Abstract
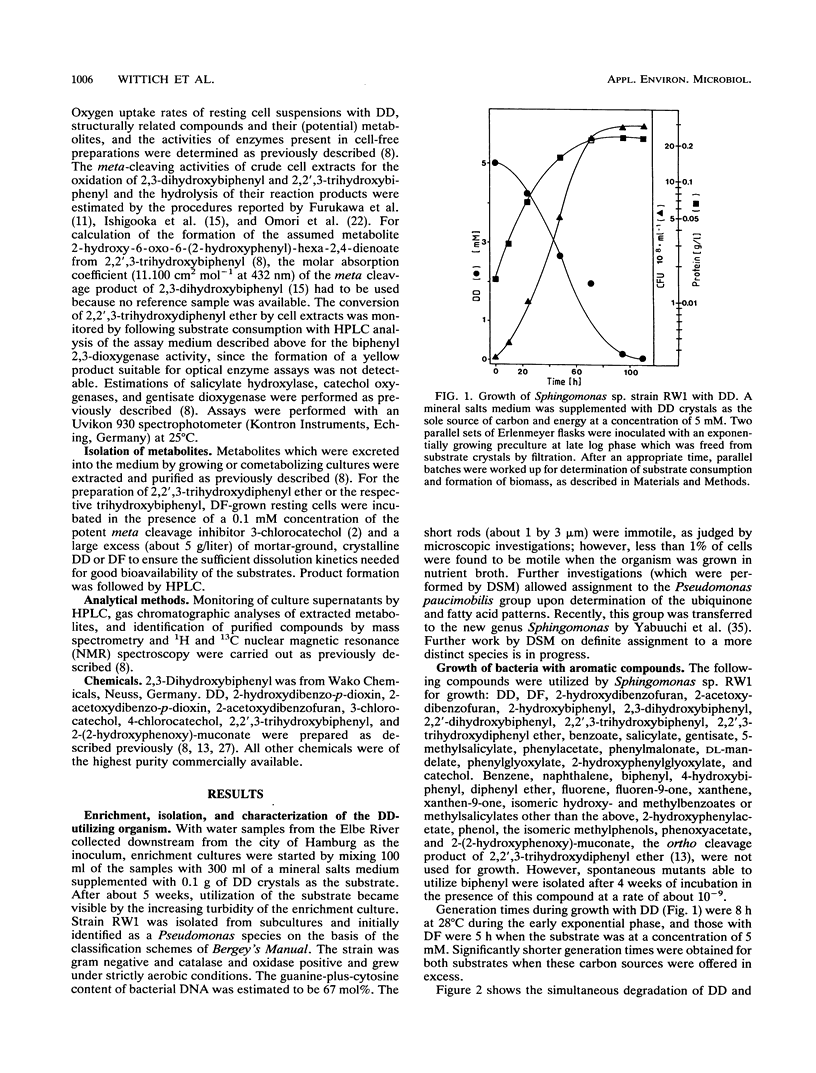
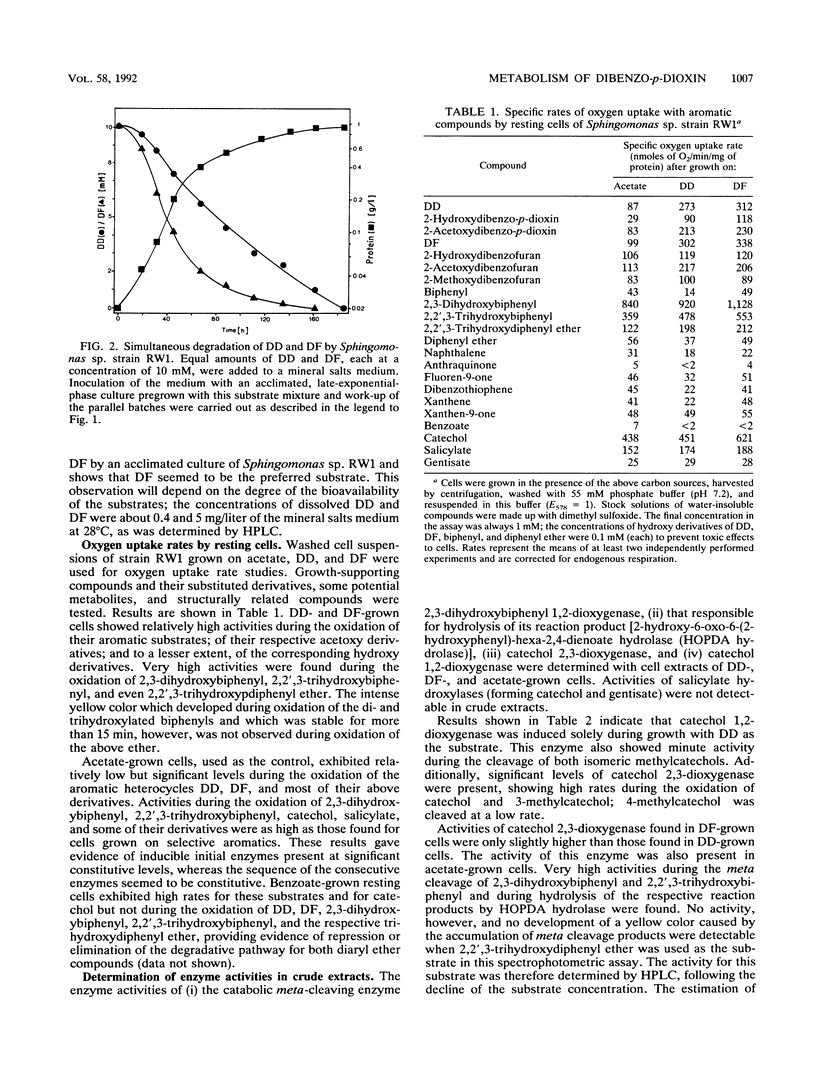
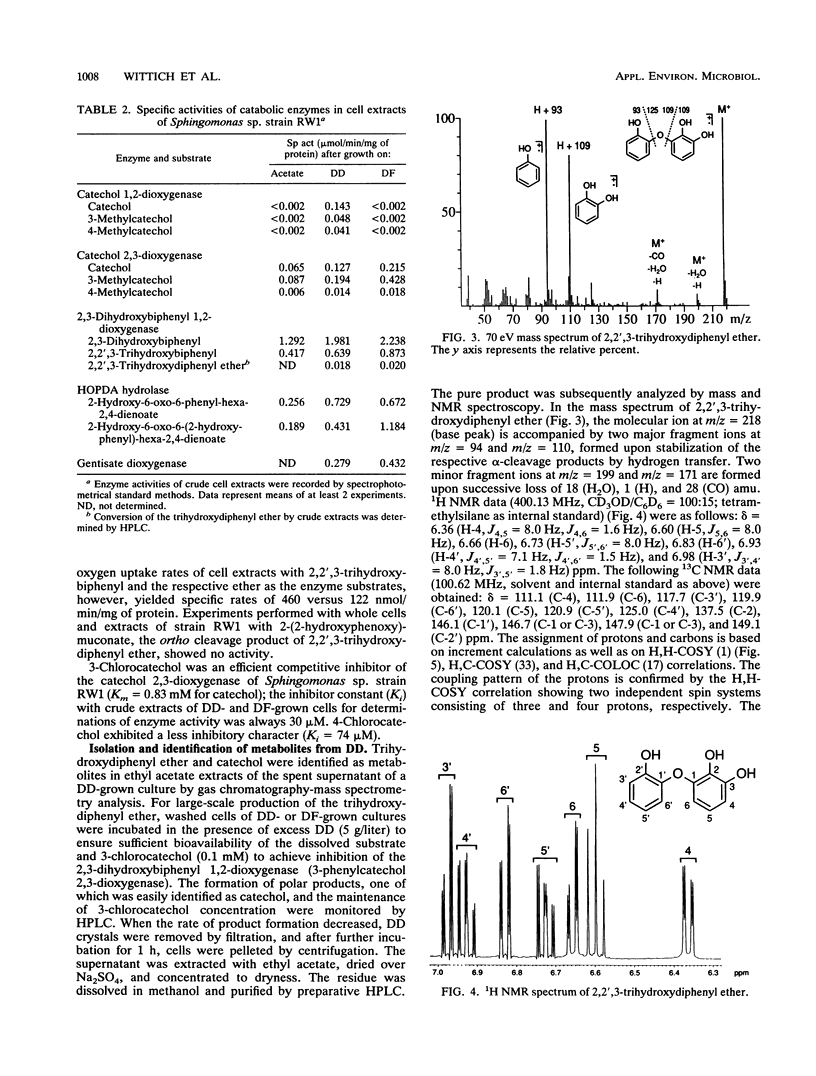
In the course of our screening for dibenzo-p-dioxin-utilizing bacteria, a Sphingomonas sp. strain was isolated from enrichment cultures inoculated with water samples from the river Elbe. The isolate grew with both the biaryl ethers dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran (DF) as the sole sources of carbon and energy, showing doubling times of about 8 and 5 h, respectively. Biodegradation of the two aromatic compounds initially proceeded after an oxygenolytic attack at the angular position adjacent to the ether bridge, producing 2,2',3-trihydroxydiphenyl ether or 2,2',3-trihydroxybiphenyl from the initially formed dihydrodiols, which represent extremely unstable hemiacetals. Results obtained from determinations of enzyme activities and oxygen consumption suggest meta cleavage of the trihydroxy compounds. During dibenzofuran degradation, hydrolysis of 2-hydroxy-6-oxo-6-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-hexa-2,4-dienoate yielded salicylate, which was branched into the catechol meta cleavage pathway and the gentisate pathway. Catechol obtained from the product of meta ring fission of 2,2',3-trihydroxydiphenyl ether was both ortho and meta cleaved by Sphingomonas sp. strain RW1 when this organism was grown with dibenzo-p-dioxin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartels I., Knackmuss H. J., Reineke W. Suicide Inactivation of Catechol 2,3-Dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida mt-2 by 3-Halocatechols. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Mar;47(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.3.500-505.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerniglia C. E., Morgan J. C., Gibson D. T. Bacterial and fungal oxidation of dibenzofuran. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 15;180(1):175–185. doi: 10.1042/bj1800175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engesser K. H., Strubel V., Christoglou K., Fischer P., Rast H. G. Dioxygenolytic cleavage of aryl ether bonds: 1,10-dihydro-1,10-dihydroxyfluoren-9-one, a novel arene dihydrodiol as evidence for angular dioxygenation of dibenzofuran. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Nov;53(1-2):205–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90392-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortnagel P., Harms H., Wittich R. M., Francke W., Krohn S., Meyer H. Cleavage of dibenzofuran and dibenzodioxin ring systems by a Pseudomonas bacterium. Naturwissenschaften. 1989 May;76(5):222–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00627694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortnagel P., Harms H., Wittich R. M., Krohn S., Meyer H., Sinnwell V., Wilkes H., Francke W. Metabolism of Dibenzofuran by Pseudomonas sp. Strain HH69 and the Mixed Culture HH27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):1148–1156. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.1148-1156.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank-Kamenetskii F. Simplification of the empirical relationship between melting temperature of DNA, its GC content and concentration of sodium ions in solution. Biopolymers. 1971;10(12):2623–2624. doi: 10.1002/bip.360101223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Simon J. R., Chakrabarty A. M. Common induction and regulation of biphenyl, xylene/toluene, and salicylate catabolism in Pseudomonas paucimobilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1356–1362. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1356-1362.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms H., Wilkes H., Sinnwell V., Wittich R. M., Figge K., Francke W., Fortnagel P. Transformation of 3-chlorodibenzofuran by Pseudomonas sp. HH69. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jun 1;65(1):25–29. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90465-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms H., Wittich R. M., Sinnwell V., Meyer H., Fortnagel P., Francke W. Transformation of Dibenzo-p-Dioxin by Pseudomonas sp. Strain HH69. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):1157–1159. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.1157-1159.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klecka G. M., Gibson D. T. Metabolism of Dibenzo-p-Dioxin and Chlorinated Dibenzo-p- Dioxins by a Beijerinckia Species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):288–296. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.288-296.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klecka G. M., Gibson D. T. Metabolism of dibenzo[1,4]dioxan by a Pseudomonas species. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 15;180(3):639–645. doi: 10.1042/bj1800639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laborde A. L., Gibson D. T. Metabolism of dibenzothiophene by a Beijerinckia species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Dec;34(6):783–790. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.6.783-790.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller J. G., Chapman P. J., Blattmann B. O., Pritchard P. H. Isolation and characterization of a fluoranthene-utilizing strain of Pseudomonas paucimobilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):1079–1086. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.1079-1086.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander P., Wittich R. M., Fortnagel P., Wilkes H., Francke W. Degradation of 1,2,4-trichloro- and 1,2,4,5-tetrachlorobenzene by pseudomonas strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1430–1440. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1430-1440.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strubel V., Engesser K. H., Fischer P., Knackmuss H. J. 3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)catechol as substrate for proximal meta ring cleavage in dibenzofuran degradation by Brevibacterium sp. strain DPO 1361. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):1932–1937. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.1932-1937.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strubel V., Rast H. G., Fietz W., Knackmuss H. J., Engesser K. H. Enrichment of dibenzofuran utilizing bacteria with high co-metabolic potential towards dibenzodioxin and other anellated aromatics. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Apr;49(2-3):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabuuchi E., Yano I., Oyaizu H., Hashimoto Y., Ezaki T., Yamamoto H. Proposals of Sphingomonas paucimobilis gen. nov. and comb. nov., Sphingomonas parapaucimobilis sp. nov., Sphingomonas yanoikuyae sp. nov., Sphingomonas adhaesiva sp. nov., Sphingomonas capsulata comb. nov., and two genospecies of the genus Sphingomonas. Microbiol Immunol. 1990;34(2):99–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1990.tb00996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


