Full text
PDF



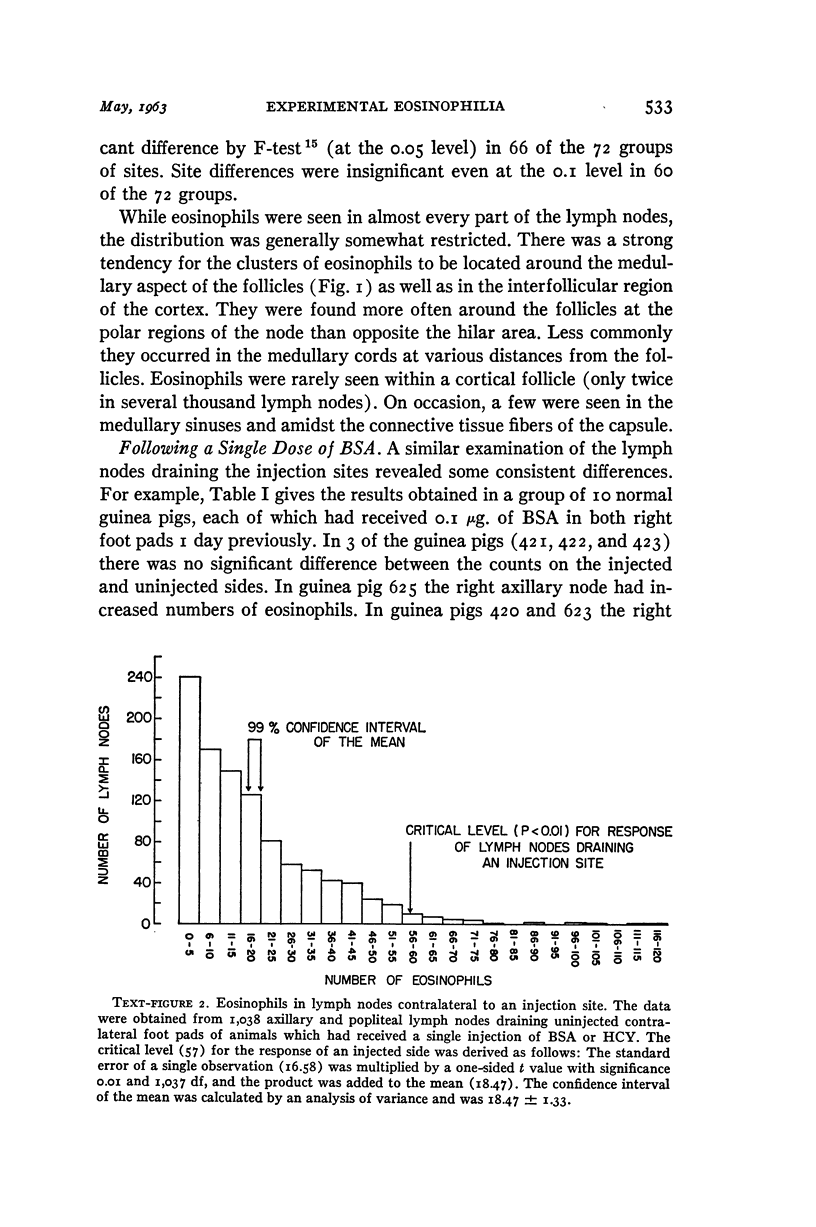






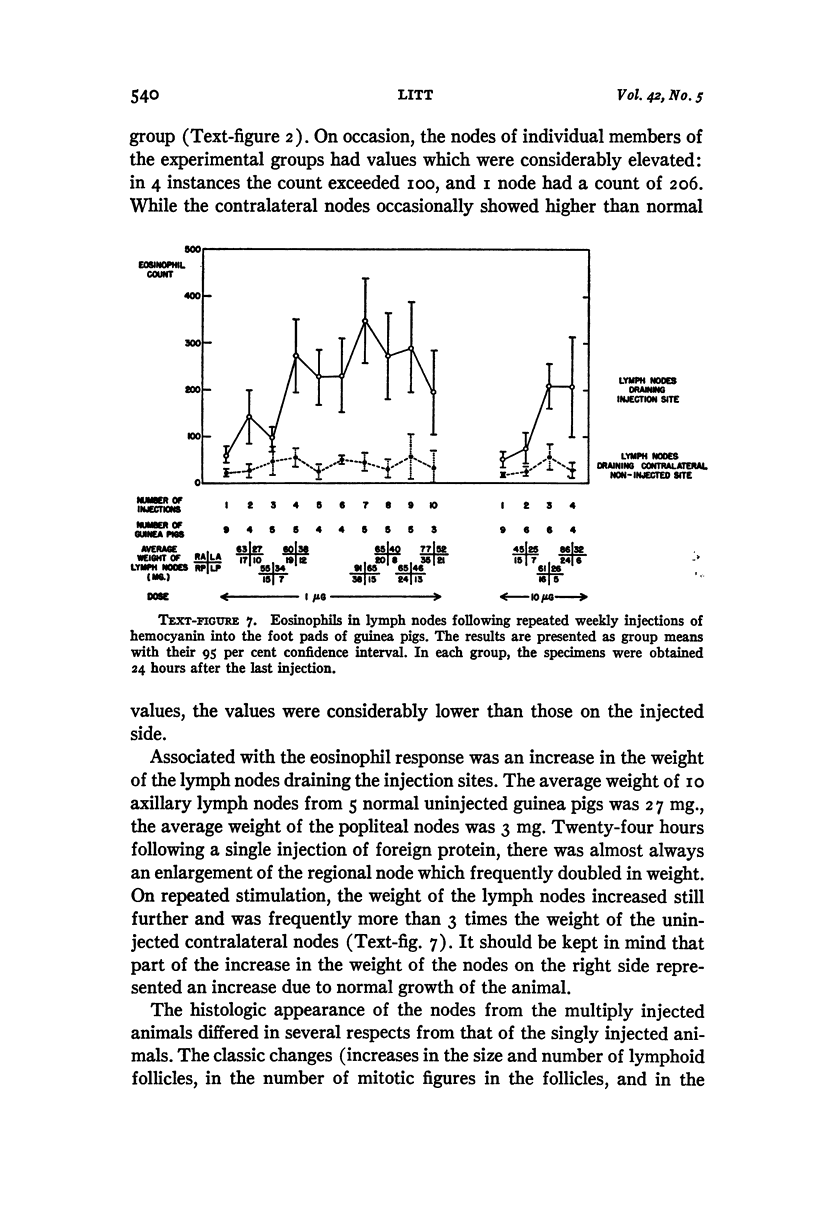









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHEN S. G., KANTOR M., GATTO L. Experimental eosinophilia. III. Regional lymph node responses to reactions of tissue sensitization. J Allergy. 1961 May-Jun;32:214–222. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(61)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. THE NATURAL-SELECTION THEORY OF ANTIBODY FORMATION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1955 Nov 15;41(11):849–857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.41.11.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDUC E. H., COONS A. H., CONNOLLY J. M. Studies on antibody production. II. The primary and secondary responses in the popliteal lymph node of the rabbit. J Exp Med. 1955 Jul 1;102(1):61–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITT M. Studies in experimental eosinophilia. II. Induction of peritoneal eosinophilia by the transfer of tissues and tissue extracts. Blood. 1960 Sep;16:1330–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITT M. Studies in experimental eosinophilia. III. The induction of peritoneal eosinophilia by the passive transfer of serum antibody. J Immunol. 1961 Nov;87:522–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNEIL C. Cellular changes in rabbits during antibody formation; response to Eberthella typhosa. Am J Pathol. 1948 Nov;24(6):1271–1287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPEIRS R. S. Advances in the knowledge of the eosinophil in relation to antibody formation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Sep 5;73(1):283–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb40804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPEIRS R. S. Physiological approaches to an understanding of the function of eosinophils and basophils. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 Mar 24;59(5):706–731. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb45980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UHR J. W., FINKELSTEIN M. S., BAUMANN J. B. Antibody formation. III. The primary and secondary antibody response to bacteriophage phi X 174 in guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:655–670. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAUGHN J. Experimental eosinophilia: local tissue reaction to Ascaris extracts. J Allergy. 1961 Nov-Dec;32:501–513. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(61)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAUGHN J. The stimulation of the eosinophil leucocyte. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1952 Jan;64(1):91–102. doi: 10.1002/path.1700640111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIGLE W. O. Immunochemical properties of the cross-reactions between anti-BSA and heterologous albumins. J Immunol. 1961 Nov;87:599–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








