Abstract
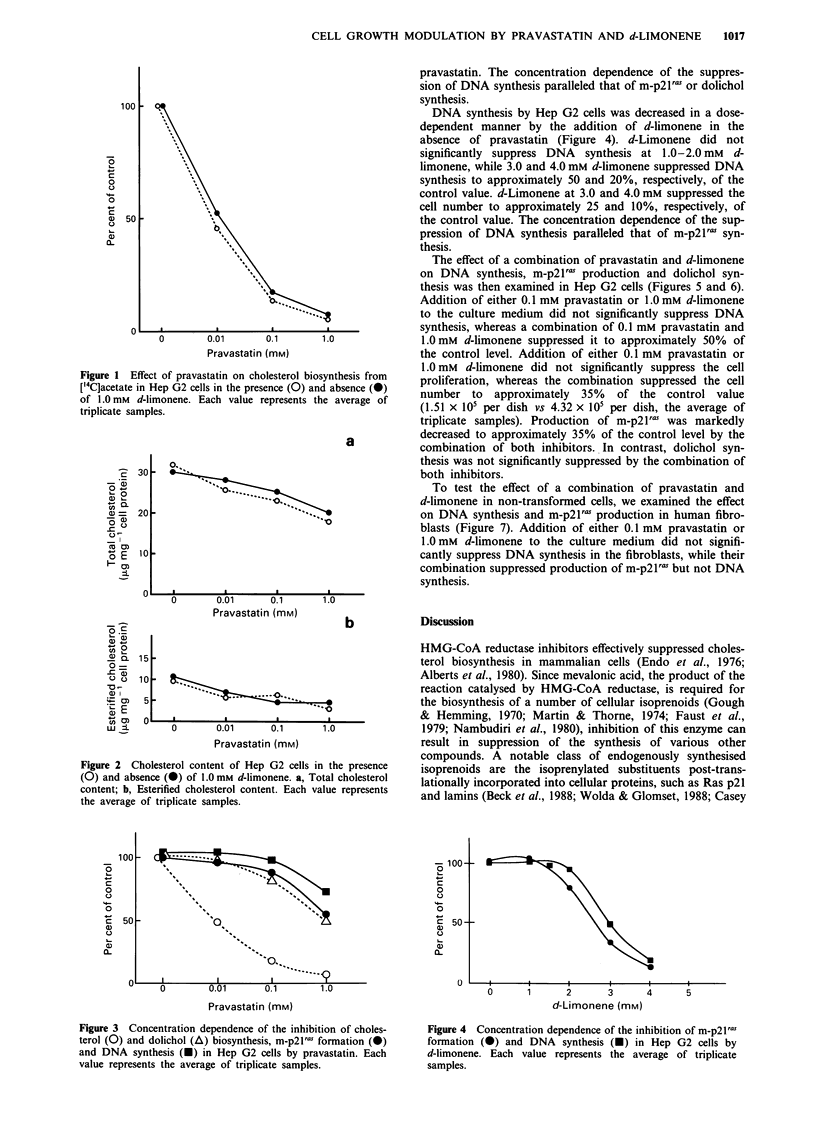
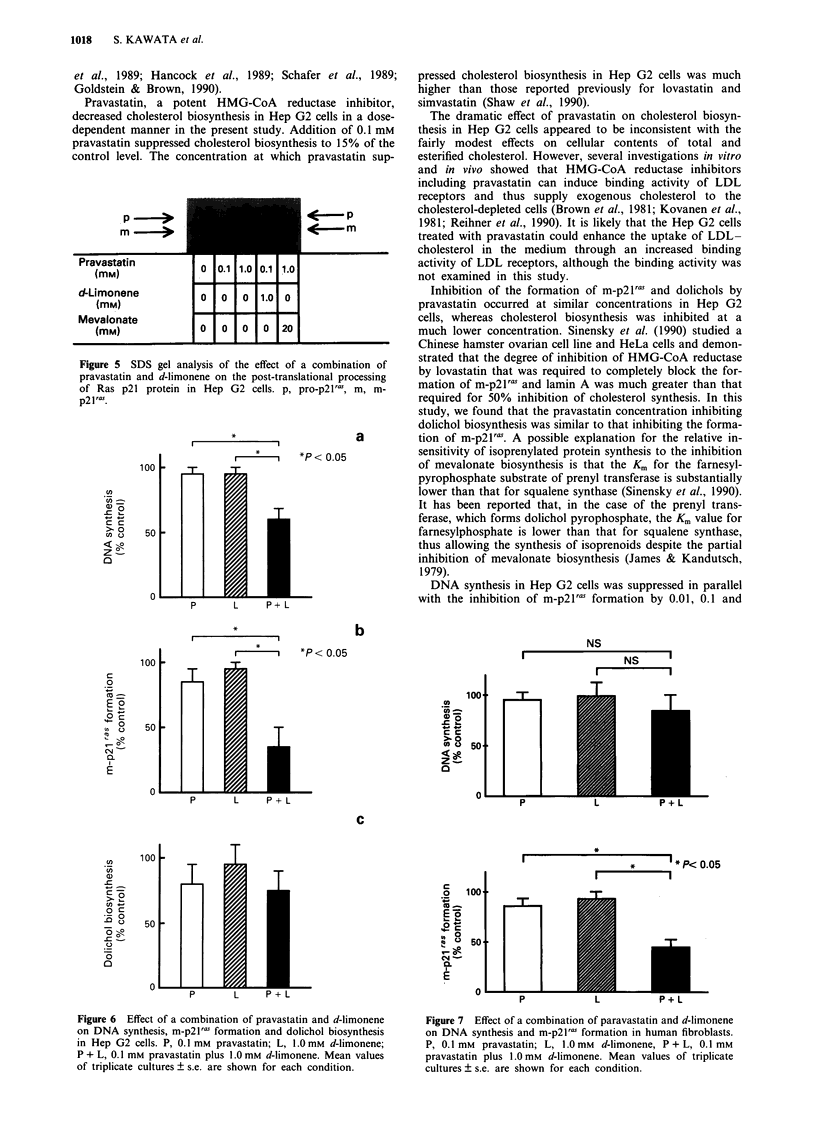
Modulation of cell growth by a combination of pravastatin [a 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor] and d-limonene (an inhibitor of protein isoprenylation) was studied using Hep G2, a human hepatoma-derived cell line. Pravastatin, at 0.1 mM, produced 85% inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis in Hep G2 cells. The combination of 0.1 mM pravastatin and 1.0 mM d-limonene had no further effect on the reduction seen with pravastatin alone. Addition of 0.1 mM pravastatin or 1.0 mM d-limonene did not significantly suppress DNA synthesis by the cells, whereas the combination suppressed it to 50% of the control level. Production of m-p21ras was markedly decreased to 35% of the control level by the combination of these two inhibitors. Both the reduction by pravastatin of farnesylpyrophosphate as substrate for protein:farnesyl transferase and inhibition of protein farnesylation by d-limonene seem to be responsible for the profound suppression of m-p21ras formation in the cells. However, dolichol synthesis was not suppressed by the combination of these inhibitors. In human fibroblasts, the combination suppressed m-p21ras production but not DNA synthesis. These findings suggest that the combination of pravastatin and d-limonene acts on cancer cell growth through inhibition of the post-translational processing of cellular proteins including p21ras, rather than through the suppression of cholesterol and dolichol biosynthesis. Thus, the combination of an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor and an inhibitor of protein isoprenylation offers potential as a new approach for cancer therapy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts A. W., Chen J., Kuron G., Hunt V., Huff J., Hoffman C., Rothrock J., Lopez M., Joshua H., Harris E. Mevinolin: a highly potent competitive inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and a cholesterol-lowering agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3957–3961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck L. A., Hosick T. J., Sinensky M. Incorporation of a product of mevalonic acid metabolism into proteins of Chinese hamster ovary cell nuclei. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1307–1316. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Familial hypercholesterolemia: defective binding of lipoproteins to cultured fibroblasts associated with impaired regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):788–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Kovanen P. T., Goldstein J. L. Regulation of plasma cholesterol by lipoprotein receptors. Science. 1981 May 8;212(4495):628–635. doi: 10.1126/science.6261329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Solski P. A., Der C. J., Buss J. E. p21ras is modified by a farnesyl isoprenoid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8323–8327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. W. The activity of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase and the rate of sterol synthesis diminish in cultures with high cell density. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Jul;108(1):91–97. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041080112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowell P. L., Chang R. R., Ren Z. B., Elson C. E., Gould M. N. Selective inhibition of isoprenylation of 21-26-kDa proteins by the anticarcinogen d-limonene and its metabolites. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17679–17685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowell P. L., Kennan W. S., Haag J. D., Ahmad S., Vedejs E., Gould M. N. Chemoprevention of mammary carcinogenesis by hydroxylated derivatives of d-limonene. Carcinogenesis. 1992 Jul;13(7):1261–1264. doi: 10.1093/carcin/13.7.1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Vass W. C., Papageorge A. G., Lowy D. R., Willumsen B. M. Inhibition of cell growth by lovastatin is independent of ras function. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 15;51(2):712–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggens I., Chojnacki T., Kenne L., Dallner G. Separation, quantitation and distribution of dolichol and dolichyl phosphate in rat and human tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 16;751(3):355–368. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90294-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elegbede J. A., Elson C. E., Qureshi A., Tanner M. A., Gould M. N. Inhibition of DMBA-induced mammary cancer by the monoterpene d-limonene. Carcinogenesis. 1984 May;5(5):661–664. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.5.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo A., Kuroda M., Tanzawa K. Competitive inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase by ML-236A and ML-236B fungal metabolites, having hypocholesterolemic activity. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 31;72(2):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80996-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson S. K., Fielding P. E. Parameters of cholesterol metabolism in the human hepatoma cell line, Hep-G2. J Lipid Res. 1986 Aug;27(8):875–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks K. P., Witte L. D., Goodman D. S. Relationship between mevalonate and mitogenesis in human fibroblasts stimulated with platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1546–1551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust J. R., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Synthesis of delta 2-isopentenyl tRNA from mevalonate in cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6546–6548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust J. R., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Synthesis of ubiquinone and cholesterol in human fibroblasts: regulation of a branched pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Jan;192(1):86–99. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia A. M., Rowell C., Ackermann K., Kowalczyk J. J., Lewis M. D. Peptidomimetic inhibitors of Ras farnesylation and function in whole cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18415–18418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):425–430. doi: 10.1038/343425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Helgeson J. A., Brown M. S. Inhibition of cholesterol synthesis with compactin renders growth of cultured cells dependent on the low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5403–5409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough D. P., Hemming F. W. The characterization and stereochemistry of biosynthesis of dolichols in rat liver. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(1):163–166. doi: 10.1042/bj1180163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez L., Magee A. I., Marshall C. J., Hancock J. F. Post-translational processing of p21ras is two-step and involves carboxyl-methylation and carboxy-terminal proteolysis. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1093–1098. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03478.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habenicht A. J., Glomset J. A., Ross R. Relation of cholesterol and mevalonic acid to the cell cycle in smooth muscle and swiss 3T3 cells stimulated to divide by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5134–5140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Magee A. I., Childs J. E., Marshall C. J. All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeg J. M., Demosky S. J., Jr, Edge S. B., Gregg R. E., Osborne J. C., Jr, Brewer H. B., Jr Characterization of a human hepatic receptor for high density lipoproteins. Arteriosclerosis. 1985 May-Jun;5(3):228–237. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.5.3.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James G. L., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Rawson T. E., Somers T. C., McDowell R. S., Crowley C. W., Lucas B. K., Levinson A. D., Marsters J. C., Jr Benzodiazepine peptidomimetics: potent inhibitors of Ras farnesylation in animal cells. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1937–1942. doi: 10.1126/science.8316834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. J., Kandutsch A. A. Inter-relationships between dolichol and sterol synthesis in mammalian cell cultures. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8442–8446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandutsch A. A., Chen H. W. Consequences of blocked sterol synthesis in cultured cells. DNA synthesis and membrane composition. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):409–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawata S., Chitranukroh A., Owen J. S., McIntyre N. Membrane lipid changes in erythrocytes, liver and kidney in acute and chronic experimental liver disease in rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 9;896(1):26–34. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90352-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawata S., Takaishi K., Nagase T., Ito N., Matsuda Y., Tamura S., Matsuzawa Y., Tarui S. Increase in the active form of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in human hepatocellular carcinoma: possible mechanism for alteration of cholesterol biosynthesis. Cancer Res. 1990 Jun 1;50(11):3270–3273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L., Jaramillo J. J., Brown M. S. Regulatory role for hepatic low density lipoprotein receptors in vivo in the dog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltese W. A., Defendini R., Green R. A., Sheridan K. M., Donley D. K. Suppression of murine neuroblastoma growth in vivo by mevinolin, a competitive inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1748–1754. doi: 10.1172/JCI112165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltese W. A. Induction of differentiation in murine neuroblastoma cells by mevinolin, a competitive inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 30;120(2):454–460. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91275-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin H. G., Thorne K. J. Synthesis of radioactive dolichol from (4S-3H)mevalonate in the regenerating rat liver. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;138(2):277–280. doi: 10.1042/bj1380277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendola C. E., Backer J. M. Lovastatin blocks N-ras oncogene-induced neuronal differentiation. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Oct;1(10):499–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley S. T., Kalinowski S. S., Schafer B. L., Tanaka R. D. Tissue-selective acute effects of inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase on cholesterol biosynthesis in lens. J Lipid Res. 1989 Sep;30(9):1411–1420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nambudiri A. M., Ranganathan S., Rudney H. The role of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity in the regulation of ubiquinone synthesis in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5894–5899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quesney-Huneeus V., Wiley M. H., Siperstein M. D. Essential role for mevalonate synthesis in DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5056–5060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reihnér E., Rudling M., Ståhlberg D., Berglund L., Ewerth S., Björkhem I., Einarsson K., Angelin B. Influence of pravastatin, a specific inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, on hepatic metabolism of cholesterol. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 26;323(4):224–228. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007263230403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. A., Short S. A., Thorgeirsson S. S., Huber B. E. Characterization of a transforming N-ras gene in the human hepatoma cell line Hep G2: additional evidence for the importance of c-myc and ras cooperation in hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 1;50(5):1521–1527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer W. R., Kim R., Sterne R., Thorner J., Kim S. H., Rine J. Genetic and pharmacological suppression of oncogenic mutations in ras genes of yeast and humans. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):379–385. doi: 10.1126/science.2569235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw M. K., Newton R. S., Sliskovic D. R., Roth B. D., Ferguson E., Krause B. R. Hep-G2 cells and primary rat hepatocytes differ in their response to inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 31;170(2):726–734. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92151-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinensky M., Beck L. A., Leonard S., Evans R. Differential inhibitory effects of lovastatin on protein isoprenylation and sterol synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19937–19941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujita Y., Kuroda M., Shimada Y., Tanzawa K., Arai M., Kaneko I., Tanaka M., Masuda H., Tarumi C., Watanabe Y. CS-514, a competitive inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase: tissue-selective inhibition of sterol synthesis and hypolipidemic effect on various animal species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 11;877(1):50–60. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wattenberg L. W., Coccia J. B. Inhibition of 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone carcinogenesis in mice by D-limonene and citrus fruit oils. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Jan;12(1):115–117. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolda S. L., Glomset J. A. Evidence for modification of lamin B by a product of mevalonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):5997–6000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu G. Y., Wu C. H., Rifici V. A., Stockert R. J. Activity and regulation of low density lipoprotein receptors in a human hepatoblastoma cell line. Hepatology. 1984 Nov-Dec;4(6):1190–1194. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



