Abstract
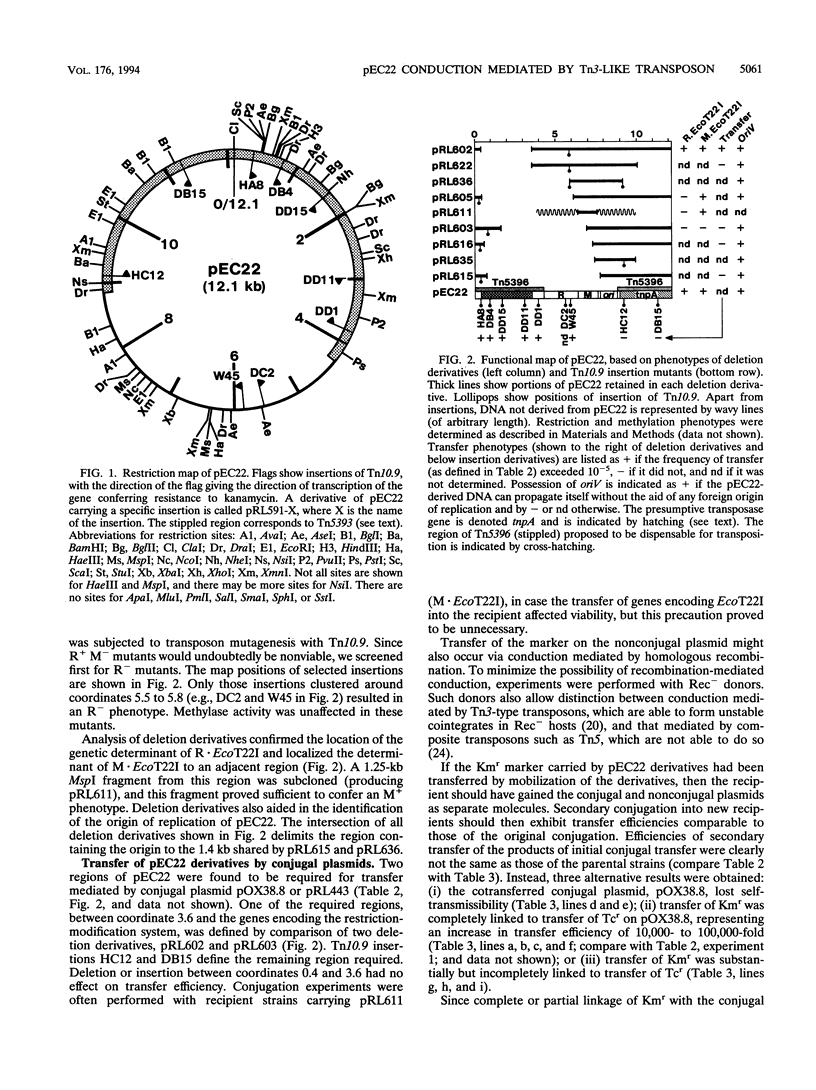
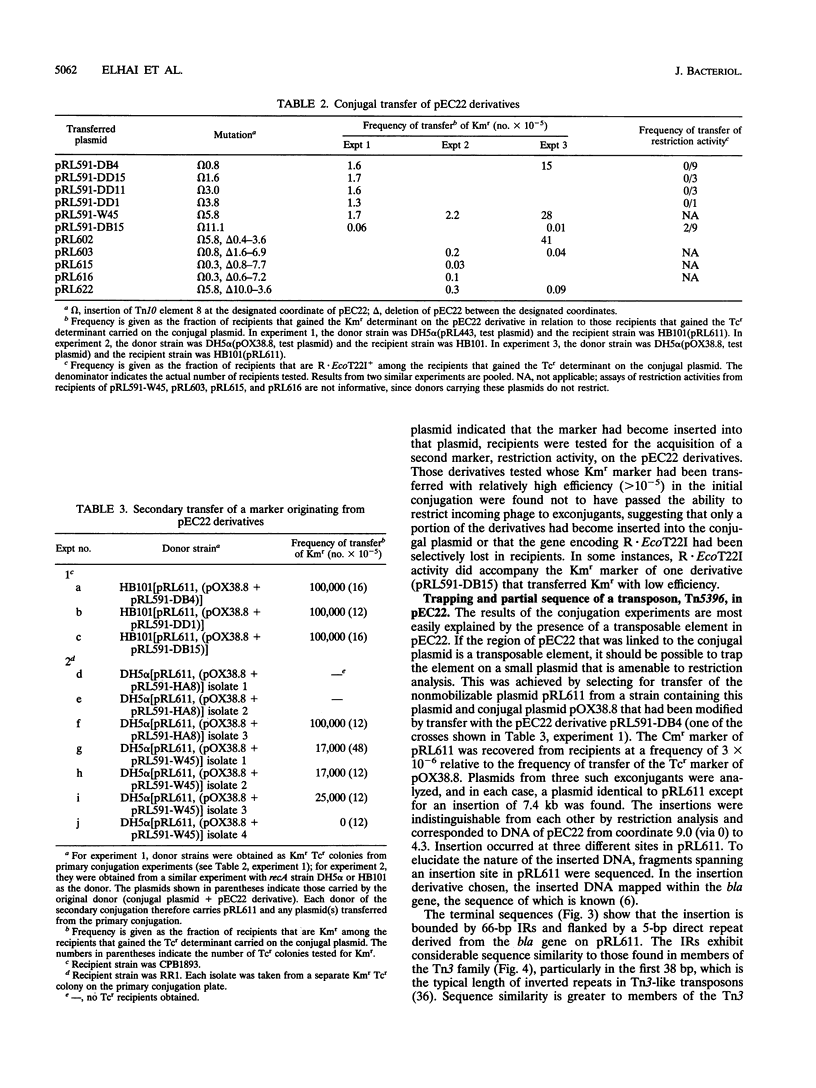
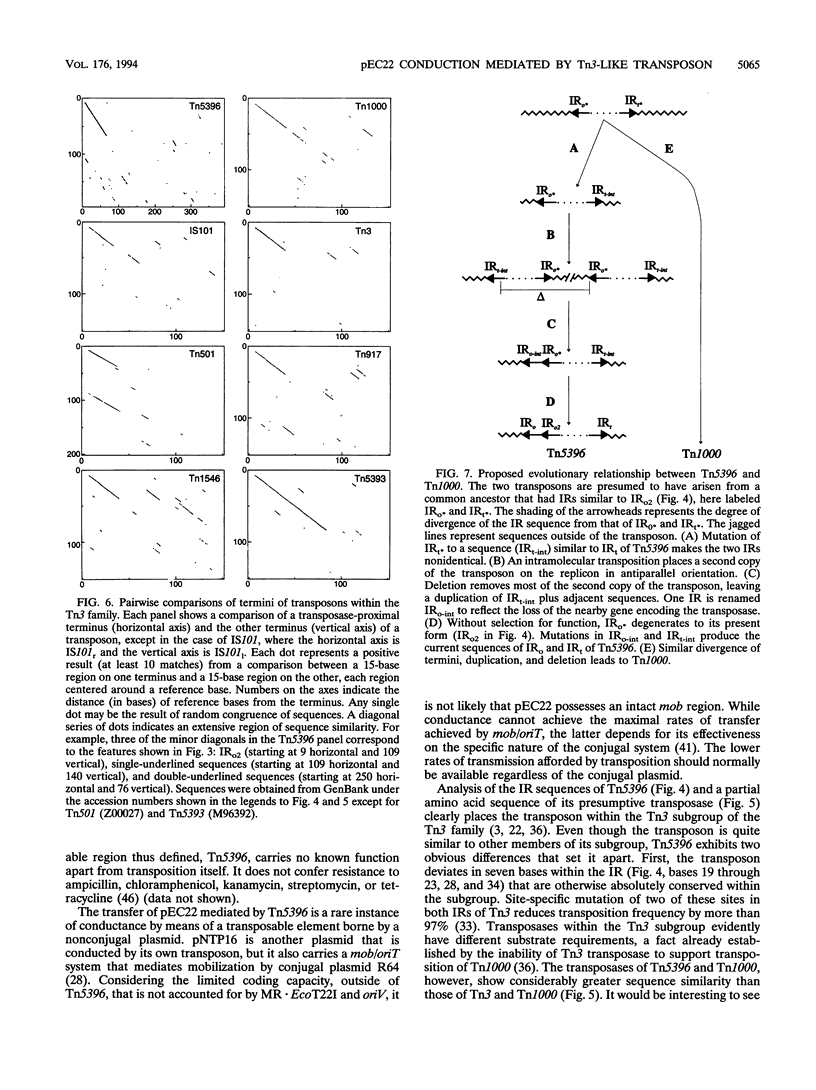
pEC22 is a small plasmid that encodes the restriction-modification system MR.EcoT22I. Restriction and functional analysis of the plasmid identified the positions of genes encoding that system. The plasmid is able to be conducted by conjugal plasmids, a process mediated by a transposon contained within pEC22. This cryptic transposon, called Tn5396, was isolated from pEC22 and partially sequenced. The sequence of Tn5396 is for the most part typical of transposons of the Tn3 family and is most similar to that of Tn1000. The transposon differs from closely related transposons in that it lacks well-conserved sequences in the inverted-repeat region and has an unusually long terminal inverted repeat. Consideration of regions of internal sequence similarity in this and other transposons in the Tn3 family supports a theory of the mechanism by which the ends of Tn3-like transposons may maintain substantial identity between their inverted repeats over the course of evolutionary time.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allmeier H., Cresnar B., Greck M., Schmitt R. Complete nucleotide sequence of Tn1721: gene organization and a novel gene product with features of a chemotaxis protein. Gene. 1992 Feb 1;111(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90597-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amemura-Maekawa J., Ohtsubo E. Functional analysis of the two domains in the terminal inverted repeat sequence required for transposition of Tn3. Gene. 1991 Jul 15;103(1):11–16. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90384-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur M., Molinas C., Depardieu F., Courvalin P. Characterization of Tn1546, a Tn3-related transposon conferring glycopeptide resistance by synthesis of depsipeptide peptidoglycan precursors in Enterococcus faecium BM4147. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(1):117–127. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.1.117-127.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdasarian M., Lurz R., Rückert B., Franklin F. C., Bagdasarian M. M., Frey J., Timmis K. N. Specific-purpose plasmid cloning vectors. II. Broad host range, high copy number, RSF1010-derived vectors, and a host-vector system for gene cloning in Pseudomonas. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):237–247. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balbás P., Soberón X., Merino E., Zurita M., Lomeli H., Valle F., Flores N., Bolivar F. Plasmid vector pBR322 and its special-purpose derivatives--a review. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):3–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90307-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R., Sherratt D. Transposon Tn1 intra-molecular transposition. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(1):117–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00334102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borck K., Beggs J. D., Brammar W. J., Hopkins A. S., Murray N. E. The construction in vitro of transducing derivatives of phage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jul 23;146(2):199–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00268089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R., Ptashne M. Mechanism of action of the lexA gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4204–4208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou C. S., Jones A. L. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a transposon (Tn5393) carrying streptomycin resistance genes in Erwinia amylovora and other gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):732–740. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.732-740.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Warren G. J. Conjugal transmission of plasmids. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:99–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.000531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Sommer H., Saedler H. Transposon Tn951 (TnLac) is defective and related to Tn3. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):241–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00272911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deragon J. M., Corriveau P., Gingras G. Plasmid from photosynthetic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira Sp. carries a transposable streptomycin resistance gene. Plasmid. 1990 May;23(3):226–236. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(90)90054-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhai J., Wolk C. P. A versatile class of positive-selection vectors based on the nonviability of palindrome-containing plasmids that allows cloning into long polylinkers. Gene. 1988 Aug 15;68(1):119–138. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90605-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhai J., Wolk C. P. Conjugal transfer of DNA to cyanobacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1988;167:747–754. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)67086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R., Heffron F., Dougan G., Falkow S. Analysis of sequences transposed by complementation of two classes of transposition-deficient mutants of Tn3. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):742–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.742-756.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinsted J., Brown N. L. A Tn21 terminal sequence within Tn501: complementation of tnpA gene function and transposon evolution. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(3):497–502. doi: 10.1007/BF00329949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinsted J., de la Cruz F., Schmitt R. The Tn21 subgroup of bacterial transposable elements. Plasmid. 1990 Nov;24(3):163–189. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(90)90001-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. M., Brookes D. E., Stokes H. W. Site-specific insertion of genes into integrons: role of the 59-base element and determination of the recombination cross-over point. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1941–1959. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschel B. J., Galas D. J., Chandler M. Cointegrate formation by Tn5, but not transposition, is dependent on recA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4530–4534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. J., Heffron F., Twu J. S., Schloemer R. H., Lee C. H. Analysis of Tn3 sequences required for transposition and immunity. Gene. 1986;41(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90263-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kans J. A., Casadaban M. J. Nucleotide sequences required for Tn3 transposition immunity. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1904–1914. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1904-1914.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert C. M., Hyde H., Strike P. Conjugal mobility of the multicopy plasmids NTP1 and NTP16. Plasmid. 1987 Sep;18(2):99–110. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloy S. R., Nunn W. D. Selection for loss of tetracycline resistance by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1110–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1110-1111.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels T., Cornelis G. Detection and characterization of Tn2501, a transposon included within the lactose transposon Tn951. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):866–871. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.866-871.