Abstract
Activation of receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) by its ligand, HMGB1, stimulates myogenesis via a Cdc42-Rac1-MKK6-p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. In addition, functional inactivation of RAGE in myoblasts results in reduced myogenesis, increased proliferation, and tumor formation in vivo. We show here that TE671 rhabdomyosarcoma cells, which do not express RAGE, can be induced to differentiate on transfection with RAGE (TE671/RAGE cells) but not a signaling-deficient RAGE mutant (RAGEΔcyto) (TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells) via activation of a Cdc42-Rac1-MKK6-p38 pathway and that TE671/RAGE cell differentiation depends on RAGE engagement by HMGB1. TE671/RAGE cells also show p38-dependent inactivation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 and c-Jun NH2 terminal protein kinase and reduced proliferation, migration, and invasiveness and increased apoptosis, volume, and adhesiveness in vitro; they also grow smaller tumors and show a lower tumor incidence in vivo compared with wild-type cells. Two other rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines that express RAGE, CCA and RMZ-RC2, show an inverse relationship between the level of RAGE expression and invasiveness in vitro and exhibit reduced myogenic potential and enhanced invasive properties in vitro when transfected with RAGEΔcyto. The rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines used here and C2C12 myoblasts express and release HMGB1, which activates RAGE in an autocrine manner. These data suggest that deregulation of RAGE expression in myoblasts might concur in rhabdomyosarcomagenesis and that increasing RAGE expression in rhabdomyosarcoma cells might reduce their tumor potential.
At a certain stage during myogenesis, myoblasts, ie, the precursors of skeletal muscle cells, cease to proliferate and start to differentiate once they attain a critical density.1,2,3,4 Extracellular factors acting via cell surface receptors as well as adhesion molecules control proliferation arrest and differentiation of myoblasts by regulating via signaling pathways the expression of muscle-specific transcription factors. This in turn coordinates the expression and activity of a cohort of factors responsible for phenotypic changes, including myoblast fusion into myotubes, the precursors of mature myofibers.1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11 In this context, extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) and c-Jun NH2 terminal protein kinase (JNK) need to be inactivated, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and Akt need to be activated for myoblasts to exit the cell cycle and for differentiation to proceed.12,13,14,15,16,17,18
Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) is a multiligand receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily expressed during development, repressed in adulthood, and re-expressed in the course of several pathological conditions.19 RAGE is expressed in rat skeletal muscle cells in a developmentally regulated manner; it is present in rat embryo skeletal muscle fibers and in rat postnatal myofibers until ∼11 days after birth and absent from adult muscle fibers,11 suggesting that it might play a role in embryonic myogenesis. RAGE can be activated by several ligands, including HMGB1 (amphoterin), and effects of RAGE engagement depend on the cell type considered.19 Thus, RAGE has been shown to transduce trophic and toxic stimuli in neurons depending on the nature and concentration of the ligand,20,21,22 to take part in the inflammatory response in monocytes/macrophages/microglia,23 and to be involved in neoplastic transformation and metastasis of neuroepithelial tumor cells.24,25,26,27 Besides, RAGE engagement by HMGB1 in myoblasts results in stimulation of differentiation via a Cdc42-Rac1-MKK6-p38 MAPK pathway,11 supporting the possibility that the HMGB1/RAGE pair might contribute to embryonic myogenesis and potentially muscle regeneration. Moreover, RAGE ligation by HMGB1 results in a decreased proliferation and increased apoptosis in wild-type (wt) myoblasts, whereas myoblasts stably overexpressing a RAGE mutant lacking the cytoplasmic and transducing domain (RAGEΔcyto) show enhanced pro-liferation, migration, and invasiveness in vitro and increased tumor formation in vivo compared with wt myoblasts.28 These latter findings suggest RAGE engagement in myoblasts, besides activating the myogenic program, might contribute to the proliferation arrest required for myoblast differentiation and that functional inactivation or repression of expression of RAGE in myoblasts might contribute to rhabdomyosarcomagenesis.
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is the most common pediatric soft-tissue sarcoma, arising from muscle precursor cells. The two most common histological subtypes are embryonal RMS, which has a more favorable prognosis, and alveolar RMS, which has a poor prognosis. The embryonal-type TE671 RMS cells, which are similar if not identical to the RMS cells, RD,29 are unable to complete the differentiation program despite the expression of muscle-specific regulatory proteins.30,31 However, persistent activation of p38 MAPK in a panel of RMS cells resulted in proliferation arrest and terminal differentiation,32 implying that defective activation of p38 MAPK might be one of the causes of the inability of RMS cells to exit the cell cycle and initiate the myogenic program.
We show here that the embryonal-type TE671 RMS cells do not express RAGE and that enforced expression of RAGE in TE671 cells results in myogenic differentiation and reduced proliferation, migration, and invasiveness in vitro and reduced tumor growth in vivo. We also show that the RMS cell lines CCA (embryonal-type) and RMZ-RC2 (alveolar-type), which do express RAGE albeit to a different extent from one another, show an inverse relationship between the level of RAGE expression and migration/invasiveness in vitro and exhibit a reduced myogenic potential and enhanced invasive properties in vitro when transfected with the signaling-deficient RAGE mutant RAGEΔcyto and an increased myogenic potential and reduced invasive properties when transfected with full-length RAGE.
Materials and Methods
Transfection and Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction
TE671 cells were cultivated in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA), 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin, in a H2O-saturated 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37°C. Transfection of TE671 cells to obtain clones stably expressing human RAGE33 or RAGEΔcyto34 was performed exactly as described for L6 myoblasts.9 TE671/RAGE cells, TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells, and TE671/wt cells were used in experiments described below, in media containing Geneticin (G-418) (125 μg/ml), in the presence of HMGB1, a polyclonal anti-HMGB1 antibody (BD Phar-Mingen, San Diego, CA), or an anti-RAGE extracellular domain antibody (N16; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) where required. Neutralization of culture medium HMGB1 using an anti-HMGB1 antibody and neutralization of RAGE in TE671/RAGE cells were performed as described previously.11 Transient transfections were performed using LipofectAMINE 2000 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) as recommended by the manufacturer. In brief, cells cultured in 5% FBS without antibiotics were transfected with expression plasmids MKK6AA (an inactive mutant of the p38 MAPK upstream kinase MKK6),35 N17Rac1 or N17Cdc42 (inactive forms of Rac1 and Cdc42, respectively),36 MKK6EE (a constitutively active form of MKK6),37 or empty vector and with muscle creatine kinase (MCK)-luc reporter gene,38 myogenin-luc reporter gene,39 or p21WAF1-luc reporter gene.40 After 6 hours in the cases of MCK, myogenin, and p21WAF1 and after 24 hours in the cases of MKK6AA, MKK6EE, N17Rac1, and N17Cdc42, the cells were washed with DMEM and cultivated in 2% FBS. After another 24 hours, the cells were harvested to measure luciferase activity. Transient transfection of TE761/wt, TE671/RAGE, CCA, and RMZ-RC2 cells with RAGE or RAGEΔcyto was done as described for MKK6AA, MKK6EE, N17Rac1, or N17Cdc42. Where used, the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 (Calbiochem, San Diego, CA), the phosphatydilinositol-3-kinase (PI3-K) inhibitor LY294002 (Calbiochem), the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibitor PD98059 (Calbiochem), and the JNK inhibitor SP600125 (Alexis, Lausen, Switzerland) were used at a final concentration of 2, 10, 30, and 10 μmol/L, respectively, in dimethylsulfoxide. For reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), TE671/RAGE, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, TE671/wt, CCA, and RMZ-RC2 cells were processed as described previously.28
Immunofluorescence, Immunocytochemistry, and Western Blotting
Immunofluorescence was performed as using a polyclonal anti-RAGE antibody (1:25, N16; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), and myosin heavy chain (MHC) was detected by immunocytochemistry, as described previously.11 For detection of F-actin, TE671 cells were fixed for 10 minutes in 3.7% formaldehyde in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), extensively washed with PBS, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 2 minutes, washed again, and incubated with fluorescein isothiocyanate-phalloidin (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) (1:250 in PBS) for 1 hour in a humid chamber at room temperature. After three washes in PBS, the cells were mounted in mounting medium (Meridian Bioscience Inc., Cincinnati, OH) and viewed on a DM Rb fluorescence microscope equipped with a digital camera (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). To detect RAGE, RAGEΔcyto, myogenin, MHC, cyclin D1, tubulin, phosphorylated and total p38 MAPK, phosphorylated and total Akt, phosphorylated and total ERK1/2, phosphorylated and total retinoblastoma suppressor protein (Rb), and phosphorylated JNK by Western blotting, cells were cultivated as detailed in the figure legends, washed twice with PBS, and solubilized with 2.5% sodium dodecyl sulfate, 10 mmol/L Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 0.1 mol/L dithiothreitol, and 0.1 mmol/L N-tosyl-l-phenylalanine chloromethyl ketoneprotease inhibitor (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). The following antibodies were used: monoclonal anti-developmental MHC antibody (1:300; Biogenesis, Poole, Dorset, UK), monoclonal anti-myogenin antibody (1:1000; PharMingen), monoclonal anti-α-tubulin antibody (1:10,000; Sigma), polyclonal anti-RAGE extracellular domain (1:2000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), monoclonal anti-RAGE antibody (1:2000; Chemicon International, Temecula, CA), polyclonal anti-phosphorylated (Thr180/Tyr182) p38 MAPK (1:1000; New England BioLabs, Ipswich, MA), polyclonal anti-phosphorylated (Ser473) Akt (1:1000; New England BioLabs), polyclonal anti-p38 MAPK antibody (1:2000; New England BioLabs), polyclonal anti-Akt antibody (1:2000; New England BioLabs), polyclonal anti-phosphorylated (Thr202/Tyr204) ERK1/2 (1:2000; New England BioLabs), polyclonal anti-ERK1/2 antibody (1:20,000; Sigma), polyclonal anti-phosphorylated (Ser-807/811) Rb antibody (1:1000; Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA), polyclonal anti-Rb antibody (1:1000; Cell Signaling Technology), polyclonal anti-phosphorylated JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) antibody (1:1000; Cell Signaling Technology), and monoclonal anti-cyclin D1 antibody (1:200; Santa Cruz Biotechnology). The immune reaction was developed by ECL [SuperSignal West Femto Maximum (Pierce, Rockford, IL) for RAGE; SuperSignal West Pico (Pierce) for all other antigens].
