Abstract
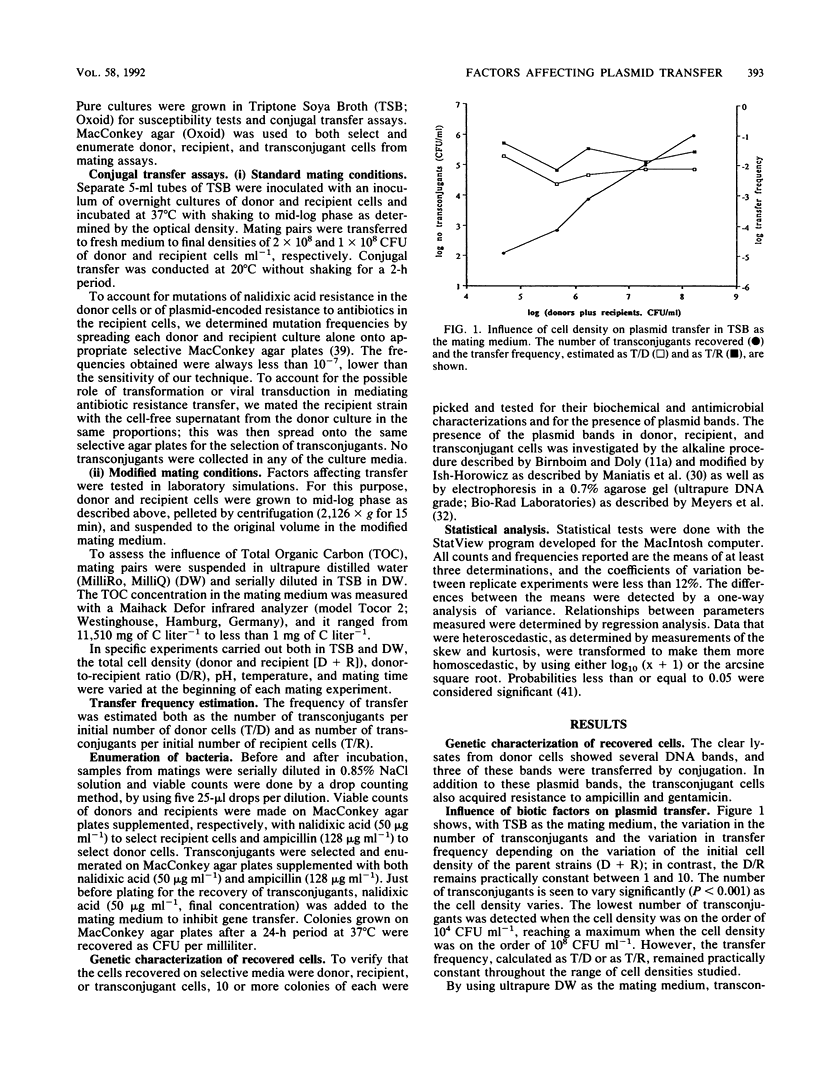
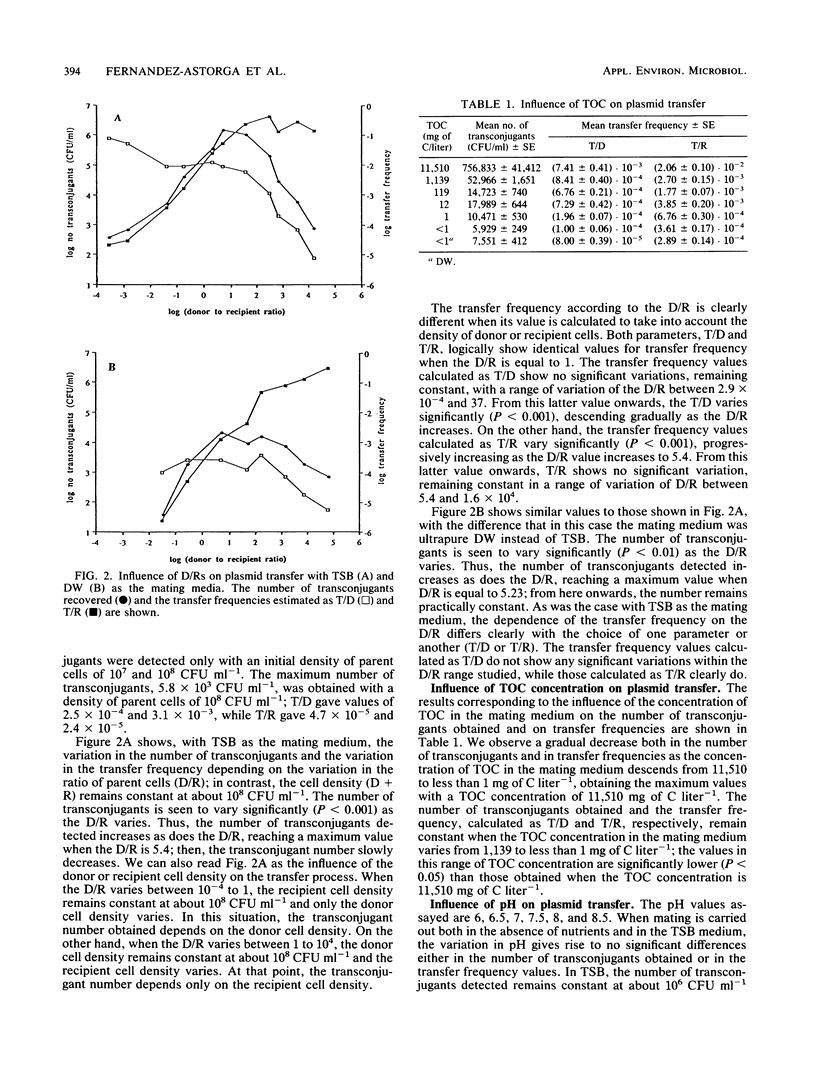
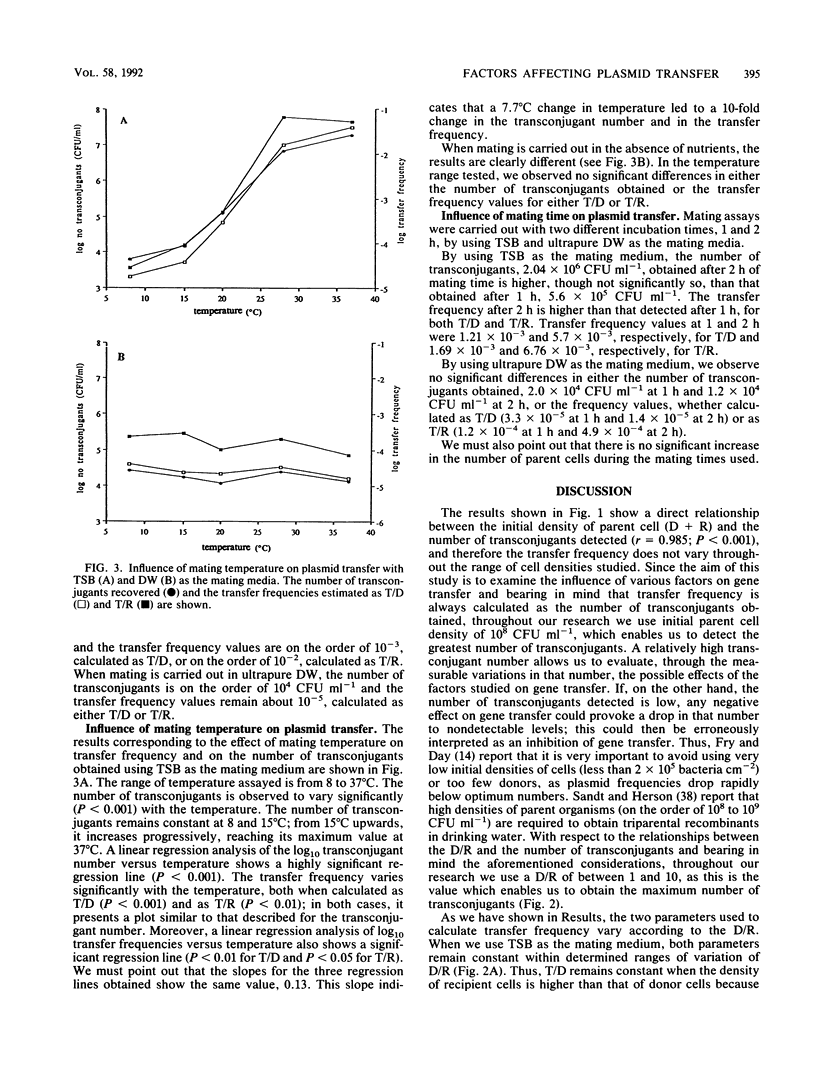
The influence of biotic and abiotic factors on plasmid transfer between Escherichia coli strains in terms of the variation in the number of transconjugants formed and the variation in transfer frequency was investigated. The density of parent cells affected the number of transconjugants, reaching a maximum when the cell density was on the order of 10(8) CFU ml-1. As the donor-to-recipient ratios varied from 10(-4) to 10(4), the number of transconjugants varied significantly (P less than 0.001), reaching a maximum with donor-to-recipient ratios between 1 and 10. The concentration of total organic carbon in the mating medium affects both the number of transconjugants and the transfer frequency, being significantly higher (P less than 0.001) when the total organic carbon concentration was higher than 1,139 mg of C liter-1. However, the transconjugants were detected even with less than 1 mg of C liter-1. Linear regression of log10 transconjugants versus mating temperature showed a highly significant regression line (P less than 0.001). Neither the transfer frequency nor the transconjugant number varied significantly in the range of pHs assayed. We can conclude that plasmid transfer by conjugation can take place within a wide range of conditions, even in such adverse conditions as the absence of nutrients and low temperatures.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcaide E., Garay E. R-plasmid transfer in Salmonella spp. isolated from wastewater and sewage-contaminated surface waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):435–438. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.435-438.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altherr M. R., Kasweck K. L. In situ studies with membrane diffusion chambers of antibiotic resistance transfer in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):838–843. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.838-843.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awong J., Bitton G., Chaudhry G. R. Microcosm for assessing survival of genetically engineered microorganisms in aquatic environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):977–983. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.977-983.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale M. J., Day M. J., Fry J. C. Novel method for studying plasmid transfer in undisturbed river epilithon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2756–2758. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2756-2758.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale M. J., Fry J. C., Day M. J. Plasmid transfer between strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on membrane filters attached to river stones. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Nov;133(11):3099–3107. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-11-3099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale M. J., Fry J. C., Day M. J. Transfer and occurrence of large mercury resistance plasmids in river epilithon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Apr;54(4):972–978. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.4.972-978.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcina I., González J. M., Iriberri J., Egea L. Effect of visible light on progressive dormancy of Escherichia coli cells during the survival process in natural fresh water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jan;55(1):246–251. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.1.246-251.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcina I., González J. M., Iriberri J., Egea L. Survival strategy of Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis in illuminated fresh and marine systems. J Appl Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;68(2):189–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1990.tb02565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. B., Macrae W. R., Elliott G. E. Incidence of R factors in coliform, fecal coliform, and Salmonella populations of the Red River in Canada. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):486–491. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.486-491.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. B., Macrae W. R., Elliott G. E. R factors in coliform-fecal coliform sewage flora of the prairies and Northwest Territories of Canada. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):204–210. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.204-210.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corliss T. L., Cohen P. S., Cabelli V. J. R-Plasmid Transfer to and from Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Human Fecal Samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):959–966. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.959-966.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Cruz N. E., Toranzos G. A., Ahearn D. G., Hazen T. C. In situ survival of plasmid-bearing and plasmidless Pseudomonas aeruginosa in pristine tropical waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2574–2577. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2574-2577.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier M. J., Cauvin F., Breittmayer J. P. Influence of salts and temperature on the transfer of mercury resistance from a marine pseudomonad to Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jul;50(1):38–40. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.1.38-40.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves J. F., Riggs H. G., Jr Anaerobic transfer of antibiotic resistance from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.1-6.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iriberri J., Unanue M., Ayo B., Barcina I., Egea L. Bacterial production and growth rate estimation from [h]thymidine incorporation for attached and free-living bacteria in aquatic systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):483–487. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.483-487.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iriberri J., Unanue M., Barcina I., Egea L. Seasonal variation in population density and heterotrophic activity of attached and free-living bacteria in coastal waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2308–2314. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2308-2314.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeler K. H. Can we guarantee the safety of genetically engineered organisms in the environment? Crit Rev Biotechnol. 1988;8(1):85–97. doi: 10.3109/07388558809150538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach P. A., Grimes D. J. R-plasmid transfer in a wastewater treatment plant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1395–1403. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1395-1403.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson P., Gealt M. A. Isolation of indigenous wastewater bacterial strains capable of mobilizing plasmid pBR325. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):904–909. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.904-909.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Morchoe S. B., Ogunseitan O., Sayler G. S., Miller R. V. Conjugal transfer of R68.45 and FP5 between Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains in a freshwater environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):1923–1929. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.1923-1929.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richaume A., Angle J. S., Sadowsky M. J. Influence of soil variables on in situ plasmid transfer from Escherichia coli to Rhizobium fredii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jul;55(7):1730–1734. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.7.1730-1734.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochelle P. A., Day M. J., Fry J. C. Occurrence, transfer and mobilization in epilithic strains of Acinetobacter of mercury-resistance plasmids capable of transformation. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Nov;134(11):2933–2941. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-11-2933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochelle P. A., Fry J. C., Day M. J. Factors affecting conjugal transfer of plasmids encoding mercury resistance from pure cultures and mixed natural suspensions of epilithic bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Feb;135(Pt 2):409–424. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-2-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandt C. H., Herson D. S. Mobilization of the genetically engineered plasmid pHSV106 from Escherichia coli HB101(pHSV106) to Enterobacter cloacae in drinking water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):194–200. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.194-200.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. R., Cabelli V. J. R-plasmid transfer frequencies from environmental isolates of Escherichia coli to laboratory and fecal strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):756–764. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.756-764.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton P., Anson A. E. Conjugal transfer of R-plasmid R1drd-19 in Escherichia coli below 22 degrees C. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):789–791. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.789-791.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toranzo A. E., Combarro P., Lemos M. L., Barja J. L. Plasmid coding for transferable drug resistance in bacteria isolated from cultured rainbow trout. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):872–877. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.872-877.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevors J. T., Oddie K. M. R-plasmid transfer in soil and water. Can J Microbiol. 1986 Jul;32(7):610–613. doi: 10.1139/m86-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley R. H. Temperature dependence of mating-pair formation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):222–224. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.222-224.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


