Abstract
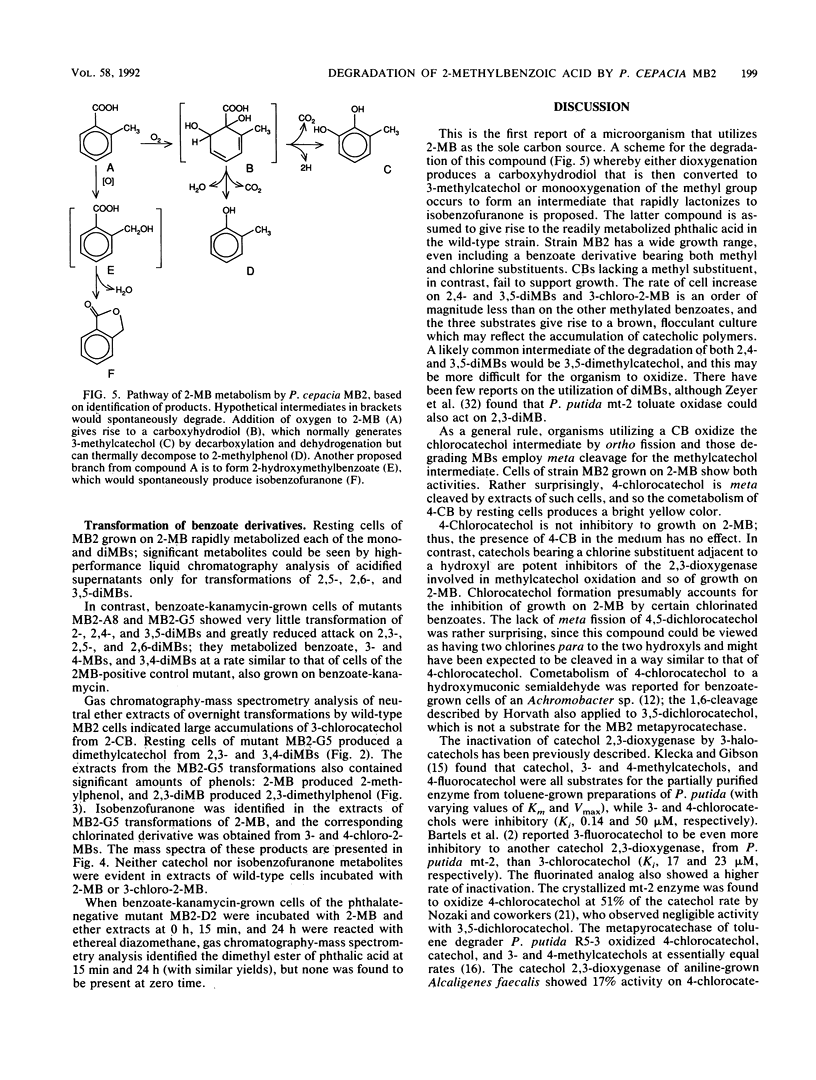
We report the isolation of Pseudomonas cepacia MB2, believed to be the first microorganism to utilize 2-methylbenzoic acid as the sole carbon source. Its growth range included all mono- and dimethylbenzoates (with the exception of 2,5- and 2,6-dimethylbenzoates) and 3-chloro-2-methylbenzoate (but not 4- or 5-chloro-2-methylbenzoate) but not chlorobenzoates lacking a methyl group. 2-Chlorobenzoate, 3-chlorobenzoate, and 2,3-, 2,4-, and 3,4-dichlorobenzoates inhibited growth of MB2 on 2-methylbenzoate as a result of cometabolism to the corresponding chlorinated catechols which blocked the key enzyme catechol 2,3-dioxygenase. A metapyrocatechase-negative mutant, MB2-G5, showed accumulation of dimethylcatechols from 2,3- and 3,4-dimethylbenzoates, and phenols were detected in resting-cell transformation extracts bearing the same substitution pattern as the original substrate, presumably following thermal degradation of the intermediate dihydrodiol. 2-Methylphenol was also found in extracts of the mutant cells with 2-methylbenzoate. These observations suggested a major route of methylbenzoate metabolism to be dioxygenation to a carboxy-hydrodiol which then forms a catechol derivative. In addition, the methyl group of 2-methylbenzoate was oxidized to isobenzofuranone (by cells of MB2-G5) and to phthalate (by cells of a separate mutant that could not utilize phthalate, MB2-D2). This pathway also generated a chlorinated isobenzofuranone from 3-chloro-2-methylbenzoate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baggi G., Barbieri P., Galli E., Tollari S. Isolation of a Pseudomonas stutzeri strain that degrades o-xylene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2129–2132. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2129-2132.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartels I., Knackmuss H. J., Reineke W. Suicide Inactivation of Catechol 2,3-Dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida mt-2 by 3-Halocatechols. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Mar;47(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.3.500-505.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey J. F., Gibson D. T. Bacterial metabolism of para- and meta-xylene: oxidation of a methyl substituent. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):923–929. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.923-929.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focht D. D., Alexander M. Aerobic cometabolism of DDT analogues by Hydrogenomonas sp. J Agric Food Chem. 1971 Jan-Feb;19(1):20–22. doi: 10.1021/jf60173a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa H., Yamaguchi M., Yamauchi T. Evidence for participation of NADH-dependent reductase in the reaction of benzoate 1,2-dioxygenase (benzoate hydroxylase). Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;74:118–126. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3270-1_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Gschwendt B., Yeh W. K., Kobal V. M. Initial reactions in the oxidation of ethylbenzene by Pseudomonas putida. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 10;12(8):1520–1528. doi: 10.1021/bi00732a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Hensley M., Yoshioka H., Mabry T. J. Formation of (+)-cis-2,3-dihydroxy-1-methylcyclohexa-4,6-diene from toluene by Pseudomonas putida. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 31;9(7):1626–1630. doi: 10.1021/bi00809a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Koch J. R., Schuld C. L., Kallio R. E. Oxidative degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by microorganisms. II. Metabolism of halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):3795–3802. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath R. S. Co-metabolism of methyl- and chloro-substituted catechols by an Achromobacter sp. possessing a new meta-cleaving oxygenase. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(5):871–876. doi: 10.1042/bj1190871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klecka G. M., Gibson D. T. Inhibition of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida by 3-chlorocatechol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 May;41(5):1159–1165. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.5.1159-1165.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröckel L., Focht D. D. Construction of chlorobenzene-utilizing recombinants by progenitive manifestation of a rare event. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2470–2475. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2470-2475.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz D. A., Chapman P. J. Catabolism of pseudocumene and 3-ethyltoluene by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence for new functions of the TOL (pWWO) plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):179–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.179-191.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnecke D. M., Hsieh D. P. Microbial metabolism of a parathion-xylene pesticide formulation. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Oct;30(4):575–580. doi: 10.1128/am.30.4.575-580.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki M., Kotani S., Ono K., Seno S. Metapyrocatechase. 3. Substrate specificity and mode of ring fission. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 11;220(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner A. M. Metabolism of benzoic acid by bacteria: 3,5-cyclohexadiene-1,2-diol-1-carboxylic acid is an intermediate in the formation of catechol. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):89–94. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.89-94.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schraa G., Bethe B. M., van Neerven A. R., Van den Tweel W. J., Van der Wende E., Zehnder A. J. Degradation 1,2-dimethylbenzene by Corynebacterium strain C125. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1987;53(3):159–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00393844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Nishino S. F. Degradation of 1,4-dichlorobenzene by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1010–1019. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1010-1019.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whited G. M., McCombie W. R., Kwart L. D., Gibson D. T. Identification of cis-diols as intermediates in the oxidation of aromatic acids by a strain of Pseudomonas putida that contains a TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):1028–1039. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.1028-1039.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Murray K. Metabolism of benzoate and the methylbenzoates by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence for the existence of a TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):416–423. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.416-423.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worsey M. J., Williams P. A. Metabolism of toluene and xylenes by Pseudomonas (putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence for a new function of the TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):7–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.7-13.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Fujisawa H. Characterization of NADH-cytochrome c reductase, a component of benzoate 1,2-dioxygenase system from Pseudomonas arvilla c-1. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8848–8853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeyer J., Lehrbach P. R., Timmis K. N. Use of cloned genes of Pseudomonas TOL plasmid to effect biotransformation of benzoates to cis-dihydrodiols and catechols by Escherichia coli cells. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Dec;50(6):1409–1413. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.6.1409-1413.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


