Abstract
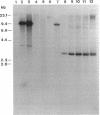
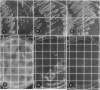
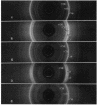
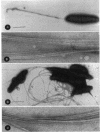
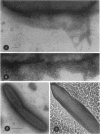
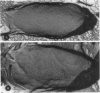
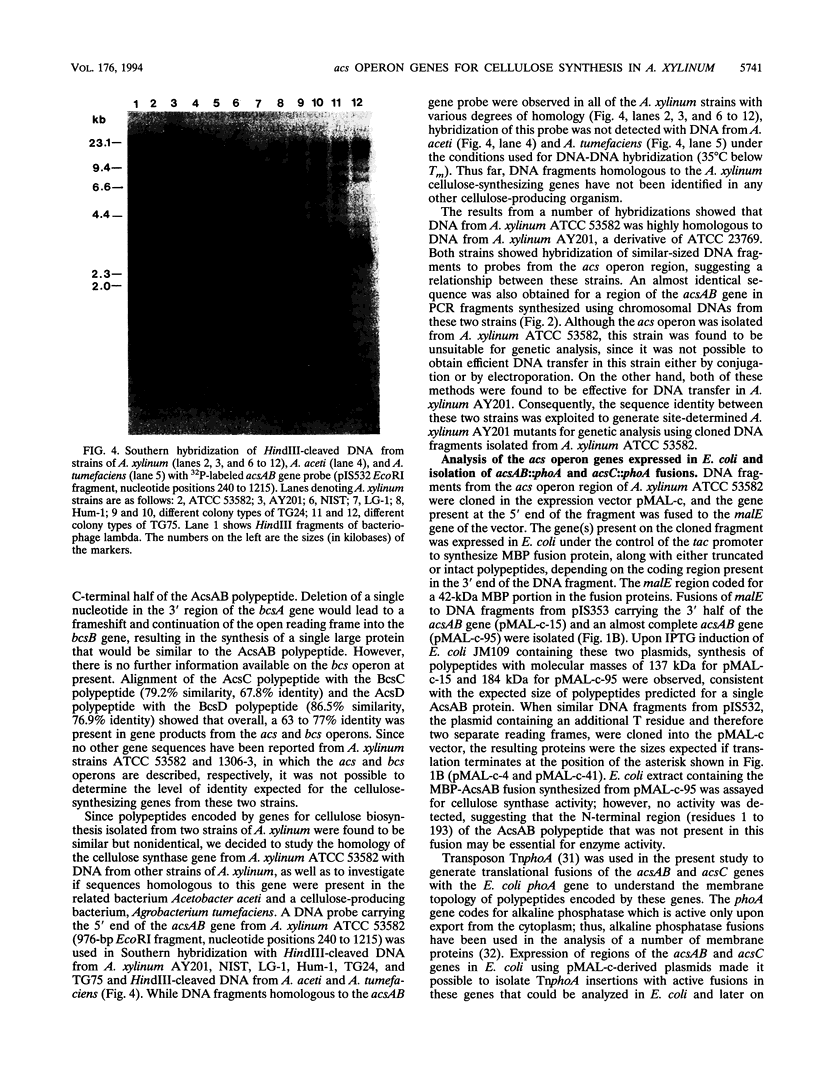
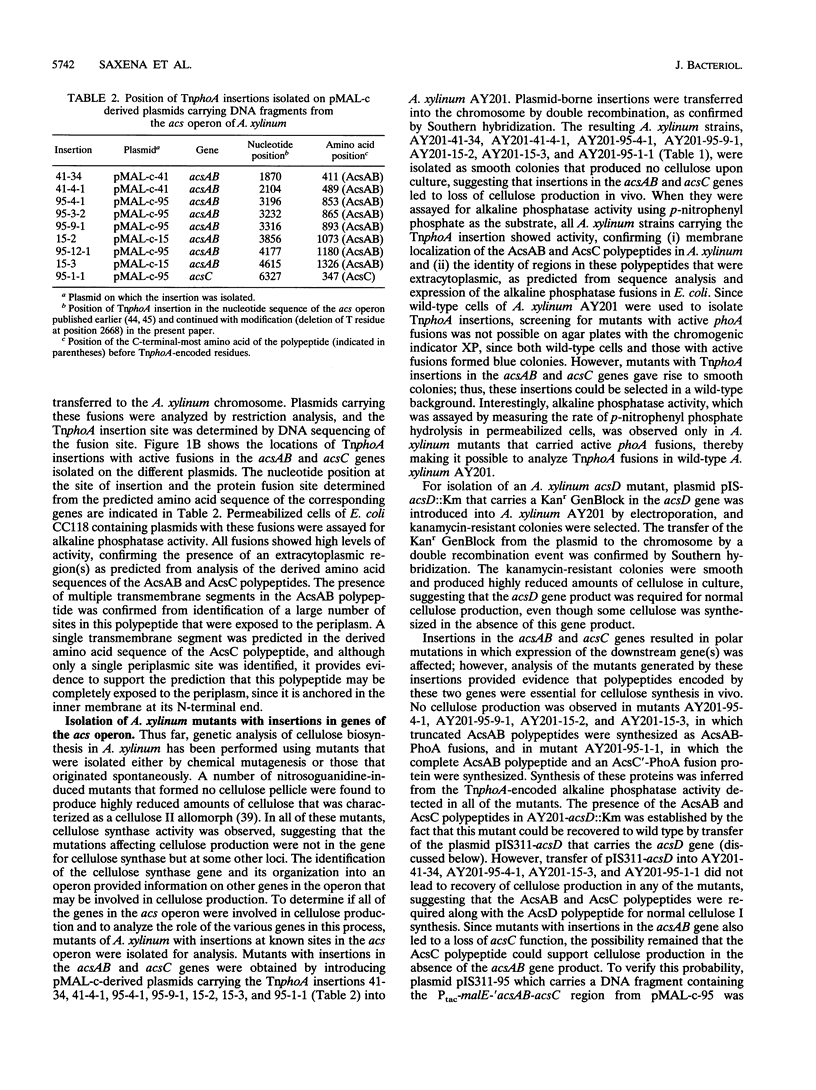
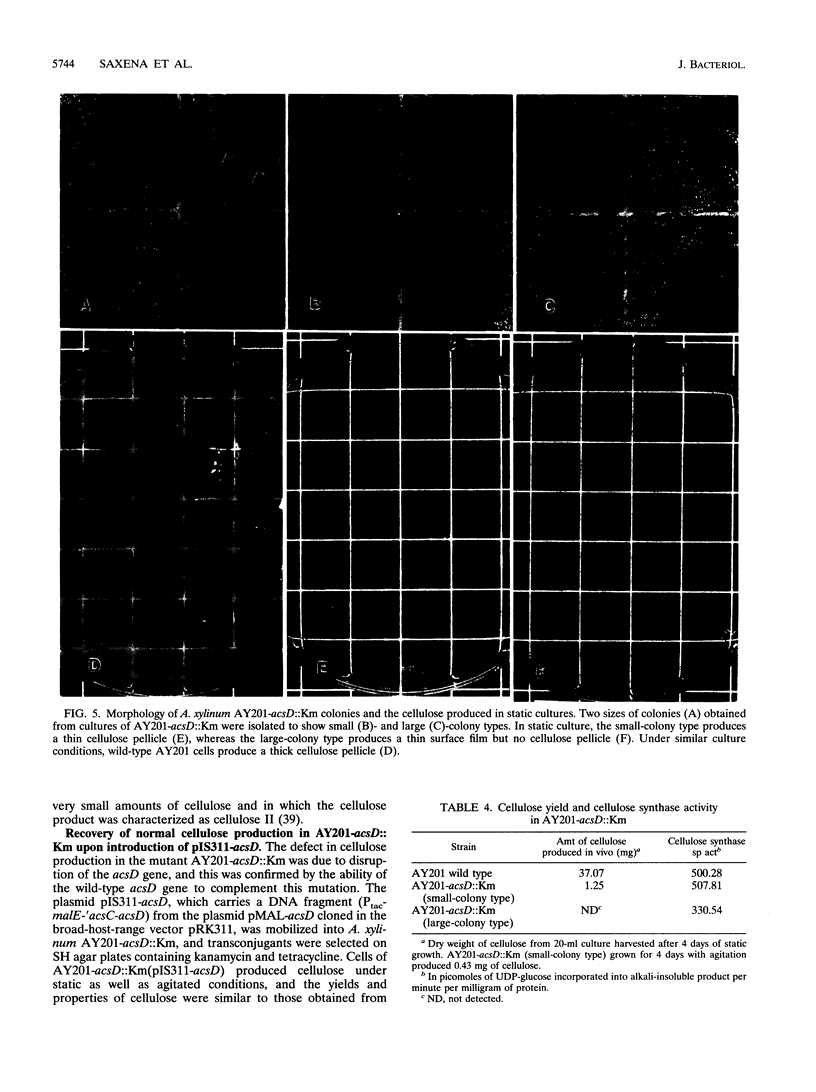
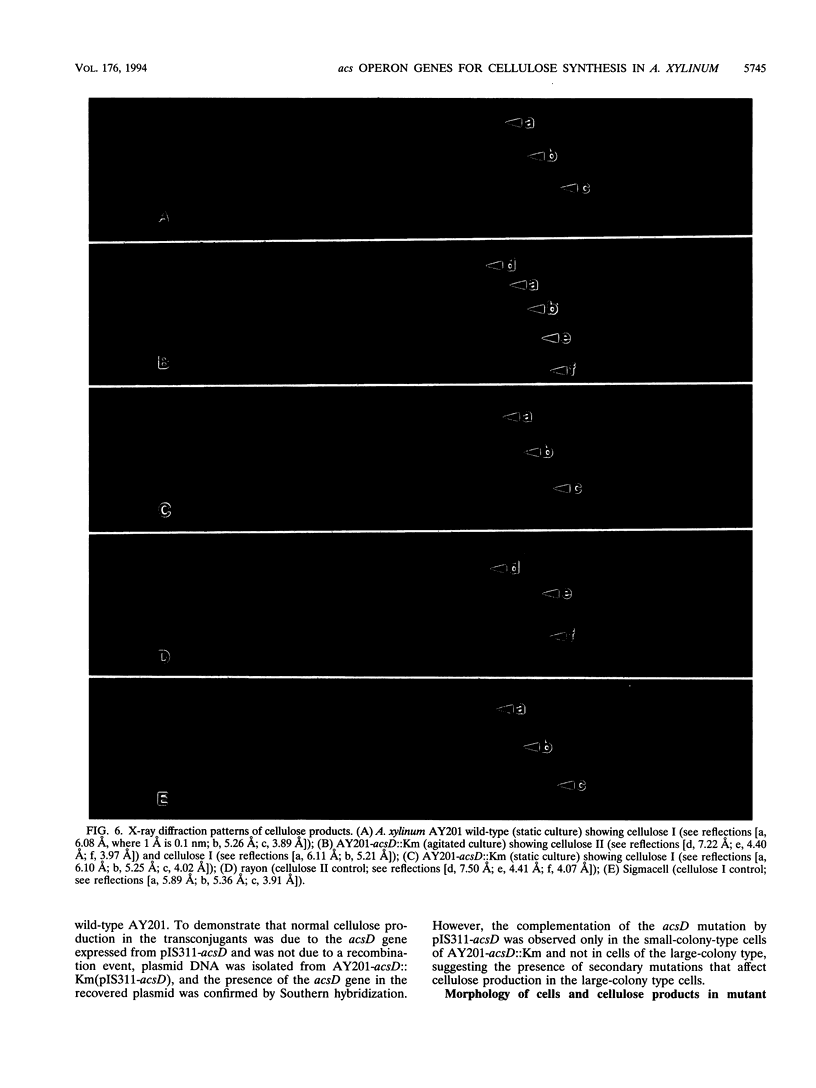
The synthesis of an extracellular ribbon of cellulose in the bacterium Acetobacter xylinum takes place from linearly arranged, membrane-localized, cellulose-synthesizing and extrusion complexes that direct the coupled steps of polymerization and crystallization. To identify the different components involved in this process, we isolated an Acetobacter cellulose-synthesizing (acs) operon from this bacterium. Analysis of DNA sequence shows the presence of three genes in the acs operon, in which the first gene (acsAB) codes for a polypeptide with a molecular mass of 168 kDa, which was identified as the cellulose synthase. A single base change in the previously reported DNA sequence of this gene, resulting in a frameshift and synthesis of a larger protein, is described in the present paper, along with the sequences of the other two genes (acsC and acsD). The requirement of the acs operon genes for cellulose production was determined using site-determined TnphoA/Kanr GenBlock insertion mutants. Mutant analysis showed that while the acsAB and acsC genes were essential for cellulose production in vivo, the acsD mutant produced reduced amounts of two cellulose allomorphs (cellulose I and cellulose II), suggesting that the acsD gene is involved in cellulose crystallization. The role of the acs operon genes in determining the linear array of intramembranous particles, which are believed to be sites of cellulose synthesis, was investigated for the different mutants; however, this arrangement was observed only in cells that actively produced cellulose microfibrils, suggesting that it may be influenced by the crystallization of the nascent glucan chains.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benziman M., Haigler C. H., Brown R. M., White A. R., Cooper K. M. Cellulose biogenesis: Polymerization and crystallization are coupled processes in Acetobacter xylinum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6678–6682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C. A rapid alkaline extraction method for the isolation of plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:243–255. