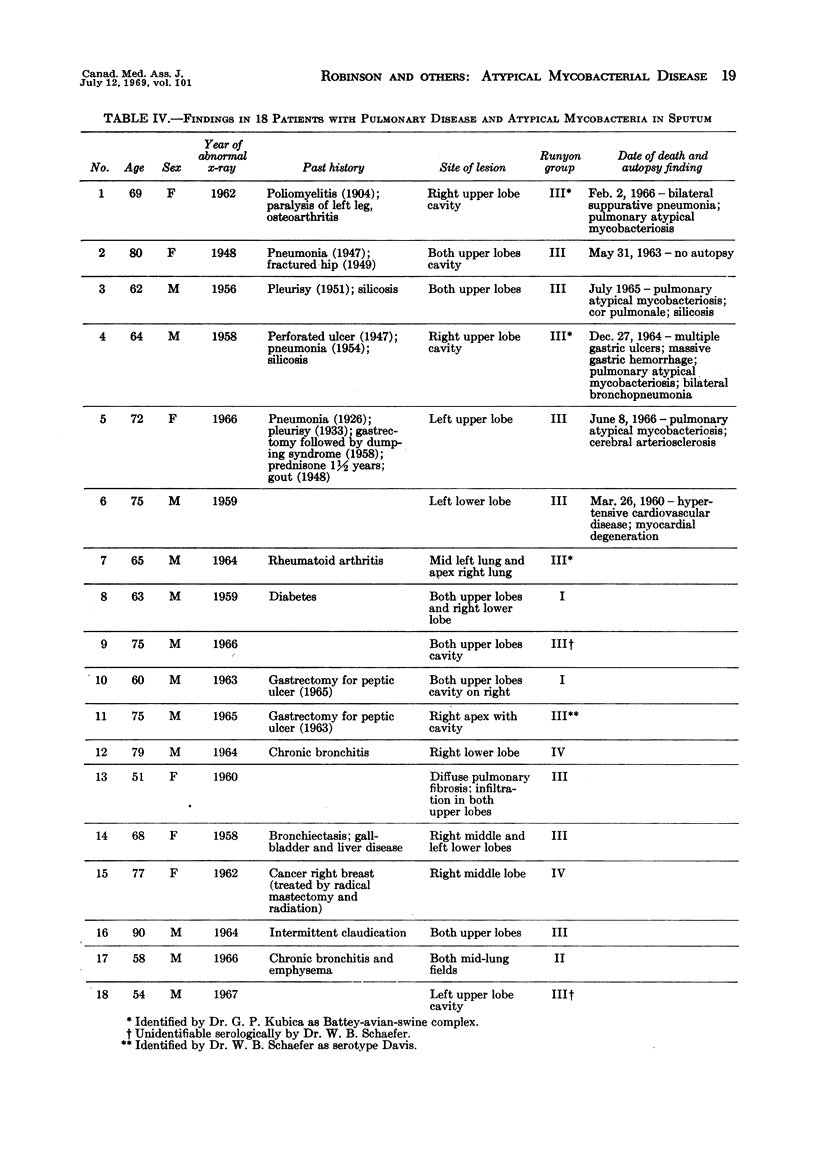
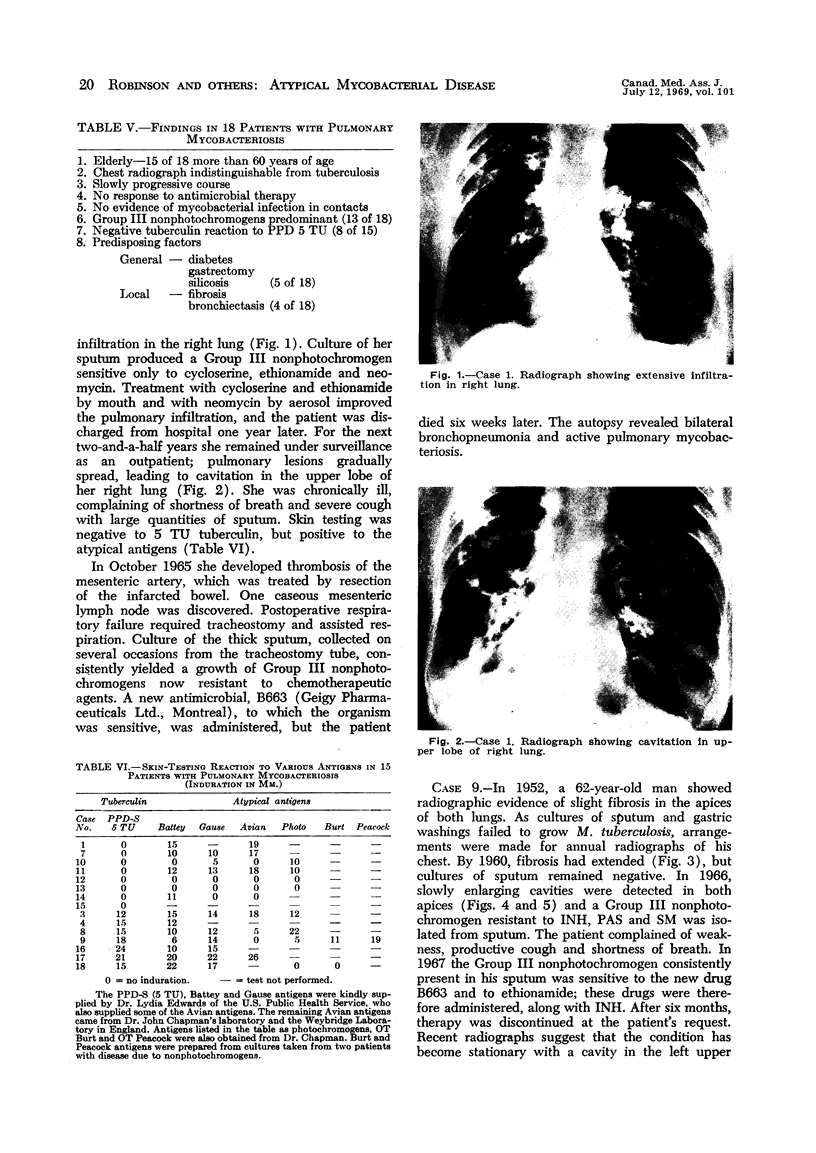
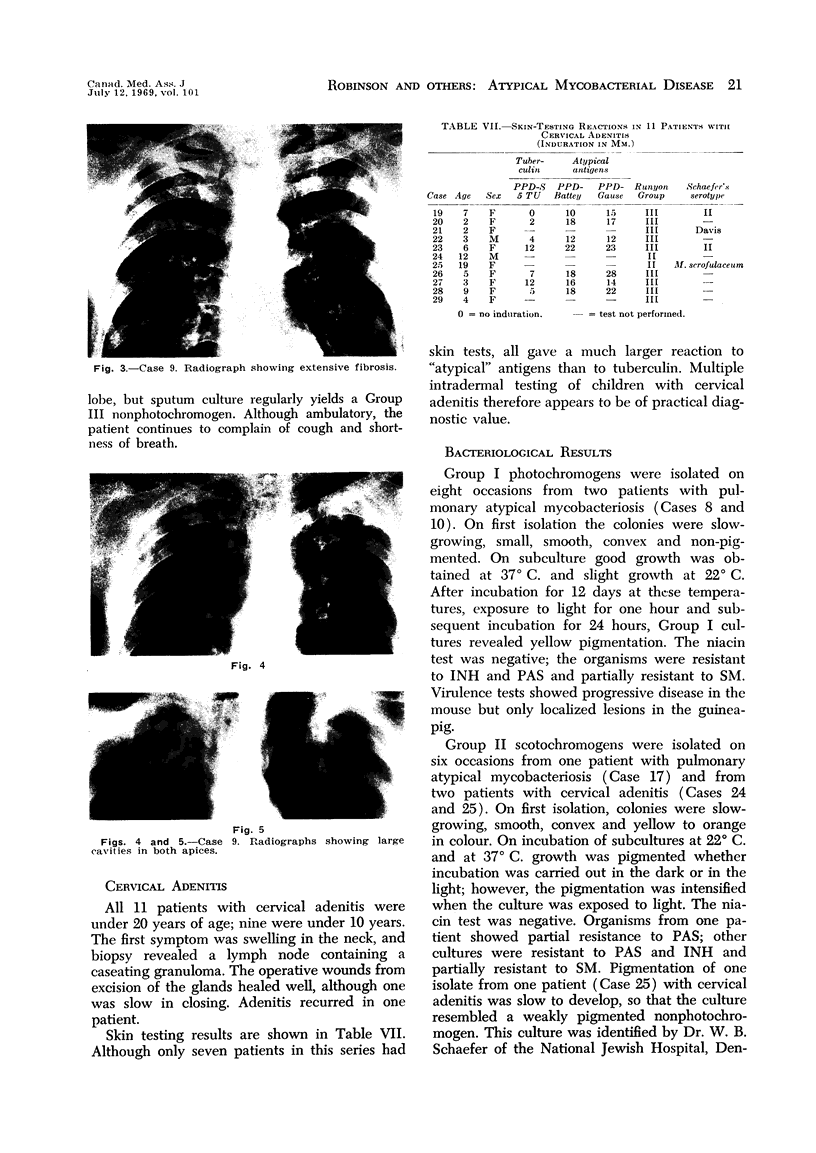
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTLER R. W., JOSEPHSON J. E. Unclassified mycobacteria isolated from human suspect tuberculosis cases in New-foundland: preliminary studies on fifteen strains. Can Med Assoc J. 1963 Feb 16;88:347–350. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARRUTHERS K. J., EDWARDS F. G. ATYPICAL MYCOBACTERIA IN WESTERN AUSTRALIA. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Jun;91:887–895. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.91.6.887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORPE R. F. CLINICAL ASPECTS, MEDICAL AND SURGICAL, IN THE MANAGEMENT OF BATTEY-TYPE PULMONARY DISEASE. Dis Chest. 1964 Apr;45:380–382. doi: 10.1378/chest.45.4.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S. D., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C. Disseminated osteomyelitis due to "Battey" mycobacteria. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1966 Feb;93(2):269–274. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1966.93.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FABER D. R., LASKY I. I., GOODWIN W. E. IDIOPATHIC UNILATERAL RENAL HEMATURIA ASSOCIATED WITH ATYPICAL ACID-FAST BACILLUS: BATTEY TYPE. CURE BY PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY. J Urol. 1965 Apr;93:435–439. