Abstract
In an attempt to detect and characterize congenital, neonatal and early childhood EBV infections, a prospective sero-epidemiological study was undertaken in 112 newborn infants and their mothers, 25 additional newborns undergoing exchange transfusion, 114 randomly selected hospitalized infants aged 0 to 3 years, and 109 siblings and parents of these infants. Leukocyte culture was attempted in all the newborns and in 25 pre- and post-transfusion.
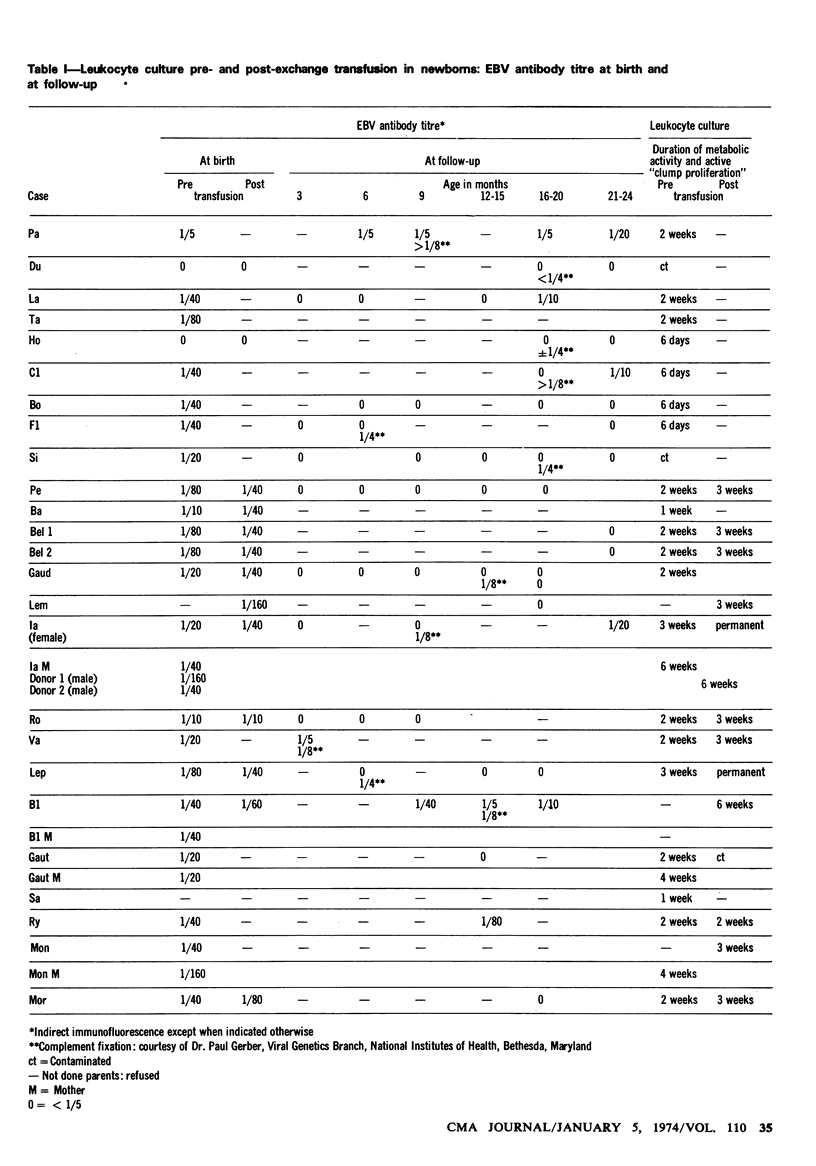
The findings of EBV seroconversion in six patients without clearly apparent illness, infectious mononucleosis in only one case with significant EBV antibody rise, seroreversion in three cases in early childhood, higher newborn than maternal EBV antibody titres in three cases and the establishment of two permanent lymphoblastoid cell lines from newborns following exchange transfusion raise the possibility of abortive primary EBV infection in early life. Congenital or neonatal infections following exchange transfusions, however, could not be substantiated with certainty since the EBV antibodies did not persist at follow-up except possibly in two cases. Parenteral transmission of the EB virus by exchange transfusion at birth is probably prevented by the presence of EBV antibodies in either donor or recipient.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banatvala J. E., Best J. M., Waller D. K. Epstein-Barr virus-specific IgM in infectious mononucleosis, Burkitt lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 1972 Jun 3;1(7762):1205–1208. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90925-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S., Hsieh M. W., Blankenship W. Cell line initiation from cord blood leukocytes treated with viruses, chemicals, and radiation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Aug;47(2):479–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S. Neutralizing activity in human sera against the leukocyte-transforming agent. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(1):50–55. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.1.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber P., Lucas S., Nonoyama M., Perlin E., Goldstein L. I. Oral excretion of Epstein-Barr virus by healthy subjects and patients with infectious mononucleosis. Lancet. 1972 Nov 11;2(7785):988–989. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92402-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanshaw J. B., Niederman J. C., Chessin L. N. Cytomegalovirus macroglobulin in cell-associated herpesvirus infections. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):304–306. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Immunofluorescence in cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1248-1256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Observations on childhood infections with the Epstein-Barr virus. J Infect Dis. 1970 Mar;121(3):303–310. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.3.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G. Epstein-Barr virus and infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Feb 1;288(5):263–264. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197302012880512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joncas J. H. Clinical significance of the EB herpesvirus infection in man. Prog Med Virol. 1972;14:200–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joncas J., Mitnyan C. Serological response of the EBV antibodies in pediatric cases of infectious mononucleosis and in their contacts. Can Med Assoc J. 1970 Jun 6;102(12):1260–1263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehane D. E. A seroepidemiologic study of infectious mononucleosis. The development of EB virus antibody in a military population. JAMA. 1970 Jun 29;212(13):2240–2242. doi: 10.1001/jama.212.13.2240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORHEAD P. S., NOWELL P. C., MELLMAN W. J., BATTIPS D. M., HUNGERFORD D. A. Chromosome preparations of leukocytes cultured from human peripheral blood. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Sep;20:613–616. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Niederman J. C., Andrews L. L. Prolonged oropharyngeal excretion of Epstein-Barr virus after infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Feb 1;288(5):229–232. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197302012880503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi I., Hasegawa H., Tsubota T., Hiraki K. Simultaneous determination of antibody to Epstein-Barr virus in prenatal mothers and new-born infants. Experientia. 1972 Feb 15;28(2):195–196. doi: 10.1007/BF01935755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederman J. C., Evans A. S., Subrahmanyan L., McCollum R. W. Prevalence, incidence and persistence of EB virus antibody in young adults. N Engl J Med. 1970 Feb 12;282(7):361–365. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197002122820704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye F. J., Lambert H. P. Epstein-Barr virus antibody in cases and contacts of infectious mononucleosis; a family study. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Mar;71(1):151–161. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400046325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Scherer M. IgM antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in infectious mononucleosis. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;37(4):332–339. doi: 10.1007/BF01241456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L. R., Hirshaut Y., Kanef D. M., Glade P. Epstein-Barr virus in infancy. J Pediatr. 1972 Jun;80(6):1025–1026. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren B., Lantorp K., Sterner G., Espmark A. EBV antibodies in family contacts of patients with infectious mononucleosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Mar;133(3):934–939. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



