Abstract
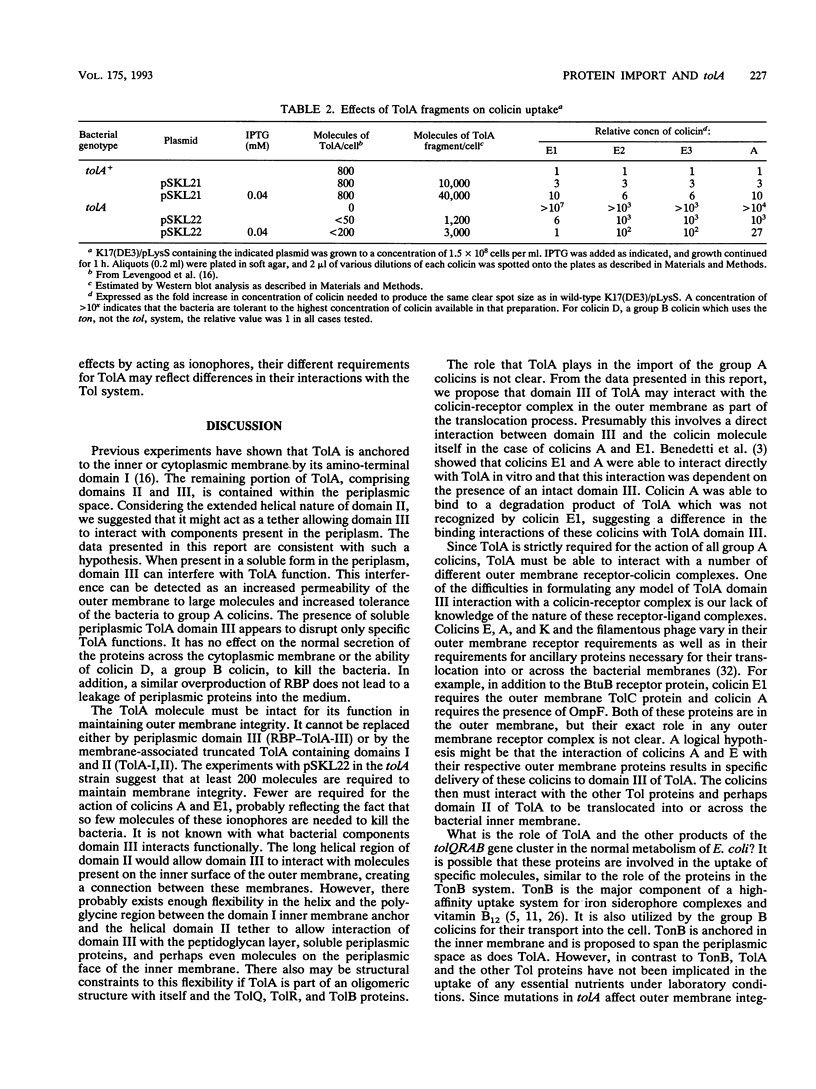
The TolA protein is involved in maintaining the integrity of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli, as mutations in tolA cause the bacteria to become hypersensitive to detergents and certain antibiotics and to leak periplasmic proteins into the medium. This protein also is required for the group A colicins to exert their effects and for many of the filamentous single-stranded bacteriophage to infect the bacterial cell. TolA is a three-domain protein, with the amino-terminal domain anchoring it to the inner membrane. The helical second domain is proposed to span the periplasmic space to allow the carboxyl-terminal third domain to interact with the outer membrane. A plasmid that allowed the synthesis and transport of the carboxyl-terminal third domain into the periplasmic space was constructed. The presence of an excess of this domain in the periplasm of a wild-type cell resulted in an increased sensitivity to deoxycholate, the release of periplasmic alkaline phosphatase and RNase into the medium, and an increased tolerance to colicins E1, E2, E3, and A. There was no effect on the cells' response to colicin D, which depends on TonB instead of TolA for its action. The presence of the free carboxyl-terminal domain of TolA in the periplasm in a tolA null mutation did not restore the wild-type phenotype, suggesting that this domain must be part of the intact TolA molecule to perform its function. Our results are consistent with a model in which the carboxyl-terminal domain of TolA interacts with components in the periplasm or on the inner surface of the outer membrane to function in maintaining the integrity of this membrane.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins J. F., Weiss R. B., Gesteland R. F. Ribosome gymnastics--degree of difficulty 9.5, style 10.0. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90007-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E. Areas of adhesion between wall and membrane of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Oct;53(3):395–404. doi: 10.1099/00221287-53-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti H., Lazdunski C., Lloubès R. Protein import into Escherichia coli: colicins A and E1 interact with a component of their translocation system. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):1989–1995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07728.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein A., Rolfe B., Onodera K. Pleiotropic properties and genetic organization of the tolA,B locus of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):74–83. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.74-83.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Günter K., Hantke K. Transport of iron across the outer membrane. Biol Met. 1991;4(1):14–22. doi: 10.1007/BF01135552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. K., Reeves P. Genetics of resistance to colicins in Escherichia coli K-12: cross-resistance among colicins of group A. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):102–117. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.102-117.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. K., Reeves P. Genetics of resistance to colicins in Escherichia coli K-12: cross-resistance among colicins of group B. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):96–101. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.96-101.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garwin J. L., Beckwith J. Secretion and processing of ribose-binding protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):789–792. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.789-792.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groarke J. M., Mahoney W. C., Hope J. N., Furlong C. E., Robb F. T., Zalkin H., Hermodson M. A. The amino acid sequence of D-ribose-binding protein from Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):12952–12956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadner R. J. Vitamin B12 transport in Escherichia coli: energy coupling between membranes. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2027–2033. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellenberger E. The 'Bayer bridges' confronted with results from improved electron microscopy methods. Mol Microbiol. 1990 May;4(5):697–705. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzaroni J. C., Fognini-Lefebvre N., Portalier R. Cloning of the excC and excD genes involved in the release of periplasmic proteins by Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Sep;218(3):460–464. doi: 10.1007/BF00332410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levengood S. K., Beyer W. F., Jr, Webster R. E. TolA: a membrane protein involved in colicin uptake contains an extended helical region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):5939–5943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.5939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levengood S. K., Webster R. E. Nucleotide sequences of the tolA and tolB genes and localization of their products, components of a multistep translocation system in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6600–6609. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6600-6609.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloubes R., Baty D., Lazdunski C. The promoters of the genes for colicin production, release and immunity in the ColA plasmid: effects of convergent transcription and Lex A protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2621–2636. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopilato J. E., Garwin J. L., Emr S. D., Silhavy T. J., Beckwith J. R. D-ribose metabolism in Escherichia coli K-12: genetics, regulation, and transport. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):665–673. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.665-673.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel de Zwaig R., Luria S. E. Genetics and physiology of colicin-tolerant mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1112–1123. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1112-1123.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Witten C. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. 3. Colicin-tolerant mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1093–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1093-1111.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Cabelli R. J., Dolan K. M., Jarosik G. P. Azide-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli alter the SecA protein, an azide-sensitive component of the protein export machinery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8227–8231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postle K. TonB and the gram-negative dilemma. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2019–2025. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiver J. W., Cramer W. A., Cohen F. S., Bishop L. J., de Jong P. J. On the explanation of the acidic pH requirement for in vitro activity of colicin E1. Site-directed mutagenesis at Glu-468. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14273–14281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. P., Webster R. E. Nucleotide sequence of a gene cluster involved in entry of E colicins and single-stranded DNA of infecting filamentous bacteriophages into Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2667–2674. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2667-2674.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. P., Webster R. E. fii, a bacterial locus required for filamentous phage infection and its relation to colicin-tolerant tolA and tolB. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):107–115. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.107-115.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. E. The tol gene products and the import of macromolecules into Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1991 May;5(5):1005–1011. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]