Abstract
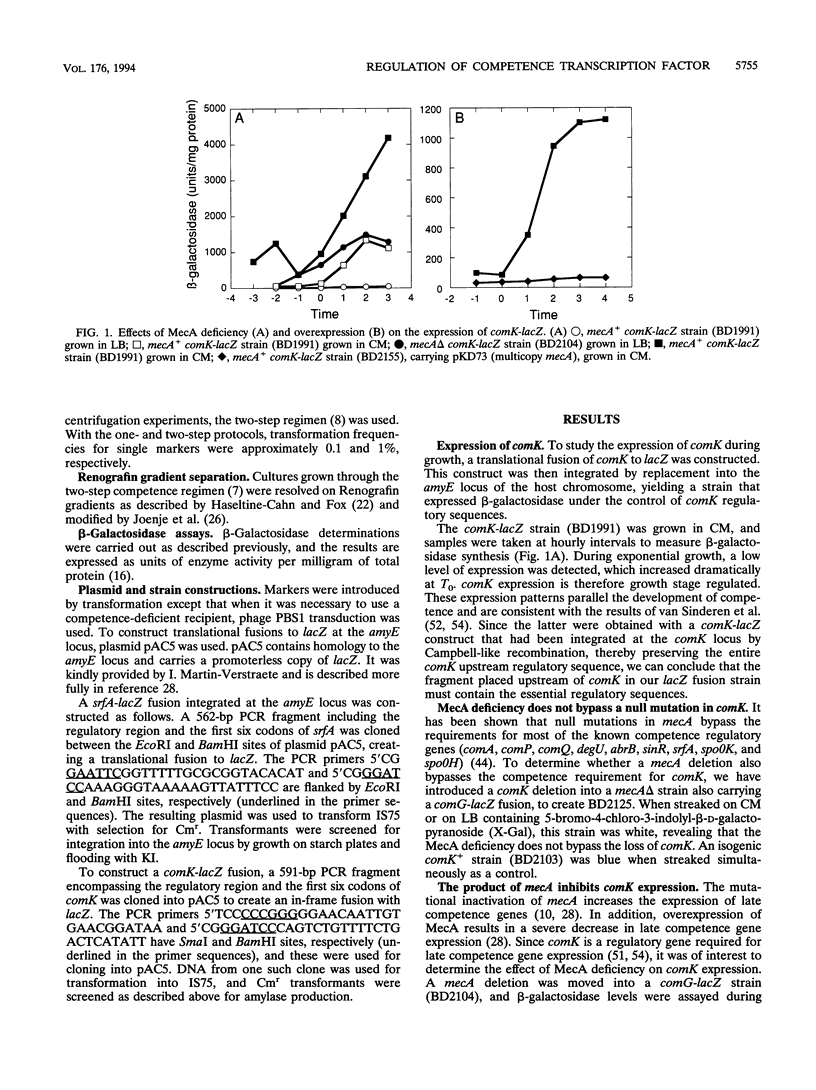
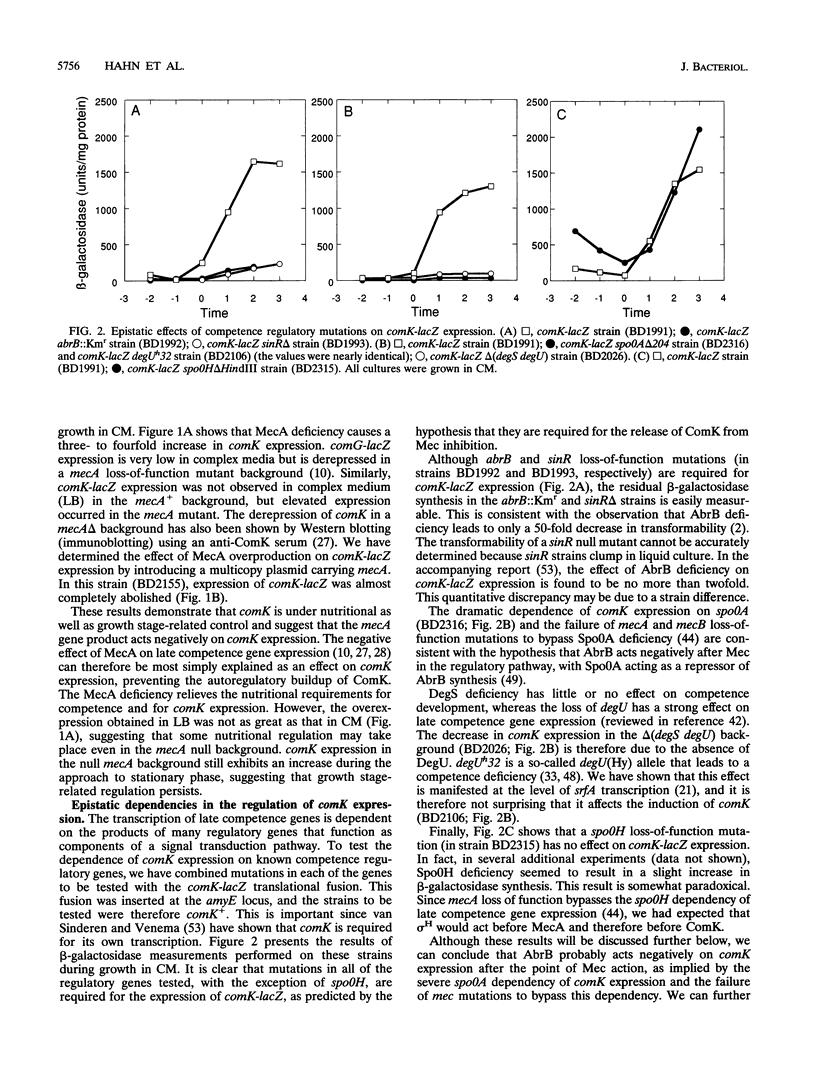
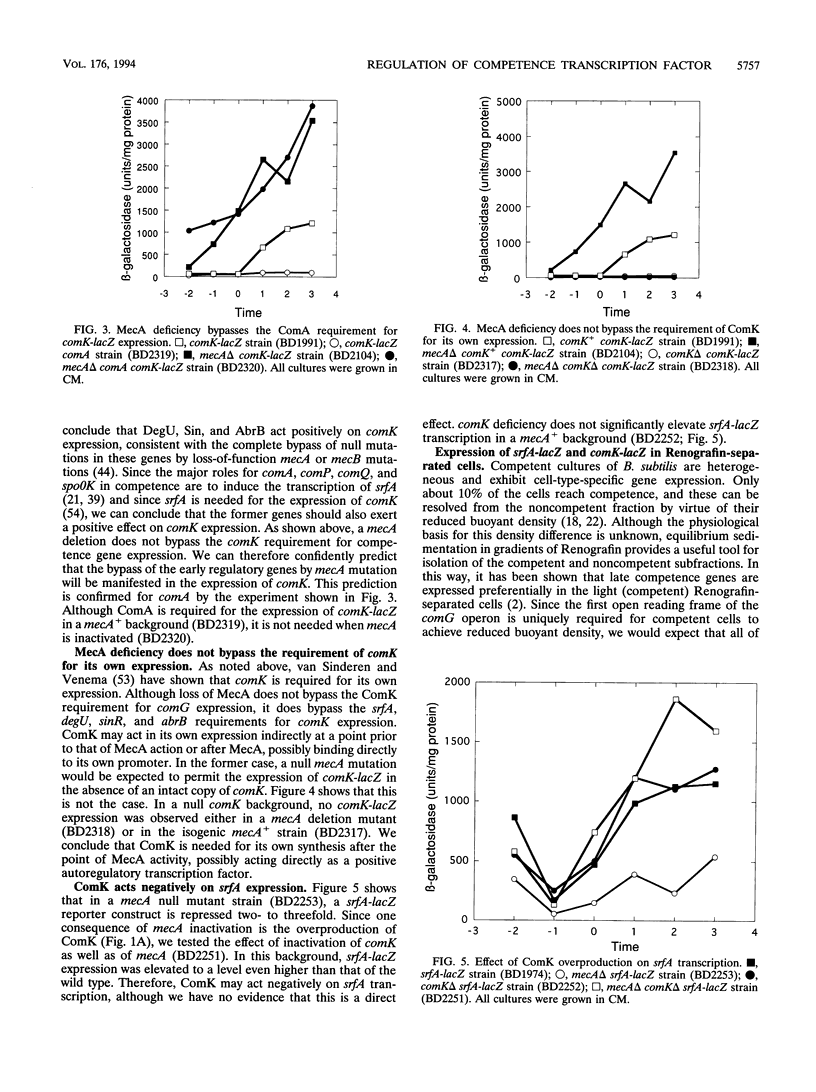
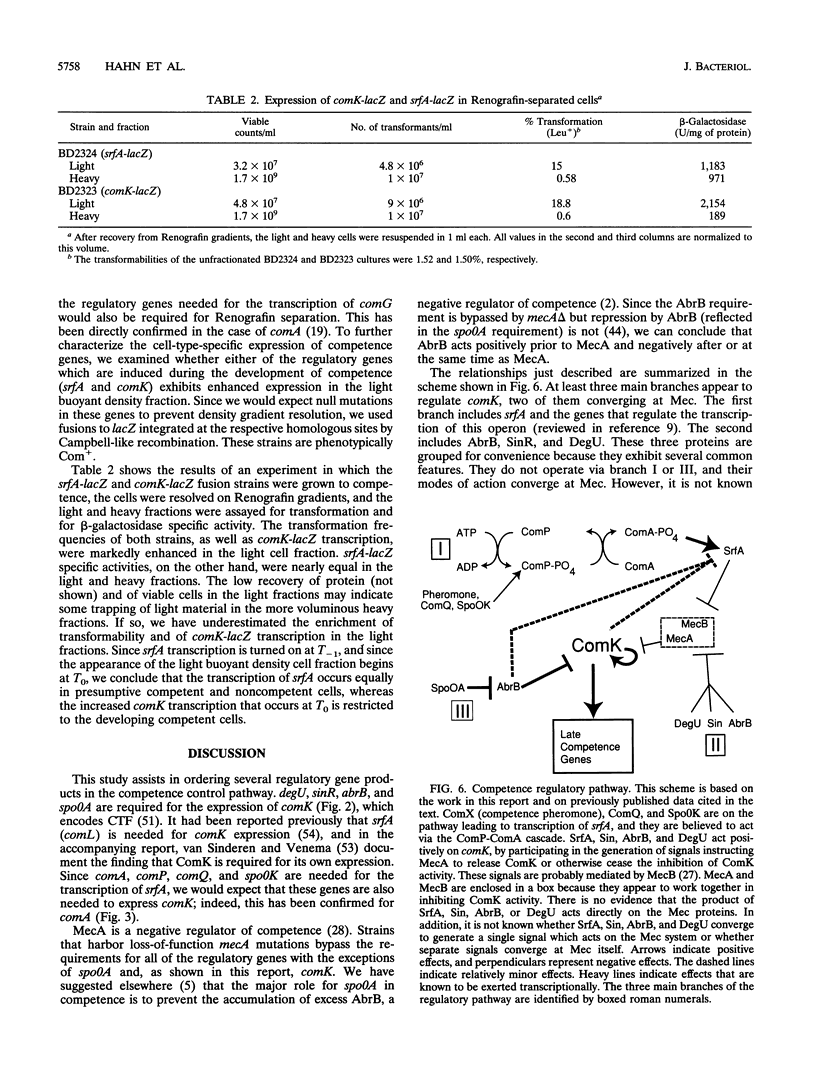
comK, which encodes the competence transcription factor, is itself transcriptionally activated at the transition from exponential growth to stationary phase in Bacillus subtilis. MecA, a negative regulator of competence, also inhibits comK transcription when overexpressed, and a mecA null mutation results in comK overexpression. Although null mutations in mecA, as well as in another gene, mecB, are known to bypass the requirements for nearly all of the competence regulatory genes, the comK requirement is not suppressed by mecA inactivation. Various competence regulatory genes (comA, srfA, degU, abrB, sin, and spo0A) are shown to be required for the expression of comK. srfA transcription is shown to occur equally in cells destined for competence and those destined not to become competent. In contrast, comK transcription is restricted to the presumptive competent cells. These and other results are combined to describe a regulatory pathway for competence.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albano M., Breitling R., Dubnau D. A. Nucleotide sequence and genetic organization of the Bacillus subtilis comG operon. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5386–5404. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5386-5404.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albano M., Hahn J., Dubnau D. Expression of competence genes in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3110–3117. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3110-3117.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai U., Mandic-Mulec I., Smith I. SinI modulates the activity of SinR, a developmental switch protein of Bacillus subtilis, by protein-protein interaction. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):139–148. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahn F. H., Fox M. S. Fractionation of transformable bacteria from ocompetent cultures of Bacillus subtilis on renografin gradients. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):867–875. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.867-875.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley D. C., Hadden C. T., Nester E. W. Macromolecular synthesis in Bacillus subtilis during development of the competent state. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):668–679. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.668-679.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Davidoff-Abelson R. Fate of transforming DNA following uptake by competent Bacillus subtilis. I. Formation and properties of the donor-recipient complex. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):209–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90460-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D. Genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):395–424. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.395-424.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Roggiani M. Growth medium-independent genetic competence mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4048–4055. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4048-4055.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau E., Weir J., Nair G., Carter L., 3rd, Moran C., Jr, Smith I. Bacillus sporulation gene spo0H codes for sigma 30 (sigma H). J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1054–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1054-1062.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaur N. K., Cabane K., Smith I. Structure and expression of the Bacillus subtilis sin operon. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1046–1053. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1046-1053.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaur N. K., Dubnau E., Smith I. Characterization of a cloned Bacillus subtilis gene that inhibits sporulation in multiple copies. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):860–869. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.860-869.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaur N. K., Oppenheim J., Smith I. The Bacillus subtilis sin gene, a regulator of alternate developmental processes, codes for a DNA-binding protein. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):678–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.678-686.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Israeli-Reches M., Dubnau D. Induction of macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance requires ribosomes able to bind inducer. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;194(3):357–361. doi: 10.1007/BF00425544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillen N., Weinrauch Y., Dubnau D. A. Cloning and characterization of the regulatory Bacillus subtilis competence genes comA and comB. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5354–5361. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5354-5361.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadden C., Nester E. W. Purification of competent cells in the Bacillus subtilis transformation system. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):876–885. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.876-885.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn J., Albano M., Dubnau D. Isolation and characterization of Tn917lac-generated competence mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3104–3109. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3104-3109.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn J., Dubnau D. Growth stage signal transduction and the requirements for srfA induction in development of competence. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7275–7282. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7275-7282.