Abstract
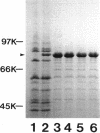
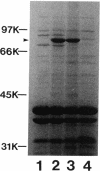
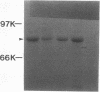
Pseudomonas aeruginosa K407, a mutant lacking a high-affinity 80,000-molecular-weight ferric enterobactin receptor protein (80K protein), exhibited poor growth (small colonies) on iron-deficient succinate minimal medium containing ethylenediamine-di(o-hydroxyphenylacetic acid) (EDDHA) and enterobactin. The gene encoding the ferric enterobactin receptor was cloned by complementation of this growth defect. The complementing DNA was subsequently localized to a 7.1-kilobase-pair (kb) SstI-HindIII fragment which was able to restore synthesis of the 80K protein in strain K407 and also to direct the synthesis of high levels of a protein of the same molecular weight in the outer membranes of Escherichia coli fepA strains MT912 and IR20. Moreover, the fragment complemented the fepA mutation in MT912, restoring both growth in EDDHA-containing medium and enterobactin-dependent uptake of 55Fe3+. Expression of the P. aeruginosa receptor in E. coli IR20 was shown to be regulated by both iron and enterobactin. The complementing DNA was further localized to a 5.3-kb SphI-SstI fragment which was then subjected to deletion analysis to obtain the smallest fragment capable of directing the synthesis of the 80K protein in the outer membrane of strain K407. A 3.2-kb DNA fragment that restored production of the receptor in strain K407 was subsequently isolated. The fragment also directed synthesis of the protein in E. coli MT912 but at levels much lower than those previously observed. Nucleotide sequencing of the fragment revealed an open reading frame (designated pfeA for Pseudomonas ferric enterobactin) of 2,241 bp capable of encoding a 746-amino-acid protein with a molecular weight of 80,967. The PfeA protein showed more than 60% homology to the E. coli FepA protein. Consistent with this, the two proteins showed significant immunological cross-reactivity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry D., Kropinski A. M. Effect of lipopolysaccharide mutations and temperature on plasmid transformation efficiency in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1986 May;32(5):436–438. doi: 10.1139/m86-082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderwood S. B., Mekalanos J. J. Iron regulation of Shiga-like toxin expression in Escherichia coli is mediated by the fur locus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4759–4764. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4759-4764.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Griffiths E. Antigenic and molecular homology of the ferric enterobactin receptor protein of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jun;131(6):1503–1509. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-6-1503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis P., Moguilevsky N., Jacques J. F., Masson P. L. Study of the siderophores and receptors in different clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1987;39:290–306. doi: 10.1159/000414354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D., Adams P. Siderophore activity of pyoverdin for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):130–138. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.130-138.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D. Effect of pyochelin on the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):17–23. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.17-23.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D. Iron uptake with ferripyochelin and ferric citrate by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):581–587. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.581-587.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H. The relationship of plasmid-mediated iron transport and bacterial virulence. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:69–89. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Casadaban M. J. In vivo cloning of Pseudomonas aeruginosa genes with mini-D3112 transposable bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3917–3925. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3917-3925.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Casadaban M. J. Mini-D3112 bacteriophage transposable elements for genetic analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3909–3916. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3909-3916.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkins M. F., Earhart C. F. Nucleotide sequence and regulation of the Escherichia coli gene for ferrienterobactin transport protein FepB. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5443–5451. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5443-5451.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Stinnett J. D., Eagon R. G. Ultrastructural and chemical alteration of the cell envelope of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, associated with resistance to ethylenediaminetetraacetate resulting from growth in a Mg2+-deficient medium. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):302–311. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.302-311.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudmundsdottir A., Bell P. E., Lundrigan M. D., Bradbeer C., Kadner R. J. Point mutations in a conserved region (TonB box) of Escherichia coli outer membrane protein BtuB affect vitamin B12 transport. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6526–6533. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6526-6533.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Hantke K., Braun V. Iron transport in Escherichia coli K-12. 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoate-promoted iron uptake. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Sep 28;114(3):231–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00446867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantke K., Braun V. A function common to iron-enterochelin transport and action of colicins B, I, V in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1975 Nov 15;59(2):277–281. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80392-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrichs D. E., Young L., Poole K. Pyochelin-mediated iron transport in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: involvement of a high-molecular-mass outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3680–3684. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3680-3684.