Abstract
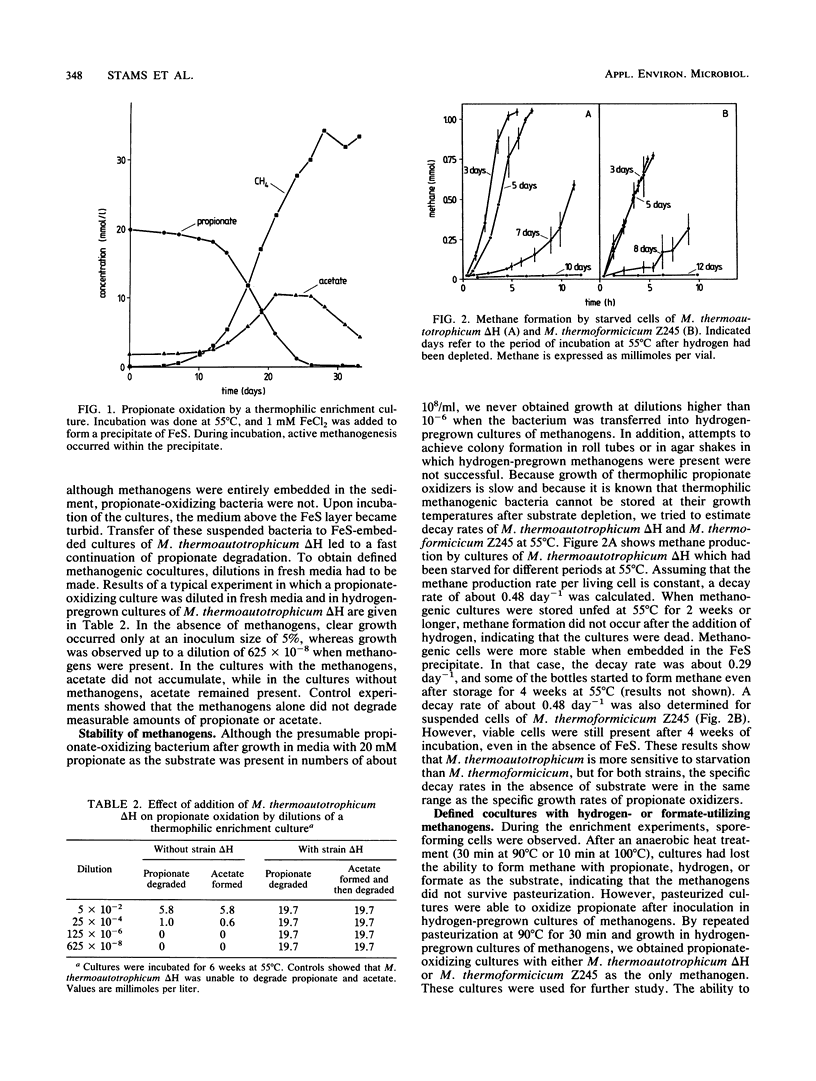
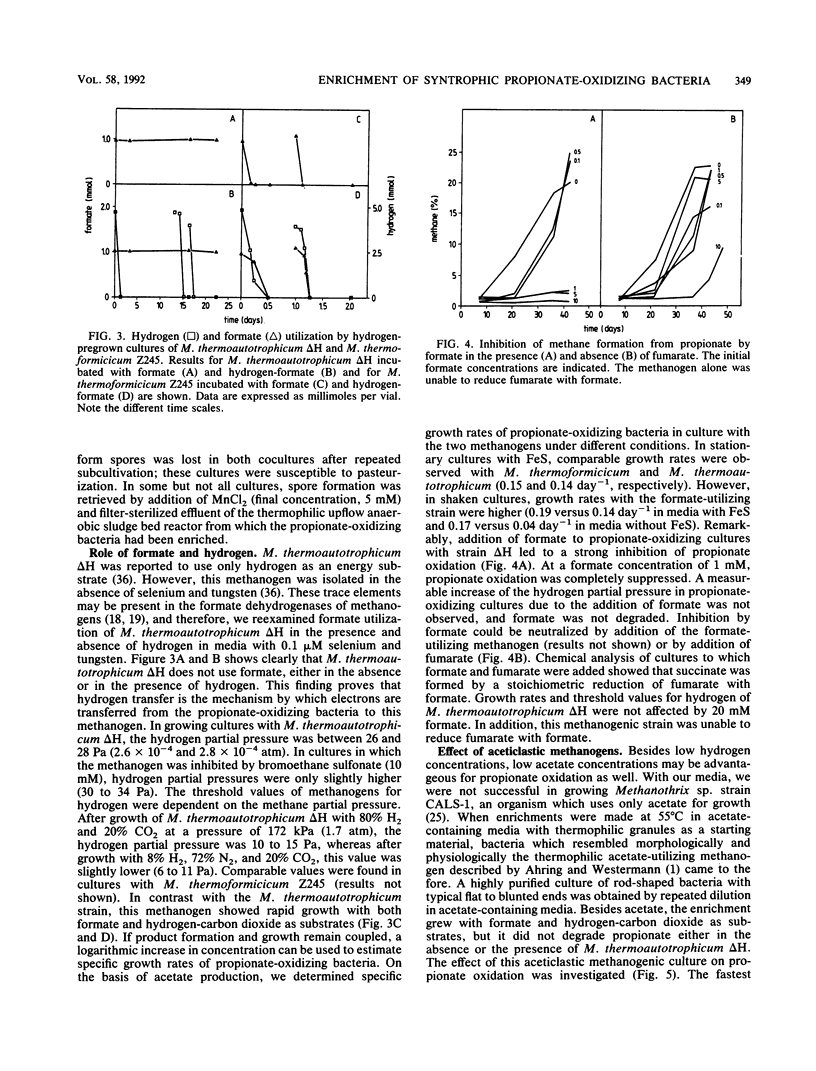
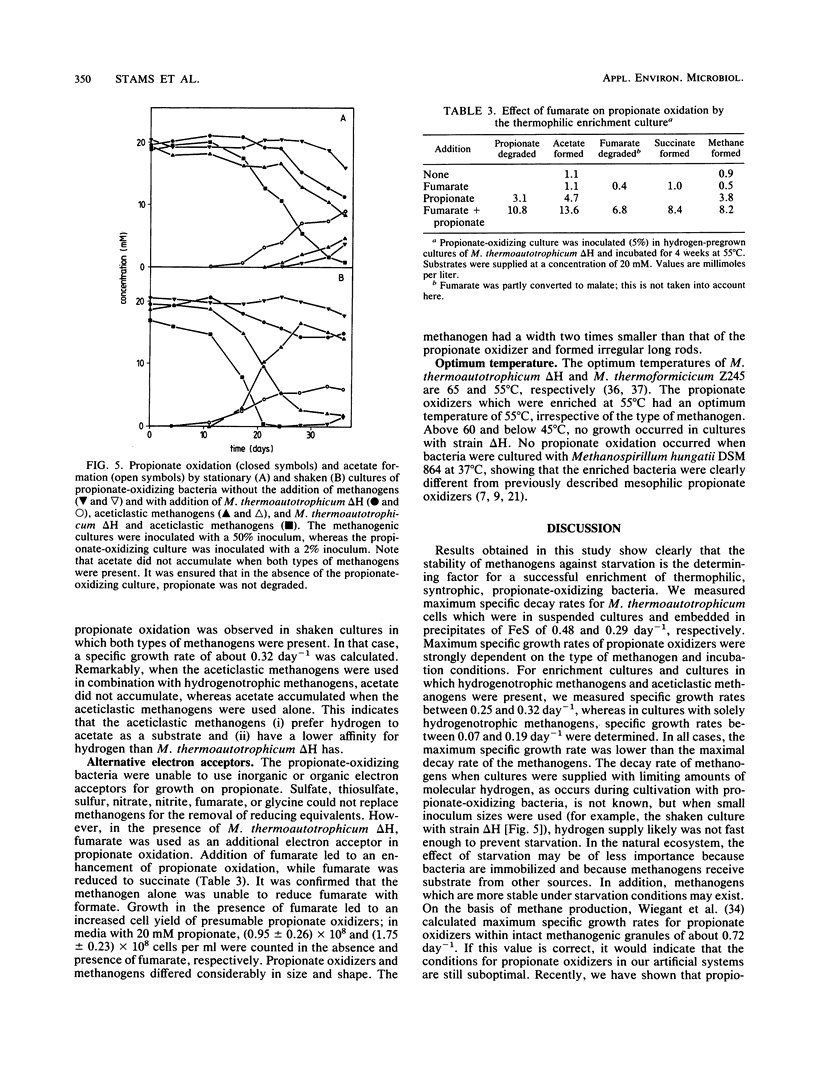
Thermophilic propionate-oxidizing, proton-reducing bacteria were enriched from the granular methanogenic sludge of a bench-scale upflow anaerobic sludge bed reactor operated at 55°C with a mixture of volatile fatty acids as feed. Thermophilic hydrogenotrophic methanogens had a high decay rate. Therefore, stable, thermophilic propionate-oxidizing cultures could not be obtained by using the usual enrichment procedures. Stable and reproducible cultivation was possible by enrichment in hydrogen-pregrown cultures of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum ΔH which were embedded in precipitates of FeS, achieved by addition of FeCl2 to the media. The propionate-oxidizing bacteria formed spores which resisted pasteurization for 30 min at 90°C or 10 min at 100°C. Highly purified cultures were obtained with either M. thermoautotrophicum ΔH or Methanobacterium thermoformicicum Z245 as the syntrophic partner organism. The optimum temperature for the two cultures was 55°C. Maximum specific growth rates of cultures with M. thermoautotrophicum ΔH were somewhat lower than those of cultures with M. thermoformicicum Z245 (0.15 and 0.19 day-1, respectively). Growth rates were even higher (0.32 day-1) when aceticlastic methanogens were present as well. M. thermoautotrophicum ΔH is an obligately hydrogen-utilizing methanogen, showing that interspecies hydrogen transfer is the mechanism by which reducing equivalents are channelled from the acetogens to this methanogen. Boundaries of hydrogen partial pressures at which propionate oxidation occurred were between 6 and 34 Pa. Formate had a strong inhibitory effect on propionate oxidation in cultures with M. thermoautotrophicum. Inhibition by formate was neutralized by addition of the formate-utilizing methanogen or by addition of fumarate. Results indicate that formate inhibited succinate oxidation to fumarate, an intermediate step in the biochemical pathway of propionate oxidation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahring B. K., Westermann P. Product inhibition of butyrate metabolism by acetate and hydrogen in a thermophilic coculture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2393–2397. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2393-2397.