Abstract
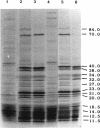
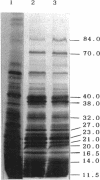
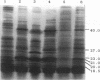
The molecular basis of tolerance to osmotic stress was investigated with a cyanobacterium, Anabaena sp. strain L-31. The inherent osmotolerance of this strain (50% growth inhibition at 350 mM sucrose) was enhanced by adaptation with 100 mM sucrose for 30 min. Addition of 10 mM KNO3 during growth also conferred significant osmoprotection, but addition of 3 mM NH4Cl did not. Exposure of cells to 350 mM sucrose induced the expression of at least 12 osmotic-stress-induced proteins (OSPs) within 30 min, in the molecular mass range of 11.5 to 84 kDa. Exposure of cells to 100 mM sucrose or to 10 mM nitrate also induced all the OSPs, but addition of ammonium did not. The observed correspondence between the presence of OSPs and osmotolerance strongly suggests a role for OSPs in osmotolerance of Anabaena sp. strain L-31.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apte S. K., Bhagwat A. A. Salinity-stress-induced proteins in two nitrogen-fixing Anabaena strains differentially tolerant to salt. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):909–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.909-915.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apte S. K., Haselkorn R. Cloning of salinity stress-induced genes from the salt-tolerant nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium Anabaena torulosa. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Nov;15(5):723–733. doi: 10.1007/BF00016122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apte S. K., Reddy B. R., Thomas J. Relationship between Sodium Influx and Salt Tolerance of Nitrogen-Fixing Cyanobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1934–1939. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1934-1939.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhagwat A. A., Apte S. K. Comparative analysis of proteins induced by heat shock, salinity, and osmotic stress in the nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain L-31. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5187–5189. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5187-5189.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumwald E., Mehlhorn R. J., Packer L. Studies of osmoregulation in salt adaptation of cyanobacteria with ESR spin-probe techniques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2599–2602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowitzka L. J., Demmerle S., Mackay M. A., Norton R. S. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance study of osmoregulation in a blue-green alga. Science. 1980 Nov 7;210(4470):650–651. doi: 10.1126/science.210.4470.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close T. J., Lammers P. J. An osmotic stress protein of cyanobacteria is immunologically related to plant dehydrins. Plant Physiol. 1993 Mar;101(3):773–779. doi: 10.1104/pp.101.3.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N. Physiological and genetic responses of bacteria to osmotic stress. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):121–147. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.121-147.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes T. A., Iyer V., Apte S. K. Differential responses of nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria to salinity and osmotic stresses. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Mar;59(3):899–904. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.3.899-904.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. E., Chaisson S. A., Matin A. Starvation-induced cross protection against osmotic challenge in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2779–2781. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2779-2781.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni Bhriain N., Dorman C. J., Higgins C. F. An overlap between osmotic and anaerobic stress responses: a potential role for DNA supercoiling in the coordinate regulation of gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jul;3(7):933–942. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00243.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. R., Apte S. K., Thomas J. Enhancement of cyanobacterial salt tolerance by combined nitrogen. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):204–210. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Potts M. Novel water stress protein from a desiccation-tolerant cyanobacterium. Purification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12546–12553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh N. K., Nelson D. E., Kuhn D., Hasegawa P. M., Bressan R. A. Molecular Cloning of Osmotin and Regulation of Its Expression by ABA and Adaptation to Low Water Potential. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jul;90(3):1096–1101. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.3.1096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. Absence of the pigments of photosystem II of photosynthesis in heterocysts of a blue-green alga. Nature. 1970 Oct 10;228(5267):181–183. doi: 10.1038/228181b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]