Analysis of Medium HMGB1
To characterize basal release of HMGB1 from mouse C2C12 myoblasts and TE671/wt, TE671/RAGE, TE671RAGEΔcyto, CCA, and RMZ-RC2 RMS cells, confluent or near-confluent cells were transferred to serum-free medium for 24 hours. The next steps were as described previously.41 In brief, individual culture media were clarified by centrifugation, added with 1/100 volume of 2% sodium deoxycholate and subjected to precipitation with 1/10 volume of 100% trichloroacetic acid. The resultant pellets were resuspended in sodium dodecyl sulfate buffer and titrated with 1 N NaOH to obtain the normal blue color of the sample buffer, boiled for 5 minutes, and subjected to Western blotting using an anti-HMGB1 antibody (BD PharMingen). Purified HMGB1 was used as a marker. HMGB1 in culture media was measured semiquantitatively by densitometry relative to known amounts of purified HMGB1. HMGB1 was also detected by Western blotting in lysates from cells, and its levels were normalized to tubulin. Culture media were also analyzed for levels of LDH to document the contribution of cell necrosis to released HMGB1. Under the present experimental conditions, negligible amounts of LDH were measured, pointing to absence of significant cell necrosis (data not shown).
Proliferation and Apoptosis Assays
To measure [3H]thymidine incorporation, TE671 cells (25 × 103 cells/well) were cultivated in 10% FBS for 24 hours in 24-multiwell plates, washed with DMEM, serum-starved for 24 hours, washed with DMEM, and cultivated in DMEM for 24 hours in the presence of 1 μCi of [3H]thymidine/ml. Parallel TE671 cells treated in the same manner in the absence of [3H]thymidine were used to count cell numbers. For cell number measurements, TE671 cells were plated in 96-multiwell plates at a density of 4 × 103 cells/well and processed by a tetrazolium-based [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium] colorimetric assay. To measure apoptosis and analyze cell cycle, TE671 cells were seeded onto 35-mm plastic dishes (18 × 104 cells/dish) for 24 hours, washed with DMEM, and cultivated for 72 hours in DMEM containing varying concentrations of FBS (see figure legends). Cells were stained with propidium iodide and subjected to fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS).42 FACS analysis was also used to measure cell size.43
Migration, Adhesiveness, and Invasiveness Assays and in Vivo Tumor Growth
For adhesion experiments, TE671/wt, TE671/RAGE, and TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells (3 × 104 cells in 0.1 ml of DMEM containing 10% FBS) were seeded in 96-multiwell plates and incubated for 3 hours. The supernatant with nonadherent cells was removed by two washes with warmed culture medium. Attached cells were fixed with 30% methanol/ethanol for 15 minutes at room temperature, stained with 0.1% crystal violet (Sigma) in PBS, extensively washed with distilled water, and dried at room temperature. The dye was resuspended with 50 μl of 0.2% Triton X-100/well, and color yield was measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay reader at 590 nm.
For migration assay, we used Boyden chambers (pore size, 8 μm) (BD Biosciences). Individual TE671 clones and CCA and RMZ-RC2 cells (5 × 104 cells in 0.5 ml of DMEM) were placed in the upper chamber, and 0.75 ml of DMEM containing 10% FBS was placed in the lower chamber. After 20 hours in culture, cells on the upper side of the filters were removed with cotton-tipped swabs, and the filters were fixed in methanol for 2 minutes and stained with 0.05% crystal violet in PBS for 15 minutes. Cells on the underside of the filters were viewed and counted under a microscope. For invasion assay, conditions were as described for migration assay except that BioCoat Matrigel invasion chambers (pore size, 8 μm) (BD Biosciences) were used.
For tumor growth in vivo, female (nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient) mice weighing ∼20 g were inoculated subcutaneously with 4 × 106 TE671/wt, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, or TE671/RAGE cells and monitored for 4 to 6 weeks. The mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation. Consent was obtained by the Ethics Committee of the University of Perugia. Tumor masses were excised and weighed, and tumor volume was calculated by the equation: tumor volume = x2y/2, where x and y correspond to the width and thickness of the tissue, respectively. Tumors were then fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS (2 days at 4°C), extensively washed in PBS, and paraffin-embedded. Sections were either stained with hematoxylin or subjected to immunohistochemistry using an anti-Ki-67 antibody (anti-MIB1, 1:10; Dako, Carpinteria, CA) to determine semiquantitatively cell proliferation. Before fixation, samples of individual tumors were subjected to RT-PCR to confirm lack of expression of RAGE in tumors arising from injected TE671/wt cells and expression of RAGEΔcyto and RAGE in tumors arising from injected TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells and TE671/RAGE cells, respectively (data not shown). Histopathology was performed by an independent pathologist.
Statistical Analysis
Each experiment was repeated at least three times. Representative experiments are depicted in the figures unless stated otherwise. The data were subjected to analysis of variance with Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc analysis using a statistical software package (GraphPad Prism version 4.0; GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA). Statistical significance was assumed when P < 0.05.
Results
Characterization of TE671/RAGE Cell
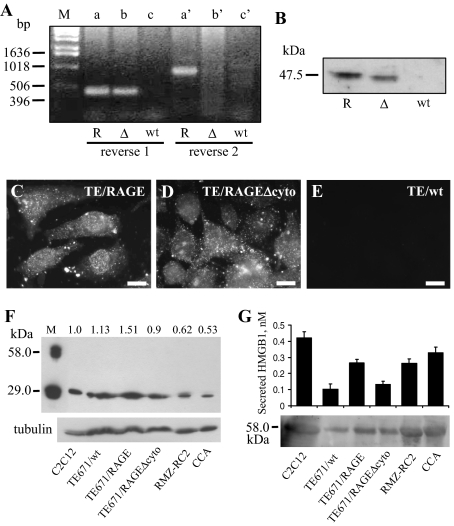
Expression of RAGE and RAGEΔcyto in TE671 clones that had been stably transfected with RAGE and RAGEΔcyto, respectively, was documented by RT-PCR, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence. Although TE671/wt cells did not express RAGE (mRNA and protein), TE671/RAGE and TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells expressed their respective mRNA and protein products (Figure 1, A and B). By immunofluorescence (Figure 1, C and D), RAGE was found in the form of focal and granular aggregates. Similar images were obtained in TE671/RAGE and TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells because the anti-RAGE antibody used recognizes RAGE extracellular domain. By contrast, TE671/wt cells showed no immunofluorescence signal (Figure 1E).
Figure 1.
Characterization of TE671/wt (embryonal type), TE671/RAGEΔcyto, and TE671/RAGE cells. A: RT-PCR products for human RAGE and RAGEΔcyto in TE671/RAGE (R), TE671/RAGEΔcyto (Δ), and TE671/wt (wt) cells. Shown are PCR products obtained with human RAGE reverse primer 1 (lanes a–c) and reverse primer 2 (lanes a′–c′). No PCR products can be seen with reverse primer 2 in the case of TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells because of specificity of this primer for a region present in full-length RAGE and absent from RAGEΔcyto. No PCR products can be seen with either primer in the case of TE671/wt cells. B: TE671/wt, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, and TE671/RAGE cells in GM were solubilized and analyzed for expression of RAGE and RAGEΔcyto by Western blotting using an anti-RAGE extracellular domain antibody (Chemicon). Note the faster migrating immunoreactive band in the TE671/RAGEΔcyto lane. C–E: TE671/wt, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, and TE671/RAGE cells were cultivated in GM and processed for immunofluorescence with the anti-RAGE extracellular domain antibody above. F and G: Lysates from C2C12 myoblasts, TE671/wt, TE671/RAGE, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, RMZ-RC2, and CCA cells (F) and culture media from these same cell lines (G) were analyzed for HMGB1 by Western blotting. Notice that purified HMGB1 (M, in F) shows two bands, one corresponding to monomeric (29-kd) and the other one to dimeric (58-kd) HMGB1, that intracellular HMGB1 migrates as a monomer exclusively (F), and that extracellular (released) HMGB1 migrates as a dimer exclusively (G). Semiquantitative analysis of HMGB1 was performed using the culture media of the cell lines as indicated (G). One representative experiment of three is shown (A–F). The numbers on top of lanes in F refer to the HMGB1-to-tubulin ratio. Averages of three independent experiments ± SD (G). Bars = 20 μm (C–E).
HMGB1 Is Expressed in and Released by C2C12 Myoblasts and RMS Cell Lines
Confluent cells were serum-starved, and the culture media and cells were analyzed for HMGB1 content by Western blotting. Mouse C2C12 myoblasts and TE671/wt, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, TE671/RAGE, RMZ-RC2, and CCA RMS cells all expressed and released HMGB1 (Figure 1, F and G). Interestingly, whereas intracellular HMGB1 was in the form of monomer, culture medium (released) HMGB1 was in the form of a dimer, pointing to disulfide complex formation likely due to the nonreducing conditions found extracellularly.44 Semiquantitative analyses revealed that the different cell lines investigated here expressed varying amounts of HMGB1 (normalized to tubulin) according to the following order: TE671/RAGE > C2C12 = TE671/wt = TE671/RAGEΔcyto > RMZ-RC2 = CCA cells (Figure 1F). Released HMGB1 amounted to 0.42, 0.10, 0.27, 0.13, 0.26, and 0.33 nmol/L in culture media from C2C12, TE671/wt, TE671/RAGE, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, RMZ-RC2, and CCA cells, respectively (Figure 1G). These HMGB1 concentrations were calculated relative to ∼1 × 106 cells in 5 ml of culture medium (DMEM without serum). Thus, the HMGB1 concentration in individual culture media was within the range of HMGB1 concentration shown to engage RAGE in myoblasts.11
RAGE Expression in TE671 Cells Induces Myogenic Differentiation: Role of HMGB1
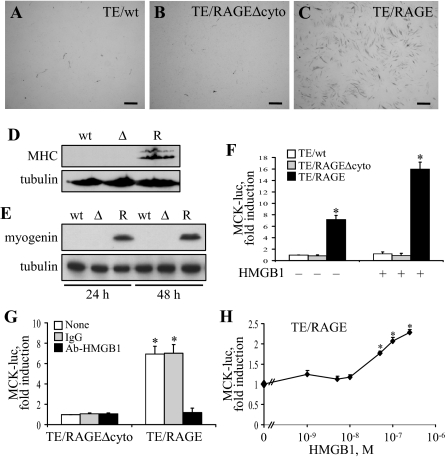
When cultivated in 2% FBS [differentiation medium (DM)] TE671/RAGE, but not TE671/RAGEΔcyto or wild-type TE671 (TE671/wt), cells showed expression of the late myogenic differentiation marker MHC (Figure 2, A–D) and the muscle-specific transcription factor myogenin, an early myogenic differentiation marker (Figure 2E). Thus, transfection with RAGE resulted in activation of the myogenic program in TE671 cells. Because HMGB1 stimulates RAGE promyogenic activity in rat L6 myoblasts11 and is released by C2C12 myoblasts and the RMS cells used in the present study (Figure 1, F and G), we reasoned that HMGB1 might activate RAGE in TE671/RAGE cells in an autocrine manner.
