Abstract
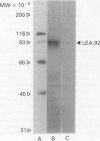
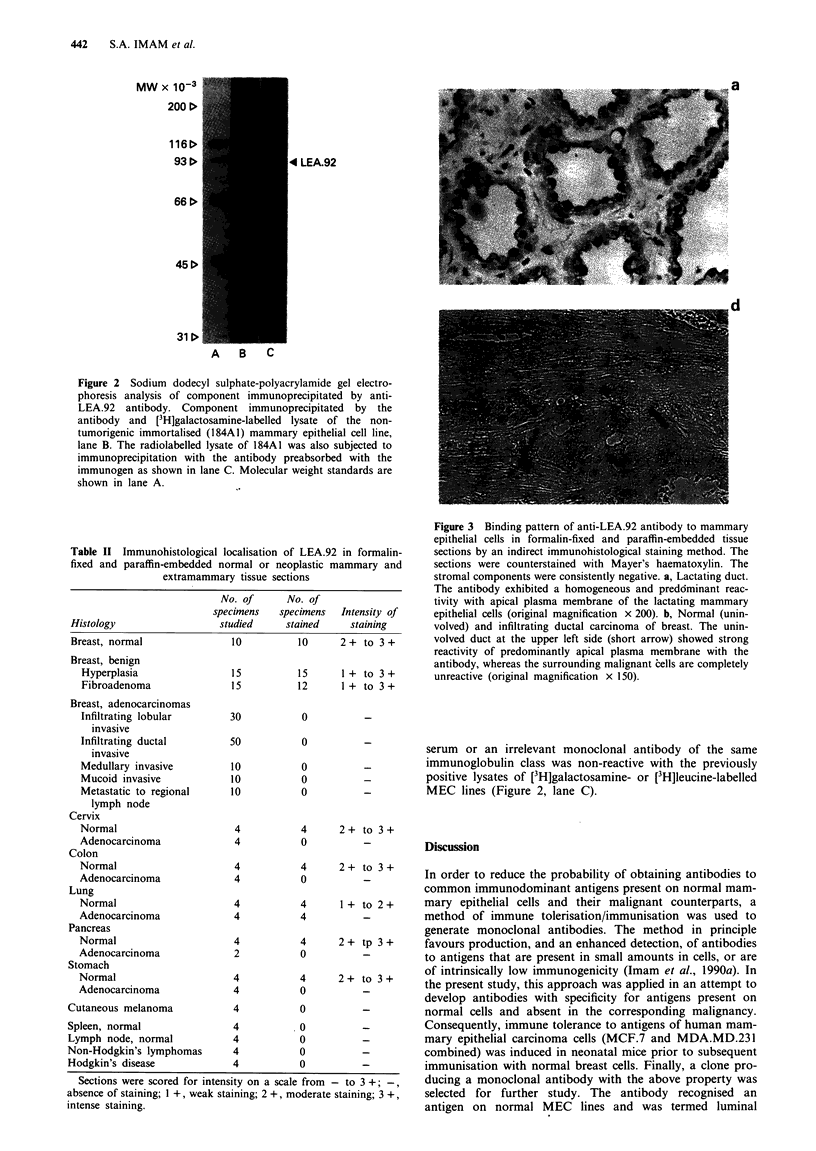
The goal of the study was to identify any normal genes that may become inactivated in malignant cells, with associated modifications or loss of gene products. Consequently, attempts were made to identify such products by generating monoclonal antibodies using an immune tolerisation-immunisation procedure. Using such a technique, a plasma membrane-associated glycoprotein with an apparent molecular weight of 92 kDa was identified. The glycoprotein was termed luminal epithelial antigen (LEA.92). The pattern of expression of LEA.92 was demonstrated by an indirect immunostaining technique. Using an in vitro model system representing various stages of breast oncogenesis, LEA.92 was detected on normal or immortalised mammary epithelial cell (MEC) lines which were dependent on epidermal growth factor (EGF) and anchorage formation for growth and non-tumorigenic in nude mice. In contrast, LEA.92 was undetectable on oncogenically transformed or established lines of mammary carcinoma cell lines which were independent of EGF or anchorage formation for growth and were highly tumorigenic. The results appear to suggest a correlation between the down-regulation of LEA.92 and the development of tumorigenicity in malignant MEC lines. Furthermore, the patterns of expression of LEA.92 on breast cells in tissue mirrored those of breast epithelial cells in cell cultures. LEA.92 was detected on the surface of normal but not malignant epithelial cells, which included breast, cervix, colon, lung, pancreas and stomach. LEA.92 appeared to be distinct from receptor for epidermal growth factor, antigens associated with milk fat globule membrane and the family of epithelium-specific keratins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali I. U., Lidereau R., Theillet C., Callahan R. Reduction to homozygosity of genes on chromosome 11 in human breast neoplasia. Science. 1987 Oct 9;238(4824):185–188. doi: 10.1126/science.3659909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arklie J., Taylor-Papadimitrious J., Bodmer W., Egan M., Millis R. Differentiation antigens expressed by epithelial cells in the lactating breast are also detectable in breast cancers. Int J Cancer. 1981 Jul 15;28(1):23–29. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Nigro J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., vanTuinen P., Ledbetter D. H., Barker D. F., Nakamura Y. Chromosome 17 deletions and p53 gene mutations in colorectal carcinomas. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):217–221. doi: 10.1126/science.2649981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchell J., Wang D., Taylor-Papadimitriou J. Detection of the tumour-associated antigens recognized by the monoclonal antibodies HMFG-1 and 2 in serum from patients with breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1984 Dec 15;34(6):763–768. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910340605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. C., Dollbaum C., Smith H. S. Loss of heterozygosity on chromosome 1q in human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7204–7207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R., Stampfer M. R., Milley R., O'Rourke E., Walen K. H., Kriegler M., Kopplin J., McCormick F. Transformation of human mammary epithelial cells by oncogenic retroviruses. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 15;48(16):4689–4694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Michalovitz D., Eliyahu S., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can inhibit oncogene-mediated focus formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8763–8767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. H., Bernards R., Rogelj S., Weinberg R. A., Rapaport J. M., Albert D. M., Dryja T. P. A human DNA segment with properties of the gene that predisposes to retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):643–646. doi: 10.1038/323643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. H., Dryja T. P., Weinberg R. A. Oncogenes and tumor-suppressing genes. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 10;318(10):618–622. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803103181007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Murphree A. L., T'Ang A., Qian J., Hinrichs S. H., Benedict W. F. Structural evidence for the authenticity of the human retinoblastoma gene. Science. 1987 Jun 26;236(4809):1657–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.2885916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genuardi M., Tsihira H., Anderson D. E., Saunders G. F. Distal deletion of chromosome Ip in ductal carcinoma of the breast. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;45(1):73–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond S. L., Ham R. G., Stampfer M. R. Serum-free growth of human mammary epithelial cells: rapid clonal growth in defined medium and extended serial passage with pituitary extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5435–5439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. F., Cavenee W. K. Genetics of cancer predisposition. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 1;47(21):5518–5527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. The analysis of malignancy by cell fusion: the position in 1988. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 15;48(12):3302–3306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyderman E., Steele K., Ormerod M. G. A new antigen on the epithelial membrane: its immunoperoxidase localisation in normal and neoplastic tissue. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Jan;32(1):35–39. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imam A., Drushella M. M., Taylor C. R., Tökés Z. A. Generation and immunohistological characterization of human monoclonal antibodies to mammary carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1985 Jan;45(1):263–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imam A., Drushella M. M., Taylor C. R., Tökés Z. A. Preferential expression of a Mr 155,000 milk-fat-globule membrane glycoprotein on luminal epithelium of lobules in human breast. Cancer Res. 1986 Dec;46(12 Pt 1):6374–6379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imam A., Laurence D. J., Neville A. M. Isolation and characterization of a major glycoprotein from milk-fat-globule membrane of human breast milk. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):47–54. doi: 10.1042/bj1930047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imam A., Laurence D. J., Neville A. M. Isolation and characterization of two individual glycoprotein components from human milk-fat-globule membranes. Biochem J. 1982 Oct 1;207(1):37–41. doi: 10.1042/bj2070037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imam A., Stathopoulos E., Holland S. L., Epstein A. L., Taylor C. R. Characterization of a cell surface molecule expressed on B-lymphocytes and Hodgkin's cells. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 1;50(5):1650–1657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imam A., Stathopoulos E., Taylor C. R. Generation and characterization of a murine monoclonal antibody to cervical glandular epithelium using mice rendered tolerant to cervical squamous epithelium. Hybridoma. 1990 Apr;9(2):157–166. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1990.9.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imam A., Taylor C. R., Tökés Z. A. Immunohistochemical study of the expression of human milk fat globule membrane glycoprotein 70. Cancer Res. 1984 May;44(5):2016–2022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. The approaching era of the tumor suppressor genes. Science. 1987 Dec 11;238(4833):1539–1545. doi: 10.1126/science.3317834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson A. G., Jr Hereditary cancer, oncogenes, and antioncogenes. Cancer Res. 1985 Apr;45(4):1437–1443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Bookstein R., Hong F., Young L. J., Shew J. Y., Lee E. Y. Human retinoblastoma susceptibility gene: cloning, identification, and sequence. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1394–1399. doi: 10.1126/science.3823889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg C., Skoog L., Cavenee W. K., Nordenskjöld M. Loss of heterozygosity in human ductal breast tumors indicates a recessive mutation on chromosome 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2372–2376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübbert M., Miller C. W., Crawford L., Koeffler H. P. p53 in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Study of mechanisms of differential expression. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):873–886. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay J., Steel C. M., Elder P. A., Forrest A. P., Evans H. J. Allele loss on short arm of chromosome 17 in breast cancers. Lancet. 1988 Dec 17;2(8625):1384–1385. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90584-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak S. Cytogenetics of epithelial malignant lesions. Cancer. 1992 Sep 15;70(6 Suppl):1660–1670. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920915)70:4+<1660::aid-cncr2820701605>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Banks-Schlegel S., McLeod J. A., Pinkus G. S. Immunoperoxidase localization of keratin in human neoplasms: a preliminary survey. Am J Pathol. 1980 Oct;101(1):41–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M. R., Bartley J. C. Induction of transformation and continuous cell lines from normal human mammary epithelial cells after exposure to benzo[a]pyrene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2394–2398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J. A case for human tumor-suppressor genes. Bioessays. 1985 Dec;3(6):252–255. doi: 10.1002/bies.950030605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J. Human tumor suppressor genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:615–657. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Nau M. M., Chiba I., Birrer M. J., Rosenberg R. K., Vinocour M., Levitt M., Pass H., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D. p53: a frequent target for genetic abnormalities in lung cancer. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):491–494. doi: 10.1126/science.2554494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Kern S. E., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Nakamura Y., White R. Allelotype of colorectal carcinomas. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):207–211. doi: 10.1126/science.2565047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walen K. H., Stampfer M. R. Chromosome analyses of human mammary epithelial cells at stages of chemical-induced transformation progression to immortality. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1989 Feb;37(2):249–261. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(89)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. Oncogenes, antioncogenes, and the molecular bases of multistep carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1989 Jul 15;49(14):3713–3721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. Tumor suppressor genes. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1138–1146. doi: 10.1126/science.1659741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]