Abstract
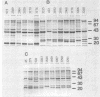
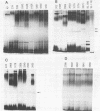
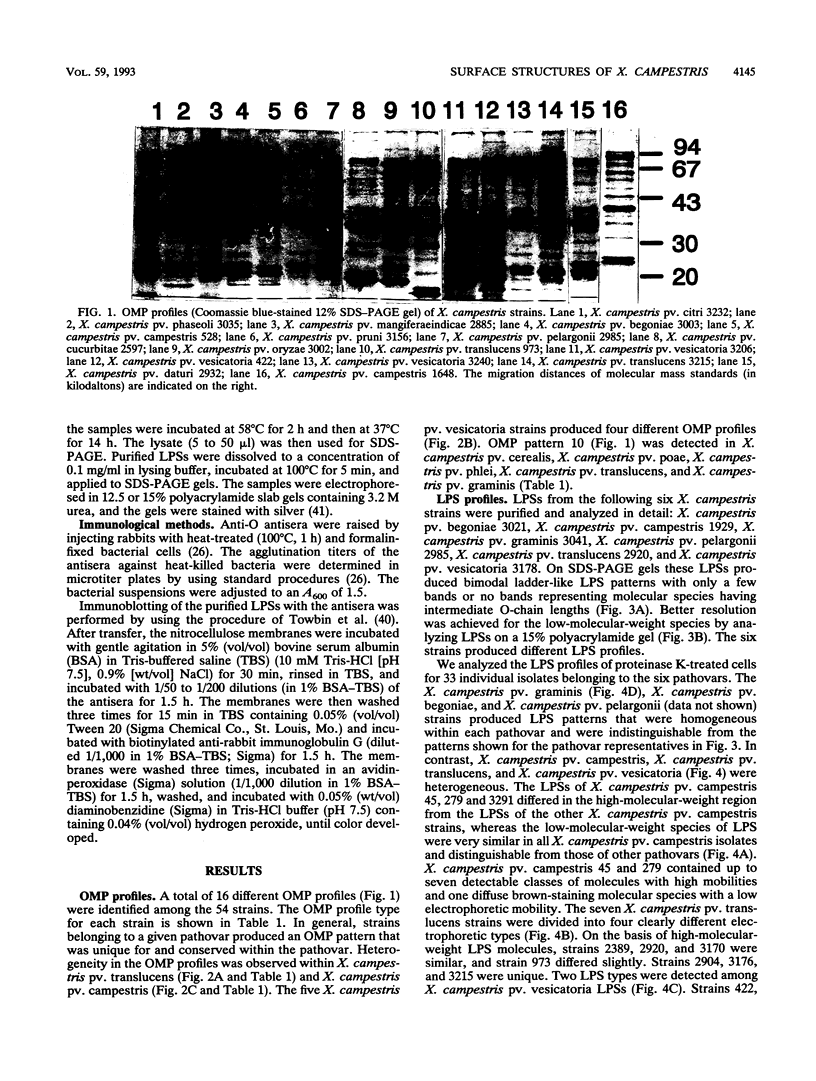
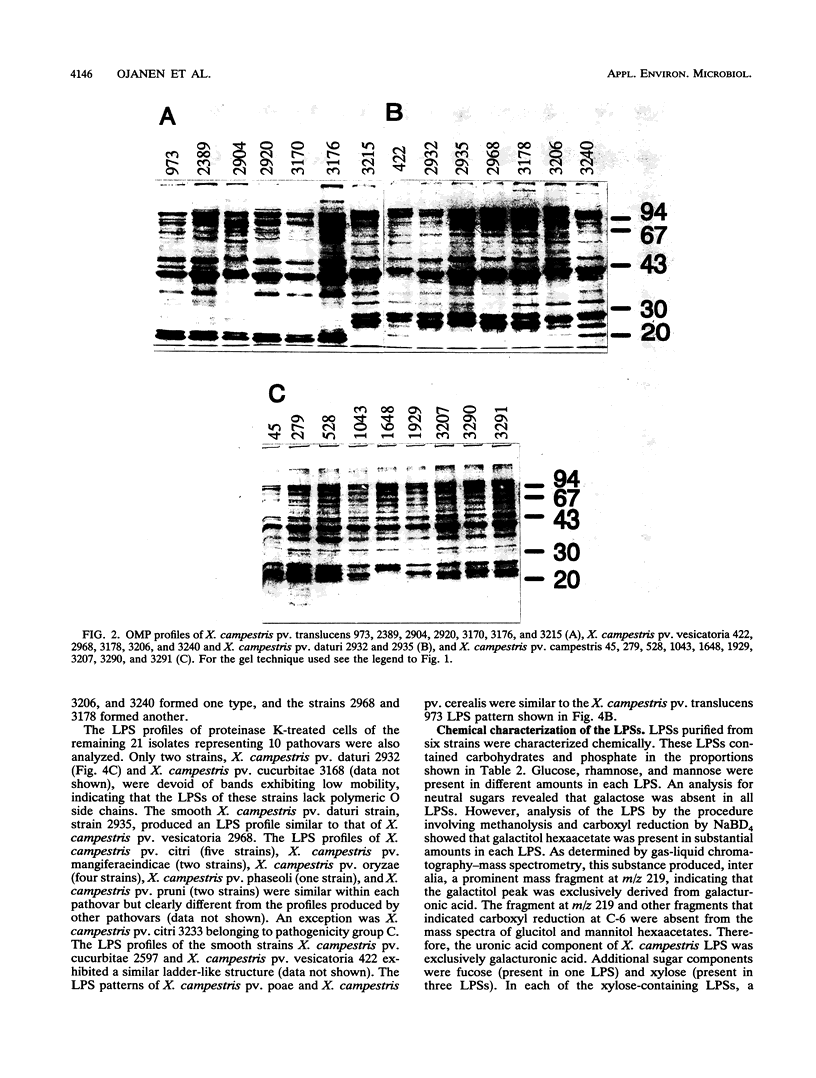
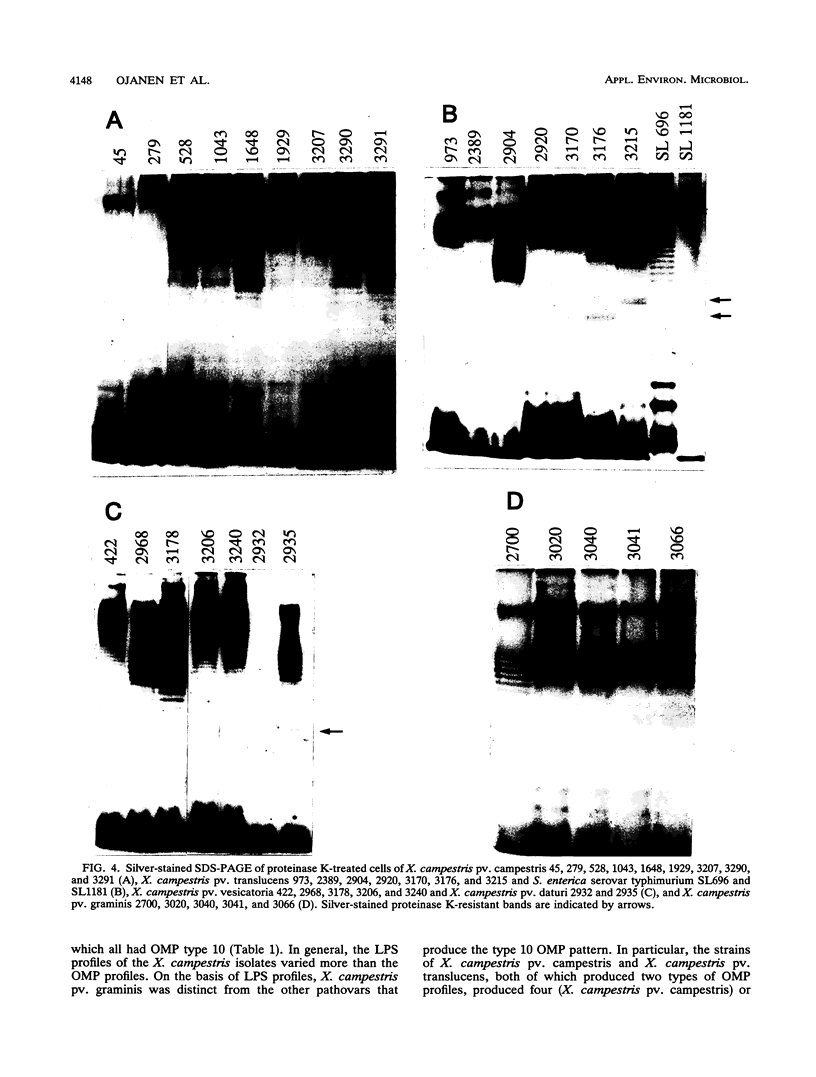
Variations in the outer membrane proteins (OMPs) and lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) of 54 isolates belonging to 16 different pathovars of Xanthomonas campestris were characterized. OMP samples prepared by sarcosyl extraction of cell walls and LPS samples prepared by proteinase K treatment of sonicated cells were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of 4 M urea. In general, the OMP and LPS profiles within each pathovar were very similar but different from the profiles of other pathovars. Heterogeneity in OMP and LPS profiles was observed within X. campestris pv. campestris, X. campestris pv. translucens, and X. campestris pv. vesicatoria. LPSs were isolated from six X. campestris pathovars, which fell into two major groups on the basis of O antigenicity. The O antigens of X. campestris pv. begoniae, X. campestris pv. graminis, and X. campestris pv. translucens cross-reacted with each other; the other group consisted of X. campestris pv. campestris, X. campestris pv. pelargonii, and X. campestris pv. vesicatoria. A chemical analysis revealed a significant difference between the compositions of the neutral sugars of the LPSs of those two groups; the LPSs of the first group contained xylose and a 6-deoxy-3-O-methyl hexose, whereas the LPSs of the other group lacked both sugars.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Mercer A., Kusecek B., Pohl A., Heuzenroeder M., Aaronson W., Sutton A., Silver R. P. Six widespread bacterial clones among Escherichia coli K1 isolates. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):315–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.315-335.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedict A. A., Alvarez A. M., Pollard L. W. Pathovar-Specific Antigens of Xanthomonas campestris pv. begoniae and X. campestris pv. pelargonii Detected with Monoclonal Antibodies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):572–574. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.572-574.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björndal H., Lindberg B., Nimmich W. Structural studies on the lipopolysaccharide from Klebsiella K73-O10. I. Methylation analysis, identification and location of 3-O-methyl-L-rhamnose. Acta Chem Scand. 