Figure 2.
Enforced expression of RAGE in TE671 cells activates the myogenic program on stimulation with HMGB1. A–C: TE671/wt, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, and TE671/RAGE cells were cultivated in DM for 4 days, fixed, and subjected to immunocytochemistry for detection of MHC. D: Same as in A–C except that the cells were solubilized and subjected to Western blotting for detection of MHC. R, wt, and Δ stand for TE671/RAGE, TE671/wt, and TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells, respectively. E: Same as in A–C except that the cells were cultivated in DM for 24 and 48 hours before Western blotting for detection of myogenin. F: TE671/wt, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, and TE671/RAGE cells were transiently transfected with MCK-luc reporter gene, switched to DM, cultivated for 24 hours in the absence or presence of added HMGB1 to 100 nmol/L, and harvested to measure luciferase activity. G: Same as in F except that TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/RAGE cells were cultivated in the presence of either 2.5 μg/ml nonimmune IgG or 2.5 μg/ml anti-HMGB1 antibody for 48 hours. H: Same as in F except that TE671/RAGE cells were cultivated in the presence of added HMGB1 to the concentrations indicated. One representative experiment of three is shown (A–E). Averages of three independent experiments ± SD (F–H). *Significantly different from control (first column from left in F and G; TE671/RAGE cells in the absence of additions in H) (P < 0.01). Bars = 200 μm (A–C).
TE671/RAGE cells in DM displayed a seven to eight times greater induction of the myogenic differentiation marker MCK compared with TE671/wt or TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells (Figure 2F). Administration of a neutralizing anti-HMGB1 antibody11 to TE671/RAGE cells resulted in decreased MCK induction (Figure 2G), suggesting that culture medium HMGB1 was responsible for RAGE activation in TE671/RAGE cells and that HMGB1 might act in an autocrine manner. Administration of HMGB1 to TE671/RAGE cells caused a further induction of MCK (Figure 2, F and H). However, the moderate (ie, twofold) increase in MCK induction detected in TE/RAGE cells exposed to administered HMGB1 (Figure 2H) compared with the remarkable (ie, ∼85%) decrease in MCK induction observed in TE/RAGE cells exposed to the HMGB1-neutralizing antibody (Figure 2G) suggested that released HMGB1 was sufficient to stimulate nearly maximally MCK induction in TE671/RAGE cells. Transient transfection of TE671/wt cells with increasing amounts of RAGE expression plasmid resulted in dose-dependent increase in myogenin and MCK induction, with a plateau between 1 and 10 μg of transfected RAGE (Supplemental Figure S1A at http://ajp.amjpathol.org). Conversely, transient transfection of TE671/RAGE cells with increasing amounts of RAGEΔcyto expression plasmid (Supplemental Figure S1B at http://ajp.amjpathol.org) or treatment of TE671/RAGE cells with a RAGE-neutralizing antibody11 (Supplemental Figure S1C at http://ajp.amjpathol.org) resulted in a dose-dependent decrease in myogenin and MCK induction. Thus, the ability of these cells to undergo myogenic differentiation seemed to be dependent on the amount of expressed RAGE and of functionally active RAGE. Collectively, these data suggested that HMGB1 engaged RAGE in TE671/RAGE cells, thereby activating a myogenic program.
RAGE Engagement by HMGB1 in TE671/RAGE Cells Activates the Promyogenic p38 MAPK and PI3-K/Akt and Relieves JNK Antimyogenic Effect
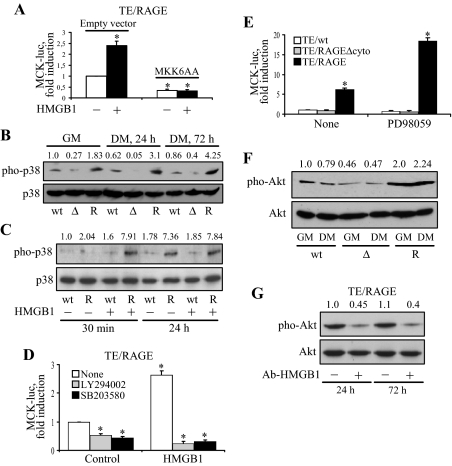
Expression of myogenin, which is under the control of p38 MAPK, governs the expression of MCK and MHC in myoblasts.5,15,17,18 Transfection of TE671/RAGE cells with MKK6AA, a functionally inactive mutant of MKK6, resulted in a reduced MCK induction irrespective of the absence or presence of added HMGB1 (Figure 3A), suggesting that the MKK6/p38 MAPK pathway was involved in the myogenic program activated by HMGB1/RAGE. Switching TE671/RAGE cells from growth medium (GM, 5% FBS) to DM consistently caused a sustained activation of p38 MAPK (Figure 3B), and administration of HMGB1 caused a further increase in p38 MAPK activation at an early time point (Figure 3C). In addition, transient transfection of TE671/wt and TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells with MKK6EE, a constitutively active mutant of the p38 MAPK upstream kinase MKK6, resulted in induction of myogenin and MCK (data not shown), in accordance with previous observations made using a panel of RMS cell lines.32 Collectively, these data supported the notion that defective activation of p38 MAPK might contribute to the inability of RMS cells to undergo myogenic differentiation32 and suggested that lack of RAGE expression in TE671/wt cells might be a cause of their inability to activate p38 MAPK persistently and to differentiate.
Figure 3.
Enforced expression of RAGE in TE671 cells activates p38 MAPK and Akt on stimulation with HMGB1. A: TE671/RAGE cells were transiently transfected with MCK-luc reporter gene and MKK6AA, switched to DM, cultivated for 24 hours under these conditions in the absence or presence of added HMGB1 to 100 nmol/L, and harvested to measure luciferase activity. B: TE671/wt (wt), TE671/RAGEΔcyto (Δ), and TE671/RAGE (R) cells were cultivated in GM for 24 hours or in DM for 24 or 72 hours and processed for detection of phosphorylated and total p38 MAPK by Western blotting. C: TE671/wt (wt), TE671/RAGEΔcyto (Δ), and TE671/RAGE (R) cells were cultivated in DM for 30 minutes or 24 hours in the absence or presence of added HMGB1 to 100 nmol/L and processed for detection of phosphorylated and total p38 MAPK. D: TE671/RAGE cells were transiently transfected with MCK-luc reporter gene, switched to DM, cultivated for 24 hours in the absence or presence of added HMGB1 to 100 nmol/L plus or minus the PI3-K inhibitor LY294002 or the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 and harvested to measure luciferase activity. E: TE671/wt, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, and TE671/RAGE cells were transiently transfected with MCK-luc reporter gene, switched to DM, cultivated for 24 hours in the absence or presence of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibitor PD98059, and harvested to measure luciferase activity. F: TE671/wt, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, and TE671/RAGE cells were cultivated in GM or DM for 24 hours and processed for detection of phosphorylated and total Akt by Western blotting. G: Same as in F except that TE671/RAGE cells were cultivated in DM for 24 hours or 72 hours in the presence of either 2.5 μg/ml nonimmune IgG or 2.5 μg/ml anti-HMGB1 antibody. One representative experiment of three is shown (B, C, F, and G). The numbers on top of lanes in B, C, F, and G refer to the phosphorylated-to-total ratio of the pertinent kinase relative to the respective control (first lane from left on each blot). Averages of three independent experiments ± SD (A, D, and E). *Significantly different from control (first column from left in A, D, and E) (P < 0.01).
Administration of the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 or the PI3-K inhibitor LY294002 resulted in reduced MCK induction in TE671/RAGE cells irrespective of the absence or presence of added HMGB1 (Figure 3D), whereas administration of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-ERK1/2 inhibitor, PD98059, resulted in increased MCK induction (Figure 3E). Data obtained with SB203580 were in line with data in Figure 3A and with the notion that p38 MAPK needs to be activated for myoblasts to differentiate15,17,18 and indicated that expression of RAGE in TE671 cells was sufficient to restore a crucial event in myogenic differentiation, ie, sustained p38 MAPK activation. By contrast, inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-ERK1/2 favored the execution of the myogenic program activated by RAGE engagement in TE671/RAGE cells (Figure 3E) in accordance with the notion that ERK1/2 inactivation results in enhanced myoblast differentiation.12,13,14 In addition, data obtained with LY294002 suggested that the PI3-K/Akt pathway became likewise activated in TE671/RAGE cells. The extent of Akt phosphorylation was consistently higher in TE671/RAGE cells than TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells in GM and in DM (Figure 3F), and neutralization of culture medium HMGB1 reduced Akt phosphorylation in TE671/RAGE cells (Figure 3G).
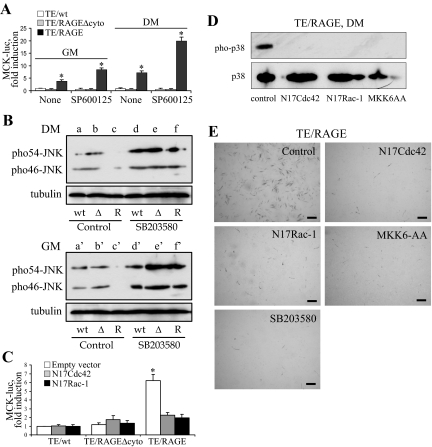
Excessive activation of the small GTPases of the Rho family, Rac1 and/or Cdc42, causes inhibition of myoblast differentiation via stimulation of JNK activity,45 and RMS cells have constitutively active Rac1 and Cdc4246 that stimulate proliferation and inhibit differentiation via JNK activation.47,48 Administration of the JNK inhibitor SP600125 to TE671/RAGE cells in DM caused a threefold stimulation of MCK induction compared with untreated TE671/RAGE cells (Figure 4A), suggesting that (excessive) activation of JNK reduced RAGE promyogenic activity and that, conversely, RAGE signaling to MKK6/p38 MAPK was able to overcome JNK antimyogenic activity in TE671/RAGE cells in part. Consistently, TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells exhibited remarkably higher levels of JNK phosphorylation (activation) compared with TE671/RAGE cells in GM and in DM, and inhibition of p38 MAPK with SB203580 in TE671/RAGE cells resulted in levels of JNK phosphorylation comparable with those found in TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells (Figure 4B). Inhibition of p38 MAPK phosphorylation by SB203580 under these conditions was verified by Western blotting (data not shown). In addition, RAGE signaling in TE671 cells resulted in a certain extent of MCK induction even in cells in GM (Figure 4A) analogous to the case of L6 myoblasts,11 and again inhibition of JNK resulted in stimulation of RAGE-dependent induction of MCK under these conditions (Figure 4A). Thus, expression of RAGE in TE671 cells relieved the antimyogenic effect of JNK in a p38 MAPK-dependent manner in part.