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra T. K., Brown N. L., Fritzinger D. C., Pridmore R. D., Barnes W. M., Haberstroh L., Silver S. Mercuric ion-resistance operons of plasmid R100 and transposon Tn501: the beginning of the operon including the regulatory region and the first two structural genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5975–5979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissley D. V., Lindh F. G., Fennewald M. A. Mutational analysis of the inverted repeats of Tn3. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):671–676. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. H., Clewell D. B. Complete nucleotide sequence of macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B-resistance transposon Tn917 in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):782–796. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.782-796.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemieniak D. R., Slightom J. L., Chung S. T. Nucleotide sequence of Streptomyces fradiae transposable element Tn4556: a class-II transposon related to Tn3. Gene. 1990 Jan 31;86(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Minegishi K., Iino T. Toluene transposons Tn4651 and Tn4653 are class II transposons. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1386–1393. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1386-1393.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G., Xu X., Chen J. M., Berg D. E., Berg C. M. Inversions and deletions generated by a mini-gamma delta (Tn1000) transposon. J Bacteriol. 1994 Mar;176(5):1332–1338. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.5.1332-1338.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. J., Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. J. ColE1 plasmid mobility and relaxation complex. Nature. 1978 Jul 20;274(5668):259–261. doi: 10.1038/274259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Davis M. A., Morisato D., Roberts D. E., Kleckner N. New Tn10 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis and for construction of lacZ operon fusions by transposition. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N., Skurray R. The conjugation system of F-like plasmids. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:41–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.000353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrighton C. J., Strike P. A pathway for the evolution of the plasmid NTP16 involving the novel kanamycin resistance transposon Tn4352. Plasmid. 1987 Jan;17(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida Y., Mise K. Occurrence of small Hsd plasmids in Salmonella typhi, Shigella boydii, and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):357–362. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.357-362.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


