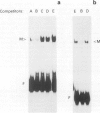
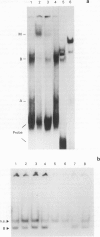
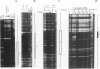
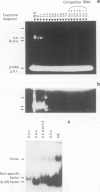
Abstract
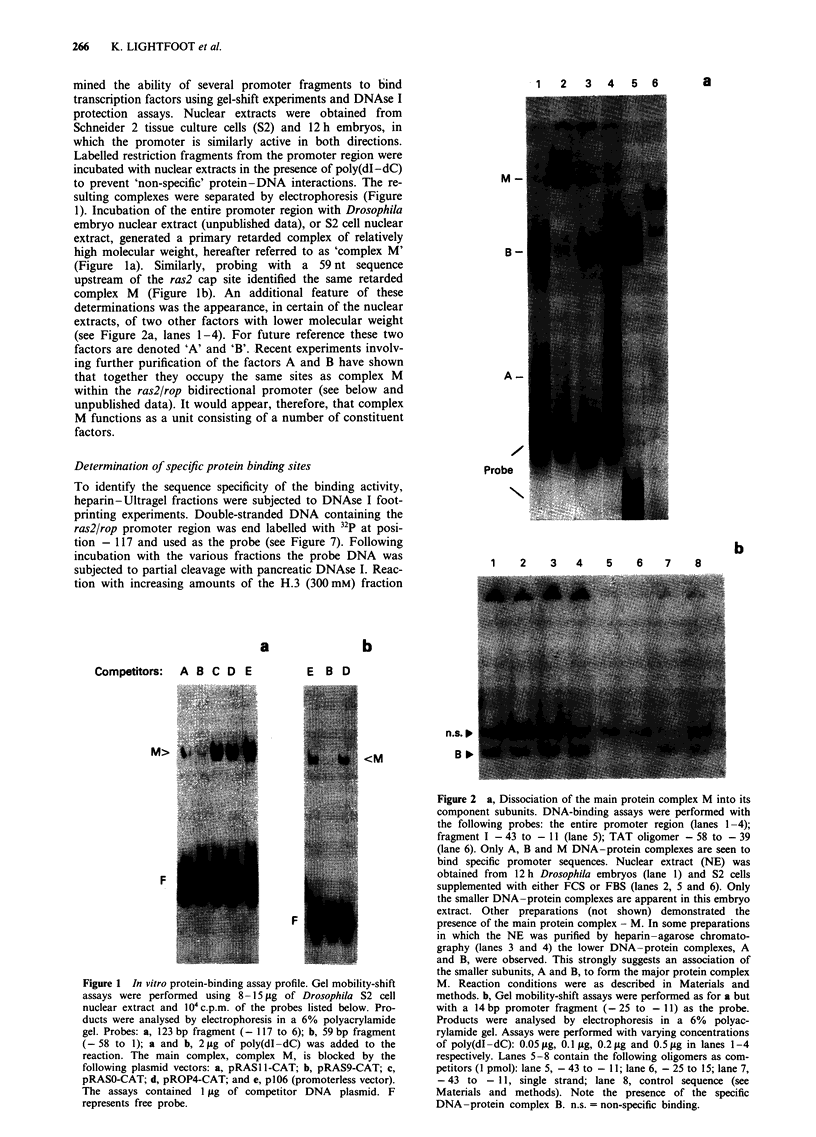
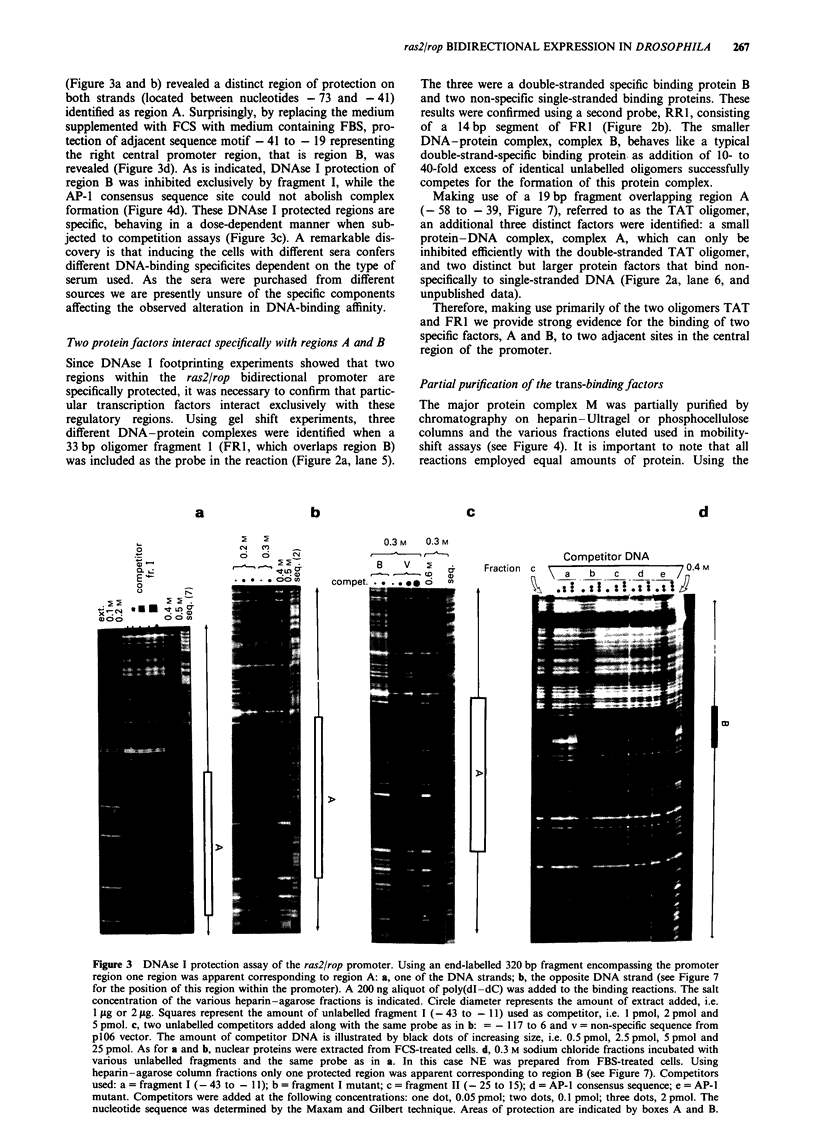
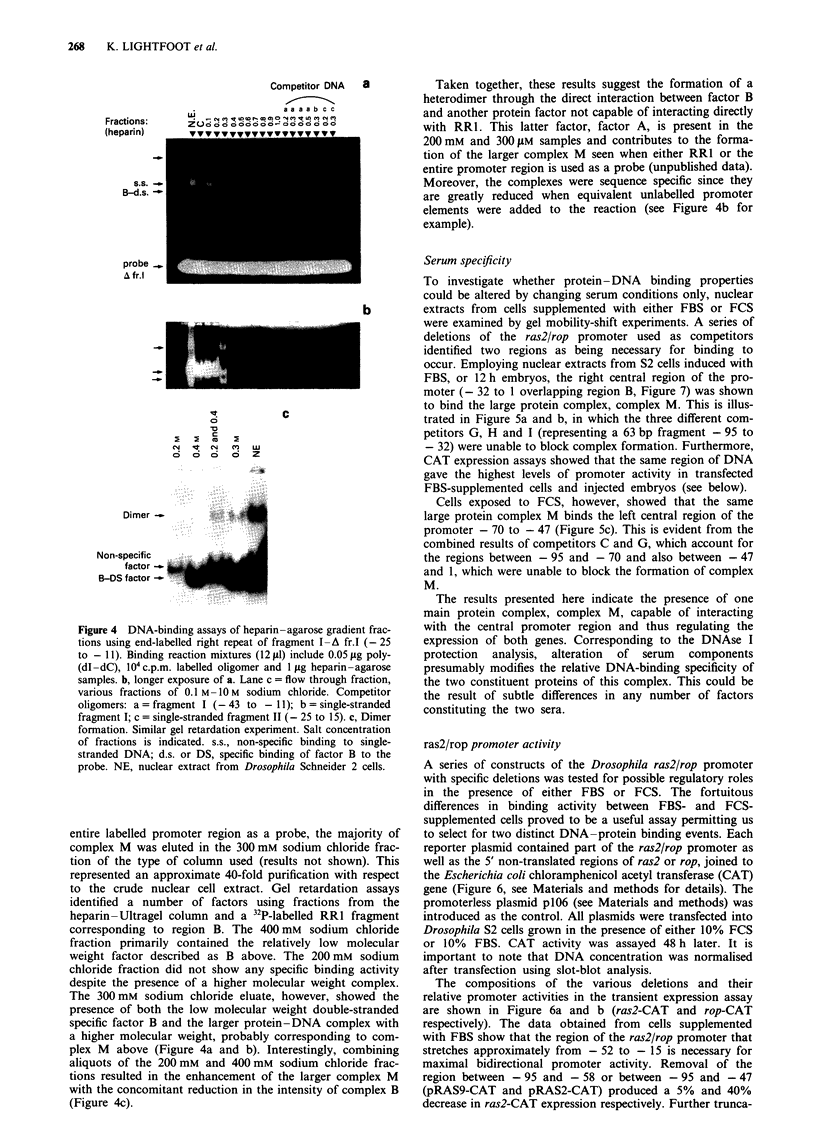
The Drosophila ras2 promoter region exhibits bidirectional activity, as has been demonstrated for the human c-Ha-ras1 and the mouse c-Ki-ras. Here we address a unique case of ras regulation, as Drosophila ras2 provides the only example to date in which the flanking gene (rop) and its product have been isolated. A linking mechanism of control suggests a mutual interaction between the two gene products. Our studies indicate that the Drosophila ras2 promoter region shares with the human c-Ha-ras1 promoter a CACCC box and an AP-1-like sequence. A 14 bp promoter fragment which holds a CACCC element is demonstrated to interact with a specific transcription factor (factor B). This CACCC promoter element represents a stretch of imperfect palindrome. We present evidence that this factor can form a complex with another specific DNA-binding protein (factor A). The binding sites (A + B) for these protein factors are essential for 95% expression of both genes flanking the promoter (ras2 and rop). Region A consists of four overlapping consensus sequences: a TATA-like element, a DSE-like motif (the core sequence of the serum response element), a DRE octamer, which has been shown to play a role in cell proliferation, and a 5 bp direct repeat representing the GATA consensus sequence. Factor A has a very weak affinity to the full promoter region, but when complexed with factor B binding efficiency is enhanced. We also show that alterations of DNA-protein binding specificities can be achieved by supplementing the growth media with different sera.
Full text
PDF

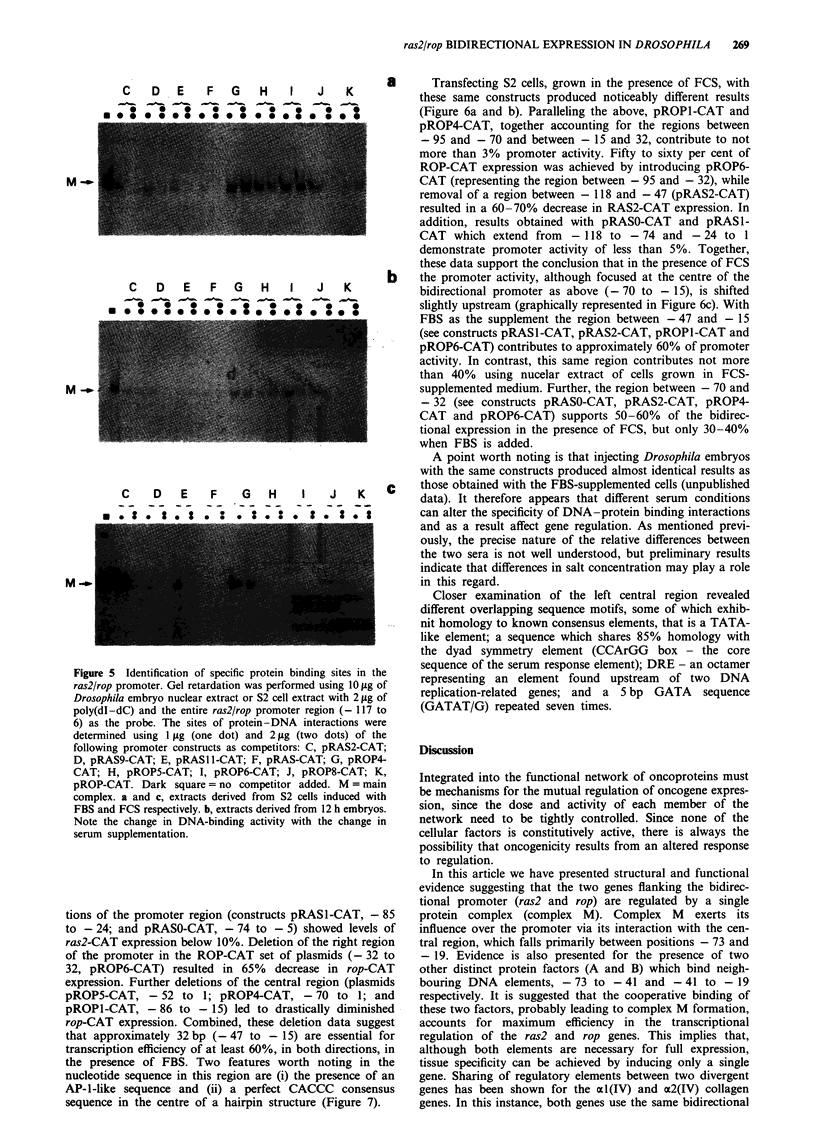


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K. Amplification of cellular oncogenes in cancer cells. Med Biol. 1984;62(6):304–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almoguera C., Shibata D., Forrester K., Martin J., Arnheim N., Perucho M. Most human carcinomas of the exocrine pancreas contain mutant c-K-ras genes. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90571-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkhipova I. R., Ilyin Y. V. Properties of promoter regions of mdg1 Drosophila retrotransposon indicate that it belongs to a specific class of promoters. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1169–1177. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08057.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection of the ras oncogene protein into PC12 cells induces morphological differentiation. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras oncogenes: their role in neoplasia. Eur J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;20(3):225–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1990.tb01848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Broek D., Wigler M. ras proteins can induce meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Müller-Brechlin R., Carstens C., Meese E., Zang K. D. Enhanced expression of four cellular oncogenes in a human glioblastoma cell line. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1987 Apr;25(2):285–292. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(87)90189-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Verlaan-de Vries M., van Boom J. H., van der Eb A. J., Vogelstein B. Prevalence of ras gene mutations in human colorectal cancers. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):293–297. doi: 10.1038/327293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L. The ras gene family and human carcinogenesis. Mutat Res. 1988 May;195(3):255–271. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(88)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L., Verlaan-de Vries M., Marshall C. J., Veeneman G. H., van Boom J. H., van der Eb A. J. A human gastric carcinoma contains a single mutated and an amplified normal allele of the Ki-ras oncogene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1209–1217. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(17):4682–4689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock H. W. Sequence and genomic structure of ras homologues Dmras85D and Dmras64B of Drosophila melanogaster. Gene. 1987;51(2-3):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher P. Weight matrix descriptions of four eukaryotic RNA polymerase II promoter elements derived from 502 unrelated promoter sequences. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 20;212(4):563–578. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbelo P. D., Martin G. R., Yamada Y. Alpha 1(IV) and alpha 2(IV) collagen genes are regulated by a bidirectional promoter and a shared enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9679–9682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang E. H., Furth M. E., Scolnick E. M., Lowy D. R. Tumorigenic transformation of mammalian cells induced by a normal human gene homologous to the oncogene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):479–483. doi: 10.1038/297479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P. Small GTP-binding proteins of the ras family: a conserved functional mechanism? Cancer Cells. 1991 Apr;3(4):117–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P. The ras superfamily proteins. Biochimie. 1988 Jul;70(7):865–868. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