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. M., Jr Cellulose microfibril assembly and orientation: recent developments. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1985;2:13–32. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1985.supplement_2.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. M., Jr, Willison J. H., Richardson C. L. Cellulose biosynthesis in Acetobacter xylinum: visualization of the site of synthesis and direct measurement of the in vivo process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4565–4569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulawa C. E., Wasco W. Chitin and nodulation. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):710–710. doi: 10.1038/353710b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bureau T. E., Brown R. M. In vitro synthesis of cellulose II from a cytoplasmic membrane fraction of Acetobacter xylinum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6985–6989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhaese P., De Greve H., Decraemer H., Schell J., Van Montagu M. Rapid mapping of transposon insertion and deletion mutations in the large Ti-plasmids of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1837–1849. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Schmidhauser T., Yakobson E., Lu P., Liang X. W., Finlay D. R., Guiney D., Helinski D. R. Plasmids related to the broad host range vector, pRK290, useful for gene cloning and for monitoring gene expression. Plasmid. 1985 Mar;13(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty B. A., van de Rijn I. Molecular characterization of hasA from an operon required for hyaluronic acid synthesis in group A streptococci. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):169–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glucksmann M. A., Reuber T. L., Walker G. C. Family of glycosyl transferases needed for the synthesis of succinoglycan by Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(21):7033–7044. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.21.7033-7044.