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahring B. K., Westermann P. Thermophilic anaerobic degradation of butyrate by a butyrate-utilizing bacterium in coculture and triculture with methanogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):429–433. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.429-433.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone D. R., Bryant M. P. Propionate-Degrading Bacterium, Syntrophobacter wolinii sp. nov. gen. nov., from Methanogenic Ecosystems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):626–632. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.626-632.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone D. R., Johnson R. L., Liu Y. Diffusion of the Interspecies Electron Carriers H(2) and Formate in Methanogenic Ecosystems and Its Implications in the Measurement of K(m) for H(2) or Formate Uptake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jul;55(7):1735–1741. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.7.1735-1741.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone D. R. Terminal reactions in the anaerobic digestion of animal waste. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):57–64. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.57-64.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone D. R., Xun L. Effects of pH, Temperature, and Nutrients on Propionate Degradation by a Methanogenic Enrichment Culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1589–1592. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1589-1592.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotenhuis J. T., Smit M., Plugge C. M., Xu Y. S., van Lammeren A. A., Stams A. J., Zehnder A. J. Bacteriological composition and structure of granular sludge adapted to different substrates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jul;57(7):1942–1949. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.7.1942-1949.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson J. M., Smith P. H. Isolation of a Butyrate-Utilizing Bacterium in Coculture with Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum from a Thermophilic Digester. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1461–1466. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1461-1466.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. B., Stadtman T. C. Methanococcus vannielii: culture and effects of selenium and tungsten on growth. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1404–1406. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1404-1406.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. B., Stadtman T. C. Selenium-dependent and selenium-independent formate dehydrogenases of Methanococcus vannielii. Separation of the two forms and characterization of the purified selenium-independent form. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):656–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch M., Dolfing J., Wuhrmann K., Zehnder A. J. Pathways of propionate degradation by enriched methanogenic cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1411–1414. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1411-1414.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInerney M. J., Bryant M. P., Hespell R. B., Costerton J. W. Syntrophomonas wolfei gen. nov. sp. nov., an Anaerobic, Syntrophic, Fatty Acid-Oxidizing Bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):1029–1039. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.1029-1039.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min H., Zinder S. H. Kinetics of Acetate Utilization by Two Thermophilic Acetotrophic Methanogens: Methanosarcina sp. Strain CALS-1 and Methanothrix sp. Strain CALS-1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):488–491. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.488-491.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. E. C nuclear magnetic resonance studies of propionate catabolism in methanogenic cocultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2260–2261. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2260-2261.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Jungermann K., Decker K. Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):100–180. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.100-180.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele Jurgen H., Zeikus J. Gregory. Control of Interspecies Electron Flow during Anaerobic Digestion: Significance of Formate Transfer versus Hydrogen Transfer during Syntrophic Methanogenesis in Flocs. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):20–29. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.20-29.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicus sp. n., an anaerobic, autotrophic, extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):707–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.707-713.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


