Full text
PDF











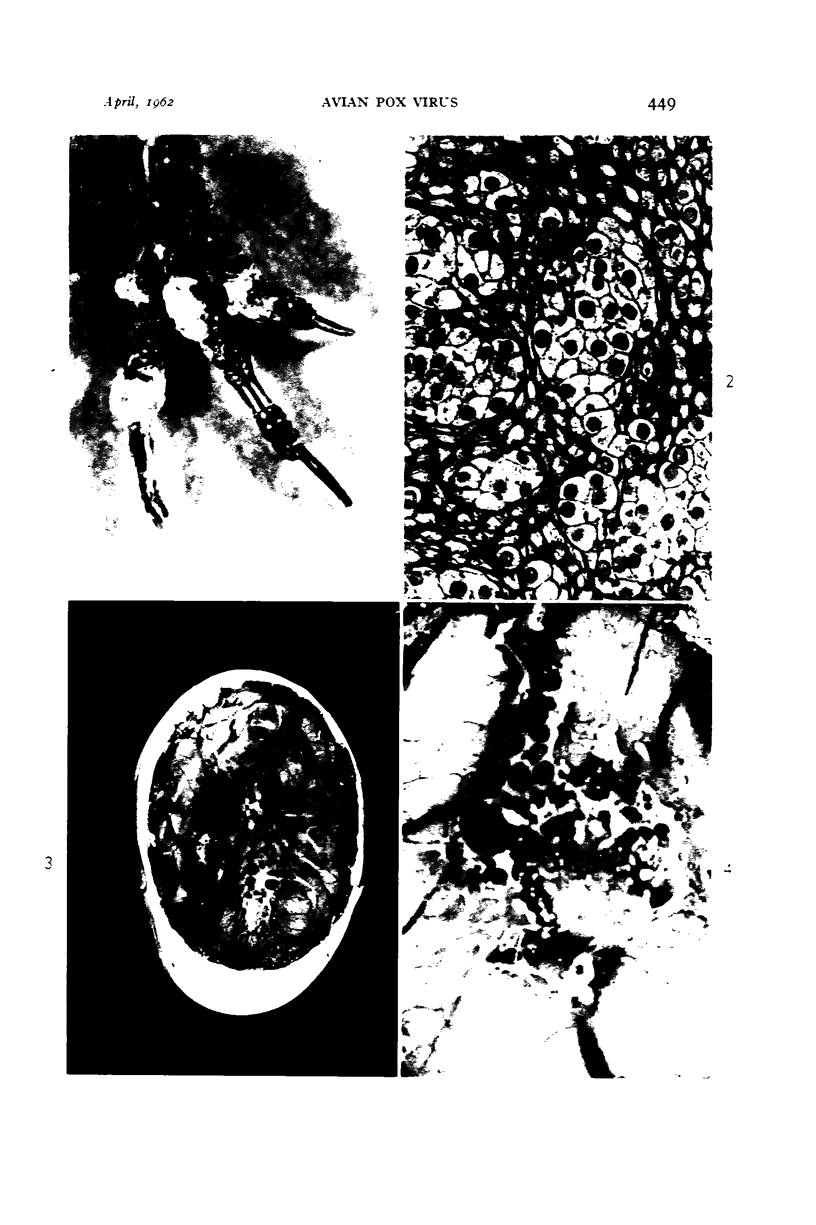

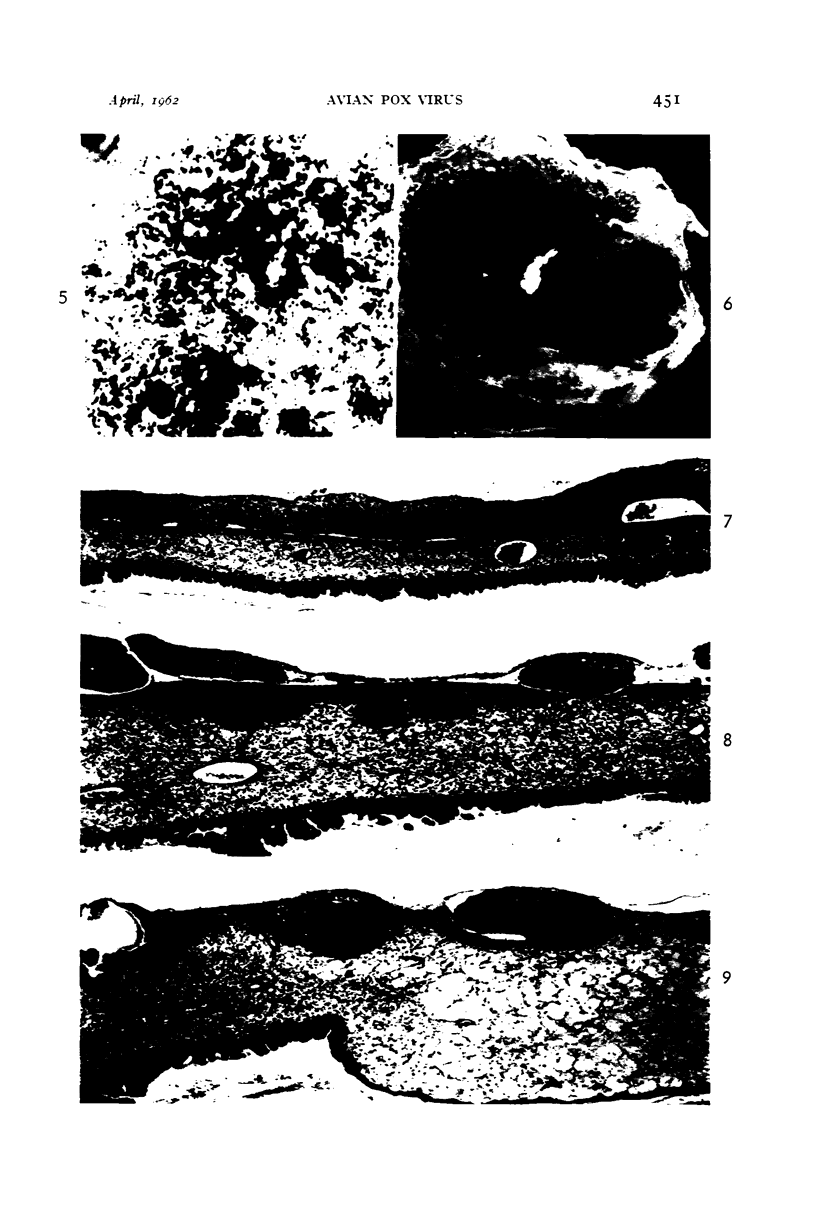

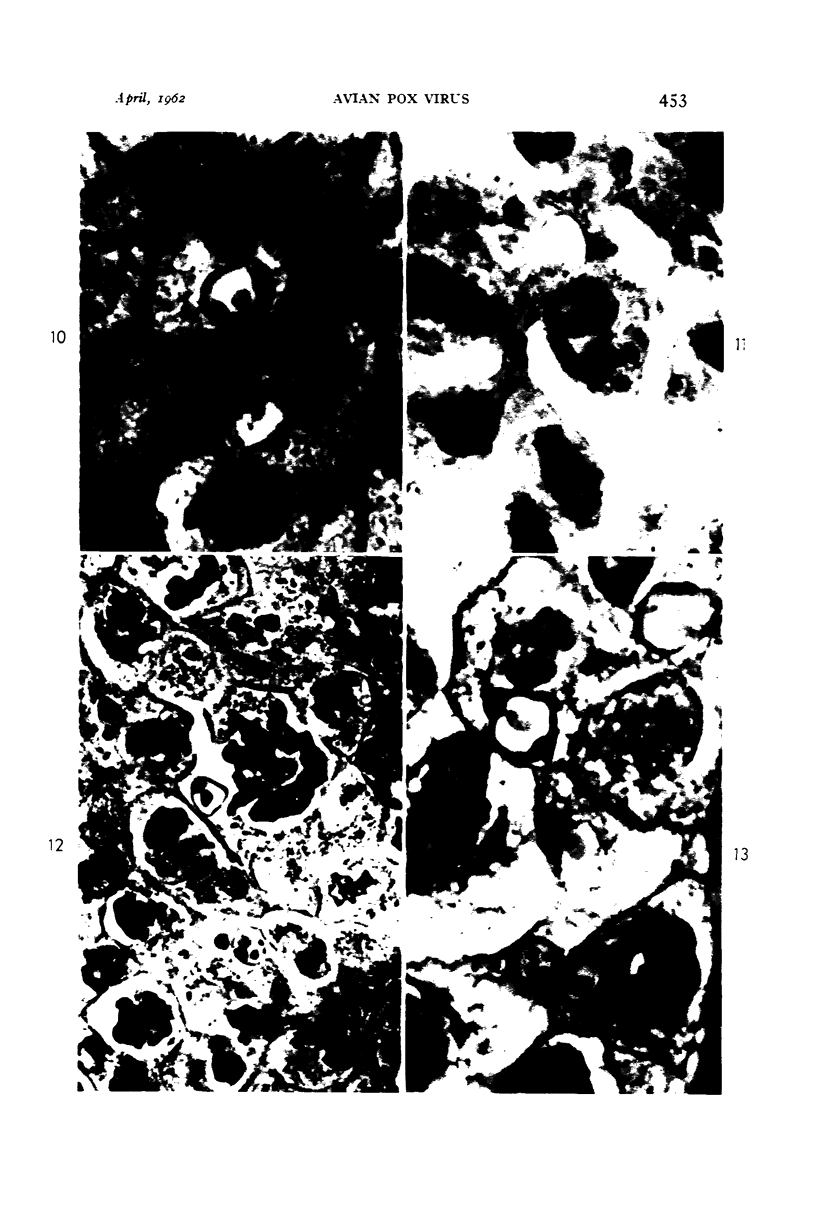
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABDUSSALAM M., BLAKEMORE F. Morphology of the elementary bodies and cell inclusions in swine pox. J Comp Pathol. 1956 Oct;66(4):373–377. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1742(56)80039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KASZA L., BOHL E. H., JONES D. O. Isolation and cultivation of swine pox virus in primary cell cultures of swine origin. Am J Vet Res. 1960 Mar;21:269–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOWRIGHT W., FERRIS R. D. The growth and cytopathogenicity of sheep-pox virus in tissue cultures. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Aug;39(4):424–435. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIER J. E., SAUER R. M., MALSBERGER R. G., SILLAMAN J. M. Studies on a pox disease of monkeys. II. Isolation of the etiologic agent. Am J Vet Res. 1960 May;21:381–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAUER R. M., PRIER J. E., BUCHANAN R. S., CREAMER A. A., FEGLEY H. C. Studies on a pox disease of monkeys. I. Pathology. Am J Vet Res. 1960 May;21:377–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff C. E., Goodpasture E. W. The Infectivity of Isolated Inclusion Bodies of Fowl-Pox. Am J Pathol. 1929 Jan;5(1):1–10.7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]