Abstract
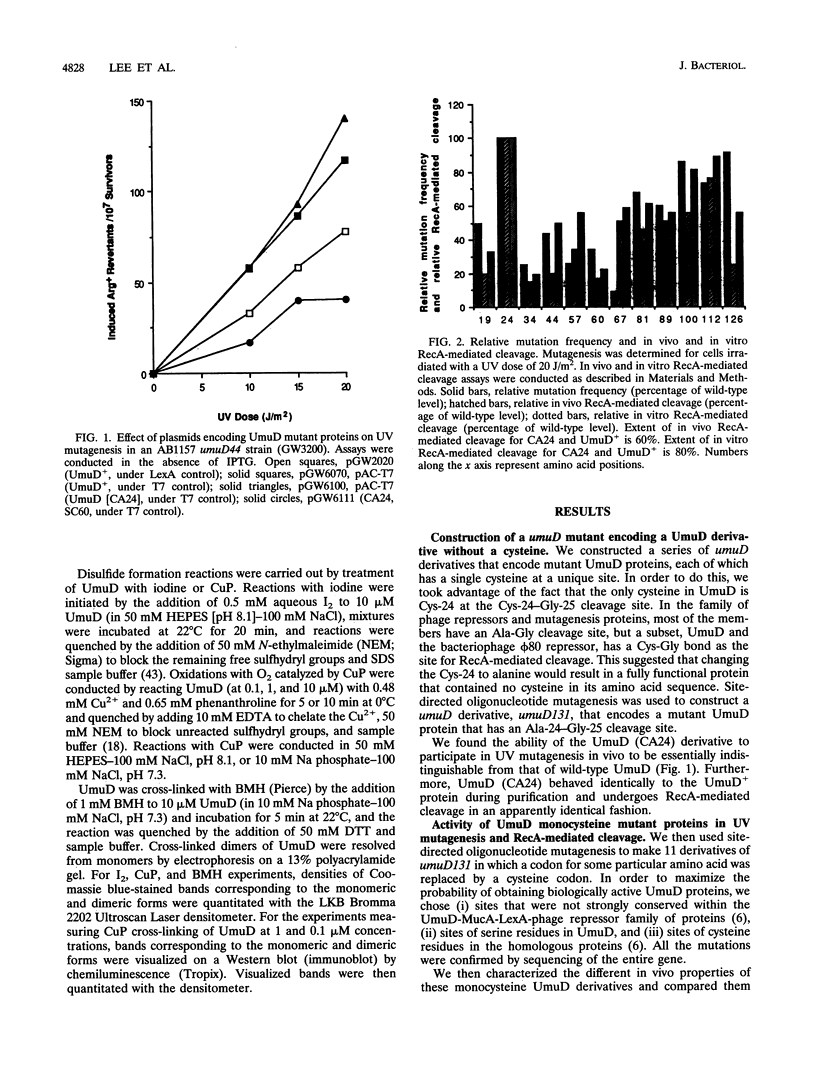
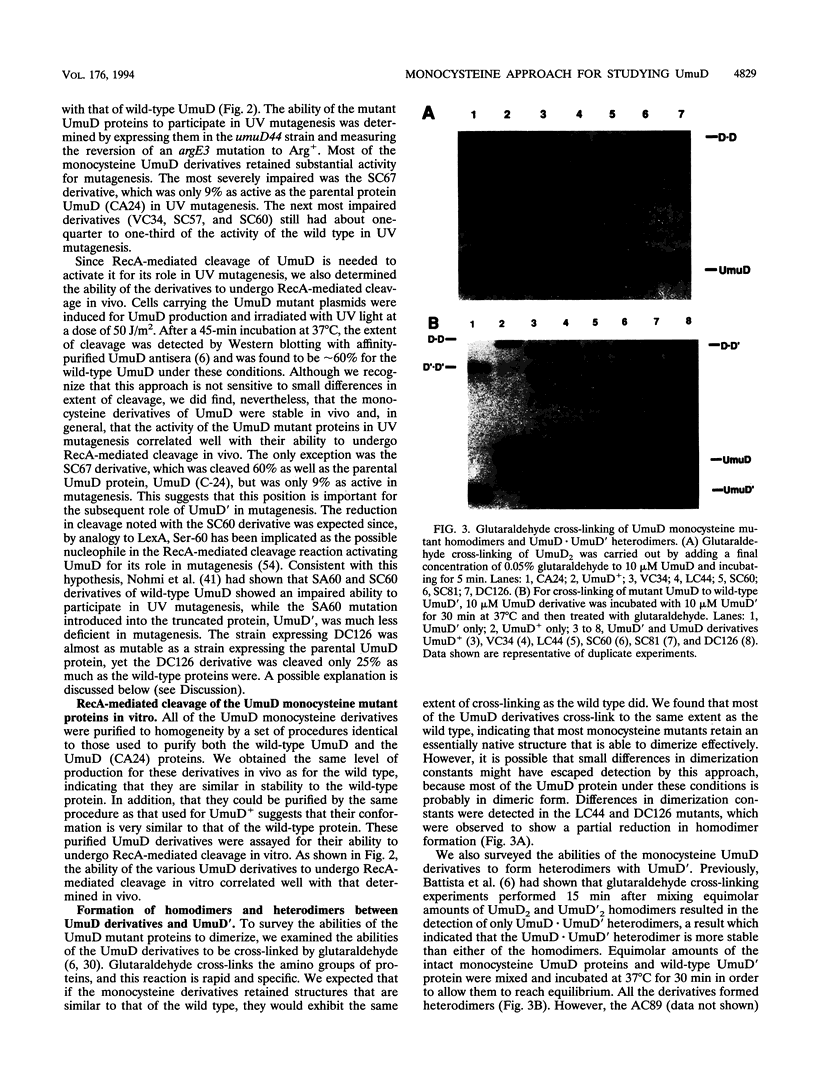
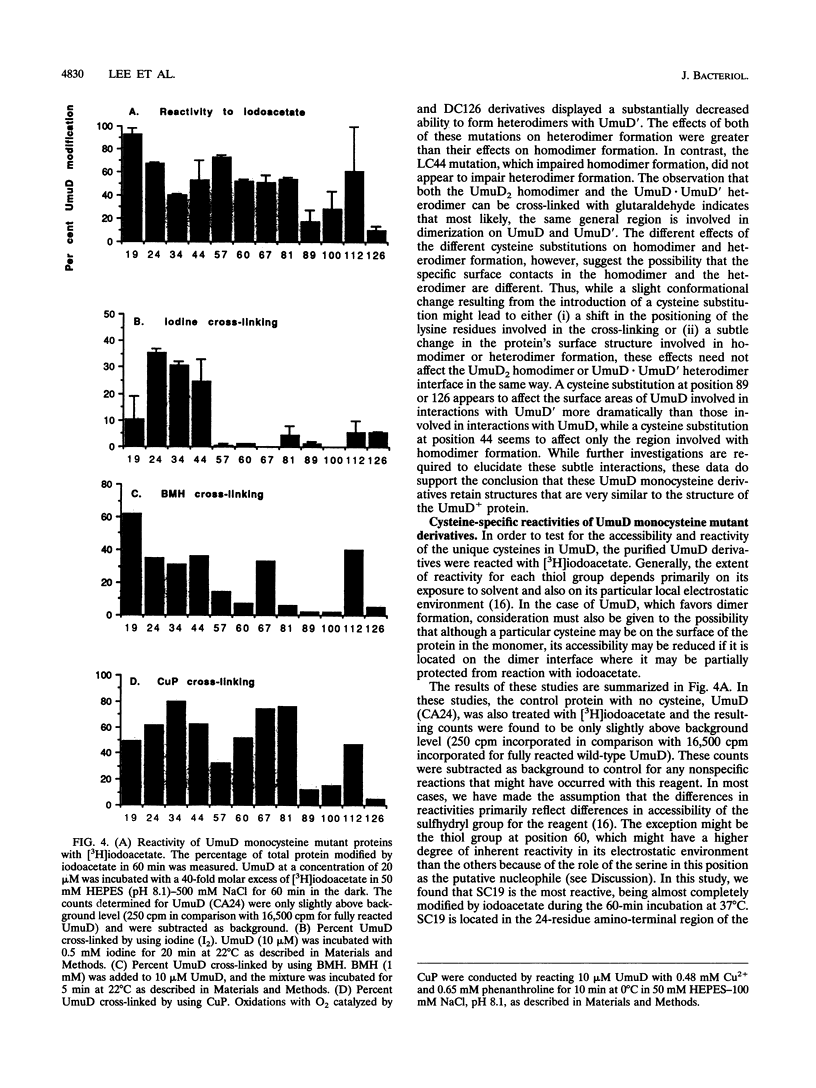
UmuD participates in a variety of protein-protein interactions that appear to be essential for its role in UV mutagenesis. To learn about these interactions, we have initiated an approach based on the construction of a series of monocysteine derivatives of UmuD and have carried out experiments exploring the chemistry of the unique thiol group in each derivative. In vivo and in vitro characterizations indicate that these proteins have an essentially native structure. In proposing a model for the interactions of UmuD in the homodimer, we have made the following assumptions: (i) the conformations of the mutant proteins are similar to that of the wild type, and (ii) the differences in reactivity of the mutant proteins are predominantly due to the positional effects of the single cysteine substitutions. The model proposes the following. The region including the Cys-24-Gly-25 cleavage site, Val-34, and Leu-44 are closer to the interface than the other positions tested as suggested by the relative ease of dimer cross-linking of the monocysteine derivatives at these positions by oxidation with iodine (I2) and by reaction with bis-maleimidohexane. The mutant with a Ser-to-Cys change at position 60 (SC60) is similar in iodoacetate reactivity to the preceding derivatives but cross-links less efficiently by I2 oxidation. This suggests that Ser-60, the site of the putative nucleophile in the cleavage reaction, is located further from the dimer interface or in a cleft region. Both Ser-19, located in the N-terminal fragment of UmuD that is removed by RecA-mediated cleavage, and Ser-67 are probably not as close to the dimer interface, since they are cross-linked more easily with bis-maleimidohexane than with I2. The SC67 mutant phenotype also suggests that this position is less important in RecA-mediated cleavage but more important in a subsequent role for UmuD in mutagenesis. Ala-89, Gln-100, and Asp-126 are probably not particularly solvent accessible and may play important roles in protein architecture.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggeler R., Capaldi R. A. ATP hydrolysis-linked structural changes in the N-terminal part of the gamma subunit of Escherichia coli F1-ATPase examined by cross-linking studies. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14576–14578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggeler R., Chicas-Cruz K., Cai S. X., Keana J. F., Capaldi R. A. Introduction of reactive cysteine residues in the epsilon subunit of Escherichia coli F1 ATPase, modification of these sites with tetrafluorophenyl azide-maleimides, and examination of changes in the binding of the epsilon subunit when different nucleotides are in catalytic sites. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 24;31(11):2956–2961. doi: 10.1021/bi00126a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altenbach C., Flitsch S. L., Khorana H. G., Hubbell W. L. Structural studies on transmembrane proteins. 2. Spin labeling of bacteriorhodopsin mutants at unique cysteines. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7806–7812. