Abstract
Although development of the adult Drosophila compound eye is very well understood, little is known about development of photoreceptors (PRs) in the simple larval eye. We show here that the larval eye is composed of 12 PRs, four of which express blue-sensitive rhodopsin5 (rh5) while the other eight contain green-sensitive rh6. This is similar to the 30:70 ratio of adult blue and green R8 cells. However, the stochastic choice of adult color PRs and the bistable loop of the warts and melted tumor suppressor genes that unambiguously specify rh5 and rh6 in R8 PRs are not involved in specification of larval PRs. Instead, primary PR precursors signal via EGFR to surrounding tissue to develop as secondary precursors, which will become Rh6-expressing PRs. EGFR signaling is required for the survival of the Rh6 subtype. Primary precursors give rise to the Rh5 subtype. Furthermore, the combinatorial action of the transcription factors Spalt, Seven-up, and Orthodenticle specifies the two PR subtypes. Therefore, even though the larval PRs and adult R8 PRs express the same rhodopsins (rh5 and rh6), they use very distinct mechanisms for their specification.
Keywords: Drosophila, visual system development, photoreceptor specification, transcription factor interaction, EGFR signaling
In spite of the morphological and developmental differences between vertebrate and invertebrate eyes, their basic function to translate light information from the environment to the brain is maintained. In Drosophila, the adult compound eye has been studied in great detail. It consists of ∼800 individual ommatidia. Each ommatidium contains eight photoreceptor cells (PRs): six outer PRs (R1–R6) and two inner PRs (R7 and R8). Different PRs are sensitive to different wavelengths of light, depending on the rhodopsin gene (rh) they express. Outer PRs are involved in motion detection and contain Rh1, a broad-spectrum photopigment. R7 and R8 each expresses a distinct rh with restricted absorption spectra—rh3, rh4, rh5, and rh6. The type of rh expressed in inner PRs defines two major types of ommatidia: The pale (p) ommatidia have R7 that contain UV-sensitive Rh3 with the corresponding R8 expressing blue Rh5, whereas in yellow (y) ommatidia, R7 expresses UV-sensitive Rh4 and R8 expresses green Rh6.
Recently, substantial progress has been achieved in understanding the molecular basis of how different subtypes of PRs are specified (Wernet and Desplan 2004; Mikeladze-Dvali et al. 2005a). Initially, R7 and R8 express the transcription factor spalt (sal) that is required to specify them as inner PRs and distinguish them from outer PR identity (Mollereau et al. 2001). Then, the expression in R7 of the gene prospero (pros), which encodes a homeodomain transcription factor, further distinguishes R7 from R8 by repressing R8 rhs, rh5, and rh6 (Cook et al. 2003).
The generation of the two types of ommatidia, yellow and pale, includes several steps. First, the stochastic expression of the transcription factor Spineless (Ss) in a subset of R7 cells specifies yellow ommatidia. Ss is required cell autonomously in yR7 for rh4 expression and, further, cell nonautonomously for the underlying R8 cell to acquire y fate and turn on rh6 expression (Wernet et al. 2006). The coordination between R7 and R8 rhodopsins requires a signal from pR7 that induces the pR8 fate. In sevenless mutants that lack R7, rh5 expression is lost while rh6 is expanded to almost all R8 (Papatsenko et al. 1997; Chou et al. 1999). The y versus p choice in R8 is then reinforced by a bistable loop of regulation between the tumor suppressor gene warts (wts) and the growth regulator melted (melt) (Mikeladze-Dvali et al. 2005b): wts is required for rh6 expression, whereas melt is essential for rh5 expression. wts and melt repress each other transcriptionally, thereby ensuring that a robust decision to express either rh5 or rh6 is made. The homeoprotein encoded by orthodenticle (otd) is required in both p R7 and R8 to activate rh3 and rh5 through direct binding to their promoter. Otd has only a permissive role: It is expressed in all PRs and its overexpression is not able to induce rh3 or rh5 expression in y ommatidia. Furthermore, the y ommatidial fate does not expand in otd mutants (Tahayato et al. 2003).
Although much is known about the development of the adult visual system, little is known about the development and function of the larval visual system. PRs of the larval eye (Bolwig Organ [BO]) extend their axonal projections to the larval pacemaker neurons, which control the larval circadian rhythm (Malpel et al. 2002; Hassan et al. 2005; Moncalvo and Campos 2005). Visual input via the larval eye is crucial for the entrainment of the molecular clock (Malpel et al. 2004; Mazzoni et al. 2005). Furthermore, both larval PRs and pacemaker neurons control larval photophobic behavior (Mazzoni et al. 2005). Very simple in structure, the larval eye contains ∼12–14 PRs (Green et al. 1993). In contrast to adult ommatidia, BO lacks accessory cells, such as pigment cells or cone cells.
BO precursor cells develop in the optic placode adjacent to the optic lobe primordium (Green et al. 1993). Development of larval PR precursor cells proceeds in a two-step process. First, primary precursors (also called BO founder cells) are specified; they express and require the proneural gene atonal (ato) and the retinal patterning genes sine oculis (so) and eyes absent (eya) as well as hedgehog (hh) signaling (Schmucker et al. 1994; Suzuki and Saigo 2000). Then, primary precursors signal to the surrounding tissue by expressing the TGFα homolog spitz (spi), which activates EGF receptor (EGFR) and recruits adjacent cells to develop as secondary precursors (Daniel et al. 1999; Suzuki and Saigo 2000). tailless (tll), which encodes an orphan nuclear receptor, opposes EGFR signaling in the surrounding optic lobe primordium, preventing adjacent cells from developing as PRs (Daniel et al. 1999). Subsequently, as immature PRs detach from the optic lobe primordium and start to differentiate, they extend their axons and remain in contact with the optic lobe (Schmucker et al. 1992, 1997; Dumstrei et al. 2002). Two distinct PR subtypes can be distinguished in the larval eye: Four PRs contain blue-sensitive Rh5 while eight contain green-sensitive Rh6. This is strongly reminiscent of adult R8 PRs, which express Rh5 in 30% of ommatidia and Rh6 in the remaining 70%. Thus, similar molecular mechanisms could act to specify the two distinct subtypes in larval PRs and in adult R8 cells.
Here we describe the genetic mechanisms underlying the specification of the two larval PR subtypes. We show that primary precursors develop independently of EGFR and give rise to the Rh5 subtype whereas secondary precursors give rise to Rh6-subtype PRs. EGFR signaling is required for the survival of secondary precursors of the Rh6 subtype. The combinatorial action of transcription factors Seven-up (Svp), Sal, and Otd is required to distinguish the two subtypes. The Rh5 subtype requires sal and otd, while the Rh6 subtype requires seven-up (svp). EGFR signaling, otd, svp, and sal are also core components of PR development in the adult retina. However, they play very different roles in the two systems. Thus, even though adult R8 and larval PRs share the same rhodopsin fates, the genetic pathways that control their expression are surprisingly different.
Results
Embryonic development of the larval eye and initiation of rhodopsin expression
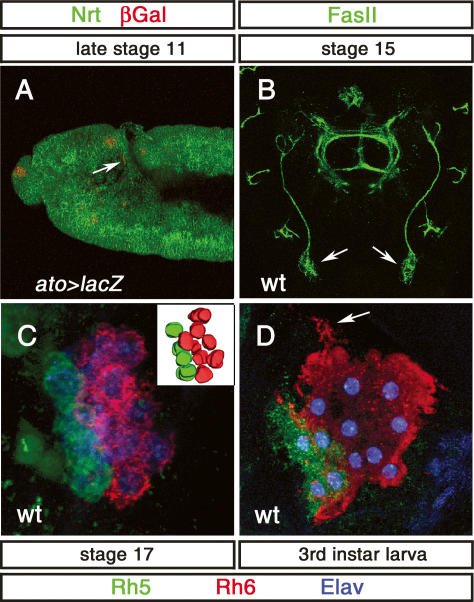
We followed BO PR development from specification of precursors until the end of larval life using anatomical and molecular markers. Larval PRs develop from a group of cells located at the ventral tip of the optic placode, adjacent to the progenitors of the optic lobe primordium (Green et al. 1993). The earliest precursor cells express the proneural gene ato in a highly dynamic manner during embryonic stages 10–12 (Fig. 1A; Daniel et al. 1999; Suzuki and Saigo 2000) (we obtained comparable results using either the ato-Gal4 driver or an anti-Ato antibody; data not shown). Expression of ato in PR precursors decreases during stage 12 until no expression is found after embryonic stage 13. During embryonic stage 12, BO precursors start to express the neuronal marker Elav as well as Krüppel (Kr) and Fasciclin II (FasII) (Schmucker et al. 1992; Daniel et al. 1999), which were used as molecular markers for immature PRs throughout embryogenesis (Figs. 1B, 3A, below). During optic lobe invagination, larval PRs remain connected with the optic lobe primordium by the Bolwig Nerve (BN), which extends while the distance between the PRs and optic lobe primordium gradually increases (Schmucker et al. 1992). By stage 15, all PRs are largely separated from the optic lobe primordium and BO is positioned at the anterior part of the embryonic head (Fig. 1B), where it becomes associated with the head skeleton at embryonic stage 17 (Green et al. 1993).
