Abstract
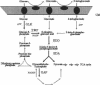
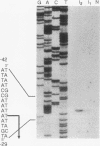
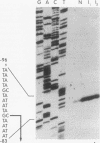
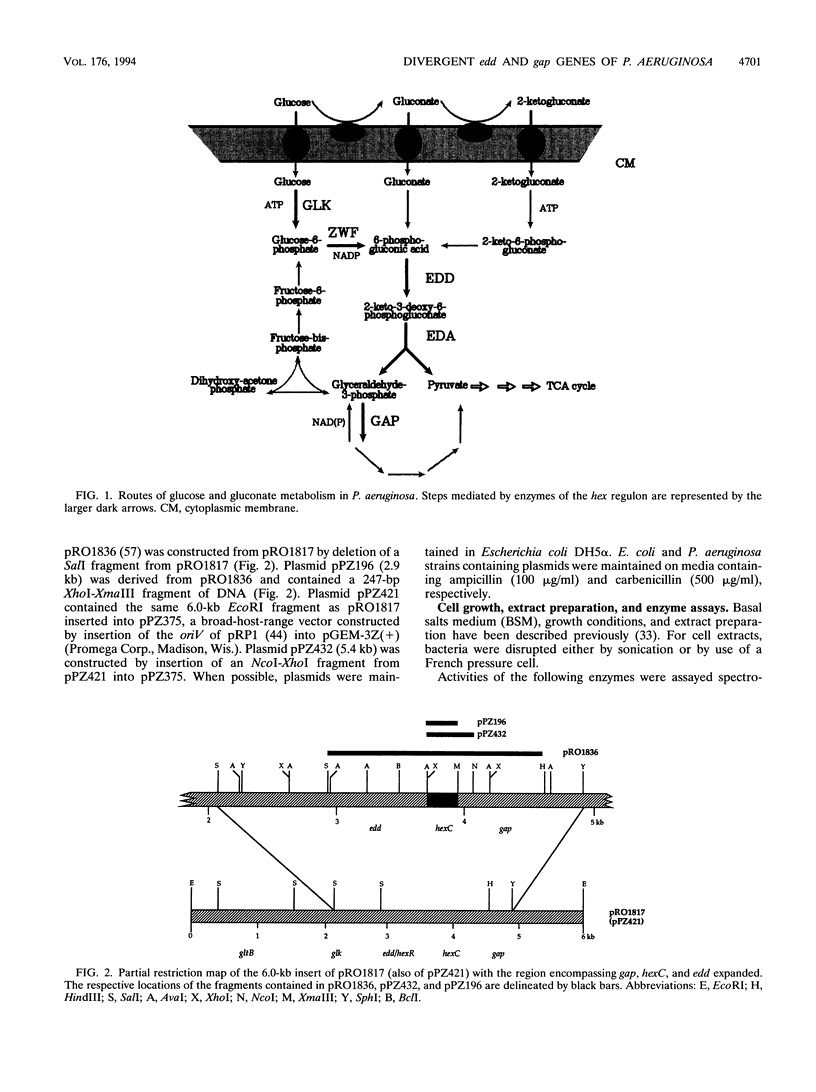
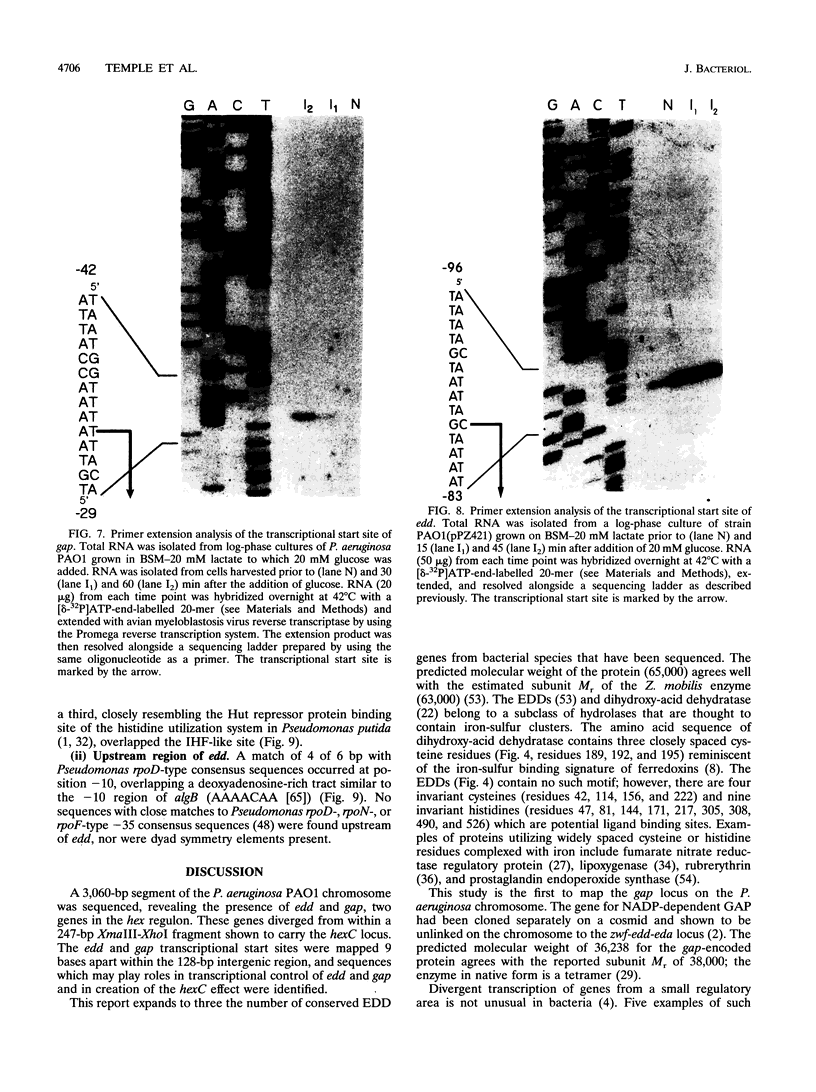
The hexC locus of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 was localized to a 247-bp segment of chromosomal DNA on the multicopy broad-host-range vector pRO1614. The presence of this plasmid (pPZ196) in strain PAO1 produced the so-called "hexC effect," a two- to ninefold increase in the activities of four carbohydrate catabolism enzymes, glucokinase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, 6-phosphogluconate dehydratase, and 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate aldolase. The extent of the hexC effect was restricted, since three independently regulated metabolic enzymes were not affected by the presence of the hexC plasmid. Furthermore, the hexC-containing plasmid did not suppress catabolite repression control. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the segment of DNA encompassing hexC revealed a 128-bp region rich in adenosine-plus-thymine (AT) content separating two divergent open reading frames (ORFs). Transcriptional start sites for these two genes were mapped to the intergenic region, demonstrating that this sequence contained overlapping divergent promoters. The intergenic region contained potential regulatory sequences such as dyad symmetry motifs, polydeoxyadenosine tracts, and a sequence matching the integration host factor recognition site in Escherichia coli. One of the ORFs encoded a 610-amino-acid protein with 55 to 60% identity to 6-phosphogluconate dehydratase from E. coli and Zymomonas mobilis. The second ORF coded for a protein of 335 amino acids that displayed 45 to 60% identity to the NAD-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAP) family of enzymes. The NAD-dependent GAP gene on the P. aeruginosa chromosome was previously unmapped. GAP was found to exhibit the hexC-dependent increase in its basal activity, establishing it as a fifth catabolic enzyme in the multioperonic hex regulon.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison S. L., Phillips A. T. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the repressor for the histidine utilization genes of Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5470–5476. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5470-5476.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee P. C., Darzins A., Maitra P. K. Gluconeogenic mutations in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: genetic linkage between fructose-bisphosphate aldolase and phosphoglycerate kinase. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Apr;133(4):1099–1107. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-4-1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnell W. O., Yi K. C., Conway T. Sequence and genetic organization of a Zymomonas mobilis gene cluster that encodes several enzymes of glucose metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7227–7240. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7227-7240.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck C. F., Warren R. A. Divergent promoters, a common form of gene organization. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Sep;52(3):318–326. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.3.318-326.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bever R. A., Iglewski B. H. Molecular characterization and nucleotide sequence of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase structural gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4309–4314. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4309-4314.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruschi M., Guerlesquin F. Structure, function and evolution of bacterial ferredoxins. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1988 Apr-Jun;4(2):155–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1988.tb02741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers L. D. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1982;89(Pt 500):326–335. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)89059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M., Crawford I. P. In vitro determination of the effect of indoleglycerol phosphate on the interaction of purified TrpI protein with its DNA-binding sites. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1590–1597. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1590-1597.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. H., Gibson J. L., McCue L. A., Tabita F. R. Identification, expression, and deduced primary structure of transketolase and other enzymes encoded within the form II CO2 fixation operon of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20447–20452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway T., Sewell G. W., Ingram L. O. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene from Zymomonas mobilis: cloning, sequencing, and identification of promoter region. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5653–5662. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5653-5662.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. L., Cox B. J., Fidanza V., Calhoun D. H. The complete nucleotide sequence of the ilvGMEDA cluster of Escherichia coli K-12. Gene. 1987;56(2-3):185–198. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuskey S. M., Phibbs P. V., Jr Chromosomal mapping of mutations affecting glycerol and glucose catabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):872–880. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.872-880.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuskey S. M., Phibbs P. V., Jr Chromosomal mapping of mutations affecting glycerol and glucose catabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):872–880. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.872-880.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Gill J. F., Chakrabarty A. M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis: nucleotide sequence and transcriptional regulation of the algD gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4567–4581. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Kammerer W., Gentz R., Bujard H. Promoters of Escherichia coli: a hierarchy of in vivo strength indicates alternate structures. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2987–2994. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04596.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew R., Lowe N. Positive control of Pseudomonas aeruginosa amidase synthesis is mediated by a transcription anti-termination mechanism. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Apr;135(4):817–823. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-4-817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan S. E., Fliege R., Tong S., Shibata A., Wolf R. E., Jr, Conway T. Molecular characterization of the Entner-Doudoroff pathway in Escherichia coli: sequence analysis and localization of promoters for the edd-eda operon. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(14):4638–4646. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4638-4646.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint D. H., Emptage M. H., Finnegan M. G., Fu W., Johnson M. K. The role and properties of the iron-sulfur cluster in Escherichia coli dihydroxy-acid dehydratase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14732–14742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich M., Ramani N., Mathew E., Sirko A., Tsui P. The role of integration host factor in gene expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2557–2563. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomada M., Inouye S., Imaishi H., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T. Analysis of an upstream regulatory sequence required for activation of the regulatory gene xylS in xylene metabolism directed by the TOL plasmid of Pseudomonas putida. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jun;233(3):419–426. doi: 10.1007/BF00265439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. L., Smith D. H., Baldridge J. S., Harkins R. N., Vasil M. L., Chen E. Y., Heyneker H. L. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression in Escherichia coli of the exotoxin A structural gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2645–2649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J., Sharrocks A. D., Green B., Geisow M., Guest J. R. Properties of FNR proteins substituted at each of the five cysteine residues. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Apr;8(1):61–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington R. E. DNA curving and bending in protein-DNA recognition. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2549–2555. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtel A., Timmis K. N., Ramos J. L. Upstream binding sequences of the XylR activator protein and integration host factor in the xylS gene promoter region of the Pseudomonas TOL plasmid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1755–1762. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L., Allison S. L., Phillips A. T. Identification of multiple repressor recognition sites in the hut system of Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4189–4195. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4189-4195.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Phibbs P. V., Jr Independent regulation of hexose catabolizing enzymes and glucose transport activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1041–1048. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90813-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Noguchi M., Miyano M., Matsumoto T., Noma M. Mutagenesis studies on the amino acid residues involved in the iron-binding and the activity of human 5-lipoxygenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 14;182(3):1482–1490. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91901-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb V. F., Jr, Bernlohr R. W. A new spectrophotometric assay for protein in cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):362–371. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz D. M., Jr, Prickril B. C. Intrapeptide sequence homology in rubrerythrin from Desulfovibrio vulgaris: identification of potential ligands to the diiron site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Nov 27;181(1):337–341. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81423-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessie T. G., Phibbs P. V., Jr Alternative pathways of carbohydrate utilization in pseudomonads. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:359–388. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao H. H., Rabinowitz J. C. Clostridial apoferredoxin messenger ribonucleic acid. Assay and partial purification. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 29;608(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer A. A., Loutit J. S. Transformation and transfection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: effects of metal ions. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):37–42. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.37-42.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr C. D., Deretic V. In vitro interactions of the histone-like protein IHF with the algD promoter, a critical site for control of mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):837–844. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92279-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., DeBusscher G., McCombie W. R. Development of broad-host-range vectors and gene banks: self-cloning of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):60–69. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.60-69.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret C., Desplan C., Thomasset M. Cholecalcin (a 9-kDa cholecalciferol-induced calcium-binding protein) messenger RNA. Distribution and induction by calcitriol in the rat digestive tract. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jul 1;150(1):211–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard A. E., Vasil M. L. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a phosphate-regulated gene encoding a secreted hemolysin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.291-298.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivers D. B., Blevins W. T. Multiple enzyme forms of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Nov;133(11):3159–3164. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-11-3159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehl R. A., Feary T. W., Phibbs P. V., Jr Clustering of mutations affecting central pathway enzymes of carbohydrate catabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1123–1129. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1123-1129.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothmel R. K., Shinabarger D. L., Parsek M. R., Aldrich T. L., Chakrabarty A. M. Functional analysis of the Pseudomonas putida regulatory protein CatR: transcriptional studies and determination of the CatR DNA-binding site by hydroxyl-radical footprinting. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4717–4724. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4717-4724.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K., Griffiths-Smith K. Use of differential dye-ligand chromatography with affinity elution for enzyme purification: 6-phosphogluconate dehydratase from Zymomonas mobilis. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;136(2):530–534. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90257-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa T., Smith W. L. Essential histidines of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase. His-309 is involved in heme binding. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6168–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple L., Cuskey S. M., Perkins R. E., Bass R. C., Morales N. M., Christie G. E., Olsen R. H., Phibbs P. V., Jr Analysis of cloned structural and regulatory genes for carbohydrate utilization in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6396–6402. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6396-6402.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari N. P., Campbell J. J. Enzymatic control of the metabolic activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown in glucose or succinate media. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 30;192(3):395–401. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90388-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Lara J. C., Lory S. The rpoN gene product of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is required for expression of diverse genes, including the flagellin gene. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):389–396. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.389-396.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Lory S. Characterization of the type a flagellin gene from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7188–7199. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7188-7199.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toussaint B., Delic-Attree I., Vignais P. M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa contains an IHF-like protein that binds to the algD promoter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Oct 15;196(1):416–421. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Iglewski B. H. Codon usage in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9323–9335. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak D. J., Ohman D. E. Involvement of the alginate algT gene and integration host factor in the regulation of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa algB gene. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(13):4145–4153. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.13.4145-4153.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorenzo V., Herrero M., Metzke M., Timmis K. N. An upstream XylR- and IHF-induced nucleoprotein complex regulates the sigma 54-dependent Pu promoter of TOL plasmid. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1159–1167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer J. R., Frijters A. C., Leveau J. H., Eggen R. I., Zehnder A. J., de Vos W. M. Characterization of the Pseudomonas sp. strain P51 gene tcbR, a LysR-type transcriptional activator of the tcbCDEF chlorocatechol oxidative operon, and analysis of the regulatory region. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3700–3708. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3700-3708.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gabain A., Belasco J. G., Schottel J. L., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Decay of mRNA in Escherichia coli: investigation of the fate of specific segments of transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]