Abstract
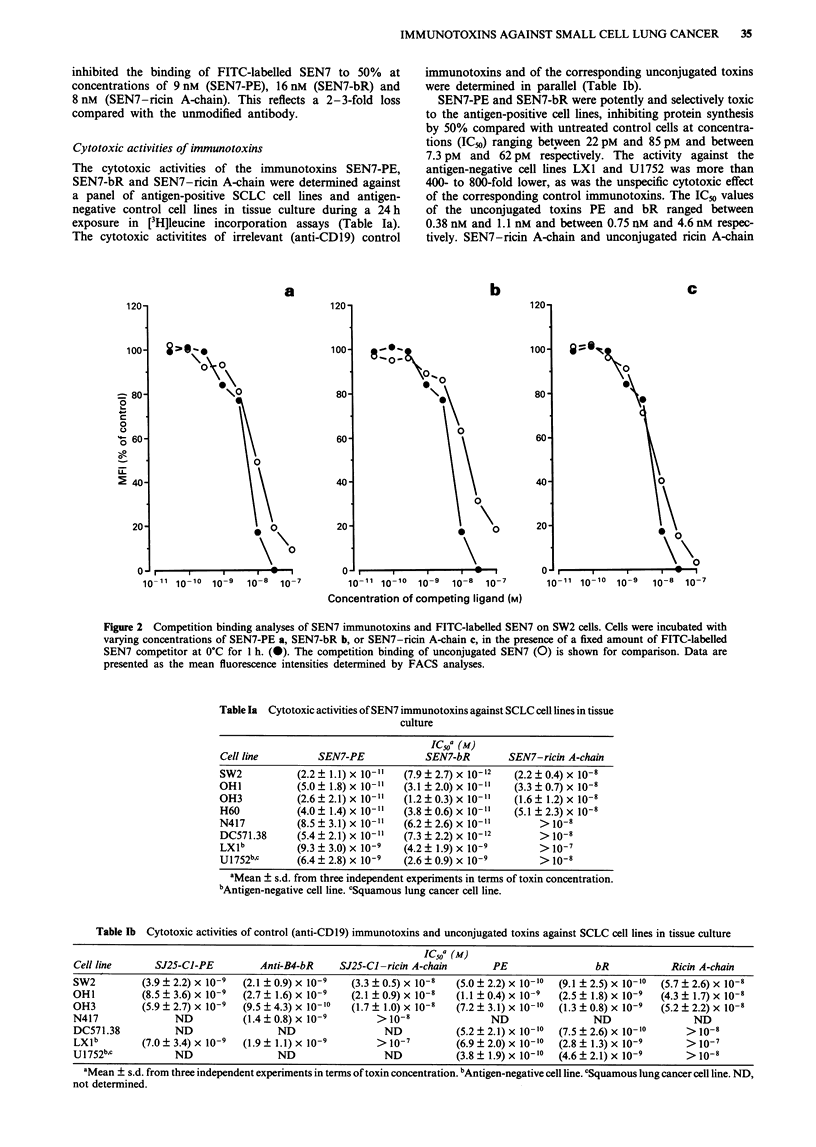
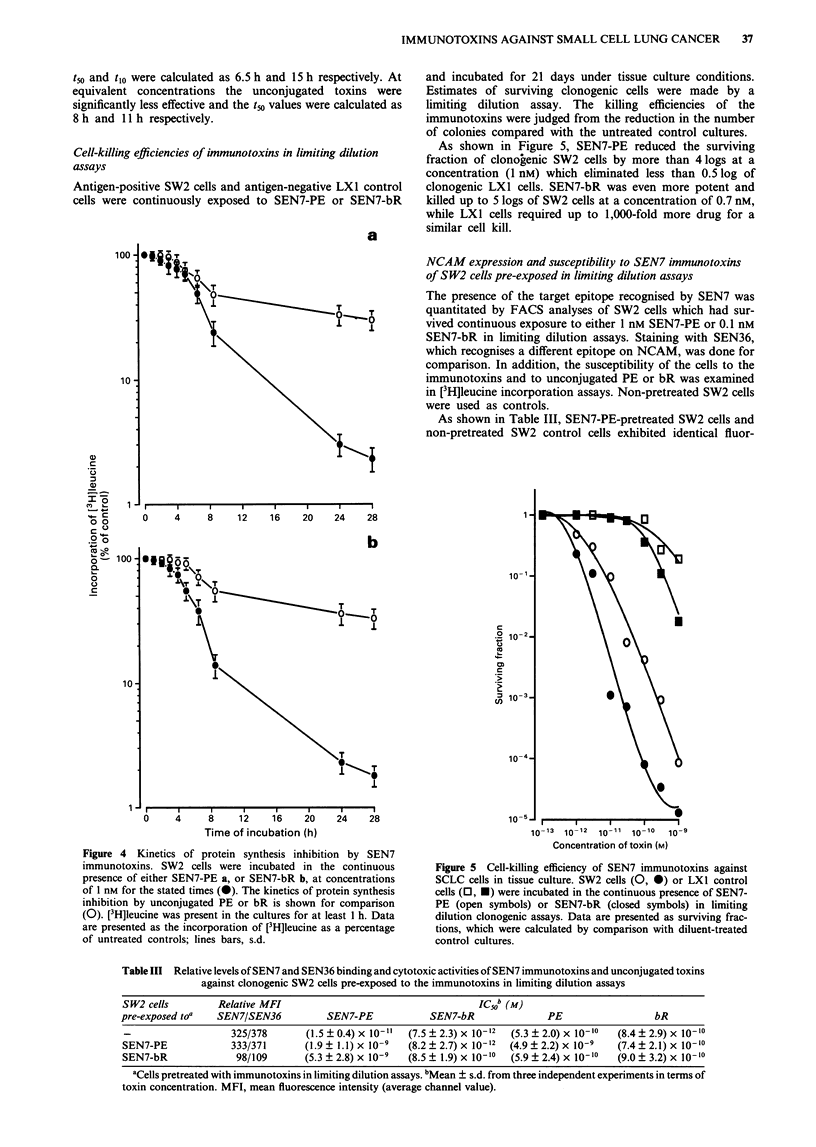
The present study describes a comparison of two potent immunotoxins which utilise an identical targeting component, a monoclonal antibody (SEN7) specific for small cell lung cancer (SCLC), conjugated to two different effector components, blocked ricin (bR) and Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE). SEN7 recognises a novel epitope on the neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) which is highly associated with SCLC. The immunotoxins SEN7-PE and SEN7-bR were selectively and potently active against a number of SCLC cell lines, of both classic and variant morphologies, inhibiting the incorporation of [3H]leucine with IC50 values ranging between 22 pM and 85 pM and between 7 pM and 62 pM for SEN7-PE and SEN7-bR respectively. Intoxication by both immunotoxins proceeded rapidly following short 2 h lag phases; the initial rates of protein synthesis inhibition occurred with t50 values of 6.5 h for SEN7-PE and 5.5 h for SEN7-bR. Monensin drastically enhanced the cytotoxic activity of the weakly active SEN7-ricin A-chain by 2,100-fold and of SEN7-bR by 80-fold but had no effect on SEN7-PE. In limiting dilution assays, four and more than 4.5 logs of clonogenic SW2 tumour cells were selectively eliminated from the cultures during continuous exposure to the immunotoxins SEN7-PE and SEN7-bR respectively, while antigen-negative cells required up to 1,000-fold more drug for a similar cell kill. SW2 cells surviving SEN7-bR treatment in the cultures did not express NCAM and consequently were not selectively killed by SEN7 immunotoxins. SW2 cells surviving continuous exposure to SEN7-PE showed no alteration in NCAM expression but were more resistant to intoxication mediated by PE. These cells were still sensitive to SEN7-bR.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carbone D. P., Koros A. M., Linnoila R. I., Jewett P., Gazdar A. F. Neural cell adhesion molecule expression and messenger RNA splicing patterns in lung cancer cell lines are correlated with neuroendocrine phenotype and growth morphology. Cancer Res. 1991 Nov 15;51(22):6142–6149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. N., De Leij L. Lung cancer biology. Semin Oncol. 1988 Jun;15(3):199–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K., Pai L. H., Batra J. K., Pastan I., Willingham M. C. Characterization of the antigen (CAK1) recognized by monoclonal antibody K1 present on ovarian cancers and normal mesothelium. Cancer Res. 1992 Jan 1;52(1):181–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumber A. J., Forrester J. A., Foxwell B. M., Ross W. C., Thorpe P. E. Preparation of antibody-toxin conjugates. Methods Enzymol. 1985;112:207–225. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)12018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire E. J., Stahel R. A., Wawrzynczak E. J. Cytotoxic properties of a ricin A chain immunotoxin recognising the cluster-5A antigen associated with human small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1992;35(6):417–420. doi: 10.1007/BF01789021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire E. J., Stahel R. A., Wawrzynczak E. J. Potentiation of a weakly active ricin A chain immunotoxin recognizing the neural cell adhesion molecule. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Sep;89(3):336–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06958.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Mitsui K., Motizuki M., Tsurugi K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 S ribosomal RNA caused by the toxins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5908–5912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald D. J., Pastan I. Pseudomonas exotoxin: recombinant conjugates as therapeutic agents. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 Nov;20(4):731–734. doi: 10.1042/bst0200731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald D. J., Willingham M. C., Cardarelli C. O., Hamada H., Tsuruo T., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. A monoclonal antibody-Pseudomonas toxin conjugate that specifically kills multidrug-resistant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4288–4292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald D., Idziorek T., Batra J. K., Willingham M., Pastan I. Antitumor activity of a thioether-linked immunotoxin: OVB3-PE. Bioconjug Chem. 1990 Jul-Aug;1(4):264–268. doi: 10.1021/bc00004a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godal A., Fodstad O., Morgan A. C., Pihl A. Human melanoma cell lines showing striking inherent differences in sensitivity to immunotoxins containing holotoxins. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Dec;77(6):1247–1253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldmacher V. S., Anderson J., Schulz M. L., Blättler W. A., Lambert J. M. Somatic cell mutants resistant to ricin, diphtheria toxin, and to immunotoxins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3205–3209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin T., Rybak M. E., Recht L., Singh M., Salimi A., Raso V. Potentiation of antitumor immunotoxins by liposomal monensin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993 Feb 17;85(4):292–298. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.4.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertler A. A., Schlossman D. M., Borowitz M. J., Blythman H. E., Casellas P., Frankel A. E. An anti-CD5 immunotoxin for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: enhancement of cytotoxicity with human serum albumin-monensin. Int J Cancer. 1989 Feb 15;43(2):215–219. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Liu P. V., Kabat D. Mechanism of action of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin Aiadenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of mammalian elongation factor 2 in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.138-144.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kounnas M. Z., Morris R. E., Thompson M. R., FitzGerald D. J., Strickland D. K., Saelinger C. B. The alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein binds and internalizes Pseudomonas exotoxin A. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12420–12423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J. M., Goldmacher V. S., Collinson A. R., Nadler L. M., Blättler W. A. An immunotoxin prepared with blocked ricin: a natural plant toxin adapted for therapeutic use. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6236–6242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J. M., McIntyre G., Gauthier M. N., Zullo D., Rao V., Steeves R. M., Goldmacher V. S., Blättler W. A. The galactose-binding sites of the cytotoxic lectin ricin can be chemically blocked in high yield with reactive ligands prepared by chemical modification of glycopeptides containing triantennary N-linked oligosaccharides. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 2;30(13):3234–3247. doi: 10.1021/bi00227a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar C. E., Muller E. J., Schol D. J., Figdor C. G., Bock E., Bitter-Suermann D., Michalides R. J. Expression of neural cell adhesion molecule-related sialoglycoprotein in small cell lung cancer and neuroblastoma cell lines H69 and CHP-212. Cancer Res. 1990 Feb 15;50(4):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. C., Jr, Sivam G., Beaumier P., McIntyre R., Bjorn M., Abrams P. G. Immunotoxins of Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE): effect of linkage on conjugate yield, potency, selectivity and toxicity. Mol Immunol. 