Abstract
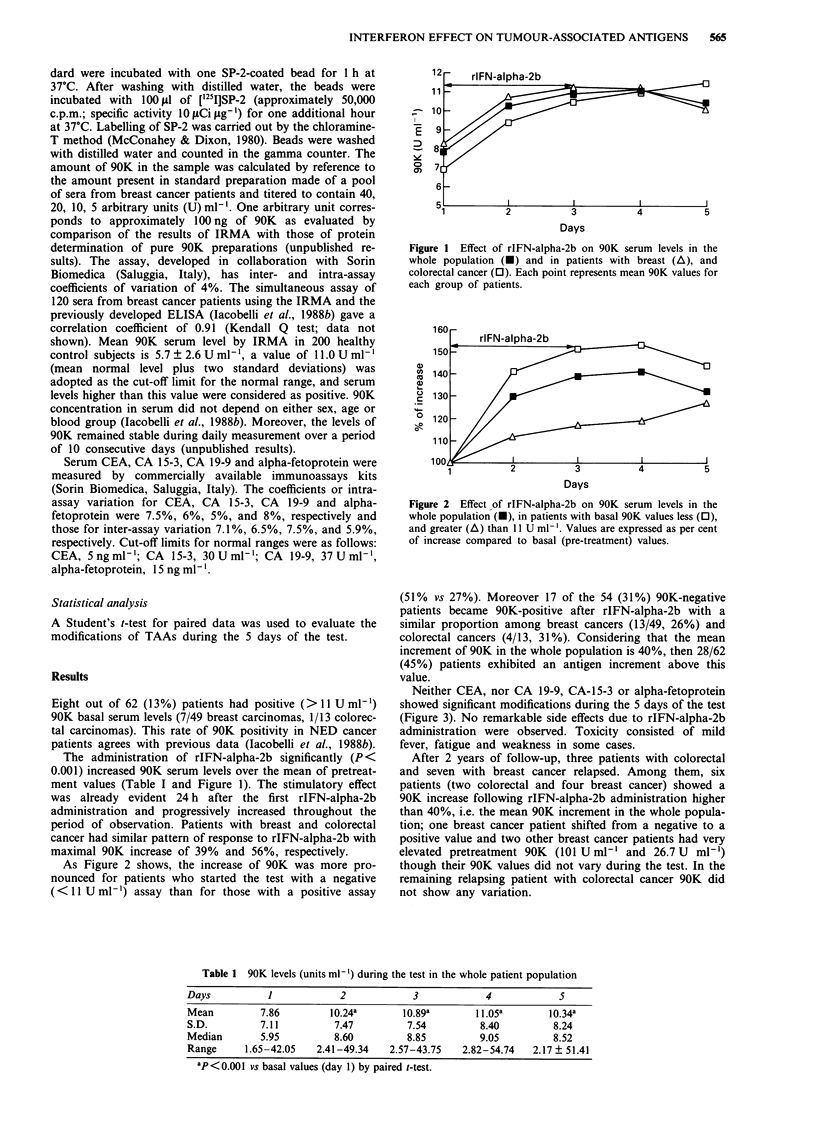
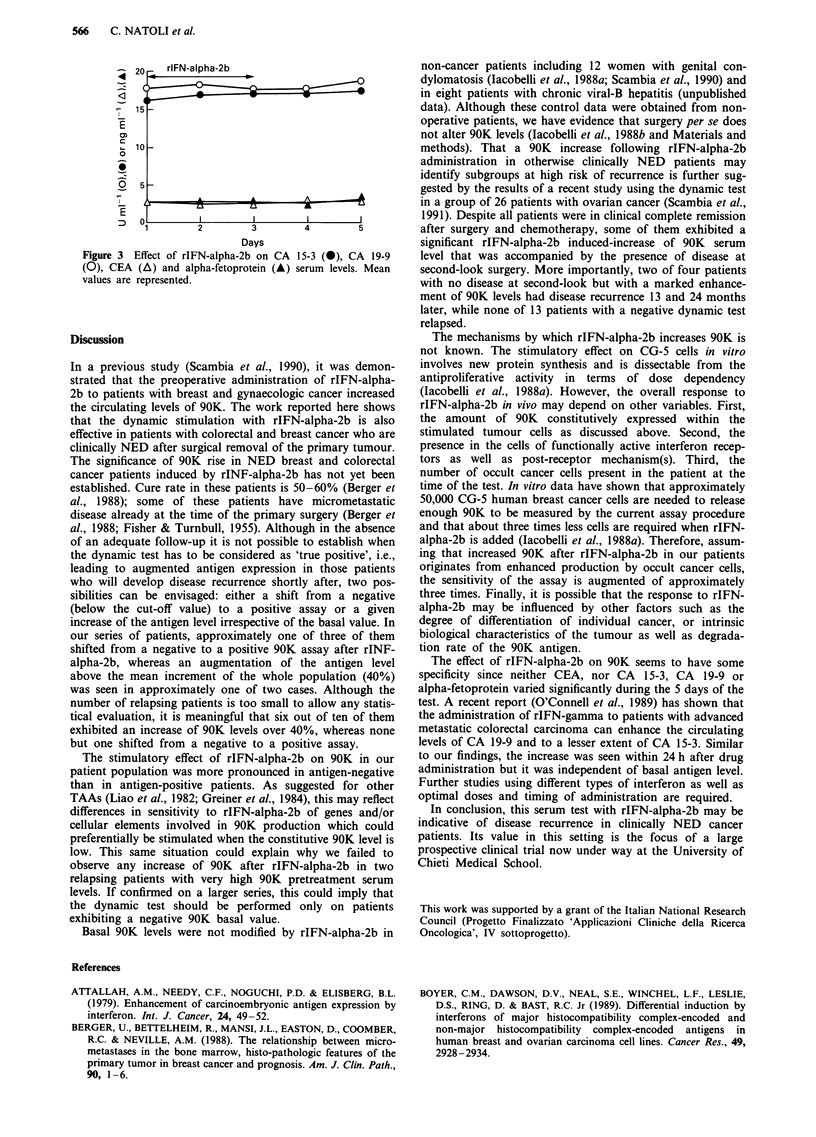
We have previously shown that a short course of recombinant interferon-alpha-2b (rIFN-alpha-2b) (3 million units day for 5 days) for patients with primary gynaecologic malignancies was able to increase the circulating levels of a newly discovered tumour associated antigen, termed 90K. In this study, we have investigated the effects of the same modality of administration of rIFN-alpha-2b in 62 patients with breast and colorectal cancer whose primary tumour was surgically removed 1 month before and who were without evidence of disease (NED) at the time of the study. A significant increase of 90K serum concentration was already observed 24 h after the first r-IFN-alpha-2b injection and persisted throughout the investigational period. The increase was more pronounced in patients with a basal 90K-negative than a 90K-positive assay. Of 54 patients who started the test with a 90K negative assay, 17 (31%) shifted to a positive assay after rIFN-alpha-2b. Twenty-eight of 62 (45%) patients exhibited a 90K value above the mean increment of the whole population. The serum levels of CEA, CA-15-3, CA 19-9, and alpha-fetoprotein measured in the same serum samples were not modified. After 2 years of follow-up, ten patients relapsed. Six of them showed a 90K increase above the mean increment of the whole population. As with ovarian cancer, the increase of 90K following r-IFN-alpha-2b administration might be of importance for the early detection of disease recurrence in clinically NED breast and colon cancer patients.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attallah A. M., Needy C. F., Noguchi P. D., Elisberg B. L. Enhancement of carcinoembryonic antigen expression by interferon. Int J Cancer. 1979 Jul 15;24(1):49–52. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger U., Bettelheim R., Mansi J. L., Easton D., Coombes R. C., Neville A. M. The relationship between micrometastases in the bone marrow, histopathologic features of the primary tumor in breast cancer and prognosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1988 Jul;90(1):1–6. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/90.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer C. M., Dawson D. V., Neal S. E., Winchell L. F., Leslie D. S., Ring D., Bast R. C., Jr Differential induction by interferons of major histocompatibility complex-encoded and non-major histocompatibility complex-encoded antigens in human breast and ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 1;49(11):2928–2934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER E. R., TURNBULL R. B., Jr The cytologic demonstration and significance of tumor cells in the mesenteric venous blood in patients with colorectal carcinoma. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1955 Jan;100(1):102–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacomini P., Imberti L., Aguzzi A., Fisher P. B., Trinchieri G., Ferrone S. Immunochemical analysis of the modulation of human melanoma-associated antigens by DNA recombinant immune interferon. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2887–2894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greiner J. W., Fisher P. B., Pestka S., Schlom J. Differential effects of recombinant human leukocyte interferons on cell surface antigen expression. Cancer Res. 1986 Oct;46(10):4984–4990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greiner J. W., Guadagni F., Noguchi P., Pestka S., Colcher D., Fisher P. B., Schlom J. Recombinant interferon enhances monoclonal antibody-targeting of carcinoma lesions in vivo. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):895–898. doi: 10.1126/science.3580039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greiner J. W., Hand P. H., Noguchi P., Fisher P. B., Pestka S., Schlom J. Enhanced expression of surface tumor-associated antigens on human breast and colon tumor cells after recombinant human leukocyte alpha-interferon treatment. Cancer Res. 1984 Aug;44(8):3208–3214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guadagni F., Witt P. L., Robbins P. F., Schlom J., Greiner J. W. Regulation of carcinoembryonic antigen expression in different human colorectal tumor cells by interferon-gamma. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 1;50(19):6248–6255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacobelli S., Arno E., Sismondi P., Natoli C., Gentiloni N., Scambia G., Giai M., Cortese P., Panici P. B., Mancuso S. Measurement of a breast cancer associated antigen detected by monoclonal antibody SP-2 in sera of cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1988 Apr;11(1):19–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01807554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacobelli S., Arnò E., D'Orazio A., Coletti G. Detection of antigens recognized by a novel monoclonal antibody in tissue and serum from patients with breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1986 Jun;46(6):3005–3010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacobelli S., Scambia G., Natoli C., Panici P. B., Baiocchi G., Perrone L., Mancuso S. Recombinant human leukocyte interferon-alpha 2b stimulates the synthesis and release of a 90K tumor-associated antigen in human breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 1988 Aug 15;42(2):182–184. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao S. K., Kwong P. C., Khosravi M., Dent P. B. Enhanced expression of melanoma-associated antigens and beta 2-microglobulin on cultured human melanoma cells by interferon. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 Jan;68(1):19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth C., Fuith L. C., Böck G., Daxenbichler G., Dapunt O. Modulation of ovarian carcinoma tumor marker CA-125 by gamma-interferon. Cancer Res. 1989 Dec 1;49(23):6538–6542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. Radioiodination of proteins by the use of the chloramine-T method. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):210–213. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell M. J., Ritts R. A., Jr, Moertel C. G., Schutt A. J., Sherwin S. A. Recombinant interferon-gamma lacks activity against metastatic colorectal cancer but increases serum levels of CA 19-9. Cancer. 1989 May 15;63(10):1998–2004. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890515)63:10<1998::aid-cncr2820631022>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlinson G., Balkwill F., Snook D., Hooker G., Epenetos A. A. Enhancement by gamma-interferon of in vivo tumor radiolocalization by a monoclonal antibody against HLA-DR antigen. Cancer Res. 1986 Dec;46(12 Pt 1):6413–6417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scambia G., Panici P. B., Baiocchi G., Gallo A., Laurelli G., Iacobelli S., Mancuso S. Recombinant alpha-2b-interferon dynamic test as a potential tool in predicting disease status during second look in ovarian cancer. A preliminary report. Cancer. 1991 Dec 15;68(12):2582–2585. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19911215)68:12<2582::aid-cncr2820681210>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scambia G., Panici P. B., Iacobelli S., Baiocchi G., Battaglia F., Perrone L., Sonsini C., Ferrandina G., Natoli C., Mancuso S. Recombinant alpha-2b-interferon enhances the circulating levels of a 90-kilodalton (K) tumor-associated antigen in patients with gynecologic and breast malignancies. Cancer. 1990 Mar 15;65(6):1325–1328. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19900315)65:6<1325::aid-cncr2820650613>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suter M., Butler J. E., Peterman J. H. The immunochemistry of sandwich ELISAs--III. The stoichiometry and efficacy of the protein-avidin-biotin capture (PABC) system. Mol Immunol. 1989 Mar;26(3):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