Figure 1.
Development of BO and rhodopsin expression. (A) Lateral view of the head region of an ato-Gal4, UAS-lacZ embryo stained with anti-β-Gal (red) and anti-Neurotactin (Nrt) (green). ato-lacZ expression is found in BO precursors (arrow) at late stage 11. (B) Dorsal view of a stage 15 embryonic head: Anti-FasII (green) staining shows the position of BO (arrow). (C) High-magnification image of the BO at late stage 17 immunolabeled with anti-Rh5 (green), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). A total of 12 PRs are observed: Eight are stained by anti-Rh6 antibody, and four are stained with anti-Rh5 antibody. (Inset) Three-dimensional reconstruction of the BO PRs. (D) High-magnification image of the BO in third instar larvae immunolabeled with anti-Rh5 (green), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). A total of 12 PRs are observed: Eight are stained by anti-Rh6 antibody, and four are stained with anti-Rh5 antibody. PRs build up arborization-like protrusions (arrow).
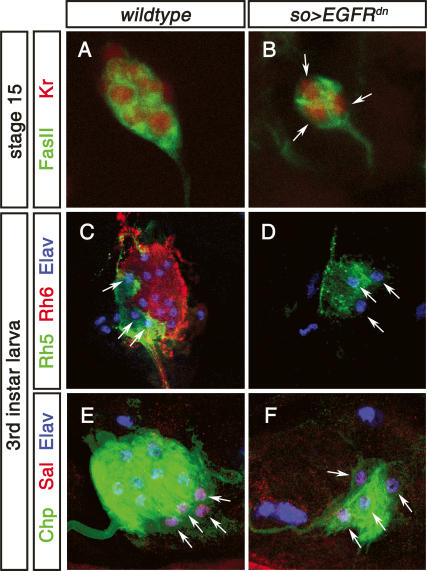
Figure 3.
Function of EGFR signaling in Rh6 PR development. (A) High-magnification image of stage 15 wild-type embryonic BO labeled with anti-FasII (green) and anti-Kr (red). (B) High-magnification image of stage 15 so-Gal4 > UAS-EGFRdn embryonic BO labeled with anti-FasII (green) and anti-Kr (red). Only three Kr-expressing immature PRs are found (arrows) as compared with 12 in the wild type (shown in A). (C) High-magnification image of third instar larva wild-type BO labeled with anti-Rh5 (green), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). A total of 12 PRs are observed: Eight are stained by anti-Rh6 antibody, and four are stained with anti-Rh5 antibody. (D) High-magnification image of third instar larva so-Gal4 > UAS-EGFRdn BO labeled with anti-Rh5 (green), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). Only three Rh5-expressing cells are found (arrows). (E) High-magnification image of third instar larva wild-type BO labeled with anti-Chp (green, 24B10), anti-Sal (red), and anti-Elav (blue). (F) High-magnification image of third instar larva so-Gal4,UAS-EGFRdn BO labeled with anti-Chp (green, 24B10), anti-Sal (red), and anti-Elav (blue). All four PRs found express Sal.
Larval PRs, whose number varies from eight to 16, start to express rh5 and rh6 by the end of embryogenesis (stage 16/17) and maintain rh expression throughout larval life (Fig. 1C,D). Three or four BO PRs express Rh5 and the remaining eight to 10 express Rh6 (Fig. 1C,D). We verified that rh1, rh3, and rh4, which had been previously reported to be expressed in BO (Pollock and Benzer 1988) were not expressed in the larval eye (data not shown). The PR-specific gene chaoptic (chp) becomes expressed in all larval PRs at about the same developmental stage (Fig. 6D, below). By the end of embryogenesis, PRs are packed tightly and do not exhibit any obvious signs of further cellular differentiation. However, during early larval life, their morphology changes dramatically; cells become loosely packed and build up arborization-like protrusions (Fig. 1D, arrow). While Ato expression quickly disappears, the expression of Chp, Kr, Elav, Rh5, and Rh6 is maintained throughout larval life.
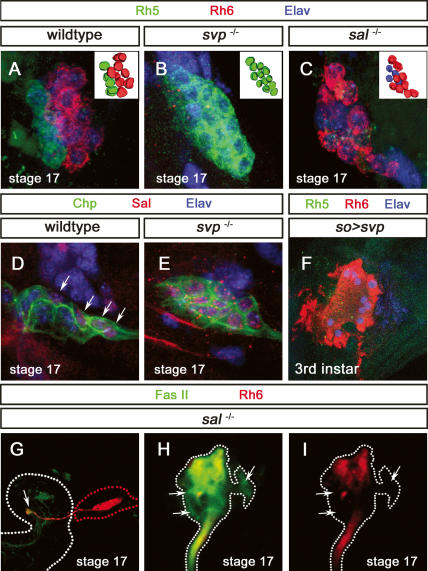
Figure 6.
Function of sal and svp in Rh5- and Rh6-subtype specification. (A) High-magnification image of stage 17 wild-type BO labeled with anti-Rh5 (green), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). (Inset) Three-dimensional reconstruction of the BO PRs. (B) High-magnification image of stage 17 svp mutant BO labeled with anti-Rh5 (green), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). A total of 12 PRs are found, all expressing Rh5. (Inset) Three-dimensional reconstruction of the BO PRs. (C) High-magnification image of stage 17 sal mutant BO labeled with anti-Rh5 (green), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). A total of 12 PRs are detected: Eight express Rh6, whereas four are devoid of anti-Rh5 or anti-Rh6 staining. (D) High-magnification image of stage 17 wild-type BO labeled with anti-Chp (green), anti-Sal (red), and anti-Elav (blue). Four cells express Sal (arrow). (E) High-magnification image of stage 17 svp mutant BO labeled with anti-Chp (green), anti-Sal (red), and anti-Elav (blue). All PRs express Sal (arrow). (F) High-magnification image of third instar larva so-Gal4,UAS-svp BO labeled with anti-Rh5 (green), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). All PRs are labeled by anti-Rh6; no anti-Rh5 staining is detected. (G) Axonal projections of larval PRs in sal mutant stage 17 embryos labeled with anti-FasII (green) and anti-Rh6 (red). Axonal terminations are properly formed (arrow). (H,I) High-magnification image of termini of larval PRs in sal mutant labeled with anti-FasII (green) and anti-Rh6 (red). Projections of “empty” PRs are devoid of Rh6 expression but labeled with the general marker FasII (cf. arrows in H,I).
The Wts/Melt pathway is not involved in the choice of Rh5 versus Rh6
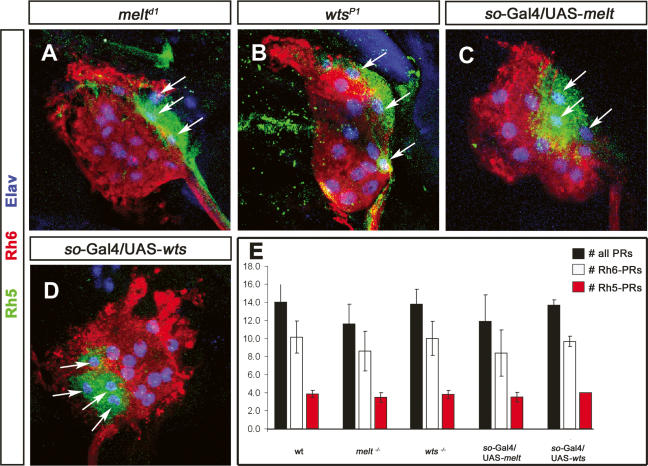
The expression of Rh5 and Rh6 in larval PRs is strongly reminiscent of the adult R8 PRs. Therefore, we tested whether wts and melt, which form a bistable loop of regulation required for the robust specification of Rh5 or Rh6 fate in adult R8, are also required in larval PRs. However we could not detect expression of wts or melt at any time during embryogenesis, as visualized using wts and melt enhancer trap lines. We also could not detect early maternal expression in embryos (data not shown). To test whether wts and melt are required for the subtype specification in the larval eye, we analyzed Rh5 and Rh6 expression in wts and melt mutant larvae. However, the expression of neither Rh5 nor Rh6 is affected (Fig. 2A,B). To manipulate the early phase of PR precursor specification and development, we made use of a sine oculis-Gal4 (so-Gal4), which starts to be expressed in the optic lobe placode at embryonic stage 10 and remains expressed in the optic lobe and all larval PRs throughout embryogenesis and larval life (Supplementary Fig. 1A,C). Interestingly, the ectopic expression of UAS-wts or UAS-melt under the control of so-Gal4 did also not affect the expression Rh5 and Rh6 (Fig. 2C,D). Furthermore the total number of larval PRs and the ratio of Rh5 PRs versus Rh6 PRs remain unaltered in both wts and melt gain of function (GOF) as well as in loss of function (LOF) (Fig. 2E). Thus, in contrast to the adult retina, the specification of the Rh5 and Rh6 subtypes does not depend on wts and melt.