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireton K., Rudner D. Z., Siranosian K. J., Grossman A. D. Integration of multiple developmental signals in Bacillus subtilis through the Spo0A transcription factor. Genes Dev. 1993 Feb;7(2):283–294. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.2.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaacks K. J., Healy J., Losick R., Grossman A. D. Identification and characterization of genes controlled by the sporulation-regulatory gene spo0H in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4121–4129. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4121-4129.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joenje H., Konings W. N., Venema G. Interactions between exogenous deoxyribonucleic acid and membrane vesicles isolated from competent and noncompetent Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):771–776. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.771-776.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong L., Dubnau D. Regulation of competence-specific gene expression by Mec-mediated protein-protein interaction in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong L., Siranosian K. J., Grossman A. D., Dubnau D. Sequence and properties of mecA, a negative regulator of genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jul;9(2):365–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandic-Mulec I., Gaur N., Bai U., Smith I. Sin, a stage-specific repressor of cellular differentiation. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3561–3569. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3561-3569.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy C., Nester E. W. Macromolecular synthesis in newly transformed cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):131–140. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.131-140.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan S., Dubnau D. Transcriptional regulation of comC: evidence for a competence-specific transcription factor in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4064–4071. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4064-4071.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Msadek T., Kunst F., Henner D., Klier A., Rapoport G., Dedonder R. Signal transduction pathway controlling synthesis of a class of degradative enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: expression of the regulatory genes and analysis of mutations in degS and degU. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):824–834. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.824-834.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Msadek T., Kunst F., Klier A., Rapoport G. DegS-DegU and ComP-ComA modulator-effector pairs control expression of the Bacillus subtilis pleiotropic regulatory gene degQ. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2366–2377. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2366-2377.