Abstract
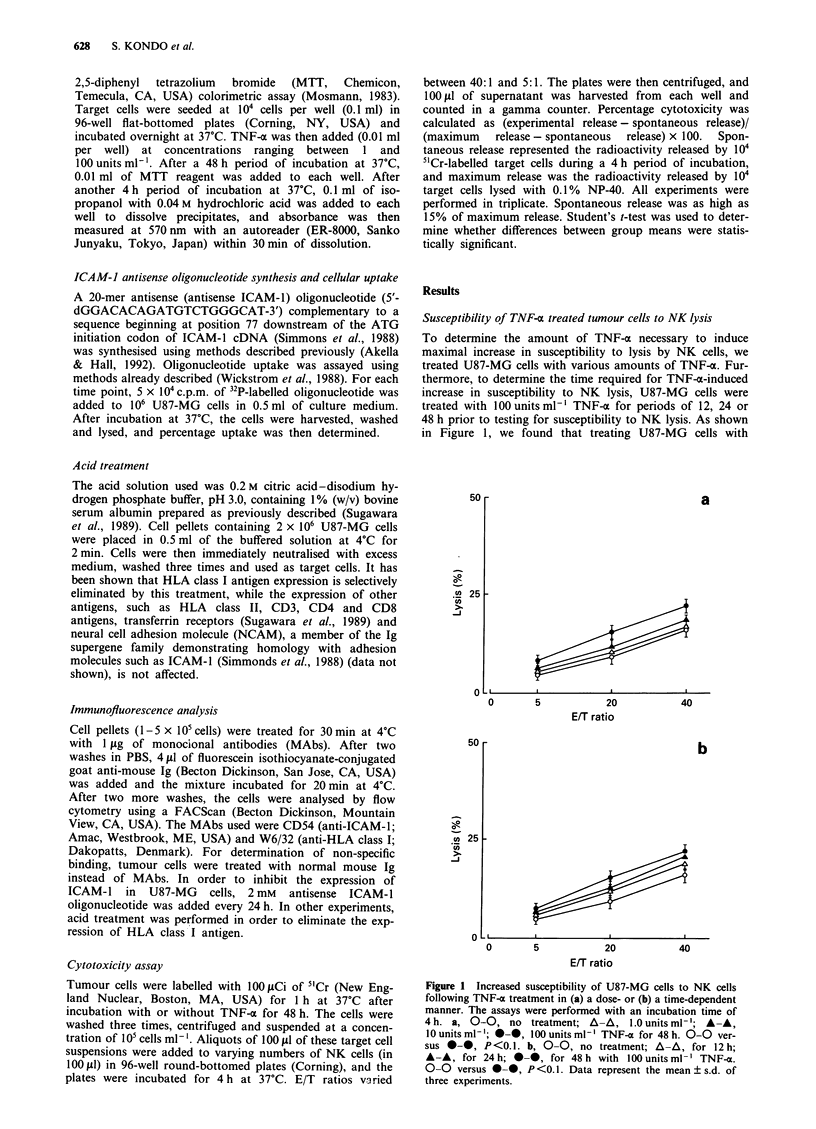
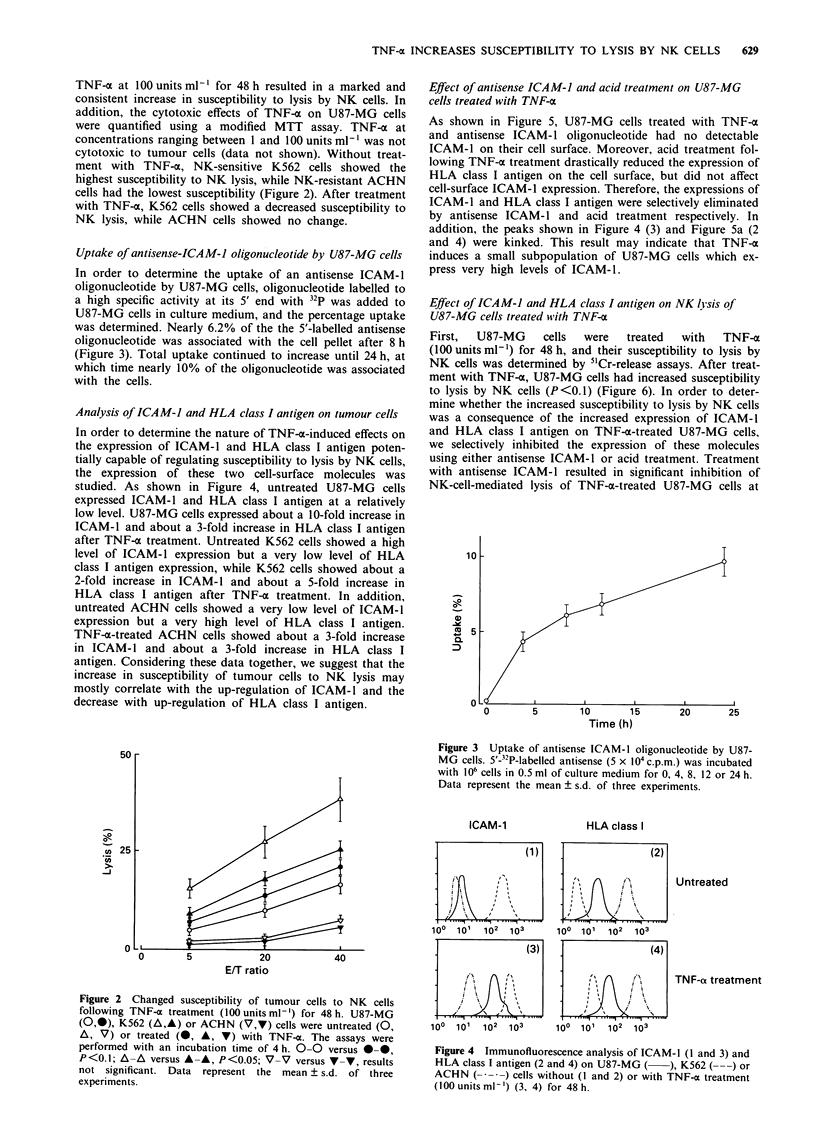
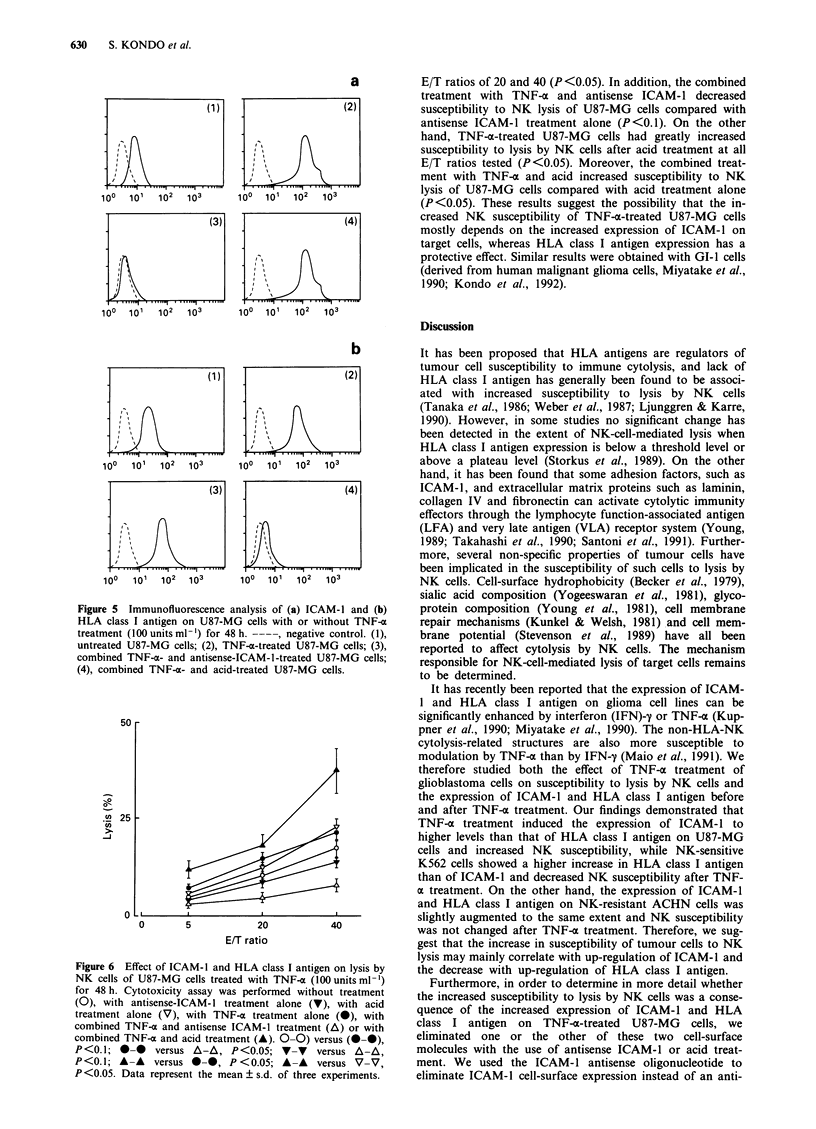
The mechanism by which tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha increases the susceptibility of U87-MG human glioblastoma cells to lysis by natural killer (NK) cells was studied. Treatment with TNF-alpha (100 units ml-1) for 48 h enhanced the susceptibility of tumour cells to lysis by NK cells. Increased susceptibility to lysis was associated with enhanced expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and HLA class I antigen. Antisense ICAM-1 oligonucleotide inhibited lysis by NK cells of TNF-alpha-treated tumour cells. In contrast, acid treatment following TNF-alpha treatment increased lysis by NK cells. These findings indicate that TNF-alpha treatment of glioblastoma cells increased their susceptibility to lysis by NK cells, since ICAM-1 up-regulation would have more profound effects on NK susceptibility than would HLA class I antigen up-regulation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akella R., Hall R. E. Expression of the adhesion molecules ICAM-1 and ICAM-2 on tumor cell lines does not correlate with their susceptibility to natural killer cell-mediated cytolysis: evidence for additional ligands for effector cell beta integrins. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Apr;22(4):1069–1074. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker S., Stendahl O., Magnusson K. E. Physico-chemical characteristics of tumour cells susceptible to lysis by natural killer (NK) cells. Immunol Commun. 1979;8(1):73–83. doi: 10.3109/08820137909044708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biassoni R., Ferrini S., Prigione I., Moretta A., Long E. O. CD3-negative lymphokine-activated cytotoxic cells express the CD3 epsilon gene. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1685–1689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. Lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) interaction with intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is one of at least three mechanisms for lymphocyte adhesion to cultured endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):321–331. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fady C., Gardner A. M., Gera J. F., Lichtenstein A. Interferon-induced increase in sensitivity of ovarian cancer targets to lysis by lymphokine-activated killer cells: selective effects on HER2/neu-overexpressing cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Feb 15;52(4):764–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. E., Schall R. P., Black L. A. A monoclonal antibody (RH1-38) which inhibits multiple systems of cell-mediated cytotoxicity--II. Evidence that the epitope recognized is involved in a late step in the cytolytic mechanism. Mol Immunol. 