Figure 2.
wts and melt are not involved in Rh5- and Rh6-subtype specification. High-magnification images of third instar mutant larva BO of melt (A), wts (B), so-Gal4/UAS-melt (C), and so-Gal4/UAS-wts (D) labeled with anti-Rh5 (green, arrow), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). (A–D) melt and wts mutants, as well as so-Gal4/UAS-wts and so-Gal4/UAS-melt, display an expression of Rh5 and Rh6 PRs comparable with wild-type larvae. (E) Comparison of the total number of PRs (black bar) and Rh6 (white bar) and Rh5 (red bar) PRs in wild-type (wt), melt LOF, wts LOF, melt GOF, and wats GOF larval eyes (error bars, SD). The number of total PRs and Rh5 and Rh6 PRs in all conditions are comparable with wild type.
Egfr signaling and tll action orchestrate the development of the Rh6 subtype
As in the adult eye, recruitment of BO PR precursor cells requires activation of the EGFR pathway. Primary BO precursors produce Spi, which is required in neighboring cells to develop as secondary precursors. In embryos mutant for spi, the immature larval eye only consists of three or four cells (Daniel et al. 1999). Therefore, we tested whether EGFR signaling is involved in the specification of larval PR subtypes and whether there is a correlation between primary precursors and rh5-expressing PRs or between secondary and rh6-expressing PRs. Because EGFR signaling has multiple earlier functions in the embryo, we misexpressed a dominant-negative form of EGFR (UAS-EGFRdn) under the control of so-Gal4 to suppress EGFR activity in BO precursors. This results in the development of only three or four immature PRs as compared with ∼14 cells in the wild type (Fig. 3A,B), a phenocopy of the BO in spi mutants (Daniel et al. 1999). All of the remaining three or four PRs all express Rh5 (Fig. 3D) as well as the general markers Elav, FasII, Kr, and Chp (Fig. 3B,F). They also express the Rh5-subtype-specific marker sal (Fig. 3F, see below), but not the Rh6-subtype-specific marker svp (see below). These results show that EGFR signaling is required for the development of Rh6 PRs and strongly suggests that primary precursors develop into the Rh5 subtype while secondary precursors give rise to the Rh6 subtype.
Activation of the EGFR pathway is relayed to the nucleus through the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade, which ultimately leads to the phosphorylation of nuclear effectors such as the Ets family transcription factors Pointed (Pnt) and Yan (O’Neill et al. 1994). Both Yan and Pnt are expressed during stage 10/11 in the developing lobe primordium when larval PRs form; however their expression decreases during embryonic stage 12/13, and no expression can be detected at stage 15 (Supplementary Fig. 2; data not shown).
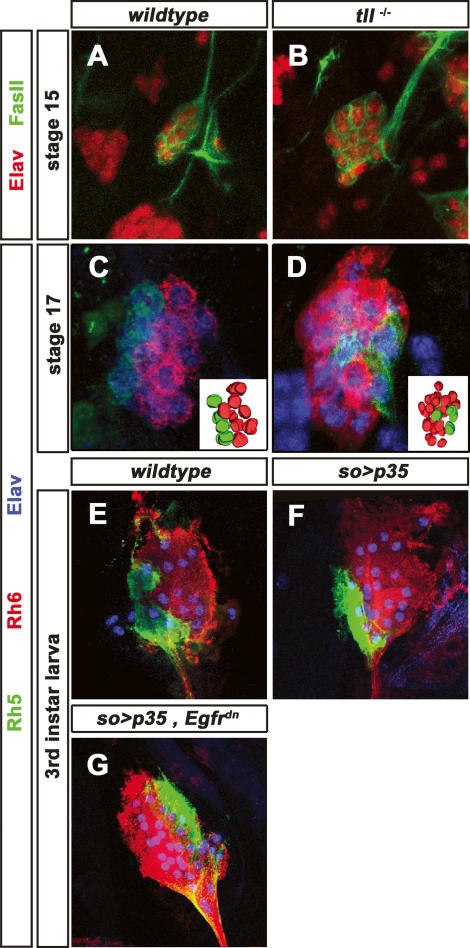
The orphan nuclear receptor Tll has an effect opposite to the EGFR signaling in specifying PR precursors versus optic lobe primordium. Tll is expressed in the optic lobe primordium but not in PR precursors. Removing tll function in the embryo leads to supernumerous immature PRs (Daniel et al. 1999), suggesting that tll acts negatively on the development of secondary precursors. To test which subset is affected, we analyzed Rh5 and Rh6 expression in tll mutants at the end of embryogenesis, before tll mutants die. The number of Rh5 PRs remains largely unchanged. However, the number of Rh6 PRs is dramatically increased to 20–25 instead of the normal eight to 10 (Fig. 4D). This suggests that tll inhibits adjacent cells from adapting the Rh6 cell fate.
Figure 4.
Function of EGFR, tll, and apoptosis in Rh6-subtype development. (A) High-magnification image of stage 15 wild-type embryonic BO labeled with anti-FasII (green) and anti-Elav (red). (B) High-magnification image of stage 15 tll mutant embryonic BO labeled with anti-FasII (green) and anti-Elav (red). The number of immature PRs is increased to ∼20–25. (C) High-magnification image of stage 17 wild-type BO labeled with anti-Rh5 (green), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). (Inset) Three-dimensional reconstruction of the BO PRs. A total of 12 PRs are observed: Eight are stained by anti-Rh6 antibody, and four are stained with anti-Rh5 antibody. (D) High-magnification image of stage 17 tll mutant BO labeled with anti-Rh5 (green), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). (Inset) Three-dimensional reconstruction of the BO PRs. The number of Rh6 PRs is increased to ∼20–25; the number of Rh5 PRs remains unchanged. (E) High-magnification image of third instar larva wild-type BO labeled with anti-Rh5 (green), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). (F) High-magnification image of third instar larva so-Gal4,UAS-p35 BO labeled with anti-Rh5 (green), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). The number of Rh6 PRs is largely increased to 20–25. (G) High-magnification image of third instar larva so-Gal4,UAS-p35, UAS-EGFRdn BO labeled with anti-Rh5 (green), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). The number of Rh6 PRs is largely increased. The number of Rh6 PRs is increased to ∼20–25; the number of Rh5 PRs remains unchanged.
Since the lack of EGFR signaling results in a smaller number of larval PRs due to cell death (Daniel et al. 1999), the increased Rh6 PRs might result from the survival of adjacent optic lobe primordium cells that failed to die. We therefore expressed the apoptosis inhibitor UAS-p35 in optic lobe primordium under the control of so-Gal4. This leads to a high increase in the number of Rh6 PRs to ∼20–25, whereas the number of Rh5 PRs remains unchanged, similar to the loss of tll function (Fig. 4F). This strongly supports the notion that EGFR signaling is required in cells surrounding the primary precursors to prevent their apoptosis induced by tll, and therefore allow their development as Rh6 PRs. In addition to its survival function, EGFR signaling might also be required for the acquisition of the Rh6 cell fate. To approach this question, we concomitantly misexpressed UAS-p35 and UAS-EGFRdn under the control of so-Gal4. This leads to a strong increase in the number of Rh6 PRs, to ∼20–25 without affecting the number of Rh5 PRs (Fig. 4G), similar to the misexpression of UAS-p35 alone. Thus EGFR signaling appears to be essential for the survival of the Rh6 subtype. However the immature precursors do not seem to depend on EGFR signaling for adapting the Rh6 cell fate. It is also possible that activity remaining in the EGFRdn context is able to induce the Rh6 fate while higher EGFR activity is required for survival.
Sal and Svp are expressed in distinct PR subtypes
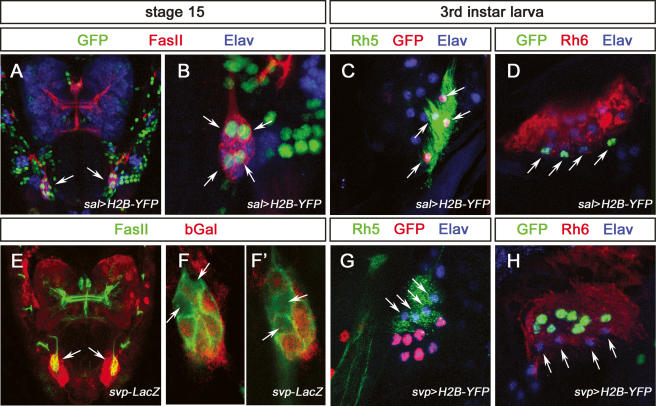
In order to analyze the development, specification, and differentiation of the two subtypes of larval PRs, we looked for genes expressed in either the Rh5 or the Rh6 subtype. Among the genes required for adult PR development, pros and ss are key players in inner PR specification. However, we could not detect expression of Pros or Ss in developing BO PRs at any point during embryogenesis (data not shown). However, sal and svp are expressed in a subtype-specific fashion in the larval eye. During embryonic development, three or four immature PRs express sal (Fig. 5A,B; comparable results were obtained using sal-Gal4 or anti-Salm antibody; data not shown). sal expression starts during stage 13/14 and is maintained throughout embryogenesis and larval life. Its expression coincides precisely with rh5 (Fig. 5C) and is excluded from the Rh6 subtype (Fig. 5D). svp shows the opposite expression pattern: Its expression is initiated during stage 13/14 and is maintained throughout embryogenesis and larval life in the Rh6 subtype, whereas it is excluded from the Rh5 subtype (Fig. 5E–H) (comparable results were obtained using svp-Gal4, svp-LacZ, or anti-Svp antibody; data not shown). Thus sal and svp are expressed in complementary subsets of larval PR subtypes. The expression of both transcription factors precedes rhodopsin expression.