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann H., Fischer E., Kraut H., Braun V. Preparation of the FhuA (TonA) receptor protein from cell envelopes of an overproducing strain of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):404–411. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.404-411.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohnadel D., Meyer J. M. Specificity of pyoverdine-mediated iron uptake among fluorescent Pseudomonas strains. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4865–4873. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4865-4873.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihara S., Mizushima S. Identification of an outer membrane protein responsible for the binding of the Fe-enterochelin complex to Escherichia coli cells. J Biochem. 1978 Jan;83(1):137–140. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka K., Bindereif A., Neilands J. B. Aerobactin-mediated utilization of transferrin iron. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 7;21(25):6503–6508. doi: 10.1021/bi00268a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langman L., Young I. G., Frost G. E., Rosenberg H., Gibson F. Enterochelin system of iron transport in Escherichia coli: mutations affecting ferric-enterochelin esterase. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1142–1149. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1142-1149.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V., Shokrani F. Biological activities of pyochelins: iron-chelating agents of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):878–890. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.878-890.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundrigan M. D., Kadner R. J. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the ferrienterochelin receptor FepA in Escherichia coli. Homology among outer membrane receptors that interact with TonB. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10797–10801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh M. A., Chenault S. S., Earhart C. F. Genetic and physiological studies on the relationship between colicin B resistance and ferrienterochelin uptake in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):653–657. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.653-657.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. M., Hohnadel D., Khan A., Cornelis P. Pyoverdin-facilitated iron uptake in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: immunological characterization of the ferripyoverdin receptor. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1401–1405. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy C. K., Kalve V. I., Klebba P. E. Surface topology of the Escherichia coli K-12 ferric enterobactin receptor. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2736–2746. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2736-2746.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Iron absorption and transport in microorganisms. Annu Rev Nutr. 1981;1:27–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.01.070181.000331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial iron compounds. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:715–731. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozenberger B. A., Nahlik M. S., McIntosh M. A. Genetic organization of multiple fep genes encoding ferric enterobactin transport functions in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3638–3646. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3638-3646.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. R., Earhart C. F. Escherichia coli K-12 envelope proteins specifically required for ferrienterobactin uptake. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):930–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.930-936.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. R., Pickett C. L., Earhart C. F. Two fep genes are required for ferrienterochelin uptake in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):330–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.330-336.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole K., Neshat S., Heinrichs D. Pyoverdine-mediated iron transport in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: involvement of a high-molecular-mass outer membrane protein. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Feb;62(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole K., Young L., Neshat S. Enterobactin-mediated iron transport in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6991–6996. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6991-6996.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postle K., Skare J. T. Escherichia coli TonB protein is exported from the cytoplasm without proteolytic cleavage of its amino terminus. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):11000–11007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. W., Storey D. G., Vasil A. I., Vasil M. L. Regulation of toxA and regA by the Escherichia coli fur gene and identification of a Fur homologue in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA103 and PA01. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2823–2831. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Iron-Binding Catechols and Virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):445–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.445-456.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutz J. M., Abdullah T., Singh S. P., Kalve V. I., Klebba P. E. Evolution of the ferric enterobactin receptor in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):5964–5974. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.5964-5974.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. 3. Evidence that the major protein of Escherichia coli O111 outer membrane consists of four distinct polypeptide species. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):442–453. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.442-453.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sriyosachati S., Cox C. D. Siderophore-mediated iron acquisition from transferrin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):885–891. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.885-891.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Breeding S. A., Lankford C. E. Enterochelin (enterobactin): virulence factor for Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):174–180. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.174-180.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]