1985 Jul;22(7):765–773. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90141-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel-Bellan A., Quillet A., Marchiol C., DeMars R., Tursz T., Fradelizi D. Natural killer susceptibility of human cells may be regulated by genes in the HLA region on chromosome 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5688–5692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo S., Miyatake S., Kikuchi H., Oda Y., Iwasaki K., Ohyama K., Namba Y. Mechanism of interferon gamma-induced protection of human gliosarcoma cells from lymphokine-activated killer lysis: division of lymphokine-activated killer cells into natural killer- and T-like cells. Neurosurgery. 1992 Sep;31(3):534–540. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199209000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. A., Welsh R. M. Metabolic inhibitors render "resistant" target cells sensitive to natural killer cell-mediated lysis. Int J Cancer. 1981 Jan 15;27(1):73–79. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910270112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppner M. C., van Meir E., Hamou M. F., de Tribolet N. Cytokine regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expression on human glioblastoma cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jul;81(1):142–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König M., Wallach D., Resch K., Holtmann H. Induction of hyporesponsiveness to an early post-binding effect of tumor necrosis factor by tumor necrosis factor itself and interleukin 1. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jul;21(7):1741–1745. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Le A. M., Civin C. I., Loken M. R., Phillips J. H. The relationship of CD16 (Leu-11) and Leu-19 (NKH-1) antigen expression on human peripheral blood NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4480–4486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren H. G., Kärre K. Host resistance directed selectively against H-2-deficient lymphoma variants. Analysis of the mechanism. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1745–1759. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren H. G., Kärre K. In search of the 'missing self': MHC molecules and NK cell recognition. Immunol Today. 1990 Jul;11(7):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90097-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh E. Y., Cwirla S., Serafini A. T., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Human T-cell-receptor delta chain: genomic organization, diversity, and expression in populations of cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9714–9718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio M., Altomonte M., Tatake R., Zeff R. A., Ferrone S. Reduction in susceptibility to natural killer cell-mediated lysis of human FO-1 melanoma cells after induction of HLA class I antigen expression by transfection with B2m gene. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):282–289. doi: 10.1172/JCI115289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Kikuchi H., Oda Y., Nishioka T., Takahashi J., Kondoh S., Matsumoto M., Yamasaki T., Iwasaki K., Aoki T. Decreased susceptibility of lined human gliosarcoma cells to lymphokine-activated killer cell cytolysis by gamma-interferon treatment. Cancer Res. 1990 Feb 1;50(3):596–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumour necrosis factor. Polypeptide mediator network. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):330–331. doi: 10.1038/326330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piontek G. E., Taniguchi K., Ljunggren H. G., Grönberg A., Kiessling R., Klein G., Kärre K. YAC-1 MHC class I variants reveal an association between decreased NK sensitivity and increased H-2 expression after interferon treatment or in vivo passage. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4281–4288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Procopio A. D., Paolini R., Gismondi A., Piccoli M., Adamo S., Cavallo G., Frati L., Santoni A. Effects of protein kinase C (PK-C) activators and inhibitors on human large granular lymphocytes (LGL): role of PK-C on natural killer (NK) activity. Cell Immunol. 1989 Feb;118(2):470–481. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90394-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. E., Bartley G., Levine H., Schlossman S. F., Ritz J. Functional characterization of LFA-1 antigens in the interaction of human NK clones and target cells. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1020–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D., Makgoba M. W., Seed B. ICAM, an adhesion ligand of LFA-1, is homologous to the neural cell adhesion molecule NCAM. Nature. 1988 Feb 18;331(6157):624–627. doi: 10.1038/331624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson D., Binggeli R., Weinstein R. C., Keck J. G., Lai M. C., Tong M. J. Relationship between cell membrane potential and natural killer cell cytolysis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(17):4842–4845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storkus W. J., Alexander J., Payne J. A., Cresswell P., Dawson J. R. The alpha 1/alpha 2 domains of class I HLA molecules confer resistance to natural killing. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3853–3857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storkus W. J., Howell D. N., Salter R. D., Dawson J. R., Cresswell P. NK susceptibility varies inversely with target cell class I HLA antigen expression. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1657–1659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara S., Abo T., Itoh H., Kumagai K. Analysis of mechanisms by which NK cells acquire increased cytotoxicity against class I MHC-eliminated targets. Cell Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;119(2):304–316. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90246-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Nakamura T., Koyanagi M., Kato K., Hashimoto Y., Yagita H., Okumura K. A murine very late activation antigen-like extracellular matrix receptor involved in CD2- and lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1-independent killer-target cell interaction. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4371–4379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Hayashi H., Hamada C., Khoury G., Jay G. Expression of major histocompatibility complex class I antigens as a strategy for the potentiation of immune recognition of tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8723–8727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita Y., Watanabe H., Kobayashi H., Nishiyama T., Tsuji S., Fujiwara M., Sato S. Interferon gamma but not tumor necrosis factor alpha decreases susceptibility of human renal cell cancer cell lines to lymphokine-activated killer cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1992;35(6):381–387. doi: 10.1007/BF01789016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. S., Jay G., Tanaka K., Rosenberg S. A. Immunotherapy of a murine tumor with interleukin 2. Increased sensitivity after MHC class I gene transfection. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1716–1733. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickstrom E. L., Bacon T. A., Gonzalez A., Freeman D. L., Lyman G. H., Wickstrom E. Human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cell proliferation and c-myc protein expression are inhibited by an antisense pentadecadeoxynucleotide targeted against c-myc mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1028–1032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogeeswaran G., Gronberg A., Hansson M., Dalianis T., Kiessling R., Welsh R. M. Correlation of glycosphingolipids and sialic acid in YAC-1 lymphoma variants with their sensitivity to natural killer-cell-mediated lysis. Int J Cancer. 1981 Oct 15;28(4):517–526. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D. Killing of target cells by lymphocytes: a mechanistic view. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jan;69(1):250–314. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.1.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. W., Jr, Durdik J. M., Urdal D., Hakomori S., Henney C. S. Glycolipid expression in lymphoma cell variants: chemical quantity, immunologic reactivity, and correlations with susceptibility to NK cells. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


