Abstract
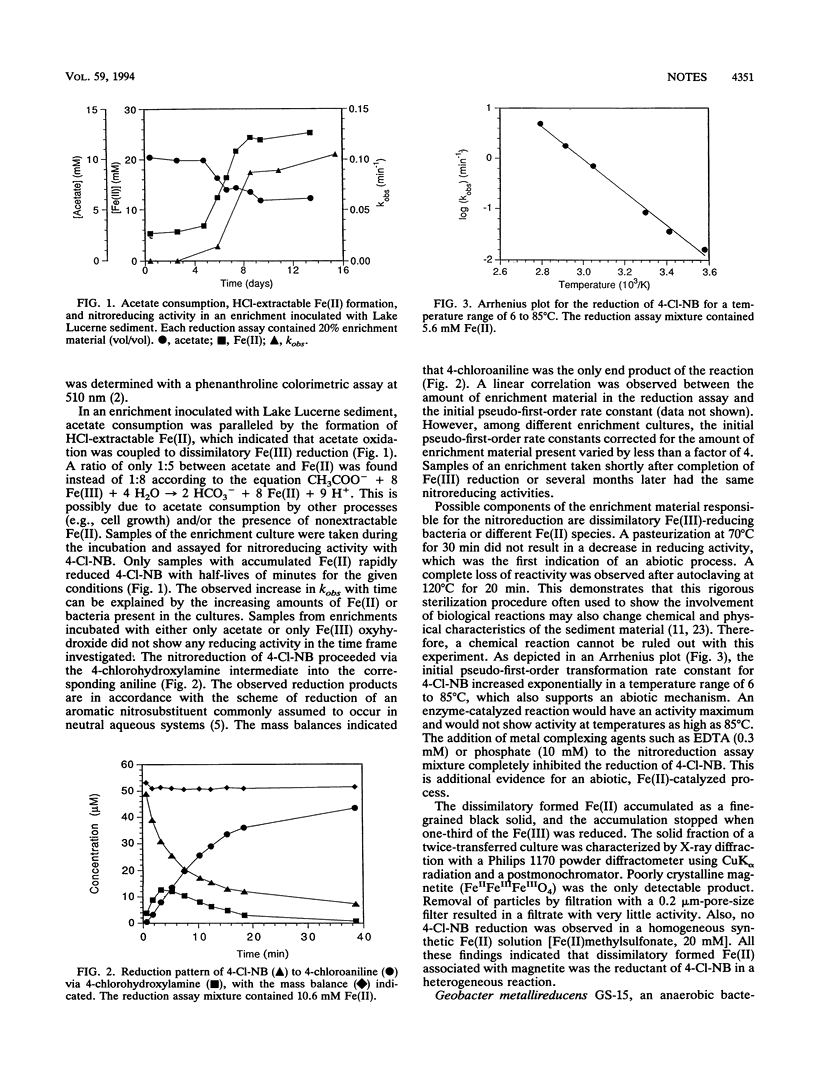
4-chloronitrobenzene (4-Cl-NB) was rapidly reduced to 4-chloroaniline with half-lives of minutes in a dissimilatory Fe(III)-reducing enrichment culture. The initial pseudo-first-order rate constants at 25°C ranged from 0.11 to 0.19 per minute. The linear Arrhenius correlation in a temperature range of 6 to 85°C and the unchanged reactivity after pasteurization indicated that the nitroreduction occurred abiotically. A fine-grained black solid which was identified as poorly crystalline magnetite (Fe3O4) by X-ray diffraction accumulated in the enrichments. Magnetite produced by the Fe(III)-reducing bacterium Geobacter metallireducens GS-15 and synthetic magnetite also reduced 4-Cl-NB. These results suggest that the reduction of 4-Cl-NB by the enrichment material was a surface-mediated reaction by dissimilatory formed Fe(II) associated with magnetite.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angermaier L., Simon H. On nitroaryl reductase activities in several Clostridia. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 Dec;364(12):1653–1663. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1983.364.2.1653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boopathy R., Kulpa C. F. Trinitrotoluene (TNT) as a sole nitrogen source for a sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfovibrio sp. (B strain) isolated from an anaerobic digester. Curr Microbiol. 1992 Oct;25(4):235–241. doi: 10.1007/BF01570724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaus M. A., Heijman C. G., Schwarzenbach R. P., Zeyer J. Reduction of nitroaromatic compounds mediated by Streptomyces sp. exudates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jun;58(6):1945–1951. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.6.1945-1951.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Giovannoni S. J., White D. C., Champine J. E., Phillips E. J., Gorby Y. A., Goodwin S. Geobacter metallireducens gen. nov. sp. nov., a microorganism capable of coupling the complete oxidation of organic compounds to the reduction of iron and other metals. Arch Microbiol. 1993;159(4):336–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00290916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Novel mode of microbial energy metabolism: organic carbon oxidation coupled to dissimilatory reduction of iron or manganese. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1472–1480. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1472-1480.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren A., Gurevich P., Henis Y. Reduction of nitrosubstituted aromatic compounds by the halophilic anaerobic eubacteria Haloanaerobium praevalens and Sporohalobacter marismortui. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Nov;57(11):3367–3370. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.11.3367-3370.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preuss A., Fimpel J., Diekert G. Anaerobic transformation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT). Arch Microbiol. 1993;159(4):345–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00290917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