1970;24(9):3414–3415. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.24-3414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade H., Galanos C., Lüderitz O. Differential determination of the 3-Deoxy-D-mannooctulosonic acid residues in lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella minnesota rough mutants. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 1;131(1):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coplin D. L., Cook D. Molecular genetics of extracellular polysaccharide biosynthesis in vascular phytopathogenic bacteria. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1990 Sep-Oct;3(5):271–279. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-3-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Truchet G. L., Hollingsworth R. I., Hrabak E. M., Pankratz H. S., Philip-Hollingsworth S., Salzwedel J. L., Chapman K., Appenzeller L., Squartini A. Rhizobium lipopolysaccharide modulates infection thread development in white clover root hairs. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5371–5384. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5371-5384.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elrod R. P., Braun A. C. Serological Studies of the Genus Xanthomonas: II. Xanthomonas translucens Group. J Bacteriol. 1947 May;53(5):519–524. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Expert D., Toussaint A. Bacteriocin-resistant mutants of Erwinia chrysanthemi: possible involvement of iron acquisition in phytopathogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):221–227. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.221-227.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham T. L., Sequeira L., Huang T. S. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides as inducers of disease resistance in tobacco. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Oct;34(4):424–432. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.4.424-432.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helander I. M., Lindner B., Brade H., Altmann K., Lindberg A. A., Rietschel E. T., Zähringer U. Chemical structure of the lipopolysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae strain I-69 Rd-/b+. Description of a novel deep-rough chemotype. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Nov 15;177(3):483–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman J., Ashwell G. Isolation of a bacterial lipopolysaccharide from Xanthomonas campestris containing 3-acetamido-3,6-dideoxy-D-galactose and D-rhamnose. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 25;241(6):1424–1428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth R. I., Abe M., Sherwood J. E., Dazzo F. B. Bacteriophage-induced acidic heteropolysaccharide lyases that convert the acidic heteropolysaccharides of Rhizobium trifolii into oligosaccharide units. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):510–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.510-516.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkhanis Y. D., Zeltner J. Y., Jackson J. J., Carlo D. J. A new and improved microassay to determine 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate in lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):595–601. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'vov V. L., Tochtamysheva N. V., Shashkov A. S., Dmitriev B. A., Capek K. 3-[(N-acetyl-L-seryl)amino]-3,6-dideoxy-D-glucose: a novel constituent of a bacterial antigenic polysaccharide. Carbohydr Res. 1983 Feb 1;112(2):233–239. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(83)88288-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., LEINER K. Y., WU M. L., FARR A. L. The quantitative histochemistry of brain. I. Chemical methods. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg B. Components of bacterial polysaccharides. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1990;48:279–318. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal D. J., Wilkinson S. G. Lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas maltophilia: structural studies of the side-chain polysaccharide from strain N.C.T.C. 10257. Carbohydr Res. 1979 Mar;69:191–201. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)85764-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Lüderitz O., Volk W. A. Nature, type of linkage, and absolute configuration of (hydroxy) fatty acids in lipopolysaccharides from Xanthomonas sinensis and related strains. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1180–1188. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1180-1188.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., PARK J. T., THOMPSON R. E. Composition of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus: its relation to the mechanism of action of penicillin. J Biol Chem. 1959 Dec;234:3263–3268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit G., Swart S., Lugtenberg B. J., Kijne J. W. Molecular mechanisms of attachment of Rhizobium bacteria to plant roots. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Oct;6(20):2897–2903. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukupolvi S., Vaara M., Helander I. M., Viljanen P., Mäkelä P. H. New Salmonella typhimurium mutants with altered outer membrane permeability. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):704–712. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.704-712.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk W. A. Cell wall lipopolysaccharides from xanthomonas species. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):39–42. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.39-42.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk W. A. Quantitative assay of polysaccharide components obtained from cell wall lipopolysaccharides of Xanthomonas species. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):980–982. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.980-982.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. G., Gemski P., Jr, Stocker B. A. Non-smooth mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: differentiation by phage sensitivity and genetic mapping. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):527–554. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maagd R., van Rossum C., Lugtenberg B. J. Recognition of individual strains of fast-growing rhizobia by using profiles of membrane proteins and lipopolysaccharides. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3782–3785. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3782-3785.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weger L. A., Jann B., Jann K., Lugtenberg B. Lipopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas spp. that stimulate plant growth: composition and use for strain identification. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1441–1446. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1441-1446.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weger L. A., van Boxtel R., van der Burg B., Gruters R. A., Geels F. P., Schippers B., Lugtenberg B. Siderophores and outer membrane proteins of antagonistic, plant-growth-stimulating, root-colonizing Pseudomonas spp. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):585–594. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.585-594.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]