Figure 5.
Expression of sal and svp in the developing and mature larval PRs. (A) Dorsal view of a sal-Gal4,UAS-H2B-YFP stage 15 embryonic head labeled with anti-GFP (green), anti-FasII (red), and anti-Elav (blue), and GFP expression in BO (arrow). (B) High-magnification image of the BO in A. Four cells are labeled by anti-GFP staining (arrow). (C) High-magnification image of BO in third instar larva sal-Gal4,UAS-H2B-YFP, labeled with anti-GFP (red), anti-Rh5 (green), and anti-Elav (blue). Anti-GFP labeling coincides with anti-Rh5 staining (arrow). (D) High-magnification image of BO in third instar larva sal-Gal4,UAS-H2B-YFP, labeled with anti-GFP (green), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). Anti-GFP labeling is excluded from anti-Rh6 staining (arrows). (E) Dorsal view of a svp-lacZ stage 15 embryonic head labeled with anti-FasII (green) and anti-βGal (red) expression in BO (arrows). (F,F′) High-magnification image of the BO in E; individual optical sections show four cells are devoid of anti-βGal staining (arrows). (G) High-magnification image of BO in third instar larva svp-Gal4,UAS-H2B-YFP, labeled with anti-GFP (red), anti-Rh5 (green), and anti-Elav (blue). Anti-GFP labeling is excluded from anti-Rh5 staining (arrows). (H) High-magnification image of BO in third instar larva svp-Gal4,UAS-H2B-YFP, labeled with anti-GFP (green), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). Anti-GFP labeling coincides with anti-Rh6 staining, and is excluded for the remaining four PRs (arrows).
spalt is required for rh5 expression in larval PRs
The sal genes encode two zinc finger transcription factors that are specifically expressed in adult inner PRs R7 and R8, where they are required to distinguish them from outer PRs (Mollereau et al. 2001). Since sal is exclusively expressed in the Rh5 subtype, prior to rh5 expression, we tested whether it is required for the development of this subtype. We thus analyzed the expression of Rh5 and Rh6 in sal mutants at the end of embryogenesis, when these mutants die. No expression of Rh5 can be detected in sal mutants, even though the correct number of Rh6-expressing cells is produced (Fig. 6C). However, the general PR markers Elav, FasII, Kr, and Chp remain expressed in all PRs, suggesting that four PRs express neither Rh5 nor Rh6 (Fig. 6C; data not shown). Since rh1, rh3, and rh4 expression cannot be detected, these four PRs appear to be “empty” and devoid of PR molecules (data not shown). PRs of the larval eye project into the region of the dendritic arborizations of the larval pacemaker neurons. Axon termini of Rh5 and Rh6 PRs are generally directly adjacent to each other (Mazzoni et al. 2005). In sal mutants, all larval PRs project into the correct target region of the late embryonic brain (Fig. 6G). We compared the projection termini of empty PRs with those of Rh6 PRs (“empty” PR termini are identified by FasII staining and the absence of Rh6 staining). At embryonic stage 17 (just before these mutants die), axonal termini of “empty” PRs project correctly to the target region, adjacent to Rh6 termini (Fig. 6H,I). Therefore sal is essential in the larval eye for the proper differentiation of the Rh5 PRs but not for their early specification or for axonal targeting.
seven-up is required for Rh6-subtype specification and to repress Rh5-subtype fate
In the adult eye, the orphan nuclear receptor svp is required posterior to the morphogenetic furrow for the specification of the R3/R4 and R1/R6 pairs, but not for their later differentiation (Mlodzik et al. 1990). In the larval eye, svp is exclusively expressed in Rh6 PRs prior to rh6 expression, suggesting that it might be involved in the development of this subtype. We analyzed the expression of Rh5 and Rh6 in svp mutant embryos at stage 17 (as for sal, svp mutants die at the end of embryogenesis). While the total number of PRs (as marked by Elav, FasII, Kr, and Chp) remains unchanged (Fig. 6B,E) in svp mutants, all PRs express Rh5 (Fig. 6B) and no Rh6 expression is detectable. Therefore, Rh6 cells appear to have switched fate toward the Rh5 fate. Consistent with the transformation of PRs into Rh5 subtype, all PRs express sal in svp mutants (Fig. 6E). This suggests that svp is necessary for the repression of sal in the Rh6 subtype, thus allowing expression of rh6. To test whether svp is sufficient for the Rh6 PR fate, we performed gain-of-function experiments using early (so-Gal4) or later sevenless-Gal4 (sev-Gal4) drivers. The sev-Gal4 driver starts to be expressed in all larval PRs during late embryonic stages 12/13, just after all immature PRs have formed. It remains expressed through larval life (Supplementary Fig. 1B,D; data not shown). In larvae that express UAS-svp under the control of so-Gal4, no Rh5 expression can be detected, while all BO PRs express rh6 with no change in the overall number of PRs (Fig. 6F). However, if sal expression is affected, it is not completely abolished, with one to three PRs still weakly expressing Sal (data not shown), arguing that Rh6 is now expressed in the Rh5 subtype. Later expression of UAS-svp under the control of sev-Gal4 does not result in alteration of Rh expression (data not shown). Thus, svp not only acts to repress sal in the Rh6 subtype, but it also acts as an activator of Rh6 expression since Sal and Rh6 can coexist in the same cell. In contrast ectopic expression of UAS-salm under the control of so-Gal4 or of sev-Gal4 leads to no change of Rh5 or Rh6 expression. Expression of Svp remains unaffected, with about eight cells still expressing Svp (data not shown). Thus svp is necessary and sufficient to induce the Rh6 fate. In contrast sal is necessary but not sufficient for the Rh5 fate.
otd is required in the Rh5 subtype for rh5 expression and rh6 repression
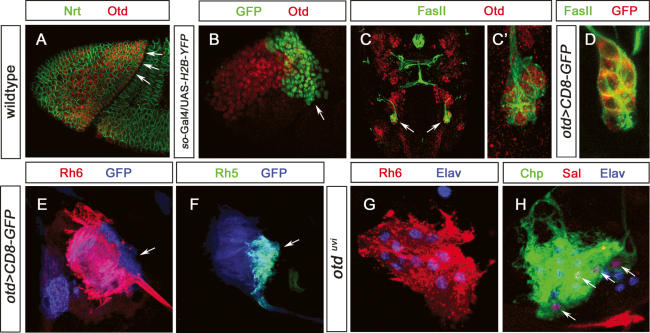
The homeodomain protein Otd is required in inner PRs of the adult retina for the activation of rh3 and rh5 in p ommatidia, whereas it is required in outer PRs to repress rh6 (Tahayato et al. 2003). In the adult retina, otd is expressed in all PRs. Similarly, otd is expressed in all embryonic immature PRs, and this expression is maintained during larval life. During early development, otd acts as a major component for patterning the anterior region of the embryo (Cohen and Jurgens 1990). During stages 8/9, otd expression spans the entire cephalic region (Fig. 7A) and becomes subsequently restricted to more anterior regions and regions giving rise to the brain. However otd expression is excluded from large parts of the optic lobe primordium as well as from the region giving rise to larval PRs (Fig. 7B). Starting at stage 12, however, otd expression is reinitiated in the ventral lateral part of the optic lobe primordium, the region that will give rise to the precursors of larval PRs. otd remains expressed in all PRs throughout embryogenesis and larval life (Fig. 7C–F). otd is not required for the formation of larval PRs (nor the larval optic lobe primordium): Even though otd-null mutant embryos show severe head involution defects, the normal number of immature PRs is formed (data not shown). To investigate whether otd is involved in larval PR-subtype specification, we analyzed Rh5 and Rh6 expression in viable otduvi mutants (Vandendries et al. 1996). In otduvi, larval PRs do not express Rh5 while the total number of PRs remains the same (Fig. 7G,H) and all PRs express Rh6 (Fig. 7G). About four cells still express sal, but these cells now express Rh6 instead of Rh5 (Fig. 7H). Interestingly, the number of Svp-expressing cells is not altered, with four Svp-negative PRs expressing Rh6 (data not shown). This indicates that, in the Rh5 subtype, otd acts as an inhibitor of rh6 expression and is required for Rh5 expression. As expression of otd is unaltered in sal mutants (data not shown), otd, like sal, seems to be necessary but not sufficient for Rh5 expression. otd and sal expression does not depend on each other, and since they are both required for Rh5 expression, they appear to act in parallel pathways.
Figure 7.