1990 Mar;27(3):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90140-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Sandvig K., Petersen O. W., van Deurs B. Immunotoxins--entry into cells and mechanisms of action. Immunol Today. 1989 Sep;10(9):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., FitzGerald D. Recombinant toxins for cancer treatment. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1173–1177. doi: 10.1126/science.1683495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K., Bourne S., Phimister B., Coakham H., Kemshead J. T. Presence of neural cell adhesion molecule on human embryonic and brain tumours. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Jun;18(3):408–410. doi: 10.1042/bst0180408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. B., Brackenbury R., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Differences in the carbohydrate structures of neural cell-adhesion molecules from adult and embryonic chicken brains. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11064–11069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougon G., Deagostini-Bazin H., Hirn M., Goridis C. Tissue- and developmental stage-specific forms of a neural cell surface antigen linked to differences in glycosylation of a common polypeptide. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1239–1244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00019.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Prydz K., Hansen S. H., van Deurs B. Ricin transport in brefeldin A-treated cells: correlation between Golgi structure and toxic effect. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):971–981. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah S. A., Halloran P. M., Ferris C. A., Levine B. A., Bourret L. A., Goldmacher V. S., Blättler W. A. Anti-B4-blocked ricin immunotoxin shows therapeutic efficacy in four different SCID mouse tumor models. Cancer Res. 1993 Mar 15;53(6):1360–1367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souhami R. L., Beverley P. C., Bobrow L. G., Ledermann J. A. Antigens of lung cancer: results of the second international workshop on lung cancer antigens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1991 May 1;83(9):609–612. doi: 10.1093/jnci/83.9.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wawrzynczak E. J., Derbyshire E. J., Henry R. V., Parnell G. D., Smith A., Waibel R., Stahel R. A. Cytotoxic activity of ricin A chain immunotoxins recognising cluster 1, w4 and 5A antigens associated with human small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer Suppl. 1991 Jun;14:71–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wawrzynczak E. J., Derbyshire E. J., Henry R. V., Parnell G. D., Smith A., Waibel R., Stahel R. A. Selective cytotoxic effects of a ricin A chain immunotoxin made with the monoclonal antibody SWA11 recognising a human small cell lung cancer antigen. Br J Cancer. 1990 Sep;62(3):410–414. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zangemeister-Wittke U., Collinson A. R., Fisch I., Jones R. M., Waibel R., Lehman H. P., Stahel R. A. Anti-tumor activity of a blocked ricin immunotoxin with specificity against the cluster-5A antigen associated with human small-cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 1993 Jul 30;54(6):1028–1035. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910540628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zangemeister-Wittke U., Lehmann H. P., Waibel R., Wawrzynczak E. J., Stahel R. A. Action of a CD24-specific deglycosylated ricin-A-chain immunotoxin in conventional and novel models of small-cell-lung-cancer xenograft. Int J Cancer. 1993 Feb 1;53(3):521–528. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910530327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]