Figure 4.
Enforced expression of RAGE in TE671 cells results in relief of the inhibitory effect of JNK on myogenic differentiation. A: TE671/wt, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, and TE671/RAGE cells were transiently transfected with MCK-luc reporter gene and cultivated in GM for 24 hours or DM for 24 hours in the absence or presence of the JNK inhibitor, SP600125. B: TE671/wt (wt), TE671/RAGE (R), and TE671/RAGEΔcyto (Δ) cells in DM (a–f) and GM (a′–f′) were analyzed for JNK phosphorylation and in the absence (a–c, a′–c′) or presence (d–f, d′–f′) of 2 μmol/L SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor) by Western blotting. C: TE671/wt, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, and TE671/RAGE cells were transiently transfected with MCK-luc reporter gene and either N17Cdc42 or N17Rac1, switched to DM, cultivated for 24 hours, and harvested to measure luciferase activity. D: TE671/RAGE cells were transiently transfected with N17Cdc42, N17Rac1, or MKK6AA, cultivated in DM for 24 hours, and processed for detection of phosphorylated and total p38 MAPK by Western blotting. E: Same as in D except that TE671/RAGE cells were cultivated in DM for 4 days and that one additional sample was treated with the p38 MAPK inhibitor, SB203580. The cells were then fixed and subjected to immunocytochemistry for detection of MHC. One representative experiment of three is shown (B, D, and E). Averages of three independent experiments ± SD (A and C). *Significantly different from control (first column from left in A and C) (P < 0.01). Bars = 200 μm (E).
Activation of the Myogenic Program in TE671/RAGE Cells Requires Cdc42/Rac1 Activity
Excessive activation and inhibition of activity of Cdc42 and Rac1 inhibit myoblast differentiation,45 implying that a certain degree of Cdc42 and Rac1 activation is required for myoblast differentiation.49 In L6 myoblasts, the HMGB1/RAGE pair signals to MKK6/p38 MAPK via Cdc42/Rac1, thereby stimulating differentiation.11 Transfection of TE671/RAGE cells with an inactive mutant of Cdc42 (N17Cdc42) or Rac1 (N17Rac1) resulted in reduction of MCK induction to the levels found in TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells (Figure 4C), suggesting that RAGE promyogenic activity required Cdc42 and Rac1 activity. Consistently, in N17Cdc42-, N17Rac1-, or MKK6AA-transfected TE671/RAGE cells, nearly no p38 MAPK phosphorylation (Figure 4D) or MHC-positive TE671/RAGE cells could be detected (Figure 4E). These data suggested that RAGE engagement by HMGB1 in TE671/RAGE cells activated the MKK6/p38 MAPK pathway via Cdc42/Rac1, thereby stimulating myogenin and MHC expression and MCK induction.
TE671/RAGE Cells Show Reduced Proliferation and Increased Apoptosis
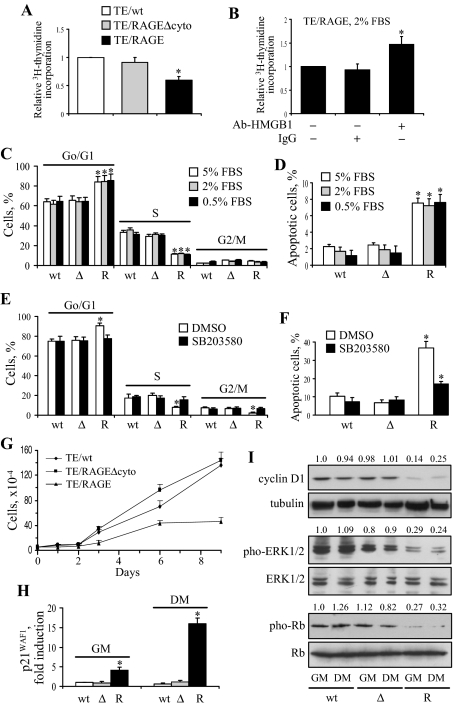
Recent work has shown that RAGE engagement in myoblasts results in reduced proliferation and increased apoptosis via p38 MAPK activation and p38 MAPK-dependent inactivation of ERK1/2 and JNK.28 In a proliferation assay, TE671/RAGE cells incorporated less [3H]thymidine compared with TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells (Figure 5A), indicating a slower proliferation rate, and administration of an anti-HMGB1 antibody to TE671/RAGE cells resulted in an increased [3H]thymidine incorporation compared with control cells (Figure 5B). In addition, under varying culture conditions (ie, 5, 2, and 0.5% FBS) and as determined by FACS analysis, a smaller fraction of TE671/RAGE cells was in the S phase, and a larger fraction was in the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle, compared with TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells (Figure 5C), again indicating a reduced proliferation of TE671/RAGE cells. This was accompanied by a larger extent of apoptosis in TE671/RAGE cells (Figure 5D), suggesting that RAGE-transducing activity interfered with mitogenic and pro-survival signaling pathways. A consistently smaller number of TE671/RAGE cells was measured on days 1 and 2 of cultivation in GM compared with TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells (Figure 5G). In addition, whereas starting at day 2, the number of TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells increased linearly up to day 9, the number of TE671/RAGE cells slightly increased between day 3 and day 6 with no further increase thereafter (Figure 5G). A similar pattern was observed with cells in DM (data not shown). Moreover, effects of RAGE transfection on TE671 cell proliferation (Figure 5E) and apoptosis (Figure 5F) were reduced in cells treated with the p38 MAPK inhibitor, SB203580. A similar reduction was observed in TE671/RAGE cells that had been treated with anti-HMGB1 antibody (data not shown). Thus, expression and activation of RAGE and RAGE ligation by HMGB1 in TE671 cells resulted in a reduced cell number via p38 MAPK activation.
Figure 5.
Enforced expression of RAGE in TE671 cells reduces proliferation and increases apoptosis. A: TE671/wt, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, and TE671/RAGE cells were subjected to a [3H]thymidine assay. B: Same as in A except that TE671/RAGE cells were cultivated in the presence of either 2.5 μg/ml nonimmune IgG or 2.5 μg/ml anti-HMGB1 antibody for 48 hours before [3H]thymidine assay. C and D: TE671/wt (wt), TE671/RAGEΔcyto (Δ), and TE671/RAGE (R) cells were cultivated for 72 hours in the presence of the FBS concentration indicated and subjected to FACS analysis to measure the fraction of cells in the various phases of the cell cycle (C) and apoptosis (D). E and F: Same as in C and D, respectively, except that the cells were cultivated in 2% FBS in the presence of the p38 MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, or vehicle [dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO)]. G: TE671/wt, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, and TE671/RAGE cells were cultivated in GM for the days indicated and processed by the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium assay. H: TE671/wt (wt), TE671/RAGEΔcyto (Δ), and TE671/RAGE (R) cells were transiently transfected with p21WAF1-luc reporter gene, switched to DM, cultivated for 48 hours and harvested to measure luciferase activity. I: TE671/wt (wt), TE671/RAGEΔcyto (Δ), and TE671/RAGE (R) cells were cultivated for 24 hours in either GM or DM and processed for detection of cyclin D1, phosphorylated and total ERK1/2, and phosphorylated and total Rb by Western blotting. A Western blot of tubulin is included below the cyclin D1 blot to show total protein loading in individual lanes. One representative experiment of three is shown (I). The numbers on top of lanes in I refer to the relative density of cyclin D1, phosphorylated ERK1/2 and phosphorylated Rb to tubulin, total ERK1/2, and total Rb, respectively. Averages of three independent experiments ± SD (A–H). *Significantly different from control (first column from left in A, B, D, F, and H) or from internal control (first column from left in each group in C and E) (P < 0.01).
TE671/RAGE Cells Show Increased Induction of p21WAF1 and Decreased Levels of Cyclin D1 and Extent of ERK1/2 and Rb Phosphorylation
Increased levels of the proliferation inhibitor p21WAF1, decreased levels of cyclin D1, and decreased extent of Rb phosphorylation accompany myoblast proliferation arrest and differentiation,50,51,52,53,54 and RMS cells contain abnormally low levels of p21WAF1 that do not change on their cultivation in DM.54 Thus, we next analyzed TE671/RAGE, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, and TE671/wt cells for levels of p21WAF1 and cyclin D1 and extent of ERK1/2 and Rb phosphorylation. We detected similar extents of p21WAF1 induction in TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells in GM and in DM and larger extents of p21WAF1 induction in TE671/RAGE cells in GM (Figure 5H). Moreover, a further increase in p21WAF1 induction was seen in TE671/RAGE cultivated in DM (Figure 5H). These latter findings correlated positively with the decreased proliferation of TE671/RAGE cells compared with TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells. In addition, similar extents of cyclin D1 expression and ERK1/2 phosphorylation were detected in TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells irrespective of the culture conditions, although remarkably lower levels were found in TE671/RAGE cells in GM and in DM (Figure 5I). Moreover, the extent of Rb phosphorylation was considerably low in TE671/RAGE cells compared with TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells (Figure 5I). Collectively, these data suggested that RAGE expression in TE671 cells triggered most of the intracellular events that lead to myoblast proliferation arrest and differentiation.
TE671/RAGE Cells Show Reduced Migration and Invasiveness
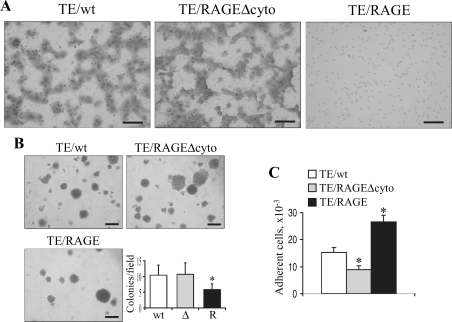
We next examined the possibility that RAGE expression might also interfere with TE671 cell migration, ability to form colonies, and invasiveness. TE671/RAGE cells exhibited reduced migration (Figure 6A) and ability to form colonies in soft agar (Figure 6B) compared with TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells, pointing to a lower tendency of TE671/RAGE cells to grow in the absence of a support and, hence, to enhanced adhesion properties of TE671/RAGE cells. Accordingly, in a cell adhesion assay, TE671/RAGE cells were more adhesive to the substratum than TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells (Figure 6C). In addition, in an invasiveness assay, whereas TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells migrated through a Matrigel barrier to the same extent, TE671/RAGE cells showed reduced or no invasiveness (data not shown). Thus, the aggressive potential of TE671 cells was remarkably reduced by RAGE expression.