Expression and function of otd in developing and mature larval PRs. (A) Lateral view of a stage 7 embryo (procephalic region) stained with anti-Nrt (green) and anti-Otd (red); the region giving rise to the optic lobe anlage and larval PRs expresses Otd (arrow). (B) Lateral view of a so-Gal4/UAS-H2B-YFP stage 10 embryonic head region stained with anti-GFP (green) and anti-Otd (red); the region giving rise to larval PRS (ventral/lateral tip) is devoid of Otd expression. (C) Dorsal view of a wild-type stage 15 embryonic head labeled with anti-FasII (green), anti-Otd (red), and anti-Otd staining in BO, indicated by arrows. (C′) High-magnification image of C. All immature PRs are labeled by anti-Otd staining. (D) High-magnification image of embryonic stage 15 otd-Gal4/UAS-CD8∷GFP BO labeled with anti-FasII (green) and anti-GFP (red). All immature PRs are labeled by anti-GFP staining. (E) High-magnification image of third instar larva otd-Gal4/UAS-CD8∷GFP BO labeled with anti-GFP (blue) and anti-Rh6 (red). (F) High-magnification image of third instar larva otd-Gal4/UAS-CD8∷GFP BO labeled with anti-GFP (blue) and anti-Rh5 (green). (G) High-magnification image of third instar larva otdvui mutant BO labeled with anti-Rh6 (red) and anti-Elav (blue). All PRs are labeled by anti-Rh6 staining. (H) High-magnification image of third instar larva otdvui mutant BO labeled with anti-Chp (green), anti-Sal (red), and anti-Elav (blue). Four PRs are labeled by anti-Sal staining.
Discussion
In this study, we describe the genetic mechanisms underlying the specification of BO PR subtypes. The larval eye consists of two distinct PR subtypes, three to four PRs containing blue-sensitive Rh5 and eight to 10 containing green-sensitive Rh6. Primary precursors, which give rise to the Rh5-subtype PRs, signal to the surrounding tissue to develop as secondary precursors, which become the Rh6 subtype. EGFR signaling is required for the survival of these secondary precursors. The combinatorial action of the three transcription factors Sal, Svp, and Otd then orchestrates the differentiation of the two PR subtypes. Interestingly, even though larval PRs and the adult R8 have the same rhodopsin content, the mechanisms to establish their fates are remarkably different.
Initial specification of PR cell fates
Specification of adult PRs starts with the proliferation of undifferentiated cells anterior to the morphogenetic furrow and the recruitment of individual PRs into ommatidia posterior to the morphogenetic furrow in a tightly regulated spatiotemporal manner. R8 is first specified by ato and does not depend on EGFR signaling (Jarman et al. 1994; Freeman 1996). Sequential recruitment of all other PRs (R2/5, R3/4, R1/6, and then R7) is dependent on EGFR signaling (Freeman 1996; Raabe 2000; Nagaraj and Banerjee 2004). Similarly, in the larval eye, primary precursors express ato and are independent of EGFR signaling while secondary precursors need EGFR signaling for their development. Primary precursors develop into the Rh5 subtype while the Rh6-subtype identity corresponds to secondary precursors.
Promoting and repressing the Rh6 subtype
During larval PR development, EGFR signaling is required for the Rh6 but not the Rh5 subtype. tll inhibits this process by preventing the adjacent optic lobe primordium from responding to EGFR signaling (Daniel et al. 1999; Dumstrei et al. 2002; Chang et al. 2003a). However, expression of tll is not negatively regulated by EGFR signaling (Daniel et al. 1999; Dumstrei et al. 2002; Chang et al. 2003a). Blocking apoptosis or removing tll function both result in supernumerary Rh6 cells, indicating that cells that should have died in response to tll function become Rh6 PRs (Fig. 8A). Secondary precursors do not appear to require maintenance of EGFR signaling to survive. During later developmental stages, all immature PRs express sevenless, another gene encoding a Receptor Tyrosine Kinase as well as its ligand, Boss (S.G. Specher and C. Desplan, unpubl.), which could act redundantly with EGFR later in development. However, we see no effect of mutating boss or sev, either on larval PR number or on Rh5/Rh6 expression (S.G. Specher and C. Desplan, unpubl.). It could be that late EGFR activity compensates for the loss of Sev activity, comparable with the adult R7 cells, where EGFR is sufficient to replace Sev (Freeman 1996).
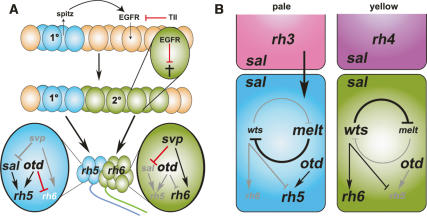
Figure 8.
Proposed model for development and the specification of rhodopsin fates in the larval eye and comparison with the adult R8. (A) Primary precursors (1°, blue) express the TGFα homolog spi, which is required in secondary precursor cells (2°, green) for their survival. tll acts in the surrounding tissue to inhibit secondary precursor development. Primary precursors give rise to the Rh5 PR subtype, whereas secondary precursors give rise to the Rh6 PR subtype. In the Rh5 PR subtype, sal and otd are required for Rh5 expression, and otd further for the repression of Rh6. In the Rh6 subtype, svp is required for Rh6 expression and for the repression of sal expression. (B) The negative feedback loop of wts and melt mediates the decision of R8 to express Rh6 or Rh5. Which way the loop swings depends on an instructive signal of the overlying R7 cell. The presence of gene expression is indicated by black type and its absence is indicated with gray type. Arrows shown in black (for activation) and red (for repression) indicate an active interaction; gray arrows indicate the absence of this interaction.
What is the function of the EGFR pathway in antagonizing tll function? The Ets transcription factors yan and pnt are both expressed during the period of secondary precursor specification. In response to EGFR signaling, Yan acts as a repressor and Pnt as an activator. Their tightly controlled activation, cross-regulation, and competition for binding sites are essential for appropriate EGFR signaling. It is difficult, however, to test their function in BO PR formation, as mutants die with strong patterning defects in the embryo. We could test the function of EGFR because we were able to inhibit its function late, specifically in the optic lobe region, by misexpressing a dominant-negative form of EGFR. This likely inhibits but might not completely abolish endogenous EGFR signaling. Thus, even though concomitantly preventing cell death and EGFR signaling restores Rh6 PRs, it is possible that basal levels of EGFR signaling are sufficient for the specification of Rh6 PR specification, but not for survival. The mechanism by which tll affects secondary precursor development remains elusive. tll might prevent cells from developing as secondary precursors, leading them to undergo apoptosis. Only cells that receive enough EGFR signal near primary PR precursors are rescued. Alternatively a second signal could make tll-expressing cells undergo apoptosis. Notch and hedgehog signaling have also been shown to be involved the development of larval PRs and may provide an alternative source for proper subtype specification and survival of secondary precursors (Green et al. 1993; Schmucker et al. 1994; Suzuki and Saigo 2000).
Network of transcription factors for PR-subtype specification
During larval eye development, sal is only required for the expression of Rh5 but not for the specification of Rh5-subtype fate. First, ectopic activation of Sal is not sufficient to induce Rh5 expression. Further, sal is still expressed in cells that have adopted the Rh6 subtype due to ectopic svp expression. In contrast, svp is required and sufficient for the Rh6 subtype where it represses the Rh5-subtype fate. Interestingly, svp is not only required for the repression of sal, but is also necessary for Rh6 expression (Fig. 8A). In the adult retina, svp is necessary for the specification of the R3/R4 and R1/R6 pairs (Mlodzik et al. 1990; Domingos et al. 2004a, b) where it is also required for the repression of sal: R3/R4 are transformed into R7 cells in svp mutants (Domingos et al. 2004b). However, the upstream mechanisms by which the expression of sal and svp is controlled in larval PRs remains elusive. There may be an unknown signal from primary precursors that induces secondary precursors by controlling svp expression. This signal is probably not EGFR, since EGFRdn secondary cells that are rescued from death by p35 still express svp.
In the adult retina otd is required for the expression of rh3 and rh5 and for the repression of Rh6 in outer PRs. In the larval eye, is also expressed in all PRs, but it is not required for the formation of larval PRs. During their terminal differentiation, otd is required, only in the Rh5 subtype, for Rh5 expression and Rh6 repression (Fig. 8A). Since otd only functions in the context of sal expression, it acts as a permissive factor for Rh regulation. It seems likely that otd and sal act in parallel in the Rh5 subtype: Otd expression is not altered in sal mutants and Sal expression is not altered in otd mutants. Further, Otd, which binds directly to the rh3, rh5, and rh6 enhancers in the adult eye, likely acts in a similar fashion in larval PRs (Tahayato et al. 2003).
Specification of PR subtypes: comparison between larval and adult eyes
There are interesting similarities and differences between PR-subtype specification in the larval and adult eyes. Most strikingly, the two Rhs expressed in the larval eye are R8 Rhs. The type of Rh expressed in R8 is instructed by R7 and maintained by the wts/melt bistable loop (Fig. 8B). In contrast, in the larva, there are no additional PRs in BO to instruct the Rh5 and Rh6 PR fate and the expression of these genes does not depend on wts and melt. Since misexpression of wts or melt does not affect larval PRs, the downstream effectors of the loop must be absent or not functioning in the larval eye. Rh5 PRs, which are specified first, might be a source of an instructive signal for the Rh6-subtype fate. Alternatively, this signal might arise from non-BO cells. However, we have not yet been able to determine its identity. Finally, larval PRs are not specified or distributed stochastically in BO, as the two groups that express Rhr or Rh6 are physically distinct, presumably explaining why there is not need for the bistable loop of wts and melt. Therefore, even though the Rh fates of larval PRs and adult R8 are identical, they achieve their fates through very distinct mechanisms.