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)63799-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor W. M., Keskin N. Atypical mycobacteria in the Niagara Peninsula. Can Med Assoc J. 1967 Feb 11;96(6):312–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobby G. L., Redmond W. B., Runyon E. H., Schaefer W. B., Wayne L. G., Wichelhausen R. H. A study on pulmonary disease associated with mycobacteria other than Mycobacterium tuberculosis: identification and characterization of the mycobacteria. 18. A report of the Veterans Administration-Armed Forces Cooperative Study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Jun;95(6):954–971. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.95.6.954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LICHTENSTEIN M. R., TAKIMURA Y., THOMPSON J. R. PHOTOCHROMOGENIC MYCOBACTERIAL PULMONARY INFECTION IN A GROUP OF HOSPITALIZED PATIENTS IN CHICAGO. II. DEMOGRAPHIC STUDIES. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Apr;91:592–595. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.91.4.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIDDLEBROOK G., COHN M. L. Bacteriology of tuberculosis: laboratory methods. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1958 Jul;48(7):844–853. doi: 10.2105/ajph.48.7.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIDDLEBROOK G. Isoniazid-resistance and catalase activity of tubercle bacilli; a preliminary report. Am Rev Tuberc. 1954 Mar;69(3):471–472. doi: 10.1164/art.1954.69.3.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TARSHIS M. S. A comparative study of the aniline-cyanogen bromide and o-tolidine-cyanogen bromide direct qualitative micro-niacin tests for differentiating human tubercle bacilli from other mycobacteria. Results obtained using fresh cultures. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1960 Nov;82:733–735. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1960.82.5.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TARSHIS M. S. Blood mediums for cultivation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. V. Results with agar-agar basal medium and varying concentrations of blood, glycerine and penicillin. Am J Clin Pathol. 1953 Jul;23(7):661–670. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/23.7.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. W., Naiman S. C., Clements D. Lymphocyte transformation by phytohemagglutinin. II. In the tuberculous patient. Can Med Assoc J. 1967 Sep 30;97(14):836–840. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]