Figure 6.
Enforced expression of RAGE in TE671 cells reduces migration, colony formation, and invasiveness and increases adhesiveness. A: TE671/wt, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, and TE671/RAGE cells were subjected to a migration assay in Boyden chambers. B: In a colony formation assay, a ∼50% decrease in the number of colonies was observed in the case of TE671/RAGE cells (R). C: In a cell adhesion assay, nearly twice as many TE671/RAGE cells adhered to the support after 3 hours as TE671/wt and TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells. One representative experiment of three is shown (A and B). *Significantly different from control (first column from left in B and C, n = 3) (P < 0.01). Bars: 100 μm (A); 500 μm (B).
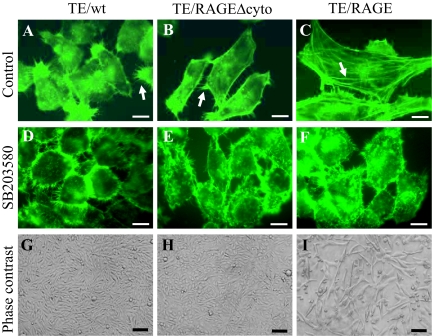
By fluorescein isothiocyanate-phalloidin staining, TE671/RAGE cells displayed a structured pattern of stress fibers, whereas TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells showed collapsed F-actin and filopodia (Figure 7, A–C) as typically seen in highly proliferating cells. In addition, by phase contrast microscopy and FACS analysis (Supplemental Figure S2, A and B, at http://ajp.amjpathol.org), TE671/RAGE cells exhibited a larger volume than TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells. Although a large fraction of MHC-positive TE671/RAGE cells in DM appeared elongated and hypertrophic (Figures 2C and 4E, control), ie, reminiscent of differentiating myoblasts, only sporadic multinucleated cells could be detected (Supplemental Figure S2A at http://ajp.amjpathol.org), as also observed in previous studies.32 However, on treatment with the p38 MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, the three TE671 clones showed a similar cell volume (Supplemental Figure S2B at http://ajp.amjpathol.org), and TE671/RAGE cells re-acquired the collapsed F-actin cytoskeleton detected in TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/wt cells (Figure 7, D–F). This suggested that RAGE-dependent activation of p38 MAPK in TE671/RAGE cells might be responsible for TE671/RAGE cell hypertrophy and stress fiber formation. Thus, RAGE transfection resulted in dramatic changes in TE671 cell shape consistent with their reduced proliferation and invasiveness, increased adhesiveness, and activation of the myogenic program.
Figure 7.
Enforced expression of RAGE in TE671 cells increases cell volume and restores stress fiber formation in a p38 MAPK-dependent manner. A–F: TE671/wt, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, and TE671/RAGE cells were cultivated in GM for 48 hours in the absence or presence of the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 (2 μmol/L for 24 hours), fixed, and incubated with fluorescein isothiocyanate-phalloidin to detect F-actin. Well-structured stress fibers (arrow in C) can be seen in TE671/RAGE cells that also exhibit a smaller number of filopodia than do TE671/wt and TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells (arrows in A and B). Note the absence of stress fibers in TE671/wt and TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells and the larger size of TE671/RAGE cells compared with TE671/wt and TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells. Treatment with SB203580 results in collapse of F-actin onto plasma membranes in the three TE671clones, acquisition of a round shape, decrease in cell volume, and appearance of numerous filopodia. G–I: TE671/wt, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, and TE671/RAGE cells were cultivated in DM for 3 days and analyzed by phase-contrast microscopy. One representative experiment of three with similar results is shown (A–I). Bars: 20 μm (A–F); 250 μm (G–I).
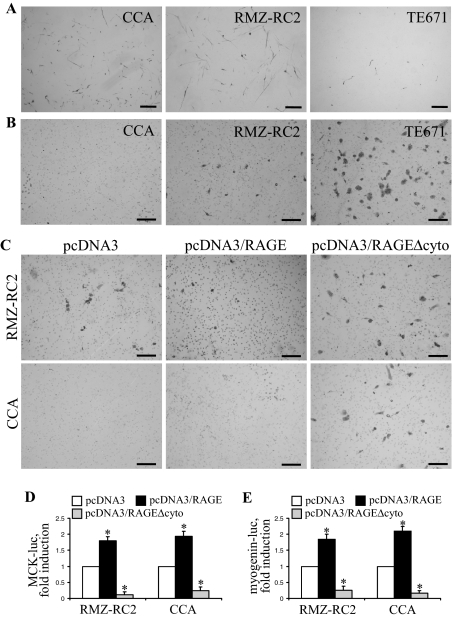
Different Extents of RAGE Expression in RMS Cell Lines: Correlation with Migration, Invasiveness, and Myogenic Differentiation in Vitro
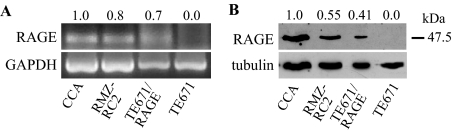
We analyzed two other RMS cell lines, ie, the embryonal-type CCA and alveolar-type RMZ-RC2, for RAGE and MHC expression and invasiveness. Differently from TE671/wt cells, by RT-PCR (Figure 8A), Western blotting (Figure 8B), and immunofluorescence (Supplemental Figure S3 at http://ajp.amjpathol.org), CCA and RMZ-RC2 cells expressed RAGE; however, RMZ-RC2 cells exhibited ∼50% less RAGE protein than CCA cells and RAGE protein levels comparable with TE671/RAGE cells, relative to tubulin (Figure 8B). Compared with TE671/wt cells, CCA and RMZ-RC2 cells showed a more pronounced MHC immunostaining intensity when cultivated in DM (Figure 9A) and exhibited reduced migration/invasiveness (Figure 9B), proportionally to the amount of RAGE protein. However, although RMZ-RC2 cells and TE671/RAGE cells expressed similar levels of RAGE protein, they behaved differently in an invasion assay, the alveolar-type RMZ-RC2 cells being more invasive than the embryonal-type TE671/RAGE cells (compare Figure 9B with Figure 6D). Thus, although in TE671/wt, RMZ-RC2, and CCA cells, a positive correlation was found between the extent of RAGE expression and that of MHC expression, and a negative correlation was found between the extent of RAGE expression and invasiveness, the levels of expression of RAGE in the alveolar-type RMZ-RC2 cells seemed to be insufficient to reduce invasiveness to the extent registered in the case of the embryonal-type TE761/RAGE cells. However, transient transfection of CCA and RMZ-RC2 cells with RAGE resulted in reduced invasiveness and enhanced MCK and myogenin induction, whereas transfection with RAGEΔcyto resulted in an increased invasiveness and a dramatic decrease in MCK and myogenin induction, compared with mock-transfected cells (Figure 9, C–E). In addition, CCA cells in DM displayed higher levels of p38 MAPK phosphorylation compared with TE671/wt cells, and inhibition of p38 MAPK by SB203580 resulted in increased migration and invasiveness of CCA cells compared with untreated cells (data not shown). Moreover, inhibition of JNK by SP600125 resulted in reduced migration and invasiveness of CCA cells (data not shown). Thus, the extent of myogenic differentiation of CCA and RMZ-RC2 cells was proportional to the level of RAGE expression, and functional inactivation of RAGE or inhibition of p38 MAPK in CCA and RMZ-RC2 cells increased their aggressive potential and reduced their myogenic potential.
Figure 8.
CCA (embryonal type) and RMZ-RC2 (alveolar type) RMS cells express RAGE. A and B: Expression of RAGE in CCA, RMZ-RC2, TE671, and TE671/RAGE cells was investigated by RT-PCR (A) and Western blotting (B). The numbers on top of lanes in A and B refer to the densities of RAGE mRNA relative to GADPH mRNA (A) and of RAGE protein relative to tubulin (B). One representative experiment of three with similar results is shown.
Figure 9.
CCA and RMZ-RC2 RMS cells show reduced invasiveness compared with TE671 cells, express MHC in DM, and exhibit increased invasiveness and reduced MCK and myogenin induction when transfected with RAGEΔcyto. A: CCA, RMZ-RC2, and TE671 cells were cultivated in GM for 24 hours, switched to DM for 4 days, and subjected to immunocytochemistry to detect MHC. B: CCA, RMZ-RC2, and TE671 cells were subjected to an invasiveness assay. C: CCA and RMZ-RC2 cells were transiently transfected with RAGE or RAGEΔcyto and subjected to an invasiveness assay. D and E: CCA and RMZ-RC2 cells transiently transfected with either RAGE or RAGEΔcyto were transfected with MCK-luc or myogenin-luc reporter gene. One representative experiment of three is shown (A–C). *Significantly different from control (first column from left in each group in D and E) (P < 0.01). Bars: 250 μm (A); 100 μm (B and C).
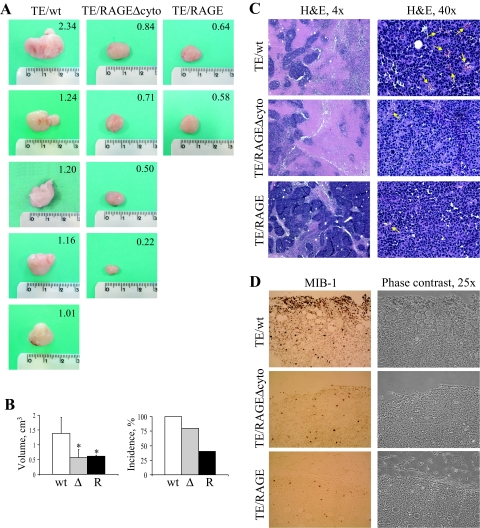
TE671/RAGE Cells Show Altered Tumor Growth in Vivo
Next, we injected immunocompromised mice with TE671/RAGE, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, or TE671/wt cells, and tumor formation was monitored for 4 to 6 weeks. All of the mice injected with TE671/wt cells, 80% of mice injected with TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells, and 40% of mice injected with TE671/RAGE cells developed a tumor (Figure 10, A and B), with tumor formation on TE671/wt cell injection preceding by ∼10 days that following TE671/RAGE or TE671/RAGEΔcyto cell injection. Volume was smaller in the case of TE671/RAGE and TE671/RAGEΔcyto tumors compared with TE671/wt tumors (Figure 10, A and B). In addition, larger areas of necrosis were detected in TE671/wt and TE671/RAGEΔcyto tumors than in TE671/RAGE tumors, and a remarkably reduced vasculature was found in TE671/RAGEΔcyto and TE671/RAGE tumors compared with the TE671/wt tumors (Figure 10C). Finally, the density of proliferating cells was high in TE671/wt tumors, intermediate in TE671/RAGEΔcyto tumors, and low in TE671/RAGE tumors (Figure 10D). Thus, expression of RAGE reduced the aggressive potential of TE671 cells in terms of tumor incidence, whereas the reduced vasculature observed in TE671/RAGE and TE671/RAGEΔcyto tumors suggested that RAGE extracellular domain might function as a decoy receptor for HMGB1, thereby reducing the ability of HMGB1 to promote reactive angiogenesis (see Discussion).55 Reduced angiogenesis might explain the reduced proliferation and tumor volume and the retarded tumor formation observed in TE671/RAGE and TE671/RAGEΔcyto tumors compared with TE671/wt tumors (Figure 10D).
