Abstract
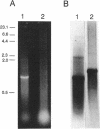
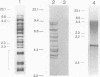
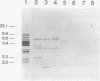
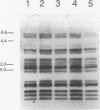
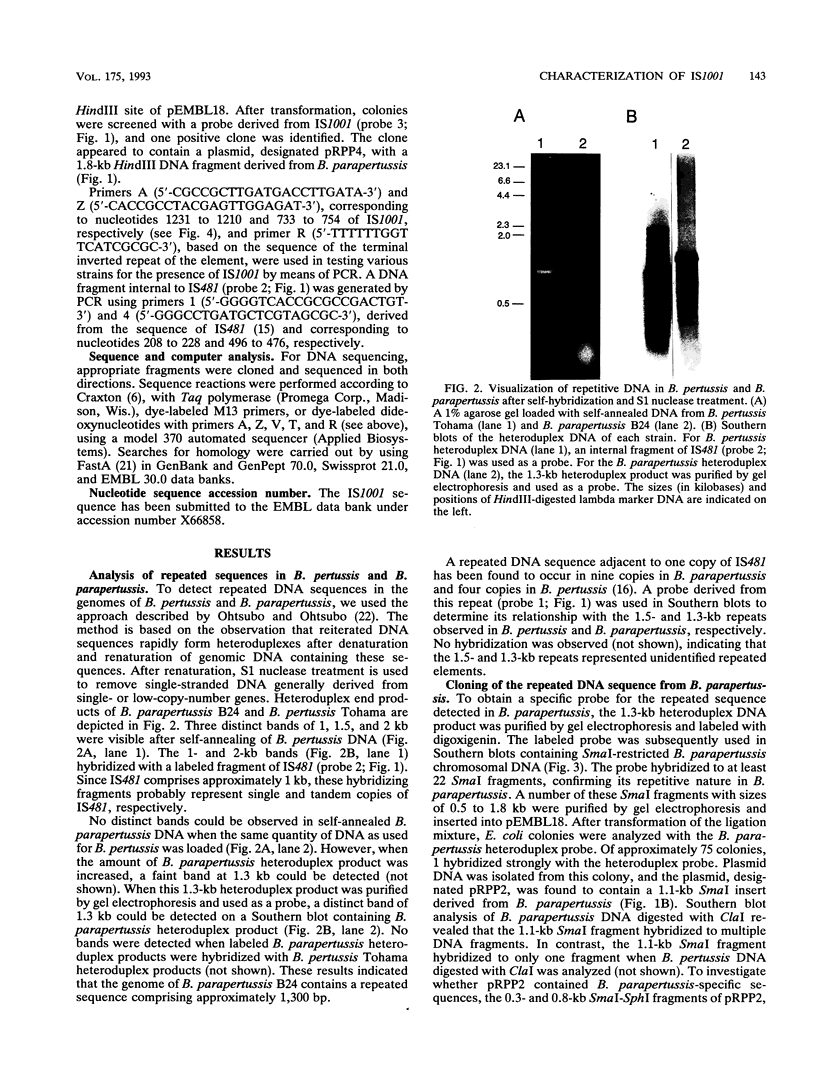
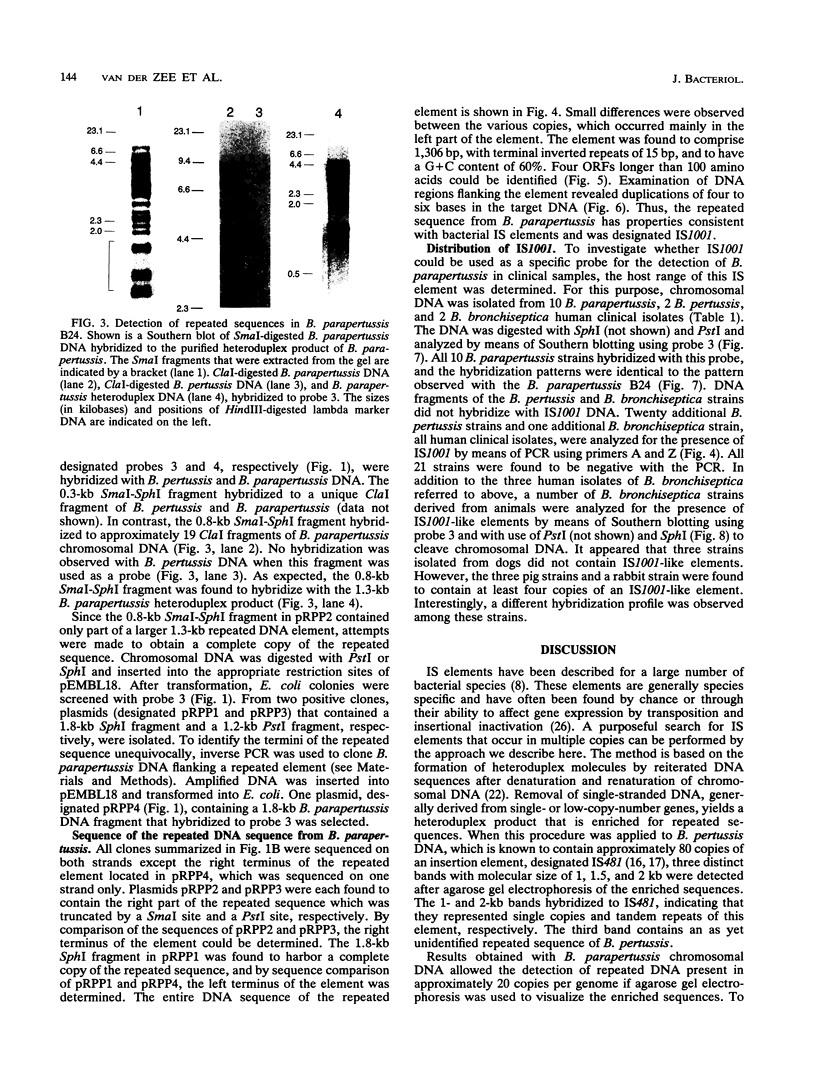
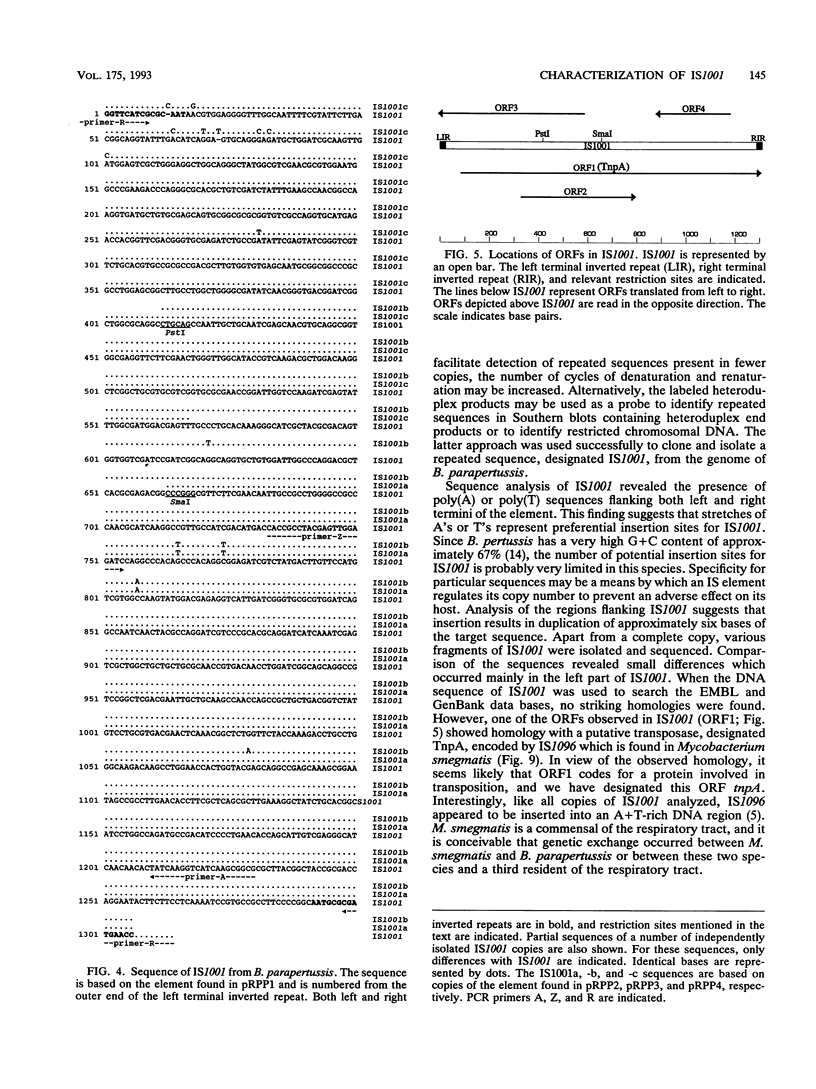
By analysis of repetitive DNA in Bordetella parapertussis, an insertion sequence element, designated IS1001, was identified. Sequence analysis revealed that IS1001 comprised 1,306 bp and contained inverted repeats at its termini. Furthermore, several open reading frames that may code for transposition functions were identified. The largest open reading frame coded for a protein comprising 406 amino acid residues and showed homology to TnpA, which is encoded by an insertion sequence element (IS1096) found in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Examination of flanking sequences revealed that insertion of IS1001 occurs preferentially in stretches of T's or A's and results in a duplication of target sequences of 6 to 8 bases. IS1001 was found in about 20 copies in 10 B. parapertussis strains analyzed. No restriction fragment length polymorphism was observed in B. parapertussis when IS1001 was used as a probe. An insertion sequence element similar or identical to IS1001 was found in B. bronchiseptica strains isolated from pigs and a rabbit. In these strains, about five copies of the IS1001-like element were present at different positions in the bacterial chromosome. Neither B. pertussis nor B. bronchiseptica strains isolated from humans and dogs contained an IS1001-like element. Therefore, IS1001 may be used as a specific probe for the detection of B. parapertussis in human clinical samples.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alsheikhly A. R., Löfdahl S. Identification of a DNA fragment in the genome of Bordetella pertussis carrying repeated DNA sequences also present in other Bordetella species. Microb Pathog. 1989 Mar;6(3):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirillo J. D., Barletta R. G., Bloom B. R., Jacobs W. R., Jr A novel transposon trap for mycobacteria: isolation and characterization of IS1096. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7772–7780. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7772-7780.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibert I., Barbé J., Casadesús J. Distribution of insertion sequence IS200 in Salmonella and Shigella. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Dec;136(12):2555–2560. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-12-2555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glare E. M., Paton J. C., Premier R. R., Lawrence A. J., Nisbet I. T. Analysis of a repetitive DNA sequence from Bordetella pertussis and its application to the diagnosis of pertussis using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1982–1987. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1982-1987.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans P. W., van Soolingen D., Dale J. W., Schuitema A. R., McAdam R. A., Catty D., van Embden J. D. Insertion element IS986 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a useful tool for diagnosis and epidemiology of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):2051–2058. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.2051-2058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houard S., Hackel C., Herzog A., Bollen A. Specific identification of Bordetella pertussis by the polymerase chain reaction. Res Microbiol. 1989 Sep;140(7):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irons L. I., Ashworth L. A., Robinson A. Release and purification of fimbriae from Bordetella pertussis. Dev Biol Stand. 1985;61:153–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnemann C. C., Perry E. B. Bordetella parapertussis. Recent experience and a review of the literature. Am J Dis Child. 1977 May;131(5):560–563. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1977.02120180074014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Keith J. M. Pertussis toxin gene: nucleotide sequence and genetic organization. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1258–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.3704651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLafferty M. A., Harcus D. R., Hewlett E. L. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of a repetitive DNA element from the genome of Bordetella pertussis with characteristics of an insertion sequence. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Aug;134(8):2297–2306. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-8-2297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPheat W. L., Hanson J. H., Livey I., Robertson J. S. Analysis of separate isolates of Bordetella pertussis repeated DNA sequences. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jun;135(6):1515–1520. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-6-1515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertsola J. Mixed outbreak of Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella parapertussis infection in Finland. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;4(2):123–128. doi: 10.1007/BF02013576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Bemis D. A., Ishikawa H., Selander R. K. Clonal diversity and host distribution in Bordetella bronchiseptica. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2793–2803. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2793-2803.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Hewlett E. L., Peppler M. S., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity and relationships in populations of Bordetella spp. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):230–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.230-237.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Arai H. Leucocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis. I. Purification and characterization. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):899–904. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.899-904.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. A. Mutations caused by the insertion of genetic material into the galactose operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Feb 28;40(1):93–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R., Hötte B., Klauke B., Kosier B. Isolation and characterization of insertion sequence elements from gram-negative bacteria by using new broad-host-range, positive selection vectors. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1502–1508. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1502-1508.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Soolingen D., Hermans P. W., de Haas P. E., Soll D. R., van Embden J. D. Occurrence and stability of insertion sequences in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains: evaluation of an insertion sequence-dependent DNA polymorphism as a tool in the epidemiology of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2578–2586. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2578-2586.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]