Abstract
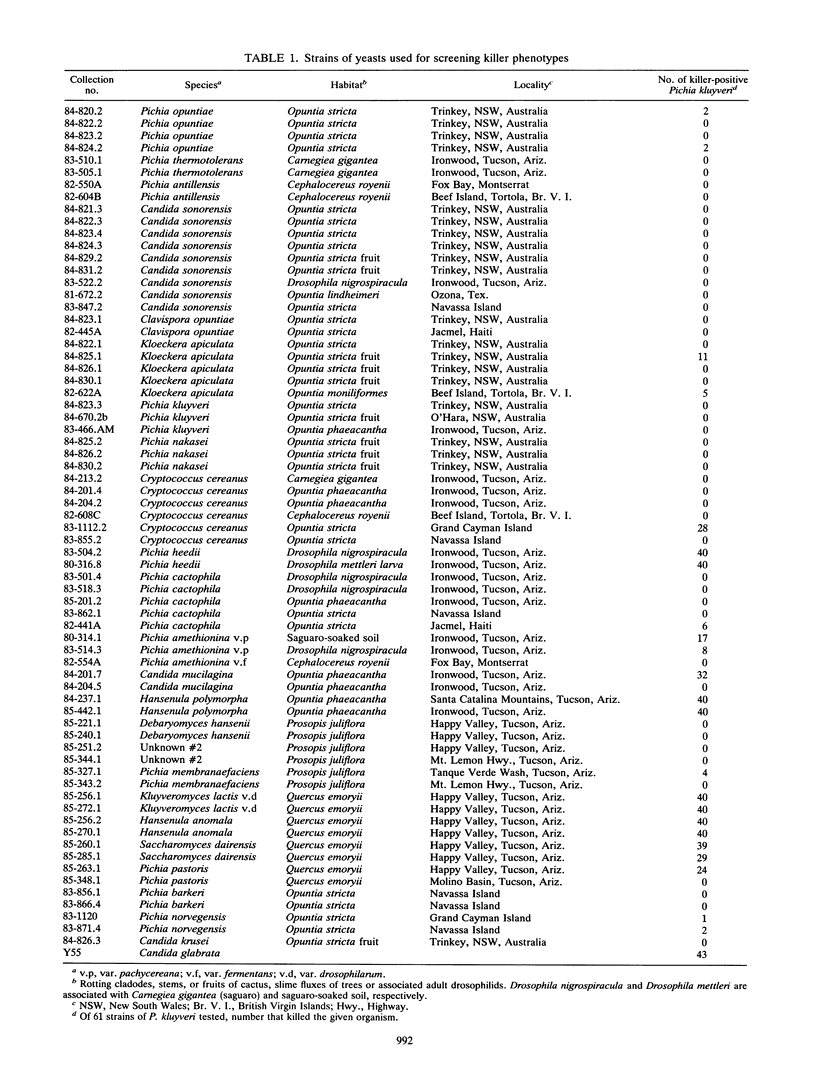
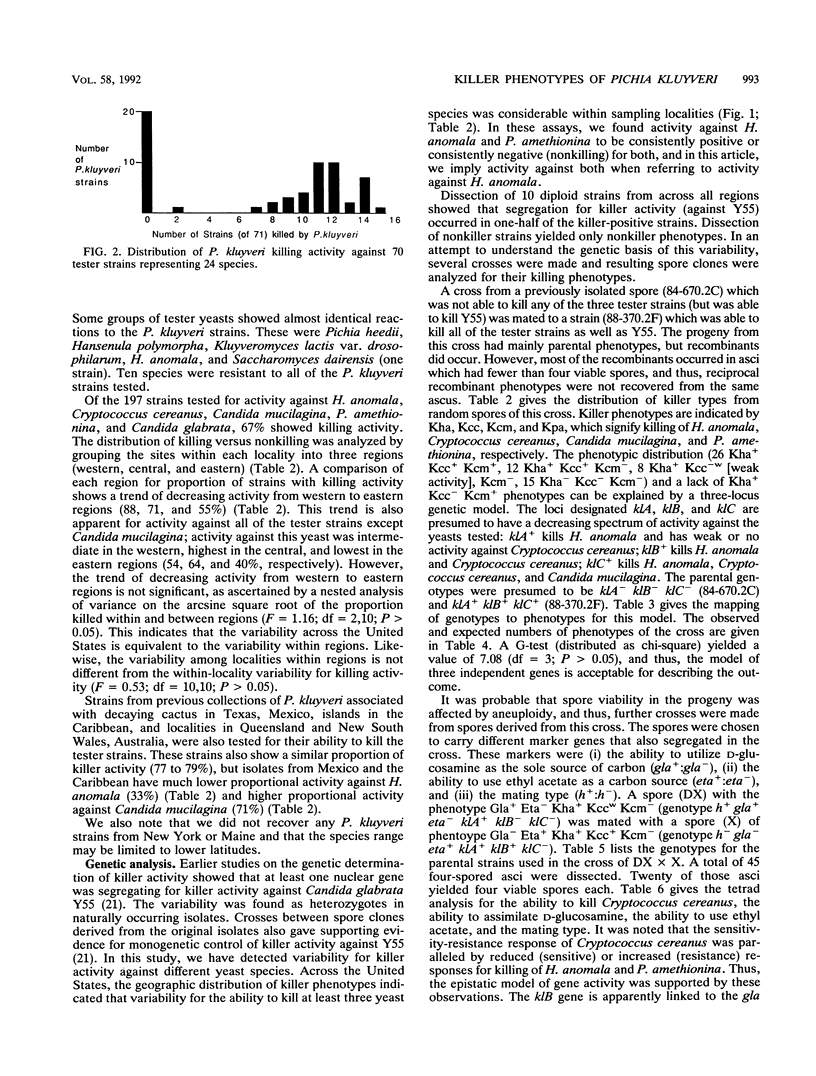
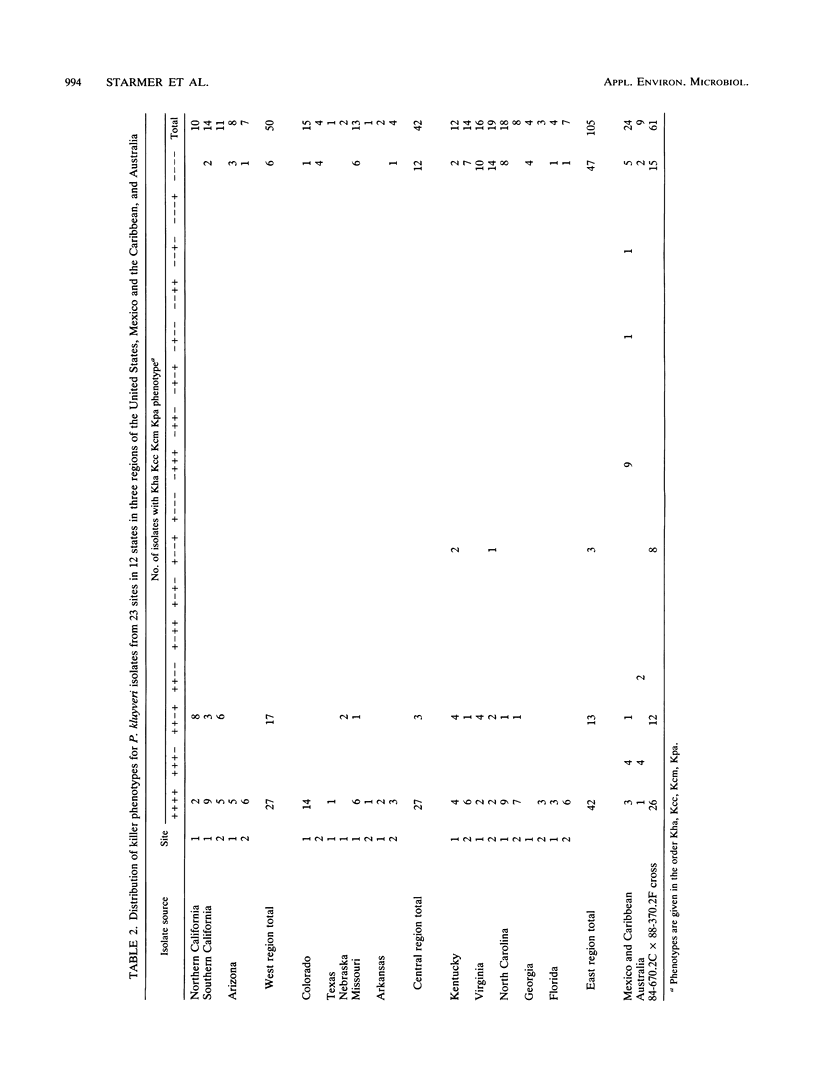
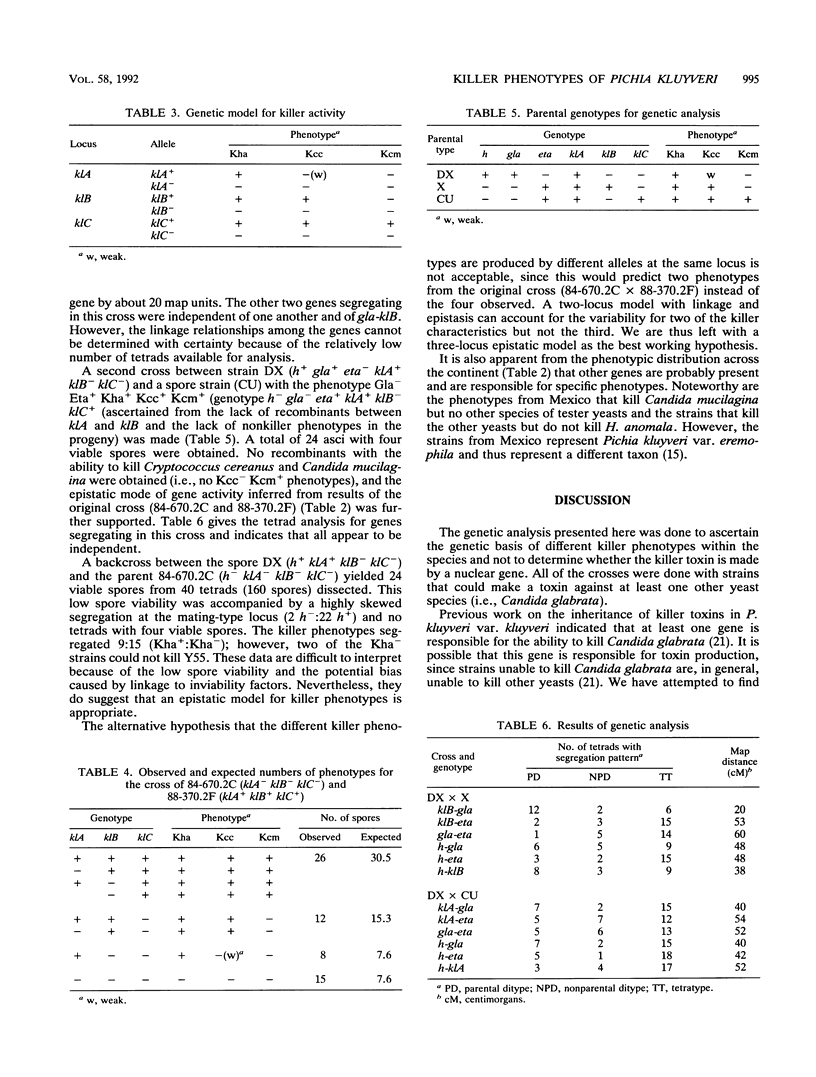
Representative strains (n = 61) of the yeast Pichia kluyveri from across the United States were studied for their ability to kill 71 other strains (representing 25 species) of yeast. This survey showed killing activity in 69% of the P. kluyveri strains tested. More extensive analysis of killer activity of 197 P. kluyveri strains against strains of five tester species showed comparable activity (67% of strains tested). This activity was shown to be equally variable within localities, within regions, and across the continent. The genetic basis of the variability was ascertained by tetrad analysis and is most likely due to alleles segregating at three epistatic loci. Evidence for the idea that killer toxins have a role in excluding other yeasts from particular habitats is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruenn J. A. Virus-like particles of yeast. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:49–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.000405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussey H. Physiology of killer factor in yeast. Adv Microb Physiol. 1981;22:93–122. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussey H., Vernet T., Sdicu A. M. Mutual antagonism among killer yeasts: competition between K1 and K2 killers and a novel cDNA-based K1-K2 killer strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Jan;34(1):38–44. doi: 10.1139/m88-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunge N., Tamaru A., Ozawa F., Sakaguchi K. Isolation and characterization of linear deoxyribonucleic acid plasmids from Kluyveromyces lactis and the plasmid-associated killer character. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):382–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.382-390.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunge N. Yeast DNA plasmids. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:253–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan B. L. Mode of action of yeast killer toxins: channel formation in lipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1983 Apr 21;302(5910):709–711. doi: 10.1038/302709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middelbeek E. J., Hermans J. M., Stumm C. Production, purification and properties of a Pichia kluyveri killer toxin. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1979;45(3):437–450. doi: 10.1007/BF00443282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middelbeek E. J., Stumm C., Vogels G. D. Effects of Pichia kluyveri killer toxin on sensitive cells. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1980;46(2):205–220. doi: 10.1007/BF00444075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philliskirk G., Young T. W. The occurrence of killer character in yeasts of various genera. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1975;41(2):147–151. doi: 10.1007/BF02565046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M., Radler F. Mannoprotein of the yeast cell wall as primary receptor for the killer toxin of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain 28. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Dec;133(12):3347–3354. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-12-3347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M. J., Boyd A., Mileham A. J., Romanos M. A. The plasmid-encoded killer system of Kluyveromyces lactis: a review. Yeast. 1990 Jan-Feb;6(1):1–29. doi: 10.1002/yea.320060102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starmer W. T., Ganter P. F., Aberdeen V., Lachance M. A., Phaff H. J. The ecological role of killer yeasts in natural communities of yeasts. Can J Microbiol. 1987 Sep;33(9):783–796. doi: 10.1139/m87-134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumm C., Hermans J. M., Middelbeek E. J., Croes A. F., de Vries G. J. Killer-sensitive relationships in yeasts from natural habitats. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1977;43(2):125–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00395667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki Y., Gunge N., Sakaguchi K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G. Kluyveromyces lactis killer toxin inhibits adenylate cyclase of sensitive yeast cells. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):464–466. doi: 10.1038/304464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J., Bostian K. A. Double-stranded ribonucleic acid killer systems in yeasts. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Jun;48(2):125–156. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.2.125-156.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkert F. C., Wilson D. W., Broach J. R. Deoxyribonucleic acid plasmids in yeasts. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):299–317. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.299-317.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young T. W., Yagiu M. A comparison of the killer character in different yeasts and its classification. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1978;44(1):59–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00400077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