Figure 10.
Inoculation of TE671/RAGE cells into mice results in reduced tumor volume and incidence. Immunocompromised mice were injected with TE671/wt, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, or TE671/RAGE cells, and tumor mass formation was followed for 4 to 6 weeks. Tumor masses were analyzed for volume (A and B), histopathology (C), and proliferating cells (D). Ample zones of necrosis are detected in TE671/wt and TE671/RAGEΔcyto tumors compared with TE671/RAGE tumors (C, left panels), and TE671/RAGEΔcyto tumors and TE671/RAGE tumors exhibit a remarkably reduced vasculature compared with TE671/wt tumors (arrows in C, right panels). In addition, a much larger number of proliferating cells is detected in TE671/wt tumors compared with TE671/RAGEΔcyto tumors that, in turn, show a larger number of proliferating cells than TE671/RAGE tumors, as investigated by Ki-67 (MIB1) immunohistochemistry (D). *Significantly different from control (first column from left in the average volume panel in B) (n = 5, P < 0.05).
Discussion
RAGE, a cell surface receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily,24 is expressed in skeletal muscles in a developmentally regulated manner and transduces a myogenic signal in L6 myoblasts, and the RAGE ligand, HMGB1 (amphoterin), engages RAGE in L6 myoblasts, thereby stimulating myogenic differentiation.11 In addition, functional inactivation of RAGE in L6 myoblasts results in reduced differentiation and apoptosis, increased proliferation, and tumor formation in vivo.28 These observations suggest that deregulation of RAGE expression and/or functionality in myoblasts might contribute to myoblast neoplastic transformation and, conversely, that restoration of RAGE expression and/or functionality in RMS cells might mitigate RMS aggressive potential. To test this hypothesis, we investigated effects of stable transfection with RAGE of embryonal-type TE671 RMS cells on differentiation, proliferation, migration, invasiveness, and tumor growth. We found that TE671 cells do not express RAGE, myogenin, or MHC; proliferate at a high rate; and are unable to complete the myoblast differentiation program. However, on transfection with RAGE, but not its signaling-deficient mutant, RAGEΔcyto, TE671 cells show signs of myogenic differentiation (ie, myogenin and MHC expression, MCK induction, and cell hypertrophy) when cultivated in DM, proliferate at a significantly reduced rate, and exhibit increased adhesiveness and reduced migration, invasiveness, and in vivo tumor growth. Moreover, because TE671/RAGE, TE671/RAGEΔcyto, and TE671/wt cells, CCA and RMZ-RC2 cells, and C2C12 myoblasts release HMGB1 and because a HMGB1-neutralizing antibody reduces effects of RAGE expression in TE671 cells, activation of RAGE likely depends on an autocrine effect of released HMGB1. Last, the ability of RAGE-transfected TE671/wt cells to undergo myogenic differentiation depends on the amount of expressed RAGE and of functionally active RAGE. Thus, enforced expression of RAGE and RAGE engagement by HMGB1 are able to reduce the neoplastic potential of and to trigger the myogenic program in TE671 cells. Likewise, the CCA and RMZ-RC2 RMS cell lines, which express RAGE and MHC in DM, show remarkably reduced invasiveness, compared with TE671/wt cells, proportionally to the amount of expressed RAGE and show increased myogenin and MCK induction when transfected with RAGE and dramatically reduced myogenin and MCK induction when transfected with RAGEΔcyto. In a specular fashion, RAGEΔcyto-transfected CCA and RMZ-RC2 RMS cells are more invasive in vitro compared with their mock-transfected counterparts. It is notable that overexpression of either CDO (cell adhesion molecule-related/down-regulated by oncogenes) or BOC (brother of CDO), two receptors that, analogous to RAGE, are members of the immunoglobulin superfamily and positive regulators of myogenesis,56 results in differentiation of RD RMS cells.57
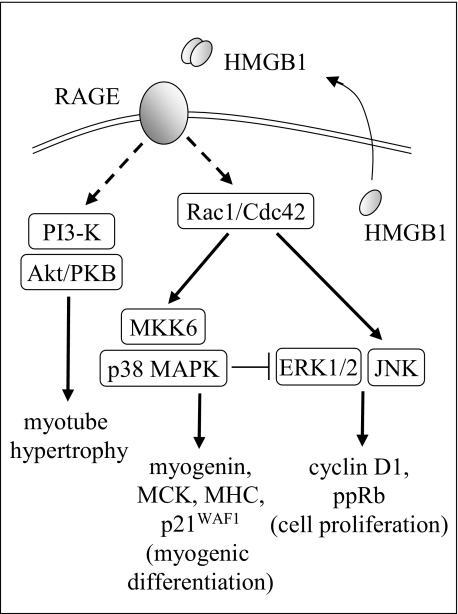
p38 MAPK activity is crucial for activation of the myogenic program in myoblasts and RMS cells, and Akt is also required for myoblast differentiation and myoblast/myotube hypertrophy.15,17,18,32 TE671/RAGE cells show increased extents of phosphorylation (activation) of the promyogenic p38 MAPK and Akt, and HMGB1 further increases them. Thus, a relationship exists in TE671/RAGE cells among RAGE expression, p38 MAPK and Akt activation, up-regulation of myogenin and MHC expression, induction of MCK, and cell hypertrophy. Transfection of TE671/RAGE cells with MKK6AA, a constitutively inactive mutant of the p38 MAPK upstream kinase, MKK6, or with a constitutively inactive mutant of either Cdc42 or Rac1 or inhibition of p38 MAPK with SB203580 in TE671/RAGE cells results in negation of effects of enforced expression of RAGE. Thus, we conclude that HMGB1-activated RAGE signals to Cdc42-Rac1-MKK6-p38 MAPK and PI3-K/Akt to induce TE671/RAGE cell differentiation and hypertrophy (Figure 11).
Figure 11.
Schematic representation of the proposed effects of enforced expression of RAGE in TE671 RMS cells. RAGE engaged by HMGB1 signals to Rac1/Cdc42 and to PI3-K via unknown intermediates, thereby stimulating myogenic differentiation through activation of the MKK6/p38 MAPK module and myotube hypertrophy through the PI3-K/Akt module. HMGB1/RAGE-dependent activation of p38 MAPK also causes inactivation of ERK1/2 and JNK with consequent inhibition of proliferation and decrease in cell survival. Shown are also monomeric HMGB1 within myoblasts and the RMS cell lines used in this study and released HMGB1, which forms disulfide cross-linked dimers in the extracellular medium.
Besides causing activation of the myogenic program, RAGE expression in TE671 cells also results in reduced proliferation, migration, invasiveness, and in vivo tumor growth/incidence and increased apoptosis and adhesiveness. These observations are at variance with data obtained with glioma, melanoma, colon cancer, and human pancreatic carcinoma cells,24,25,26,27 in which a positive correlation was found among RAGE expression, neoplastic transformation, and metastasis, but are consistent with the differentiating activity of HMGB1/RAGE in neurons and L6 myoblasts.11,34 However, our data are consistent with observations made with non-small lung carcinoma cells,58 in which down-regulation of RAGE was found to be associated with neoplastic transformation and with previous work showing that RAGE-induced neuronal differentiation is associated with proliferation arrest.26
The reduced proliferation of TE671/RAGE cells in vitro compared with TE671/wt and TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells is accompanied by an increased induction of the proliferation inhibitor p21WAF1 and remarkably decreased levels of cyclin D1 and extent of ERK1/2 and Rb phosphorylation. The reduced proliferation of TE671/RAGE cells depends on a rapid and sustained activation of p38 MAPK, which is known to stabilize the p21WAF1 transcript in cells of the myogenic lineage59 and to cause proliferation arrest when persistently activated in RMS cells.32 In the present case, sustained activation of p38 MAPK depends on HMGB1/RAGE-induced activation of Cdc42-Rac1 (Figure 4C). Notably, activation of the MKK6-p38 MAPK pathway by a number of upstream intermediates, including Cdc42, has been reported to cause cell proliferation arrest.60,61 Thus, our results suggest that expression and activation of RAGE in cells of the myogenic lineage might cause proliferation arrest, a critical event in the process of myoblast differentiation and in the control of neoplastic transformation. Consistent with this conclusion is the finding that the extent of phosphorylation (activation) of JNK, a mitogenic kinase particularly active in RMS cells and suggested to play an important role in rhabdomyosarcomagenesis,47,48 is remarkably reduced in TE671/RAGE cells, compared with TE671/wt and TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells, again in a p38 MAPK-dependent manner (Figure 3B). In addition, as mentioned above, forced expression of RAGE in TE671 cells results in down-regulation of expression of cyclin D1 (Figure 5I), which is overexpressed in highly proliferating, metastatic cells, including RMS cells, has an important role in cellular survival and DNA synthesis, and is induced by sustained activation of ERK1/2.62,63,64,65,66 Our data suggest that RAGE signaling in TE671/RAGE cells might down-regulate the expression of cyclin D1 via p38 MAPK-dependent inhibition of ERK1/2 and JNK activities.28,67 After the submission of the present work, data have appeared showing that p38 MAPK causes myoblast proliferation arrest by inactivating JNK via up-regulation of MAPK phosphatase-1.68 On this basis, we propose that inability of TE671 cells to express RAGE might contribute to their high proliferation rate and hence to their malignancy and that re-expression of RAGE might reduce TE671 cell aggressiveness (Figure 11), which might have important implications for our understanding of the biology of RMSs and, potentially, therapeutic intervention.
