Abstract
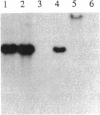
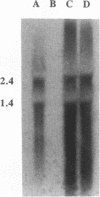
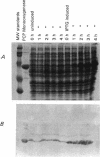
The pcpB gene of Flavobacterium sp. strain ATCC 39723 was cloned by using a degenerate primer designed from the N-terminal sequence of the purified enzyme. The nucleotide sequence of pcpB was determined and found to encode an open reading frame of 1,614 nucleotides, yielding a predicted translation product of 538 amino acids, in agreement with the estimated size of the purified protein analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The transcriptional start of pcpB was found to be 80 bp upstream of the translational start, and the transcript was found to be induced in Flavobacterium sp. strain ATCC 39723 by the presence of pentachlorophenol but to be constitutive in the Escherichia coli pcpB clone. DNA hybridizations with genomic DNAs from Arthrobacter sp. strain ATCC 33790 and Pseudomonas sp. strain SR3 revealed a similar-size 3.0-kb EcoRI fragment, whereas there was no positive hybridization with genomic DNA from Rhodococcus chlorophenolicus. Cell extracts from an E. coli pcpB overexpression strain, as well as the whole cells, were proficient in the dechlorination of pentachlorophenol to tetrachlorohydroquinone. Protein data base comparisons of the predicted translation products revealed regions of homology with other microbial monooxygenases, including phenol-2-monooxygenase and tryptophan-2-monooxygenase.
Full text
PDF


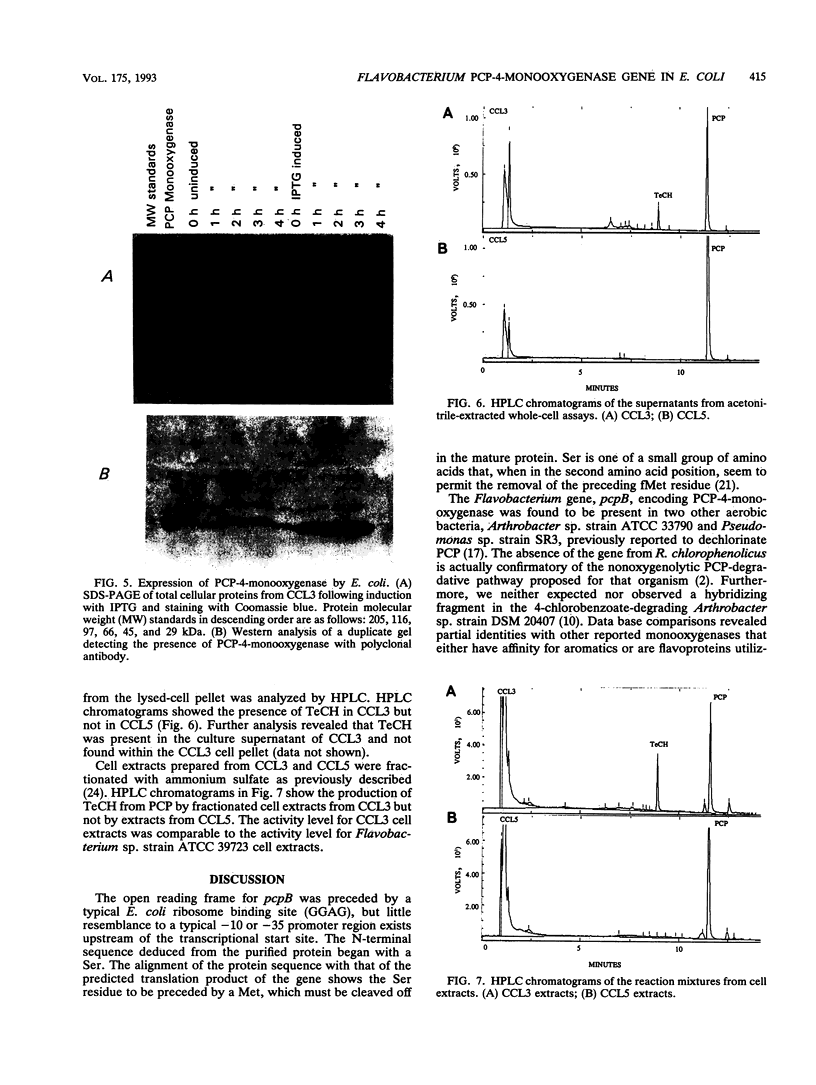

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apajalahti J. H., Salkinoja-Salonen M. S. Dechlorination and para-hydroxylation of polychlorinated phenols by Rhodococcus chlorophenolicus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):675–681. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.675-681.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunel F., Davison J. Cloning and sequencing of Pseudomonas genes encoding vanillate demethylase. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4924–4930. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4924-4930.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Sal G., Manfioletti G., Schneider C. The CTAB-DNA precipitation method: a common mini-scale preparation of template DNA from phagemids, phages or plasmids suitable for sequencing. Biotechniques. 1989 May;7(5):514–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohana Rao J. K., Argos P. A conformational preference parameter to predict helices in integral membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 30;869(2):197–214. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90295-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Oltmanns R. H., Lingens F. Enzymatic dehalogenation of 4-chlorobenzoate by extracts from Arthrobacter sp. SU DSM 20407. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1988 Jul;369(7):567–571. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1988.369.2.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins E. J., Gordon M. P., Caceres O., Lurquin P. F. Organization and sequence analysis of the 2,4-dichlorophenol hydroxylase and dichlorocatechol oxidative operons of plasmid pJP4. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2351–2359. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2351-2359.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saber D. L., Crawford R. L. Isolation and characterization of Flavobacterium strains that degrade pentachlorophenol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Dec;50(6):1512–1518. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.6.1512-1518.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk T., Müller R., Mörsberger F., Otto M. K., Lingens F. Enzymatic dehalogenation of pentachlorophenol by extracts from Arthrobacter sp. strain ATCC 33790. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5487–5491. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5487-5491.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sejlitz T., Wernstedt C., Engström A., Neujahr H. Y. Amino acid sequences around the pyridoxal-5'-phosphate-binding sites of phenol hydroxylase. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 12;187(1):225–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. C. A simple method for extraction of RNA from E. coli utilizing diethyl pyrocarbonate. Anal Biochem. 1970 Feb;33(2):459–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T. Metabolism of pentachlorophenol by a soil microbe. J Environ Sci Health B. 1977;12(2):113–127. doi: 10.1080/03601237709372057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunasawa S., Stewart J. W., Sherman F. Amino-terminal processing of mutant forms of yeast iso-1-cytochrome c. The specificities of methionine aminopeptidase and acetyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5382–5391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xun L. Y., Orser C. S. Purification of a Flavobacterium pentachlorophenol-induced periplasmic protein (PcpA) and nucleotide sequence of the corresponding gene (pcpA). J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2920–2926. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2920-2926.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xun L., Orser C. S. Purification and properties of pentachlorophenol hydroxylase, a flavoprotein from Flavobacterium sp. strain ATCC 39723. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4447–4453. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4447-4453.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xun L., Topp E., Orser C. S. Confirmation of oxidative dehalogenation of pentachlorophenol by a Flavobacterium pentachlorophenol hydroxylase. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(17):5745–5747. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.17.5745-5747.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xun L., Topp E., Orser C. S. Diverse substrate range of a Flavobacterium pentachlorophenol hydroxylase and reaction stoichiometries. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):2898–2902. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2898-2902.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Palm C. J., Brooks B., Kosuge T. Nucleotide sequences of the Pseudomonas savastanoi indoleacetic acid genes show homology with Agrobacterium tumefaciens T-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6522–6526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]