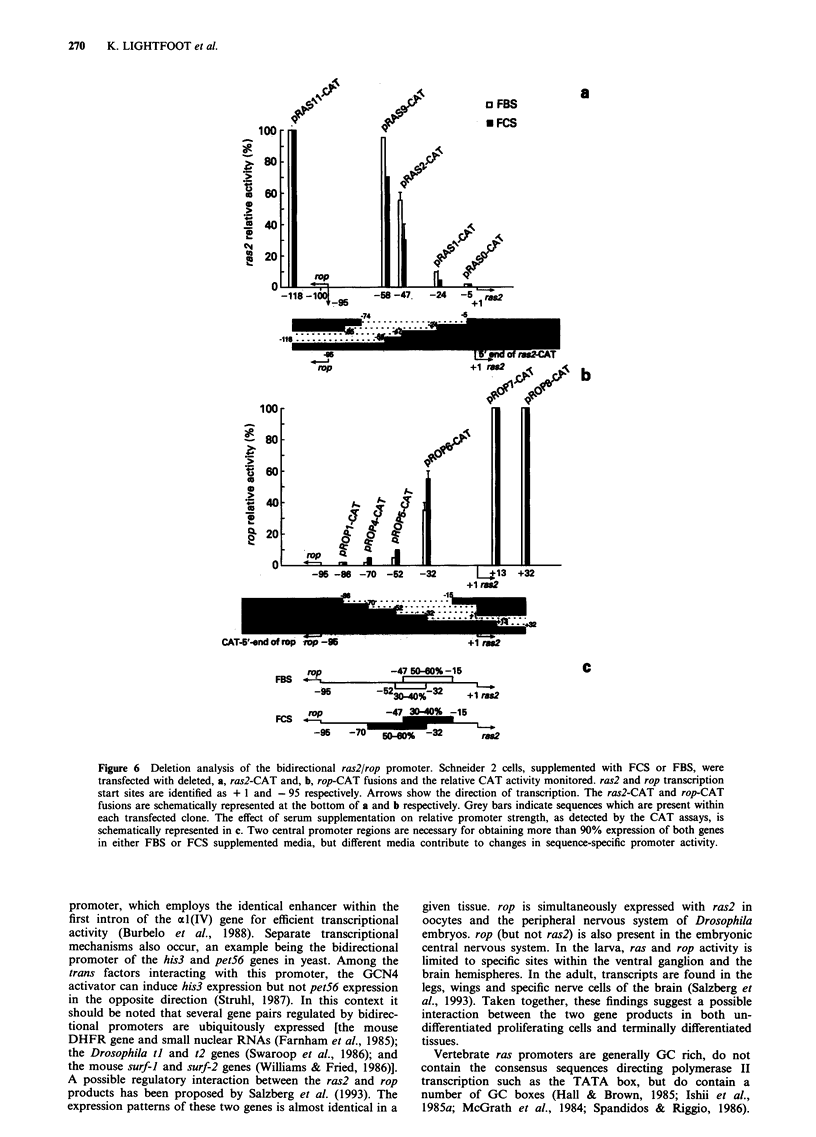
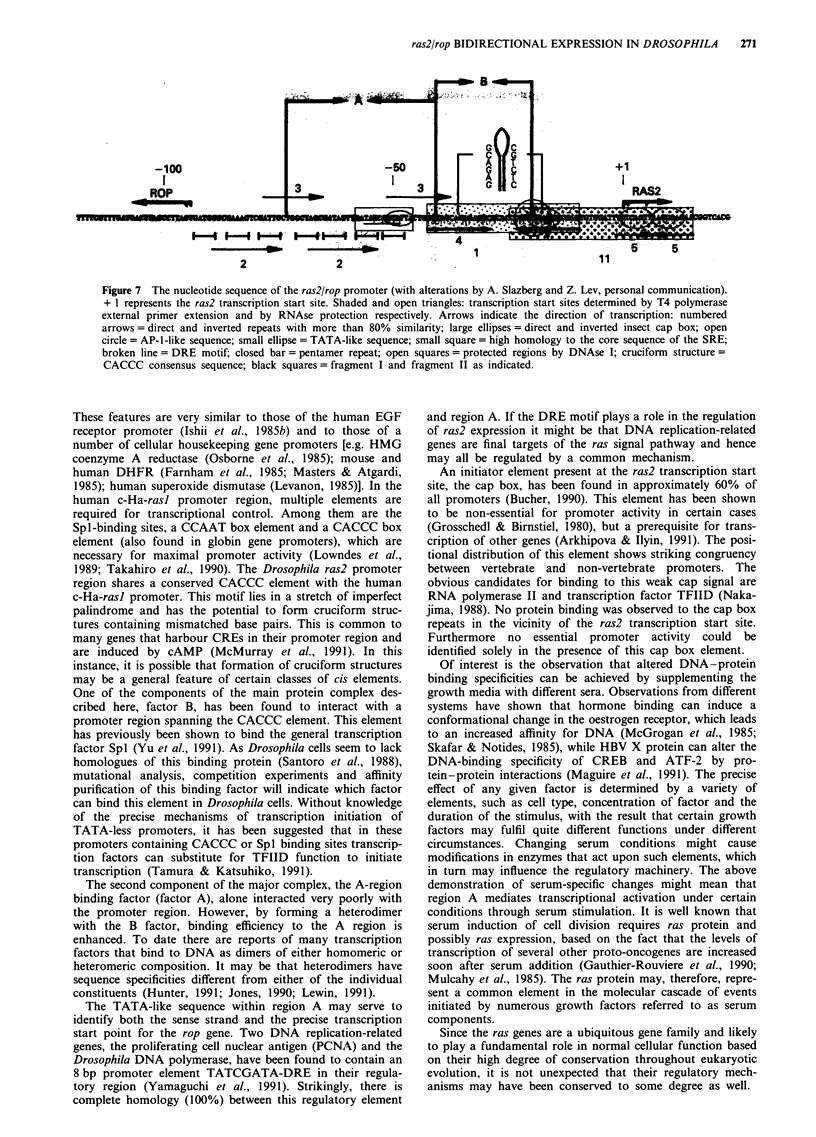
- Cohen N., Salzberg A., Lev Z. A bidirectional promoter is regulating the Drosophila ras2 gene. Oncogene. 1988 Aug;3(2):137–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Fromental C., Augereau P., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Cell-type specific protein binding to the enhancer of simian virus 40 in nuclear extracts. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):544–548. doi: 10.1038/323544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Biasi F., Del Sal G., Hand P. H. Evidence of enhancement of the ras oncogene protein product (p21) in a spectrum of human tumors. Int J Cancer. 1989 Mar 15;43(3):431–435. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., Nieto A., Koller R., DeFeo-Jones D., Scolnick E. M. Nucleotide sequence of two rasH related-genes isolated from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3611–3618. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J. The ras superfamily of small GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):469–472. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90300-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan S. E., Giddings B. W., Brooks M. W., Buday L., Sizeland A. M., Weinberg R. A. Association of Sos Ras exchange protein with Grb2 is implicated in tyrosine kinase signal transduction and transformation. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):45–51. doi: 10.1038/363045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Abrams J. M., Schimke R. T. Opposite-strand RNAs from the 5' flanking region of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3978–3982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano O., Aldrich T., Tamanoi F., Taparowsky E., Furth M., Wigler M. Analysis of the transforming potential of the human H-ras gene by random mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4008–4012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Gross M., Kamata T., Rosenberg M., Sweet R. W. Microinjection of the oncogene form of the human H-ras (T-24) protein results in rapid proliferation of quiescent cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester K., Almoguera C., Han K., Grizzle W. E., Perucho M. Detection of high incidence of K-ras oncogenes during human colon tumorigenesis. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):298–303. doi: 10.1038/327298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallick G. E., Kurzrock R., Kloetzer W. S., Arlinghaus R. B., Gutterman J. U. Expression of p21ras in fresh primary and metastatic human colorectal tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1795–1799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier-Rouvière C., Fernandez A., Lamb N. J. ras-induced c-fos expression and proliferation in living rat fibroblasts involves C-kinase activation and the serum response element pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):171–180. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08093.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagag N., Halegoua S., Viola M. Inhibition of growth factor-induced differentiation of PC12 cells by microinjection of antibody to ras p21. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):680–682. doi: 10.1038/319680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A., Brown R. Human N-ras: cDNA cloning and gene structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5255–5268. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):635–640. doi: 10.1126/science.2116664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand P. H., Thor A., Wunderlich D., Muraro R., Caruso A., Schlom J. Monoclonal antibodies of predefined specificity detect activated ras gene expression in human mammary and colon carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5227–5231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan I. K., Carthew R. W., Rubin G. M. The Drosophila roughened mutation: activation of a rap homolog disrupts eye development and interferes with cell determination. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):717–722. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. K., Trusko S. P., Freeman N., George D. L. Structural and functional characterization of the promoter region of the mouse c-Ki-ras gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2592–2596. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Cooperation between oncogenes. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):249–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90637-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Promoter region of the human Harvey ras proto-oncogene: similarity to the EGF receptor proto-oncogene promoter. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1378–1381. doi: 10.1126/science.2999983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Xu Y. H., Stratton R. H., Roe B. A., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Characterization and sequence of the promoter region of the human epidermal growth factor receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4920–4924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. Transcriptional regulation by dimerization: two sides to an incestuous relationship. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):9–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90207-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitayama H., Sugimoto Y., Matsuzaki T., Ikawa Y., Noda M. A ras-related gene with transformation suppressor activity. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90985-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev Z., Kimchie Z., Hessel R., Segev O. Expression of ras cellular oncogenes during development of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1540–1542. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levanon D., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Dafni N., Wigderson M., Sherman L., Bernstein Y., Laver-Rudich Z., Danciger E., Stein O., Groner Y. Architecture and anatomy of the chromosomal locus in human chromosome 21 encoding the Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):77–84. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02320.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Oncogenic conversion by regulatory changes in transcription factors. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90640-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh E., Glazer L., Segal D., Schlessinger J., Shilo B. Z. The Drosophila EGF receptor gene homolog: conservation of both hormone binding and kinase domains. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):599–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowndes N. F., Paul J., Wu J., Allan M. c-Ha-ras gene bidirectional promoter expressed in vitro: location and regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3758–3770. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire H. F., Hoeffler J. P., Siddiqui A. HBV X protein alters the DNA binding specificity of CREB and ATF-2 by protein-protein interactions. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):842–844. doi: 10.1126/science.1827531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters J. N., Attardi G. Discrete human dihydrofolate reductase gene transcripts present in polysomal RNA map with their 5' ends several hundred nucleotides upstream of the main mRNA start site. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):493–500. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. ras GTPase activating protein: signal transmitter and signal terminator. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90976-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Capon D. J., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Comparative biochemical properties of normal and activated human ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):644–649. doi: 10.1038/310644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrogan M., Simonsen C. C., Smouse D. T., Farnham P. J., Schimke R. T. Heterogeneity at the 5' termini of mouse dihydrofolate reductase mRNAs. Evidence for multiple promoter regions. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2307–2314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurray C. T., Wilson W. D., Douglass J. O. Hairpin formation within the enhancer region of the human enkephalin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):666–670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozer B., Marlor R., Parkhurst S., Corces V. Characterization and developmental expression of a Drosophila ras oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):885–889. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy L. S., Smith M. R., Stacey D. W. Requirement for ras proto-oncogene function during serum-stimulated growth of NIH 3T3 cells. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):241–243. doi: 10.1038/313241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase T., Ueno Y., Ishii S. Transcriptional control of the human Harvey ras proto-oncogene: role of multiple elements in the promoter region. Gene. 1990 Oct 15;94(2):249–253. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90395-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification, genetic specificity, and TATA box-promoter interactions of TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4028–4040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuman-Silberberg F. S., Schejter E., Hoffmann F. M., Shilo B. Z. The Drosophila ras oncogenes: structure and nucleotide sequence. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1027–1033. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90437-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne T. F., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. 5' end of HMG CoA reductase gene contains sequences responsible for cholesterol-mediated inhibition of transcription. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):203–212. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papageorge A. G., Defeo-Jones D., Robinson P., Temeles G., Scolnick E. M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae synthesizes proteins related to the p21 gene product of ras genes found in mammals. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):23–29. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinones S., Saus J., Otani Y., Harris E. D., Jr, Kurkinen M. Transcriptional regulation of human stromelysin. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8339–8344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Reynolds R. K., Santos E., Barbacid M. A point mutation is responsible for the acquisition of transforming properties by the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):149–152. doi: 10.1038/300149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reymond C. D., Gomer R. H., Mehdy M. C., Firtel R. A. Developmental regulation of a Dictyostelium gene encoding a protein homologous to mammalian ras protein. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. Signal transduction and the fate of the R7 photoreceptor in Drosophila. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):372–377. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90258-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan W. A., Jr, Franza B. R., Jr, Gilman M. Z. Two distinct cellular phosphoproteins bind to the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1785–1792. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzberg A., Cohen N., Halachmi N., Kimchie Z., Lev Z. The Drosophila Ras2 and Rop gene pair: a dual homology with a yeast Ras-like gene and a suppressor of its loss-of-function phenotype. Development. 1993 Apr;117(4):1309–1319. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.4.1309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Mermod N., Andrews P. C., Tjian R. A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):218–224. doi: 10.1038/334218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schejter E. D., Shilo B. Z. Characterization of functional domains of p21 ras by use of chimeric genes. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):407–412. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03643.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider I. Cell lines derived from late embryonic stages of Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1972 Apr;27(2):353–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D., Shilo B. Z. Tissue localization of Drosophila melanogaster ras transcripts during development. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2241–2248. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skafar D. F., Notides A. C. Modulation of the estrogen receptor's affinity for DNA by estradiol. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12208–12213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J. A nonchromatographic assay for expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in eucaryotic cells. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A. Oncogene activation in malignant transformation: a study of H-ras in human breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 1987 Sep-Oct;7(5B):991–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Riggio M. Promotor and enhancer like activity at the 5'-end of normal and T24 Ha-ras1 genes. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 28;203(2):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80736-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Promoters, activator proteins, and the mechanism of transcriptional initiation in yeast. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):295–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaroop A., Sun J. W., Paco-Larson M. L., Garen A. Molecular organization and expression of the genetic locus glued in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):833–841. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabin C. J., Bradley S. M., Bargmann C. I., Weinberg R. A., Papageorge A. G., Scolnick E. M., Dhar R., Lowy D. R., Chang E. H. Mechanism of activation of a human oncogene. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):143–149. doi: 10.1038/300143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Mikoshiba K. Role of a GC-rich motif in transcription regulation of the adenovirus type 2 IVa2 promoter which lacks typical TATA-box element. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 22;282(1):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80450-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Slamon D. J., Battifora H., Cline M. J. Expression of p21 ras oncoproteins in human cancers. Cancer Res. 1986 Mar;46(3):1465–1470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taparowsky E., Suard Y., Fasano O., Shimizu K., Goldfarb M., Wigler M. Activation of the T24 bladder carcinoma transforming gene is linked to a single amino acid change. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):762–765. doi: 10.1038/300762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theillet C., Lidereau R., Escot C., Hutzell P., Brunet M., Gest J., Schlom J., Callahan R. Loss of a c-H-ras-1 allele and aggressive human primary breast carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1986 Sep;46(9):4776–4781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth S. C., Vincent W. S., 3rd, Bilodeau-Wentworth D. A Drosophila genomic sequence with homology to human epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):178–180. doi: 10.1038/314178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J., Fried M. The MES-1 murine enhancer element is closely associated with the heterogeneous 5' ends of two divergent transcription units. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4558–4569. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Ferrandon D., Rosales R., Vigneron M., Macchi M., Ruffenach F., Chambon P. One cell-specific and three ubiquitous nuclear proteins bind in vitro to overlapping motifs in the domain B1 of the SV40 enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3005–3013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Hirose F., Nishida Y., Matsukage A. Repression of the Drosophila proliferating-cell nuclear antigen gene promoter by zerknüllt protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4909–4917. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. Y., Motamed K., Chen J., Bailey A. D., Shen C. K. The CACC box upstream of human embryonic epsilon globin gene binds Sp1 and is a functional promoter element in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8907–8915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]