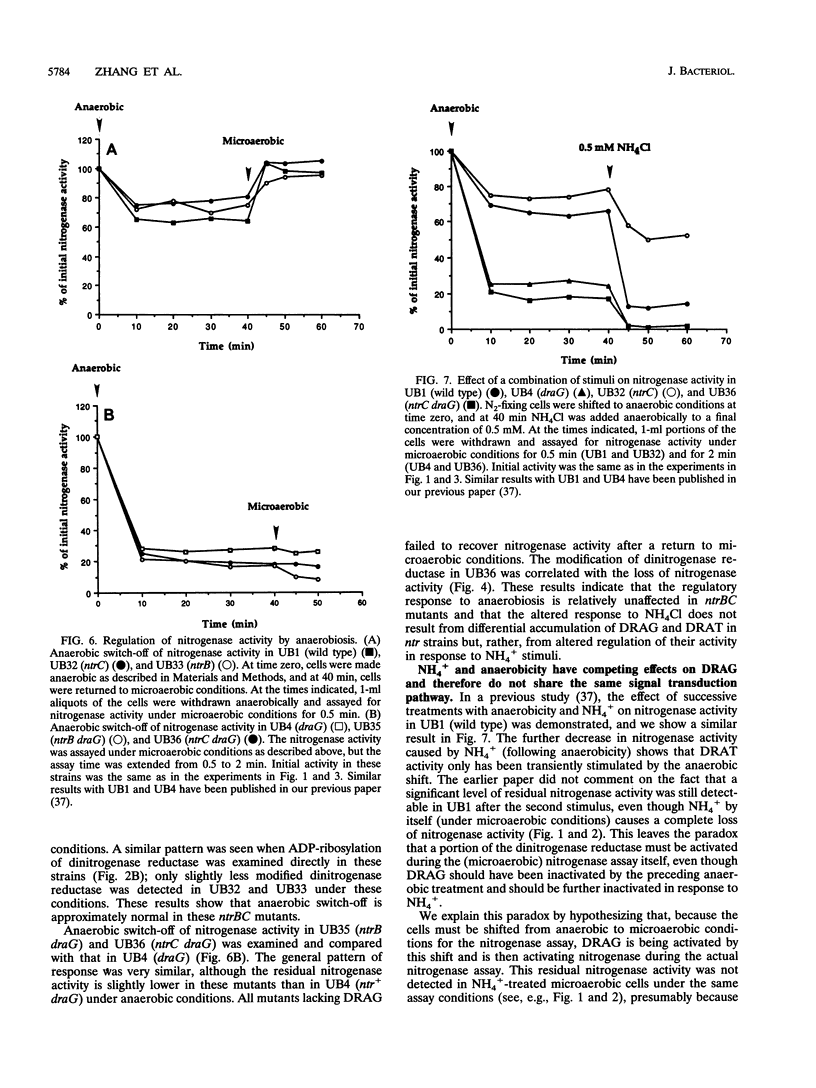
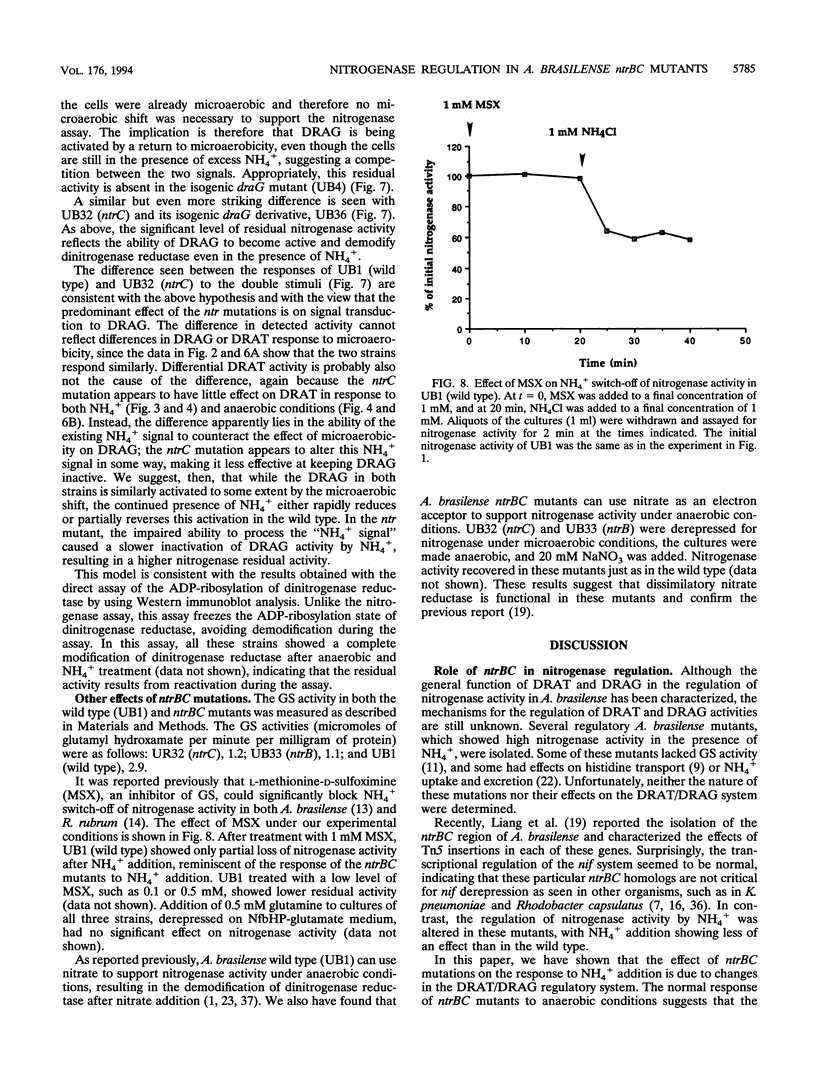
Abstract
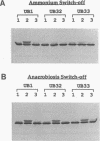
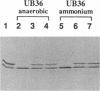
Nitrogenase activity is regulated by reversible ADP-ribosylation in response to NH4+ and anaerobic conditions in Azospirillum brasilense. The effect of mutations in ntrBC on this regulation was examined. While NH4+ addition to ntrBC mutants caused a partial loss of nitrogenase activity, the effect was substantially smaller than that seen in ntr+ strains. In contrast, nitrogenase activity in these mutants was normally regulated in response to anaerobic conditions. The analysis of mutants lacking both the ntrBC gene products and dinitrogenase reductase activating glycohydrolase (DRAG) suggested that the primary effect of the ntrBC mutations was to alter the regulation of DRAG activity. Although nif expression in the ntr mutants appeared normal, as judged by activity, glutamine synthetase activity was significantly lower in ntrBC mutants than in the wild type. We hypothesize that this lower glutamine synthetase activity may delay the transduction of the NH4+ signal necessary for the inactivation of DRAG, resulting in a reduced response of nitrogenase activity to NH4+. Finally, data presented here suggest that different environmental stimuli use independent signal pathways to affect this reversible ADP-ribosylation system.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burris R. H. Nitrogenases. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9339–9342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espin G., Alvarez-Morales A., Merrick M. Complementation analysis of glnA-linked mutations which affect nitrogen fixation in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):213–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00272907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellay R., Frey J., Krisch H. Interposon mutagenesis of soil and water bacteria: a family of DNA fragments designed for in vitro insertional mutagenesis of gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer M., Levy E., Geller T. Regulatory mutation that controls nif expression and histidine transport in Azospirillum brasilense. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):423–426. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.423-426.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu H. A., Hartmann A., Lowery R. G., Fitzmaurice W. P., Roberts G. P., Burris R. H. Posttranslational regulatory system for nitrogenase activity in Azospirillum spp. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4679–4685. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4679-4685.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann A., Burris R. H. Regulation of nitrogenase activity by oxygen in Azospirillum brasilense and Azospirillum lipoferum. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):944–948. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.944-948.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann A., Fu H., Burris R. H. Regulation of nitrogenase activity by ammonium chloride in Azospirillum spp. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):864–870. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.864-870.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanemoto R. H., Ludden P. W. Amino acid concentrations in Rhodospirillum rubrum during expression and switch-off of nitrogenase activity. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3035–3043. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3035-3043.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanemoto R. H., Ludden P. W. Effect of ammonia, darkness, and phenazine methosulfate on whole-cell nitrogenase activity and Fe protein modification in Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):713–720. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.713-720.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranz R. G., Haselkorn R. Characterization of nif regulatory genes in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata using lac gene fusions. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):203–215. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. D., Hu C. Z., Yoch D. C. Changes in amino acid and nucleotide pools of Rhodospirillum rubrum during switch-off of nitrogenase activity initiated by NH4+ or darkness. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):231–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.231-237.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang J. H., Nielsen G. M., Lies D. P., Burris R. H., Roberts G. P., Ludden P. W. Mutations in the draT and draG genes of Rhodospirillum rubrum result in loss of regulation of nitrogenase by reversible ADP-ribosylation. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(21):6903–6909. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.21.6903-6909.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang Y. Y., Arsène F., Elmerich C. Characterization of the ntrBC genes of Azospirillum brasilense Sp7: their involvement in the regulation of nitrogenase synthesis and activity. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Aug;240(2):188–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00277056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowery R. G., Ludden P. W. Purification and properties of dinitrogenase reductase ADP-ribosyltransferase from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16714–16719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludden P. W., Roberts G. P. Regulation of nitrogenase activity by reversible ADP ribosylation. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1989;30:23–56. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152830-0.50004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyra C. A., Van Berkum P. Nitrate reduction nitrogenase activity in Spirillum lipoferum1. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Mar;23(3):306–310. doi: 10.1139/m77-045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul T. D., Ludden P. W. Adenine nucleotide levels in Rhodospirillum rubrum during switch-off of whole-cell nitrogenase activity. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):961–969. doi: 10.1042/bj2240961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierrard J., Ludden P. W., Roberts G. P. Posttranslational regulation of nitrogenase in Rhodobacter capsulatus: existence of two independent regulatory effects of ammonium. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(5):1358–1366. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.5.1358-1366.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saari L. L., Triplett E. W., Ludden P. W. Purification and properties of the activating enzyme for iron protein of nitrogenase from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15502–15508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soliman A., Nordlund S. Studies on the effect of NAD(H) on nitrogenase activity in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Microbiol. 1992;157(5):431–435. doi: 10.1007/BF00249100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarrand J. J., Krieg N. R., Döbereiner J. A taxonomic study of the Spirillum lipoferum group, with descriptions of a new genus, Azospirillum gen. nov. and two species, Azospirillum lipoferum (Beijerinck) comb. nov. and Azospirillum brasilense sp. nov. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Aug;24(8):967–980. doi: 10.1139/m78-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toukdarian A., Kennedy C. Regulation of nitrogen metabolism in Azotobacter vinelandii: isolation of ntr and glnA genes and construction of ntr mutants. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):399–407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04225.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall J. D., Braddock K. Mapping of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata nif genes. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):404–410. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.404-410.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Burris R. H., Ludden P. W., Roberts G. P. Posttranslational regulation of nitrogenase activity by anaerobiosis and ammonium in Azospirillum brasilense. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(21):6781–6788. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.21.6781-6788.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Burris R. H., Roberts G. P. Cloning, sequencing, mutagenesis, and functional characterization of draT and draG genes from Azospirillum brasilense. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3364–3369. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3364-3369.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumft W. G., Castillo F. Regulatory properties of the nitrogenase from Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Apr 27;117(1):53–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00689351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Zamaroczy M., Delorme F., Elmerich C. Characterization of three different nitrogen-regulated promoter regions for the expression of glnB and glnA in Azospirillum brasilense. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Dec;224(3):421–430. doi: 10.1007/BF00262437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Zamaroczy M., Paquelin A., Elmerich C. Functional organization of the glnB-glnA cluster of Azospirillum brasilense. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2507–2515. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2507-2515.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]