Larval PR development: similarities to chordotonal organ development
Primary sensory precursors also induce secondary precursors in the development of the peripheral nervous system, in chordotonal and external sensory organs. After the delamination of chordotonal or sensory organ precursors (SOP), these cells signal to the overlaying ectoderm to induce delamination of secondary precursors (Okabe and Okano 1997; zur Lage and Jarman 1999; zur Lage et al. 2004). EGFR signaling is essential for the survival of BO secondary precursors, whereas in SOPs, it induces the delamination of secondary precursors. sal is also required to adopt the proper final cell fate both in larval PR precursors (Rh5 vs. Rh6) and embryonic SOPs (nonneuronal oenocytes vs. sensory neurons) (Elstob et al. 2001). However, oenocyte specification completely depends on sal, whereas larval eye primary precursors only require sal for Rh5 expression (Elstob et al. 2001). Thus, the two systems use EGFR signaling and Sal differently.
Larval PR precursors do not further divide, while SOPs later undergo asymmetric cell division to produce two nonidentical daughter cells. This may be due to the fact that BO only contain two different subtypes, whose identity correlate with primary or secondary precursors. Further, larval PR precursors develop in a group of adjacent cells as part of a placode. Thus, classical SOP specification using Notch signaling and lateral inhibition does not seem to occur to specify PR precursors. It will of great interest to further investigate the similarities and differences in the molecular mechanisms underlying the development of these sensory organs and how they are controlled.
Materials and methods
Drosophila strains and genetics
For wild-type comparison we used yw122; yw122, sp/CyO, TM2/TM6b; or heterozygous siblings of mutant alleles. For sal mutant analysis, the sal16 and a small Deficiency—Df(2L)32FP-5, which removes salm and salr—were used, balanced over CyO, Dfd-YFP; both fly strains gave comparable results (Kuhnlein et al. 1994; Elstob et al. 2001). For svp mutant analysis, the svpE22 was used, balanced over TM6b, Dfd-YFP (Mlodzik et al. 1990). For tll mutant analysis, the tll1 and tll149 were used, balanced over TM6b, Dfd-YFP. For sal, tll, and svp, homozygous mutants were identified by the absence of Dfd-YFP (Bloomington Stock Center). We used the viable otduvi allele (Vandendries et al. 1996). The following fly strains were used: so-Gal4 (Chang et al. 2003b), sev-Gal4 (Therrien et al. 1999), otd-Gal4 (T. Cook, pers. comm.), ato-Gal4 (Hassan et al. 2000), svpH162-LacZ (Elstob et al. 2001), svp724-Gal4 (Kyoto Stock Center; kindly provided by J. Urban), sal-Gal4 (Mollereau et al. 2000), UAS-EGFRdn (O’Keefe et al. 1997), wtsP1, meltD1, melt-LacZ, wts-Gal4, UAS-melt, UAS-lats (Mikeladze-Dvali et al. 2005b), UAS-H2B∷YFP (anti-GFP antibody/Biogenesis recognizes the YFP antigen), r (Bellaiche et al. 2001), UAS-salm (Kuhnlein and Schuh 1996), UAS-svp (Kramer et al. 1995), UAS-CD8GFP, UAS-p35, UAS-pntP1, and UAS-yan (Bloomington). Embryos were staged according to Campos-Ortega and Hartenstein (1997).
Immunohistochemistry and preparation of embryonic and larval specimen
Embryos were dechorionated, fixed, and immunostained according to previously published protocols (Therianos et al. 1995). Primary antibodies were rabbit anti-Rh6 1:10,000 (Tahayato et al. 2003), mouse anti-Rh5 1:20, anti-Rh3 1:20, or anti-Rh4 1:20 (Chou et al. 1996), mouse anti-Nrt 1:10 (Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank [DSHB]), mouse anti-Rh1 1:20 (DSHB), mouse anti-FasII 1:10 (Lin and Goodman 1994), rat anti-Elav 1:30 (DSHB), goat anti-Ato 1:1000 (Jarman et al. 1993), sheep anti-GFP (Biogenesis), rabbit anti-Sal 1:200 (Kuhnlein et al. 1994), mouse anti-Svp 1:1000 (Kanai et al. 2005), mouse anti-Pros 1:50 (DSHB), mouse anti-Chp 1:10 (DSHB), rat anti-Otd 1:200 (Hirth et al. 2003), rat anti-Kr 1:300 (Kosman et al. 1998), rab anti-PntP1 (Alvarez et al. 2003), anti-Yan (Rebay and Rubin 1995), guinea pig anti-Ss 1:500 (Kim et al. 2006), and mouse anti-βGAL 1:20 (DSHB). Secondary antibodies used for confocal microscopic analysis were Alexa-488, Alexa-555, and Alexa-647 antibodies generated in goat (Molecular probes), all at 1:300–1:500 dilution. Embryos were mounted in Vectashield H-1000 (Vector). For the analysis of the larval BO, the head skeleton was separated from epidermis, imaginal discs, and brain and fixed for 15 min in 4% formaldehyde/PBS. The chitinous head skeleton was then carefully opened on the dorsal and ventral midline using sharpened minutien pins (0.1-mm diameter, Fisher Scientific Tools).
Laser confocal microscopy and image processing
For laser confocal microscopy, a Leica TCS SP was used. Optical sections ranged from 0.2 to 1.5 μm, recorded in line average mode with a picture size of 512 × 512 pixels or 1024 × 1024 pixels. Captured images from optical sections were arranged and processed using Leica confocal Software (LCS). Complete series of optical sections were imported and processed using ImageJ. Generation of three-dimensional digital models and raw tiff stacks (stacks of optical sections) were done using AMIRA (Mercury Computer Systems) as previously described (Sprecher et al. 2006).
Acknowledgments
We thank A.H. Brand, S. Britt, T. Cook, the Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank (DSHB), B. Hassan, V. Hartenstein, Y. Hiromi, F. Hirth, Y.N. Jan, A. Jarman, the Kyoto Stock Center, K. Matthews, M. Mlodzik, B. Mollerau, H. Reichert, J. Reinitz, J. Skeath, and J. Urban for flies and antibodies. We also thank J. Blau, R.J. Johnston, D. Pistillo, and D. Vasiliauskas for discussion and comments on the manuscript. This work was funded by a grant EY013010 from the National Eye Institute/NIH to C.D., and the Swiss National Science Foundation, the Novartis Foundation, and the Janggen-Pöhn Stiftung to S.G.S., and was conducted in a facility constructed with the support of a Research Facilities Improvement Grant C06 RR-15518-01 from the NCRR, NIH.
Footnotes
Supplemental material is available at http://www.genesdev.org.