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagg A., Kenyon C. J., Walker G. C. Inducibility of a gene product required for UV and chemical mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5749–5753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battista J. R., Ohta T., Nohmi T., Sun W., Walker G. C. Dominant negative umuD mutations decreasing RecA-mediated cleavage suggest roles for intact UmuD in modulation of SOS mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7190–7194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges B. A., Woodgate R. Mutagenic repair in Escherichia coli: products of the recA gene and of the umuD and umuC genes act at different steps in UV-induced mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4193–4197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bubis J., Khorana H. G. Sites of interaction in the complex between beta- and gamma-subunits of transducin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12995–12999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burckhardt S. E., Woodgate R., Scheuermann R. H., Echols H. UmuD mutagenesis protein of Escherichia coli: overproduction, purification, and cleavage by RecA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1811–1815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Fix O., Livneh Z. Biochemical analysis of UV mutagenesis in Escherichia coli by using a cell-free reaction coupled to a bioassay: identification of a DNA repair-dependent, replication-independent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3300–3304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Knoll B. J., Little J. W., Mount D. W. Preferential cleavage of phage lambda repressor monomers by recA protease. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):182–184. doi: 10.1038/294182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. M., McEntee K., Lehman I. R. A simple and rapid procedure for the large scale purification of the recA protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4676–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutreix M., Moreau P. L., Bailone A., Galibert F., Battista J. R., Walker G. C., Devoret R. New recA mutations that dissociate the various RecA protein activities in Escherichia coli provide evidence for an additional role for RecA protein in UV mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2415–2423. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2415-2423.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eguchi Y., Ogawa T., Ogawa H. Cleavage of bacteriophage phi 80 CI repressor by RecA protein. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):565–573. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90286-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Walker G. C. Proteins required for ultraviolet light and chemical mutagenesis. Identification of the products of the umuC locus of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 25;164(2):175–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falke J. J., Dernburg A. F., Sternberg D. A., Zalkin N., Milligan D. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Structure of a bacterial sensory receptor. A site-directed sulfhydryl study. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14850–14858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falke J. J., Koshland D. E., Jr Global flexibility in a sensory receptor: a site-directed cross-linking approach. Science. 1987 Sep 25;237(4822):1596–1600. doi: 10.1126/science.2820061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- First E. A., Bubis J., Taylor S. S. Subunit interaction sites between the regulatory and catalytic subunits of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Identification of a specific interchain disulfide bond. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5176–5182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flitsch S. L., Khorana H. G. Structural studies on transmembrane proteins. 1. Model study using bacteriorhodopsin mutants containing single cysteine residues. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7800–7805. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank E. G., Hauser J., Levine A. S., Woodgate R. Targeting of the UmuD, UmuD', and MucA' mutagenesis proteins to DNA by RecA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8169–8173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitag N., McEntee K. "Activated"-RecA protein affinity chromatography of LexA repressor and other SOS-regulated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8363–8367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimble F. S., Sauer R. T. Lambda repressor inactivation: properties of purified ind- proteins in the autodigestion and RecA-mediated cleavage reactions. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 5;192(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90462-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimble F. S., Sauer R. T. Lambda repressor mutants that are better substrates for RecA-mediated cleavage. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90521-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S. Minimizing proteolysis in Escherichia coli: genetic solutions. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:119–129. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85013-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hevroni D., Livneh Z. Bypass and termination at apurinic sites during replication of single-stranded DNA in vitro: a model for apurinic site mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5046–5050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonczyk P., Fijalkowska I., Ciesla Z. Overproduction of the epsilon subunit of DNA polymerase III counteracts the SOS mutagenic response of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9124–9127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Shinoura Y. Isolation and characterization of mutants of Escherichia coli deficient in induction of mutations by ultraviolet light. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Nov 14;156(2):121–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00283484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim B., Little J. W. LexA and lambda Cl repressors as enzymes: specific cleavage in an intermolecular reaction. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1165–1173. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90645-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima C. D., Wang J. C., Mondragón A. Three-dimensional structure of the 67K N-terminal fragment of E. coli DNA topoisomerase I. Nature. 1994 Jan 13;367(6459):138–146. doi: 10.1038/367138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Little J. W. Autodigestion and RecA-dependent cleavage of Ind- mutant LexA proteins. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 5;210(3):439–452. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Little J. W. Isolation and characterization of noncleavable (Ind-) mutants of the LexA repressor of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2163–2173. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2163-2173.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W. Autodigestion of lexA and phage lambda repressors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1375–1379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Edmiston S. H., Pacelli L. Z., Mount D. W. Cleavage of the Escherichia coli lexA protein by the recA protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3225–3229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh Z. Mechanism of replication of ultraviolet-irradiated single-stranded DNA by DNA polymerase III holoenzyme of Escherichia coli. Implications for SOS mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9526–9533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan D. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Site-directed cross-linking. Establishing the dimeric structure of the aspartate receptor of bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6268–6275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. H., Gulbis J. M., Dodson E. J., Demple B., Moody P. C. Crystal structure of a suicidal DNA repair protein: the Ada O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase from E. coli. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 1;13(7):1495–1501. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohmi T., Battista J. R., Dodson L. A., Walker G. C. RecA-mediated cleavage activates UmuD for mutagenesis: mechanistic relationship between transcriptional derepression and posttranslational activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1816–1820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T., Sturtevant J. M., Ptashne M. The lambda repressor contains two domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1608–1612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakula A. A., Simon M. I. Determination of transmembrane protein structure by disulfide cross-linking: the Escherichia coli Tar receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4144–4148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park H. S., Tao T., Chantler P. D. Proximity relationships between sites on myosin and actin. Resonance energy transfer determination of the following distances, using a hybrid myosin: those between Cys-55 on the Mercenaria regulatory light chain, SH-1 on the Aequipecten myosin heavy chain, and Cys-374 of actin. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 2;30(13):3189–3195. doi: 10.1021/bi00227a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry K. L., Elledge S. J., Mitchell B. B., Marsh L., Walker G. C. umuDC and mucAB operons whose products are required for UV light- and chemical-induced mutagenesis: UmuD, MucA, and LexA proteins share homology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4331–4335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. R., Ossanna N., Thliveris A. T., Ennis D. G., Mount D. W. Derepression of specific genes promotes DNA repair and mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.1-4.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopalan M., Lu C., Woodgate R., O'Donnell M., Goodman M. F., Echols H. Activity of the purified mutagenesis proteins UmuC, UmuD', and RecA in replicative bypass of an abasic DNA lesion by DNA polymerase III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10777–10781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland K. L., Little J. W. Reaction of LexA repressor with diisopropyl fluorophosphate. A test of the serine protease model. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12828–12835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland K. L., Smith M. H., Rupley J. A., Little J. W. In vitro analysis of mutant LexA proteins with an increased rate of specific cleavage. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 20;228(2):395–408. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90829-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T., Yocum R. R., Doolittle R. F., Lewis M., Pabo C. O. Homology among DNA-binding proteins suggests use of a conserved super-secondary structure. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):447–451. doi: 10.1038/298447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa H., Iwasaki H., Kato T., Nakata A. RecA protein-dependent cleavage of UmuD protein and SOS mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1806–1810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa H., Kato T., Ise T., Makino K., Nakata A. Cloning and characterization of the umu operon responsible for inducible mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1983 Aug;23(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slilaty S. N., Little J. W. Lysine-156 and serine-119 are required for LexA repressor cleavage: a possible mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):3987–3991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.3987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slilaty S. N., Rupley J. A., Little J. W. Intramolecular cleavage of LexA and phage lambda repressors: dependence of kinetics on repressor concentration, pH, temperature, and solvent. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6866–6875. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer S., Bailone A., Devoret R. The appearance of the UmuD'C protein complex in Escherichia coli switches repair from homologous recombination to SOS mutagenesis. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Dec;10(5):963–971. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinborn G. Uvm mutants of Escherichia coli K12 deficient in UV mutagenesis. I. Isolation of uvm mutants and their phenotypical characterization in DNA repair and mutagenesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Sep 20;165(1):87–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00270380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Story R. M., Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. The structure of the E. coli recA protein monomer and polymer. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):318–325. doi: 10.1038/355318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman R., Alexander H. B. Structural analysis of the carboxy terminus of bacteriophage lambda repressor determined by antipeptide antibodies. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1235–1244. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1235-1244.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweasy J. B., Witkin E. M., Sinha N., Roegner-Maniscalco V. RecA protein of Escherichia coli has a third essential role in SOS mutator activity. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3030–3036. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3030-3036.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadmor Y., Ascarelli-Goell R., Skaliter R., Livneh Z. Overproduction of the beta subunit of DNA polymerase III holoenzyme reduces UV mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2517–2524. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2517-2524.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao T., Scheiner C. J., Lamkin M. Site-specific photo-cross-linking studies on interactions between troponin and tropomyosin and between subunits of troponin. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7633–7639. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Inducible DNA repair systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:425–457. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z., Gergely J., Tao T. Characterization of the Ca(2+)-triggered conformational transition in troponin C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11814–11817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgate R., Rajagopalan M., Lu C., Echols H. UmuC mutagenesis protein of Escherichia coli: purification and interaction with UmuD and UmuD'. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7301–7305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagursky R. J., Berman M. L. Cloning vectors that yield high levels of single-stranded DNA for rapid DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]