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Msadek T., Kunst F., Rapoport G. MecB of Bacillus subtilis, a member of the ClpC ATPase family, is a pleiotropic regulator controlling competence gene expression and growth at high temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):5788–5792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.5788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller J. P., Bukusoglu G., Sonenshein A. L. Transcriptional regulation of Bacillus subtilis glucose starvation-inducible genes: control of gsiA by the ComP-ComA signal transduction system. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4361–4373. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4361-4373.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NESTER E. W., STOCKER B. A. BIOSYNTHETIC LATENCY IN EARLY STAGES OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACIDTRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:785–796. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.785-796.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M. M., Magnuson R., Myers A., Curry J., Grossman A. D., Zuber P. srfA is an operon required for surfactin production, competence development, and efficient sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1770–1778. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1770-1778.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M. M., Zuber P. Cloning and characterization of srfB, a regulatory gene involved in surfactin production and competence in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5347–5353. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5347-5353.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M. M., Zuber P. The primary role of comA in establishment of the competent state in Bacillus subtilis is to activate expression of srfA. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7269–7274. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7269-7274.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perego M., Spiegelman G. B., Hoch J. A. Structure of the gene for the transition state regulator, abrB: regulator synthesis is controlled by the spo0A sporulation gene in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):689–699. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggiani M., Dubnau D. ComA, a phosphorylated response regulator protein of Bacillus subtilis, binds to the promoter region of srfA. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(10):3182–3187. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.10.3182-3187.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggiani M., Hahn J., Dubnau D. Suppression of early competence mutations in Bacillus subtilis by mec mutations. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4056–4063. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4056-4063.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudner D. Z., LeDeaux J. R., Ireton K., Grossman A. D. The spo0K locus of Bacillus subtilis is homologous to the oligopeptide permease locus and is required for sporulation and competence. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1388–1398. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1388-1398.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Kunst F., Dedonder R. Mapping of mutations affecting synthesis of exocellular enzymes in Bacillus subtilis. Identity of the sacUh, amyB and pap mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Nov 17;148(3):281–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00332902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch M. A., Spiegelman G. B., Perego M., Johnson W. C., Burbulys D., Hoch J. A. The transition state transcription regulator abrB of Bacillus subtilis is a DNA binding protein. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1615–1621. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03546.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch M., Webb V., Spiegelman G., Hoch J. A. The SpoOA protein of Bacillus subtilis is a repressor of the abrB gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1801–1805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrauch Y., Guillen N., Dubnau D. A. Sequence and transcription mapping of Bacillus subtilis competence genes comB and comA, one of which is related to a family of bacterial regulatory determinants. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5362–5375. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5362-5375.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrauch Y., Msadek T., Kunst F., Dubnau D. Sequence and properties of comQ, a new competence regulatory gene of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5685–5693. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5685-5693.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrauch Y., Penchev R., Dubnau E., Smith I., Dubnau D. A Bacillus subtilis regulatory gene product for genetic competence and sporulation resembles sensor protein members of the bacterial two-component signal-transduction systems. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):860–872. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Sinderen D., Venema G. comK acts as an autoregulatory control switch in the signal transduction route to competence in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1994 Sep;176(18):5762–5770. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.18.5762-5770.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Sinderen D., Withoff S., Boels H., Venema G. Isolation and characterization of comL, a transcription unit involved in competence development of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Dec;224(3):396–404. doi: 10.1007/BF00262434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Sinderen D., ten Berge A., Hayema B. J., Hamoen L., Venema G. Molecular cloning and sequence of comK, a gene required for genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Feb;11(4):695–703. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