Article is online at http://www.genesdev.org/cgi/doi/10.1101/gad.1565407
References
- Alvarez A.D., Shi W.Y., Wilson B.A., Skeath J.B., Shi W.Y., Wilson B.A., Skeath J.B., Wilson B.A., Skeath J.B., Skeath J.B. pannier and pointedP2 act sequentially to regulate Drosophila heart development. Development. 2003;130:3015–3026. doi: 10.1242/dev.00488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellaiche Y., Gho M., Kaltschmidt J.A., Brand A.H., Schweisguth F., Gho M., Kaltschmidt J.A., Brand A.H., Schweisguth F., Kaltschmidt J.A., Brand A.H., Schweisguth F., Brand A.H., Schweisguth F., Schweisguth F. Frizzled regulates localization of cell-fate determinants and mitotic spindle rotation during asymmetric cell division. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001;3:50–57. doi: 10.1038/35050558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Ortega J.A., Hartenstein V., Hartenstein V. The embryonic development of Drosophila melanogaster. Springer; Heidleberg, Germany: 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Chang T., Shy D., Hartenstein V., Shy D., Hartenstein V., Hartenstein V. Antagonistic relationship between Dpp and EGFR signaling in Drosophila head patterning. Dev. Biol. 2003a;263:103–113. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(03)00448-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T., Younossi-Hartenstein A., Hartenstein V., Younossi-Hartenstein A., Hartenstein V., Hartenstein V. Development of neural lineages derived from the sine oculis positive eye field of Drosophila. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2003b;32:303–317. doi: 10.1016/j.asd.2003.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou W., Hall K., Wilson D., Wideman C., Townson S., Chadwell L., Britt S., Hall K., Wilson D., Wideman C., Townson S., Chadwell L., Britt S., Wilson D., Wideman C., Townson S., Chadwell L., Britt S., Wideman C., Townson S., Chadwell L., Britt S., Townson S., Chadwell L., Britt S., Chadwell L., Britt S., Britt S. Identification of a novel opsin reveals specific patterning of the R7 and R8 photoreceptor cells. Neuron. 1996;17:1101–1115. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou W.H., Huber A., Bentrop J., Schulz S., Schwab K., Chadwell L.V., Paulsen R., Britt S.G., Huber A., Bentrop J., Schulz S., Schwab K., Chadwell L.V., Paulsen R., Britt S.G., Bentrop J., Schulz S., Schwab K., Chadwell L.V., Paulsen R., Britt S.G., Schulz S., Schwab K., Chadwell L.V., Paulsen R., Britt S.G., Schwab K., Chadwell L.V., Paulsen R., Britt S.G., Chadwell L.V., Paulsen R., Britt S.G., Paulsen R., Britt S.G., Britt S.G. Patterning of the R7 and R8 photoreceptor cells of Drosophila: Evidence for induced and default cell-fate specification. Development. 1999;126:607–616. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.4.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S.M., Jurgens G., Jurgens G. Mediation of Drosophila head development by gap-like segmentation genes. Nature. 1990;346:482–485. doi: 10.1038/346482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook T., Pichaud F., Sonneville R., Papatsenko D., Desplan C., Pichaud F., Sonneville R., Papatsenko D., Desplan C., Sonneville R., Papatsenko D., Desplan C., Papatsenko D., Desplan C., Desplan C. Distinction between color photoreceptor cell fates is controlled by Prospero in Drosophila. Dev. Cell. 2003;4:853–864. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(03)00156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel A., Dumstrei K., Lengyel J.A., Hartenstein V., Dumstrei K., Lengyel J.A., Hartenstein V., Lengyel J.A., Hartenstein V., Hartenstein V. The control of cell fate in the embryonic visual system by atonal, tailless and EGFR signaling. Development. 1999;126:2945–2954. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.13.2945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingos P.M., Brown S., Barrio R., Ratnakumar K., Frankfort B.J., Mardon G., Steller H., Mollereau B., Brown S., Barrio R., Ratnakumar K., Frankfort B.J., Mardon G., Steller H., Mollereau B., Barrio R., Ratnakumar K., Frankfort B.J., Mardon G., Steller H., Mollereau B., Ratnakumar K., Frankfort B.J., Mardon G., Steller H., Mollereau B., Frankfort B.J., Mardon G., Steller H., Mollereau B., Mardon G., Steller H., Mollereau B., Steller H., Mollereau B., Mollereau B. Regulation of R7 and R8 differentiation by the spalt genes. Dev. Biol. 2004a;273:121–133. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.05.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingos P.M., Mlodzik M., Mendes C.S., Brown S., Steller H., Mollereau B., Mlodzik M., Mendes C.S., Brown S., Steller H., Mollereau B., Mendes C.S., Brown S., Steller H., Mollereau B., Brown S., Steller H., Mollereau B., Steller H., Mollereau B., Mollereau B. Spalt transcription factors are required for R3/R4 specification and establishment of planar cell polarity in the Drosophila eye. Development. 2004b;131:5695–5702. doi: 10.1242/dev.01443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumstrei K., Wang F., Shy D., Tepass U., Hartenstein V., Wang F., Shy D., Tepass U., Hartenstein V., Shy D., Tepass U., Hartenstein V., Tepass U., Hartenstein V., Hartenstein V. Interaction between EGFR signaling and DE-cadherin during nervous system morphogenesis. Development. 2002;129:3983–3994. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.17.3983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elstob P.R., Brodu V., Gould A.P., Brodu V., Gould A.P., Gould A.P. spalt-dependent switching between two cell fates that are induced by the Drosophila EGF receptor. Development. 2001;128:723–732. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.5.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman M. Reiterative use of the EGF receptor triggers differentiation of all cell types in the Drosophila eye. Cell. 1996;87:651–660. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P., Hartenstein A.Y., Hartenstein V., Hartenstein A.Y., Hartenstein V., Hartenstein V. The embryonic development of the Drosophila visual system. Cell Tissue Res. 1993;273:583–598. doi: 10.1007/BF00333712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan B.A., Bermingham N.A., He Y., Sun Y., Jan Y.N., Zoghbi H.Y., Bellen H.J., Bermingham N.A., He Y., Sun Y., Jan Y.N., Zoghbi H.Y., Bellen H.J., He Y., Sun Y., Jan Y.N., Zoghbi H.Y., Bellen H.J., Sun Y., Jan Y.N., Zoghbi H.Y., Bellen H.J., Jan Y.N., Zoghbi H.Y., Bellen H.J., Zoghbi H.Y., Bellen H.J., Bellen H.J. atonal regulates neurite arborization but does not act as a proneural gene in the Drosophila brain. Neuron. 2000;25:549–561. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)81059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan J., Iyengar B., Scantlebury N., Moncalvo V.R., Campos R., Iyengar B., Scantlebury N., Moncalvo V.R., Campos R., Scantlebury N., Moncalvo V.R., Campos R., Moncalvo V.R., Campos R., Campos R. Photic input pathways that mediate the Drosophila larval response to light and circadian rhythmicity are developmentally related but functionally distinct. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005;481:266–275. doi: 10.1002/cne.20383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirth F., Kammermeier L., Frei E., Walldorf U., Noll M., Reichert H., Kammermeier L., Frei E., Walldorf U., Noll M., Reichert H., Frei E., Walldorf U., Noll M., Reichert H., Walldorf U., Noll M., Reichert H., Noll M., Reichert H., Reichert H. An urbilaterian origin of the tripartite brain: Developmental genetic insights from Drosophila. Development. 2003;130:2365–2373. doi: 10.1242/dev.00438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarman A.P., Grau Y., Jan L.Y., Jan Y.N., Grau Y., Jan L.Y., Jan Y.N., Jan L.Y., Jan Y.N., Jan Y.N. atonal is a proneural gene that directs chordotonal organ formation in the Drosophila peripheral nervous system. Cell. 1993;73:1307–1321. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90358-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarman A.P., Grell E.H., Ackerman L., Jan L.Y., Jan Y.N., Grell E.H., Ackerman L., Jan L.Y., Jan Y.N., Ackerman L., Jan L.Y., Jan Y.N., Jan L.Y., Jan Y.N., Jan Y.N. Atonal is the proneural gene for Drosophila photoreceptors. Nature. 1994;369:398–400. doi: 10.1038/369398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai M.I., Okabe M., Hiromi Y., Okabe M., Hiromi Y., Hiromi Y. seven-up Controls switching of transcription factors that specify temporal identities of Drosophila neuroblasts. Dev. Cell. 2005;8:203–213. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2004.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M.D., Jan L.Y., Jan Y.N., Jan L.Y., Jan Y.N., Jan Y.N. The bHLH-PAS protein Spineless is necessary for the diversification of dendrite morphology of Drosophila dendritic arborization neurons. Genes & Dev. 2006;20:2806–2819. doi: 10.1101/gad.1459706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosman D., Small S., Reinitz J., Small S., Reinitz J., Reinitz J. Rapid preparation of a panel of polyclonal antibodies to Drosophila segmentation proteins. Dev. Genes Evol. 1998;208:290–294. doi: 10.1007/s004270050184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer S., West S.R., Hiromi Y., West S.R., Hiromi Y., Hiromi Y. Cell fate control in the Drosophila retina by the orphan receptor seven-up: Its role in the decisions mediated by the ras signaling pathway. Development. 1995;121:1361–1372. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.5.1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhnlein R.P., Schuh R., Schuh R. Dual function of the region-specific homeotic gene spalt during Drosophila tracheal system development. Development. 1996;122:2215–2223. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.7.2215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhnlein R.P., Frommer G., Friedrich M., Gonzalez-Gaitan M., Weber A., Wagner-Bernholz J.F., Gehring W.J., Jackle H., Schuh R., Frommer G., Friedrich M., Gonzalez-Gaitan M., Weber A., Wagner-Bernholz J.F., Gehring W.J., Jackle H., Schuh R., Friedrich M., Gonzalez-Gaitan M., Weber A., Wagner-Bernholz J.F., Gehring W.J., Jackle H., Schuh R., Gonzalez-Gaitan M., Weber A., Wagner-Bernholz J.F., Gehring W.J., Jackle H., Schuh R., Weber A., Wagner-Bernholz J.F., Gehring W.J., Jackle H., Schuh R., Wagner-Bernholz J.F., Gehring W.J., Jackle H., Schuh R., Gehring W.J., Jackle H., Schuh R., Jackle H., Schuh R., Schuh R. spalt encodes an evolutionarily conserved zinc finger protein of novel structure which provides homeotic gene function in the head and tail region of the Drosophila embryo. EMBO J. 1994;13:168–179. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06246.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin D.M., Goodman C.S., Goodman C.S. Ectopic and increased expression of Fasciclin II alters motoneuron growth cone guidance. Neuron. 1994;13:507–523. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malpel S., Klarsfeld A., Rouyer F., Klarsfeld A., Rouyer F., Rouyer F. Larval optic nerve and adult extra-retinal photoreceptors sequentially associate with clock neurons during Drosophila brain development. Development. 