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glucksmann M. A., Reuber T. L., Walker G. C. Genes needed for the modification, polymerization, export, and processing of succinoglycan by Rhizobium meliloti: a model for succinoglycan biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(21):7045–7055. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.21.7045-7055.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler C. H., Brown R. M., Jr, Benziman M. Calcofluor white ST Alters the in vivo assembly of cellulose microfibrils. Science. 1980 Nov 21;210(4472):903–906. doi: 10.1126/science.7434003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding N. E., Cleary J. M., Cabañas D. K., Rosen I. G., Kang K. S. Genetic and physical analyses of a cluster of genes essential for xanthan gum biosynthesis in Xanthomonas campestris. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2854–2861. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2854-2861.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs T. W., Egelhoff T. T., Long S. R. Physical and genetic map of a Rhizobium meliloti nodulation gene region and nucleotide sequence of nodC. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):469–476. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.469-476.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P., Kanehisa M., DeLisi C. The detection and classification of membrane-spanning proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 28;815(3):468–476. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90375-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A., Coplin D. L. Exopolysaccharides in plant-bacterial interactions. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1992;46:307–346. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.46.100192.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerouge P., Roche P., Faucher C., Maillet F., Truchet G., Promé J. C., Dénarié J. Symbiotic host-specificity of Rhizobium meliloti is determined by a sulphated and acylated glucosamine oligosaccharide signal. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):781–784. doi: 10.1038/344781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessl M., Balzer D., Pansegrau W., Lanka E. Sequence similarities between the RP4 Tra2 and the Ti VirB region strongly support the conjugation model for T-DNA transfer. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20471–20480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. C., Brown R. M., Jr, Drake R. R., Jr, Haley B. E. Identification of the uridine 5'-diphosphoglucose (UDP-Glc) binding subunit of cellulose synthase in Acetobacter xylinum using the photoaffinity probe 5-azido-UDP-Glc. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):4782–4784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C. Analysis of membrane protein topology using alkaline phosphatase and beta-galactosidase gene fusions. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;34:61–75. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61676-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Mekalanos J. J., Beckwith J. Alkaline phosphatase fusions: sensors of subcellular location. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):515–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.515-518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer R., Ross P., Weinhouse H., Amikam D., Volman G., Ohana P., Calhoon R. D., Wong H. C., Emerick A. W., Benziman M. Polypeptide composition of bacterial cyclic diguanylic acid-dependent cellulose synthase and the occurrence of immunologically crossreacting proteins in higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5472–5476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. Practical aspects of preparing phage and plasmid DNA: growth, maintenance, and storage of bacteria and bacteriophage. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:145–170. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noti J. D., Jagadish M. N., Szalay A. A. Site-directed Tn5 and transplacement mutagenesis: methods to identify symbiotic nitrogen fixation genes in slow-growing Rhizobium. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:197–217. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross P., Mayer R., Benziman M. Cellulose biosynthesis and function in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):35–58. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.35-58.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHRAMM M., HESTRIN S. Factors affecting production of cellulose at the air/liquid interface of a culture of Acetobacter xylinum. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Aug;11(1):123–129. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena I. M., Lin F. C., Brown R. M., Jr Cloning and sequencing of the cellulose synthase catalytic subunit gene of Acetobacter xylinum. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Nov;15(5):673–683. doi: 10.1007/BF00016118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena I. M., Lin F. C., Brown R. M., Jr Identification of a new gene in an operon for cellulose biosynthesis in Acetobacter xylinum. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Jun;16(6):947–954. doi: 10.1007/BF00016067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Manoil C., Mekalanos J. J. Broad-host-range vectors for delivery of TnphoA: use in genetic analysis of secreted virulence determinants of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1870–1878. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1870-1878.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. E., Akiyoshi D. E., Regier D., Datta A., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Characterization of the virB operon from an Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5804–5814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. E., Akiyoshi D. E., Regier D., Datta A., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Correction: characterization of the virB operon from Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4768–4768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Johnson F. D., Burns D. L. Molecular characterization of an operon required for pertussis toxin secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2970–2974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong H. C., Fear A. L., Calhoon R. D., Eichinger G. H., Mayer R., Amikam D., Benziman M., Gelfand D. H., Meade J. H., Emerick A. W. Genetic organization of the cellulose synthase operon in Acetobacter xylinum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8130–8134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaar K. Visualization of pores (export sites) correlated with cellulose production in the envelope of the gram-negative bacterium Acetobacter xylinum. J Cell Biol. 1979 Mar;80(3):773–777. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.3.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]