Although tumor incidence in mice inoculated with TE671/RAGE cells is 50% lower than that registered in mice inoculated with TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells, tumor volume is, unexpectedly, essentially the same (Figure 10B). However, a reduced reactive angiogenesis is found in TE671/RAGE and TE671/RAGEΔcyto tumors compared with TE671/wt tumors (Figure 10C). These observations raise the possibility that RAGE extracellular domain in the inoculated TE671/RAGE and TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells might sequester endogenous HMGB1 (likely the HMGB1 released by the inoculated cells), thereby reducing the ability of HMGB1 to promote reactive angiogenesis.55 The following observations support this possibility. i) RAGE engagement by HMGB1 in TE671/RAGE cells in vitro results in reduced proliferation and increased apoptosis, and this effect requires an intact RAGE (ie, TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells behave like TE671/wt cells). ii) The number of proliferating cells in the tumor masses is small in TE671/RAGE tumors, intermediate in TE671/RAGEΔcyto tumors, and high in TE671/wt tumors (Figure 10D). iii) TE671/wt, TE671/RAGE and TE671/RAGEΔcyto, CCA, and RMZ-RC2 cells release HMGB1. The concentration of released HMGB1 ranges from a minimum of 0.10 nmol/L in the case of TE671/wt cells to a maximum of 0.42 nmol/L in the case of C2C12 myoblasts in vitro. We have no information concerning the concentration of released HMGB1 at sites of inoculation of TE671/wt, TE671/RAGE, and TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells and of tumor formation, but any released HMGB1 at these sites may well engage RAGE in TE671/RAGE cells and bind to RAGE extracellular domain in TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells, thereby stimulating the myogenic and antiproliferative potential of RAGE (in the case of inoculated TE671/RAGE cells) and preventing efficient interaction with endothelial RAGE (in the case of inoculated TE671/RAGE and TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells). Thus, whereas the reduced proliferation of TE671/RAGE cells in vitro is an intrinsic property because of the presence of full-length RAGE, the reduced tumor progression of TE671/RAGE cells in vivo might result from this intrinsic property and the likely decoy function of RAGE extracellular domain toward released HMGB1 (with consequent reduction of the pro-angiogenic activity of HMGB1). TE671/RAGEΔcyto tumors are midway because although TE671/RAGEΔcyto cells are incapable of arresting their proliferation in vitro similarly to TE671/wt cells, their RAGE extracellular domain might sequester endogenous HMGB1, the pro-angiogenic activity of which55 would so be reduced. Although further in vivo analyses are required to substantiate this possibility, we note that RAGE extracellular domain has long been known to act as a decoy receptor for RAGE ligands, including HMGB1.19,24
The CCA and RMZ-RC2 RMS cell lines, which do express RAGE although to a different extent from one another, show invasiveness in an inverse proportion to the extent of RAGE expression and show a lower invasiveness compared with TE671/wt cells. In addition, functional inactivation of RAGE in these cells by transient transfection with RAGEΔcyto results in an increased aggressive potential and a reduced myogenic potential. Similar results were obtained after inhibition of p38 MAPK (data not shown). These data support our proposal that RAGE expression and engagement might reduce the aggressive potential of RMS cells and might be important for tumor grade diagnosis, whereas repression of RAGE expression or functional inactivation of RAGE might enhance RMS cell aggressiveness. However, although the amount of RAGE expressed in individual TE671/wt, CCA, and RMZ-RC2 cells, relative to tubulin, influences their behavior in terms of myogenic differentiation in DM and invasiveness (the higher the levels of RAGE in individual cell lines, the lower the invasiveness and vice versa), at similar levels of RAGE expression relative to tubulin, the alveolar-type RMZ-RC2 cells are more invasive than the embryonal-type TE671/RAGE cells (compare Figure 9B with Figure 6D). These data suggest that the levels of endogenous RAGE in the alveolar-type RMZ-RC2 cells are not sufficient to reduce the invasiveness to the extent observed in the embryonal-type TE671/RAGE cells. Thus, the recurrent chromosomal translocations t(2;13) or t(1;13) occurring in alveolar RMSs and resulting in the formation of chimeric transcription factors PAX3-FOXO1a and PAX7-FOXO1a, respectively,69 and other events occurring in alveolar and embryonal RMSs might have more profound effects than RAGE expression on the ability of RMS cells to stop proliferating, differentiate, and fuse into myotubes. However, enforced expression of RAGE in the RAGE-negative embryonal-type TE671 RMS cells results in reduced proliferation and invasiveness and decreased tumor growth/incidence in vivo along with increased apoptosis and restoration of the ability to express markers of myogenic differentiation. In addition, transient transfection of the RAGE-positive CCA and RMZ-RC2 cells with RAGE results in a reduced invasiveness and enhanced MCK and myogenin induction, whereas transfection with RAGEΔcyto results in an increased invasiveness and a remarkable decrease in MCK and myogenin induction compared with mock-transfected cells. This suggests that the presence and/or increased dosage of a functional RAGE might mitigate the aggressive potential of RMS cells, and conversely, repression of RAGE expression or functional inactivation of RAGE in RMS cells might result in an increased aggressive potential. It is tempting to speculate that loss of RAGE and/or reduced RAGE activity might contribute to rhabdomyosarcomagenesis. Specifically, we propose that although re-routing signaling pathways (by any of the several causes proposed to be responsible for myoblast neoplastic transformation) likely is a major event in rhabdomyosarcomagenesis, reduced activity of p38 MAPK consequent to repression of RAGE expression and/or function likely is an important cause of such a re-routing. By virtue of its ability to persistently activate p38 MAPK in myoblasts, RAGE might reduce or interrupt JNK and ERK1/2 activities, thereby preventing uncontrolled proliferation, promoting apoptosis, and stimulating differentiation.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Heikki Rauvala (Helsinki, Finland) for providing the RAGE, RAGEΔcyto, N17Rac1, and N17Cdc42 constructs and recombinant HMGB1; Pier Lorenzo Puri (La Jolla, CA) for providing the MKK6AA, MKK6EE, p21WAF1-luc, and MCK-luc constructs; Eyal Bengal (Haifa, Israel) for providing the myogenin-luc constructs; Mario Rende (Perugia, Italy) for providing the TE671 rhabdomyosarcoma cell line; and Pier-Luigi Lollini (Bologna, Italy) for providing the CCA and RMZ-RC2 rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines.
Footnotes
Address reprint requests to Rosario Donato, Department of Experimental Medicine and Biochemical Sciences, Section of Anatomy, University of Perugia, Via del Giochetto C.P. 81 Succ. 3, 06122 Perugia, Italy. E-mail: donato@unipg.it.
Supported by Ministero dell’Istruzione, dell’Università e della Ricerca-University of Perugia (grant PRIN 2004054293), Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca contro il Cancro (grant AIRC 1110), and Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio di Perugia (grant 2004.0282.020) (all to R.D.).
F.R. and G.S. contributed equally to this work.
Supplemental material for this article can be found on http://ajp.amjpathol.org.
References
- Andrés V, Walsh K. Myogenin expression, cell cycle withdrawal, and phenotypic differentiation are temporally separable events that precede cell fusion upon myogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1996;132:657–666. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.4.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold HH, Winter B. Muscle differentiation: more complexity to the network of myogenic regulators. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1998;8:539–544. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(98)80008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chargé SB, Rudnicki MA. Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:209–238. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00019.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham M. Myogenic progenitor cells and skeletal myogenesis in vertebrates. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006;16:525–532. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2006.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar AB, Skapek SX, Novitch B. Regulatory mechanisms that coordinate skeletal muscle differentiation and cell cycle withdrawal. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994;6:788–794. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini JR, Ewton DZ, Coolican SA. Growth hormone and the insulin-like growth factor system in myogenesis. Endocr Rev. 1996;17:481–517. doi: 10.1210/edrv-17-5-481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langen RC, Schols AM, Kelders MC, Wouters EF, Janssen-Heininger YM. Inflammatory cytokines inhibit myogenic differentiation through activation of nuclear factor-κB. FASEB J. 2001;15:1169–1180. doi: 10.1096/fj.00-0463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCroskery S, Thomas M, Maxwell L, Sharma M, Kambadurm R. Myostatin negatively regulates satellite cell activation and self-renewal. J Cell Biol. 2003;162:1135–11347. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200207056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorci G, Agneletti AL, Riuzzi F, Marchetti C, Donato R. S100B inhibits myogenic differentiation and myotube formation in a RAGE-independent manner. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:4870–4881. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.14.4870-4881.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang JS, Yi MJ, Zhang W, Feinleib JL, Cole F, Krauss RS. Netrins and neogenin promote myotube formation. J Cell Biol. 2004;167:493–404. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200405039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorci G, Riuzzi F, Arcuri C, Giambanco I, Donato R. Amphoterin stimulates myogenesis and counteracts the antimyogenic factors basic fibroblast growth factor and S100B via RAGE binding. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:4880–4894. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.11.4880-4894.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett AM, Tonks NK. Regulation of distinct stages of skeletal muscle differentiation by mitogen-activated protein kinases. Science. 1997;278:1288–1291. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5341.1288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter B, Arnold H-H. Activated raf kinase inhibits muscle cell differentiation through a MEF2-dependent mechanism. J Cell Sci. 2000;113:4211–4220. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.23.4211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry RL, Parker MH, Rudnicki MA. Activated MEK1 binds the nuclear MyoD transcriptional complex to repress transactivation. Mol Cell. 2001;8:291–301. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z, Woodring PJ, Bhakta KS, Tamura K, Wen F, Feramisco JR, Karin M, Wang JYJ, Puri PL. p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinases regulate the myogenic program at multiple steps. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:3951–3964. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.11.3951-3964.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttridge DC. Signaling pathways weigh in on decisions to make or break skeletal muscle. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2004;7:443–450. doi: 10.1097/01.mco.0000134364.61406.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lluís F, Perdiguero E, Nebreda AR, Munoz-Canoves P. Regulation of skeletal muscle gene expression by p38 MAP kinases. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16:36–44. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2005.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios D, Puri PL. The epigenetic network regulating muscle development and regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2006;207:1–11. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt AM, Yan SD, Yan SF, Stern D. The biology of the receptor for advanced glycation end products and its ligands. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1498:99–111. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(00)00087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan SD, Chen X, Fu J, Chen M, Zhu H, Roher A, Slattery T, Zhao L, Nagashima M, Morser J, Migheli A, Nawroth P, Stern D, Schmidt AM. RAGE and amyloid-β peptide neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 1996;382:685–691. doi: 10.1038/382685a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttunen HJ, Kuja-Panula J, Rauvala H. Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) signaling induces CREB-dependent chromogranin expression during neuronal differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:38635–38646. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M202515200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttunen HJ, Kuja-Panula J, Sorci G, Agneletti AL, Donato R, Rauvala H. Coregulation of neurite outgrowth and cell survival by amphoterin and S100 proteins through RAGE activation. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:40096–40105. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006993200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann MA, Drury S, Fu C, Qu W, Taguchi A, Lu Y, Avila C, Kambham N, Bierhaus A, Nawroth P, Neurath MF, Slattery T, Beach D, McClary J, Nagashima M, Morser J, Stern D, Schmidt AM. Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) signaling induces CREB-dependent chromogranin expression during neuronal differentiation. Cell. 1999;97:889–901. [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi A, Blood DC, del Toro G, Canet A, Lee DC, Qu W, Tanji N, Lu Y, Lalla E, Fu C, Hofmann MA, Kislinger T, Ingram M, Lu A, Tanaka H, Hori O, Ogawa S, Stern DM, Schmidt AM. Blockade of RAGE-amphoterin signalling suppresses tumour growth and metastases. Nature. 2000;405:354–360. doi: 10.1038/35012626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada M, Koizumi T, Toyama H, Suzuki Y, Kuroda Y. Differential expression of RAGE in human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Hepatogastroenterology. 2001;48:1577–1578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttunen HJ, Fages C, Kuja-Panula J, Ridley AJ, Rauvala H. Receptor for advanced glycation end products-binding COOH-terminal motif of amphoterin inhibits invasive migration and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2002;62:4805–4811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuniyasu H, Chihara Y, Kondo H. Differential effects between amphoterin and advanced glycation end products on colon cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2003;104:722–727. doi: 10.1002/ijc.11016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riuzzi F, Sorci G, Donato R. The amphoterin/RAGE pair modulates myoblast proliferation, apoptosis, adhesiveness, migration and invasiveness: functional inactivation of RAGE in L6 myoblasts results in tumor formation in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:8242–8253. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509436200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton MR, Darling J, Pilkington GJ, Lantos PL, Reeves BR, Cooper CS. Characterization of the human cell line TE671. Carcinogenesis. 1989;10:899–905. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.5.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott SJ, Thayer MJ, Weintraub H. Deficiency in rhabdomyosarcomas of a factor required for MyoD activity and myogenesis. Science. 1993;259:1450–1453. doi: 10.1126/science.8383879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten AD, Firpo EJ, Gerber AN, Brody LL, Roberts JM, Tapscott SJ. Inactivation of MyoD-mediated expression of p21 in tumor cell lines. Cell Growth Differ. 1997;8:1151–1160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri PL, Wu Z, Zhang P, Wood LD, Bhakta KS, Han J, Feramisco JR, Karin M, Wang JYJ. Induction of terminal differentiation by constitutive activation of p38 MAP kinase in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Genes Dev. 2000;14:574–584. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neeper M, Schmidt AM, Brett J, Yan SD, Wang F, Pan YC, Elliston K, Stern D, Shaw A. Cloning and expression of a cell surface receptor for advanced glycosylation end products of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:14998–15004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttunen HJ, Fages C, Rauvala H. Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE)-mediated neurite outgrowth and activation of NF-κB require the cytoplasmic domain of the receptor but different downstream signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:19919–19924. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.28.19919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X, McGowan CH, Zhao M, He L, Downey JS, Fearns C, Wang Y, Huang S, Han J. Involvement of the MKK6–p38γ cascade in γ-radiation-induced cell cycle arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:4543–4552. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.13.4543-4552.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron E, Hall A. Identification of two distinct mechanisms of phagocytosis controlled by different Rho GTPases. Science. 1998;282:1717–1721. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5394.1717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raingeaud J, Whitmarsh AJ, Barrett T, Derijard B, Davis RJ. MKK3- and MKK6-regulated gene expression is mediated by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:1247–1255. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.3.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent CK, Gualberto A, Patel CV, Walsh K. Different regulatory sequences control creatine kinase-M gene expression in directly injected skeletal and cardiac muscle. Mol Cell Biol. 1993;13:1264–1272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber AN, Klesert TR, Bergstrom DA, Tapscott SJ. Two domains of MyoD mediate transcriptional activation of genes in repressive chromatin: a mechanism for lineage determination in myogenesis. Genes Dev. 1997;11:436–450. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.4.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993;75:817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charoonpatrapong K, Shah R, Robling AG, Alvarez M, Clapp DW, Chen S, Kopp RP, Pavalko FM, Yu J, Bidwell JP. HMGB1 expression and release by bone cells. J Cell Physiol. 2006;207:480–490. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC, Grignani F, Riccardi C. A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1991;139:271–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90198-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadzadeh M, Hussain SF, Faber DL. Effector CD4 T cells are biochemically distinct from the memory subset: evidence for long-term persistence of effectors in vivo. J Immunol. 1999;163:3053–3063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauvala H, Pihlaskari R. Isolation and some characteristics of an adhesive factor of brain that enhances neurite outgrowth in central neurons. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:16625–16635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meriane M, Roux P, Primig M, Fort P, Gauthier-Rouviere C. Critical activities of Rac1 and Cdc42Hs in skeletal myogenesis: antagonistic effects of JNK and p38 pathways. Mol Biol Cell. 2000;11:2513–2528. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.8.2513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meriane M, Charrasse S, Comunale F, Mery A, Fort P, Roux P, Gauthier-Rouviere C. Participation of small GTPases Rac1 and Cdc42Hs in myoblast transformation. Oncogene. 2002;21:2901–2907. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauro A, Ciccarelli C, De Cesaris P, Scoglio A, Bouclé M, Molinaro M, Aquino A, Zani BM. PKCα-mediated ERK, JNK and p38 activation regulates the myogenic program in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:3587–3599. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charrasse S, Causeret M, Comunale F, Bonet-Kerrache A, Gauthier-Rouviere C. Rho GTPases and cadherin-based cell adhesion in skeletal muscle development. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2003;24:309–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan BA, Mitchell DC, Zhao L, Ma W, Stafford LJ, Teng B-B, Liu M. modulation of muscle regeneration, myogenesis, and adipogenesis by the Rho family guanine nucleotide exchange factor GEFT. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:11089–11101. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.24.11089-11101.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetser A, Gredinger E, Bengal E. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway promotes skeletal muscle differentiation: participation of the Mef2c transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:5193–5200. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.8.5193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Missero C, Calautti E, Eckner R, Chin J, Tsai LH, Livingston DM, Dotto GP. Involvement of the cell-cycle inhibitor Cip1/WAF1 and the E1A-associated p300 protein in terminal differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:5451–5455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao SS, Kohtz DS. Positive and negative regulation of D-type cyclin expression in skeletal myoblasts by basic fibroblast growth factor and transforming growth factor β: a role for cyclin D1 in control of myoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:4093–4100. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.8.4093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porrello A, Cerone MA, Coen S, Gurtner A, Fontemaggi G, Cimino L, Piaggio G, Sacchi A, Soddu S. p53 regulates myogenesis by triggering the differentiation activity of pRb. J Cell Biol. 2000;151:1295–1304. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.6.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen B, He L, Savell VH, Jenkins JJ, Parham DM. Inhibition of the interferon-gamma/signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) pathway by hypermethylation at a STAT-binding site in the p21WAF1 promoter region. Cancer Res. 2000;60:3290–3298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitola S, Belleri M, Urbinati C, Coltrini D, Sparatore B, Pedrazzi M, Melloni E, Presta M. Cutting edge: extracellular high mobility group box-1 protein is a proangiogenic cytokine. J Immunol. 2006;176:12–15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss RS, Cole F, Gaio U, Takaesu G, Zhang W, Kang J-S. Close encounters: regulation of vertebrate skeletal myogenesis by cell-cell contact. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:2355–2362. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegorzewska M, Krauss RS, Kang J-S. Overexpression of the immunoglobulin superfamily members CDO and BOC enhances differentiation of human rhabdomyosarcoma cell line RD. Mol Carcinog. 2003;37:1–4. doi: 10.1002/mc.10121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartling B, Hofmann HS, Weigle B, Silber RE, Simm A. Down-regulation of the receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) supports non-small cell lung carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26:293–301. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgh333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briata P, Forcales SV, Ponassi M, Corte G, Chen C-Y, Karin M, Puri PL, Gherzi R. p38-dependent phosphorylation of the mRNA decay-promoting factor KSRP controls the stability of select myogenic transcripts. Mol Cell. 2005;20:891–903. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.10.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnár A, Theodoras AM, Zon LI, Kyriakis JM. Cdc42Hs, but not Rac1, inhibits serum-stimulated cell cycle progression at G1/S through a mechanism requiring p38/ERK. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:13229–13235. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.20.13229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haq R, Brenton JD, Takahashi M, Finan D, Finkielsztein A, Damaraju S, Rottapel R, Zanke B. Constitutive p38HOG mitogen-activated protein kinase activation induces permanent cell cycle arrest and senescence. Cancer Res. 2002;62:5076–5082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. G1 cell-cycle control and cancer. Nature. 2004;432:298–306. doi: 10.1038/nature03094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J, Hu S, Schofield DE, Sorensen PH, Triche TJ. Selective usage of D-type cyclins by Ewing’s tumors and rhabdomyosarcomas. Cancer Res. 2004;64:6026–6034. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-2594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu M, Wang C, Rao M, Wu X, Bouras T, Zhang X, Li Z, Jiao X, Yang J, Li A, Perkins ND, Thimmapaya B, Kung AL, Munoz A, Giordano A, Lisanti M, Pestell RG. Cyclin D1 represses p300 transactivation through a cyclin-dependent kinase-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:29728–29742. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503188200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albanese C, Wu K, D’Amico M, Jarrett C, Joyce D, Hughes J, Hulit J, Sakamaki T, Fu M, Ben-Ze’ev A, Bromberg JF, Lamberti C, Verma U, Gaynor RB, Byers SW, Pestell RG. IKKα regulates mitogenic signaling through transcriptional induction of cyclin D1 via Tcf. Mol Biol Cell. 2003;14:585–599. doi: 10.1091/mbc.02-06-0101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber JD, Raben DM, Phillips PJ, Baldassare JJ. Sustained activation of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) is required for the continued expression of cyclin D1 in G1 phase. Biochem J. 1997;326:61–68. doi: 10.1042/bj3260061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J, Hong F, Kwon S, Kim SS, Kim DO, Kang HS, Lee SJ, Ha J, Kim SS. Activation of p38 MAPK induces cell cycle arrest via inhibition of Raf/ERK pathway during muscle differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;298:765–771. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(02)02562-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdiguero E, Ruiz-Bonilla V, Gresh L, Hui L, Ballestar E, Sousa-Victor P, Baeza-Raja B, Jardi M, Bosch-Comas A, Esteller M, Caelles C, Serrano AL, Wagner EF, Munoz-Canoves P. Genetic analysis of p38 MAP kinases in myogenesis: fundamental role of p38α in abrogating myoblast proliferation. EMBO J. 2007;26:1245–1256. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr FG. Gene fusions involving PAX and FOX family members in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncogene. 2001;20:5736–5746. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.