2002;129:1443–1453. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.6.1443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malpel S., Klarsfeld A., Rouyer F., Klarsfeld A., Rouyer F., Rouyer F. Circadian synchronization and rhythmicity in larval photoperception-defective mutants of Drosophila. J. Biol. Rhythms. 2004;19:10–21. doi: 10.1177/0748730403260621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzoni E.O., Desplan C., Blau J., Desplan C., Blau J., Blau J. Circadian pacemaker neurons transmit and modulate visual information to control a rapid behavioral response. Neuron. 2005;45:293–300. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.12.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikeladze-Dvali T., Desplan C., Pistillo D., Desplan C., Pistillo D., Pistillo D. Flipping coins in the fly retina. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2005a;69:1–15. doi: 10.1016/S0070-2153(05)69001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikeladze-Dvali T., Wernet M.F., Pistillo D., Mazzoni E.O., Teleman A.A., Chen Y.W., Cohen S., Desplan C., Wernet M.F., Pistillo D., Mazzoni E.O., Teleman A.A., Chen Y.W., Cohen S., Desplan C., Pistillo D., Mazzoni E.O., Teleman A.A., Chen Y.W., Cohen S., Desplan C., Mazzoni E.O., Teleman A.A., Chen Y.W., Cohen S., Desplan C., Teleman A.A., Chen Y.W., Cohen S., Desplan C., Chen Y.W., Cohen S., Desplan C., Cohen S., Desplan C., Desplan C. The growth regulators warts/lats and melted interact in a bistable loop to specify opposite fates in Drosophila R8 photoreceptors. Cell. 2005b;122:775–787. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mlodzik M., Hiromi Y., Weber U., Goodman C.S., Rubin G.M., Hiromi Y., Weber U., Goodman C.S., Rubin G.M., Weber U., Goodman C.S., Rubin G.M., Goodman C.S., Rubin G.M., Rubin G.M. The Drosophila seven-up gene, a member of the steroid receptor gene superfamily, controls photoreceptor cell fates. Cell. 1990;60:211–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90737-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollereau B., Wernet M.F., Beaufils P., Killian D., Pichaud F., Kuhnlein R., Desplan C., Wernet M.F., Beaufils P., Killian D., Pichaud F., Kuhnlein R., Desplan C., Beaufils P., Killian D., Pichaud F., Kuhnlein R., Desplan C., Killian D., Pichaud F., Kuhnlein R., Desplan C., Pichaud F., Kuhnlein R., Desplan C., Kuhnlein R., Desplan C., Desplan C. A green fluorescent protein enhancer trap screen in Drosophila photoreceptor cells. Mech. Dev. 2000;93:151–160. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(00)00287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollereau B., Dominguez M., Webel R., Colley N.J., Keung B., de Celis J.F., Desplan C., Dominguez M., Webel R., Colley N.J., Keung B., de Celis J.F., Desplan C., Webel R., Colley N.J., Keung B., de Celis J.F., Desplan C., Colley N.J., Keung B., de Celis J.F., Desplan C., Keung B., de Celis J.F., Desplan C., de Celis J.F., Desplan C., Desplan C. Two-step process for photoreceptor formation in Drosophila. Nature. 2001;412:911–913. doi: 10.1038/35091076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncalvo V.G.R., Campos A.R., Campos A.R. Genetic dissection of trophic interactions in the larval optic neuropil of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev. Biol. 2005;286:549–558. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.08.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraj R., Banerjee U., Banerjee U. The little R cell that could. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2004;48:755–760. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.041881rn. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okabe M., Okano H., Okano H. Two-step induction of chordotonal organ precursors in Drosophila embryogenesis. Development. 1997;124:1045–1053. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.5.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’Keefe L., Dougan S.T., Gabay L., Raz E., Shilo B.Z., DiNardo S., Dougan S.T., Gabay L., Raz E., Shilo B.Z., DiNardo S., Gabay L., Raz E., Shilo B.Z., DiNardo S., Raz E., Shilo B.Z., DiNardo S., Shilo B.Z., DiNardo S., DiNardo S. Spitz and Wingless, emanating from distinct borders, cooperate to establish cell fate across the Engrailed domain in the Drosophila epidermis. Development. 1997;124:4837–4845. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.23.4837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill E.M., Rebay I., Tjian R., Rubin G.M., Rebay I., Tjian R., Rubin G.M., Tjian R., Rubin G.M., Rubin G.M. The activities of two Ets-related transcription factors required for Drosophila eye development are modulated by the Ras/MAPK pathway. Cell. 1994;78:137–147. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90580-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papatsenko D., Sheng G., Desplan C., Sheng G., Desplan C., Desplan C. A new rhodopsin in R8 photoreceptors of Drosophila: Evidence for coordinate expression with Rh3 in R7 cells. Development. 1997;124:1665–1673. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.9.1665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock J., Benzer S., Benzer S. Transcript localization of four opsin genes in the three visual organs of Drosophila: RH2 is ocellus specific. Nature. 1988;333:779–782. doi: 10.1038/333779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raabe T. The sevenless signaling pathway: Variations of a common theme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2000;1496:151–163. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(00)00020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebay I., Rubin G.M., Rubin G.M. Yan functions as a general inhibitor of differentiation and is negatively regulated by activation of the Ras1/MAPK pathway. Cell. 1995;81:857–866. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmucker D., Taubert H., Jackle H., Taubert H., Jackle H., Jackle H. Formation of the Drosophila larval photoreceptor organ and its neuronal differentiation require continuous Kruppel gene activity. Neuron. 1992;9:1025–1039. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90063-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmucker D., Su A.L., Beermann A., Jackle H., Jay D.G., Su A.L., Beermann A., Jackle H., Jay D.G., Beermann A., Jackle H., Jay D.G., Jackle H., Jay D.G., Jay D.G. Chromophore-assisted laser inactivation of patched protein switches cell fate in the larval visual system of Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1994;91:2664–2668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmucker D., Jackle H., Gaul U., Jackle H., Gaul U., Gaul U. Genetic analysis of the larval optic nerve projection in Drosophila. Development. 1997;124:937–948. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.5.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprecher S.G., Urbach R., Technau G.M., Rijli F.M., Reichert H., Hirth F., Urbach R., Technau G.M., Rijli F.M., Reichert H., Hirth F., Technau G.M., Rijli F.M., Reichert H., Hirth F., Rijli F.M., Reichert H., Hirth F., Reichert H., Hirth F., Hirth F. The columnar gene vnd is required for tritocerebral neuromere formation during embryonic brain development of Drosophila. Development. 2006;133:4331–4339. doi: 10.1242/dev.02606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Saigo K., Saigo K. Transcriptional regulation of atonal required for Drosophila larval eye development by concerted action of eyes absent, sine oculis and hedgehog signaling independent of fused kinase and cubitus interruptus. Development. 2000;127:1531–1540. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.7.1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahayato A., Sonneville R., Pichaud F., Wernet M.F., Papatsenko D., Beaufils P., Cook T., Desplan C., Sonneville R., Pichaud F., Wernet M.F., Papatsenko D., Beaufils P., Cook T., Desplan C., Pichaud F., Wernet M.F., Papatsenko D., Beaufils P., Cook T., Desplan C., Wernet M.F., Papatsenko D., Beaufils P., Cook T., Desplan C., Papatsenko D., Beaufils P., Cook T., Desplan C., Beaufils P., Cook T., Desplan C., Cook T., Desplan C., Desplan C. Otd/Crx, a dual regulator for the specification of ommatidia subtypes in the Drosophila retina. Dev. Cell. 2003;5:391–402. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(03)00239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therianos S., Leuzinger S., Hirth F., Goodman C.S., Reichert H., Leuzinger S., Hirth F., Goodman C.S., Reichert H., Hirth F., Goodman C.S., Reichert H., Goodman C.S., Reichert H., Reichert H. Embryonic development of the Drosophila brain: Formation of commissural and descending pathways. Development. 1995;121:3849–3860. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.11.3849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therrien M., Wong A.M., Kwan E., Rubin G.M., Wong A.M., Kwan E., Rubin G.M., Kwan E., Rubin G.M., Rubin G.M. Functional analysis of CNK in RAS signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1999;96:13259–13263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.23.13259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandendries E.R., Johnson D., Reinke R., Johnson D., Reinke R., Reinke R. orthodenticle is required for photoreceptor cell development in the Drosophila eye. Dev. Biol. 1996;173:243–255. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.0020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernet M.F., Desplan C., Desplan C. Building a retinal mosaic: Cell-fate decision in the fly eye. Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14:576–584. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2004.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernet M.F., Mazzoni E.O., Celik A., Duncan D.M., Duncan I., Desplan C., Mazzoni E.O., Celik A., Duncan D.M., Duncan I., Desplan C., Celik A., Duncan D.M., Duncan I., Desplan C., Duncan D.M., Duncan I., Desplan C., Duncan I., Desplan C., Desplan C. Stochastic spineless expression creates the retinal mosaic for colour vision. Nature. 2006;440:174–180. doi: 10.1038/nature04615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Lage P., Jarman A.P., Jarman A.P. Antagonism of EGFR and notch signalling in the reiterative recruitment of Drosophila adult chordotonal sense organ precursors. Development. 1999;126:3149–3157. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.14.3149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Lage P.I., Powell L.M., Prentice D.R., McLaughlin P., Jarman A.P., Powell L.M., Prentice D.R., McLaughlin P., Jarman A.P., Prentice D.R., McLaughlin P., Jarman A.P., McLaughlin P., Jarman A.P., Jarman A.P. EGF receptor signaling triggers recruitment of Drosophila sense organ precursors by stimulating proneural gene autoregulation. Dev. Cell. 2004;7:687–696. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2004.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]