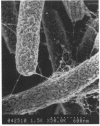
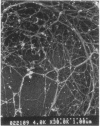
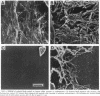
Abstract
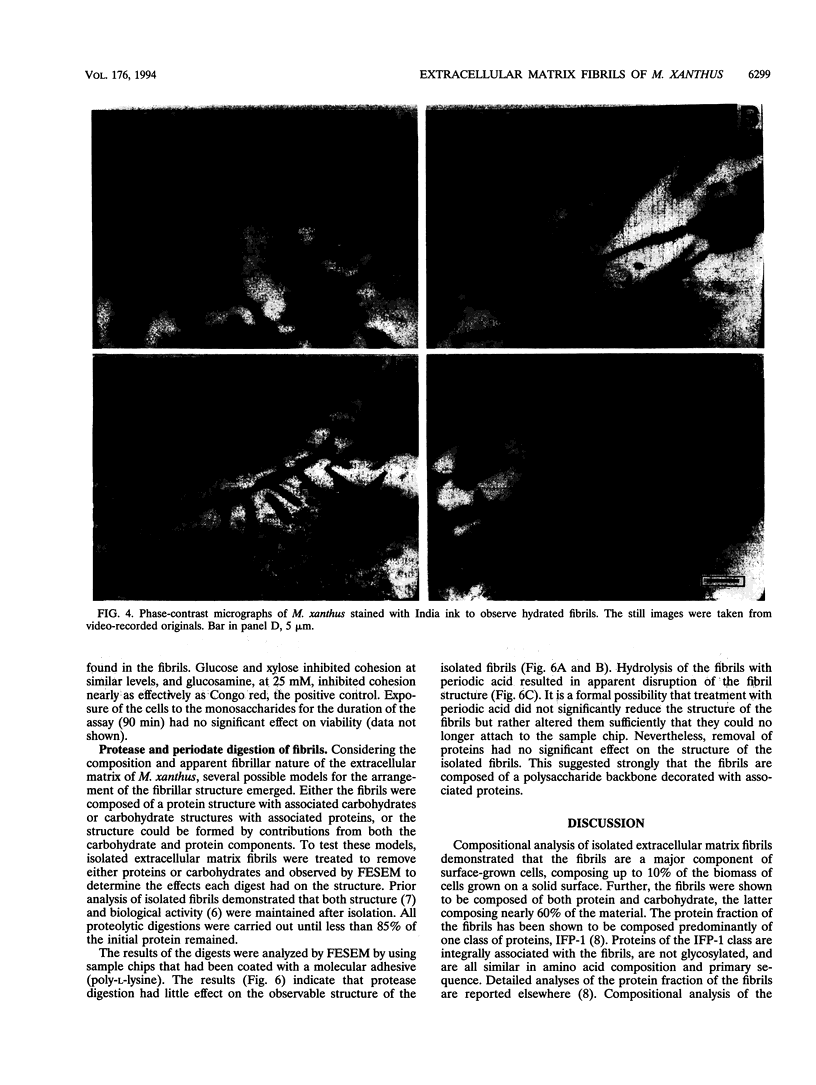
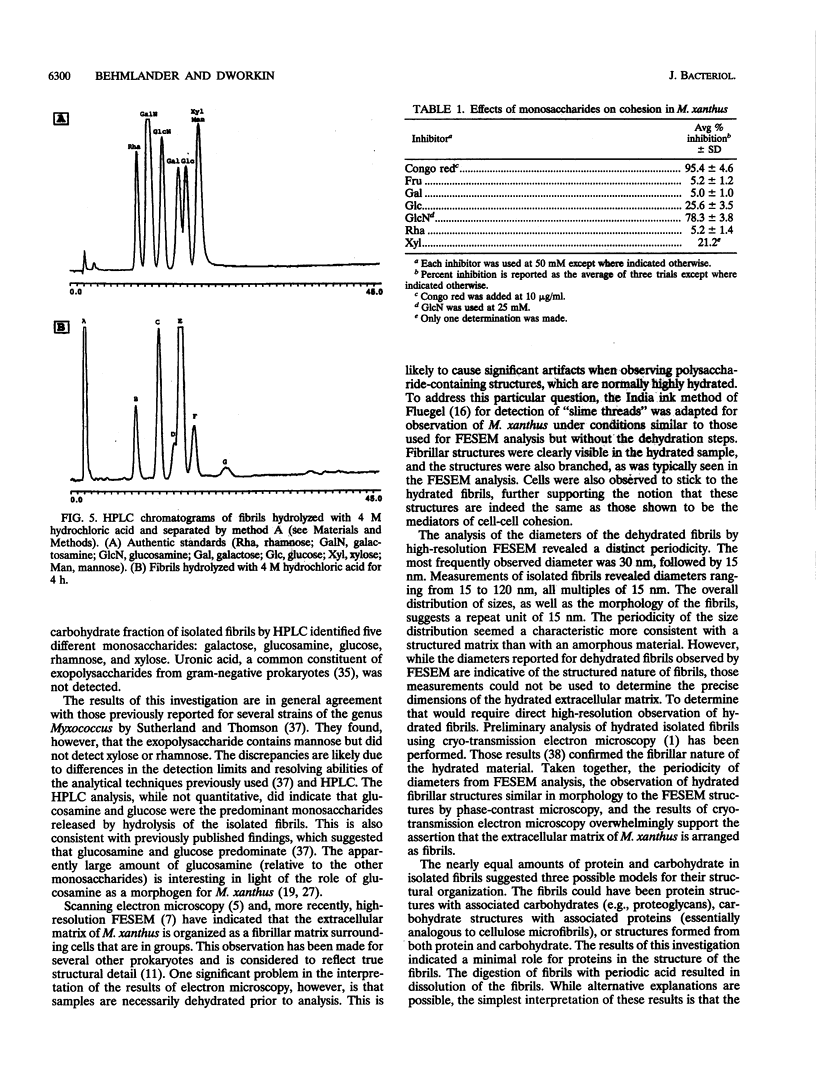
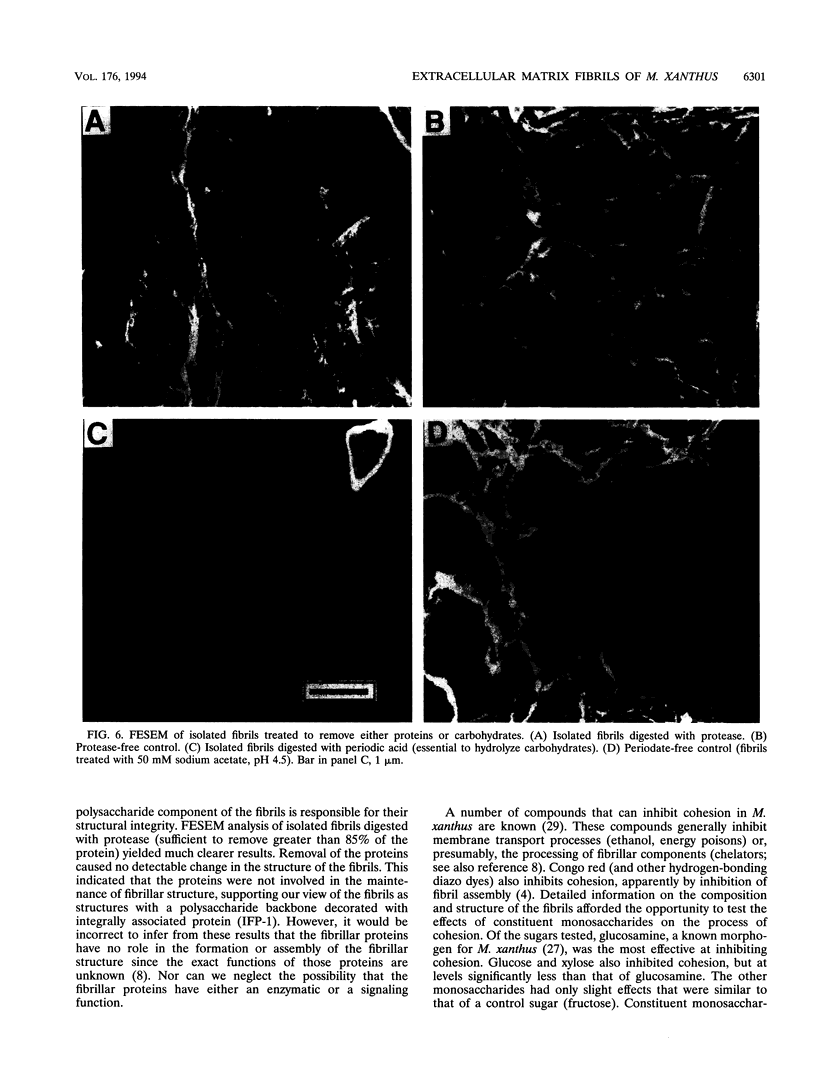
It is characteristic of myxobacteria to produce large amounts of extracellular material. This report demonstrates that this material in Myxococcus xanthus is fibrillar and describes the structure and chemical composition of the fibrils. The extracellular matrix fibrils are the mediators of cell-cell cohesion in M. xanthus. As such, the fibrils play an important role in the cell-cell interactions that form the basis for the social and developmental lifestyle of this organism. The fibrils are composed of protein and carbohydrate in a 1.0:1.2 ratio. Combined, the two fractions accounted for greater than 85% of the mass of isolated fibrils, and the fibrils were found to compose up to 10% of the dry weight of cells grown at high density on a solid surface. The polysaccharide portion of the fibrils was shown to be composed of five different monosaccharides: galactose, glucosamine, glucose, rhamnose, and xylose. Glucosamine, one of the component monosaccharides of the fibrils and a known morphogen for M. xanthus, inhibited cohesion to a level near that of Congo red (the positive control for cohesion inhibition). Glucose and xylose also inhibited cohesion but less than did glucosamine. Analysis of the morphology of the fibrils, the periodicities within the distribution of fibril diameters observed by field emission scanning electron microscopy, and the observation of fibrils on hydrated cells strongly suggested that the extracellular matrix of M. xanthus was indeed arranged as fibrils. Furthermore, results suggested that the fibrils were constructed as carbohydrate structures with associated proteins.
Full text
PDF

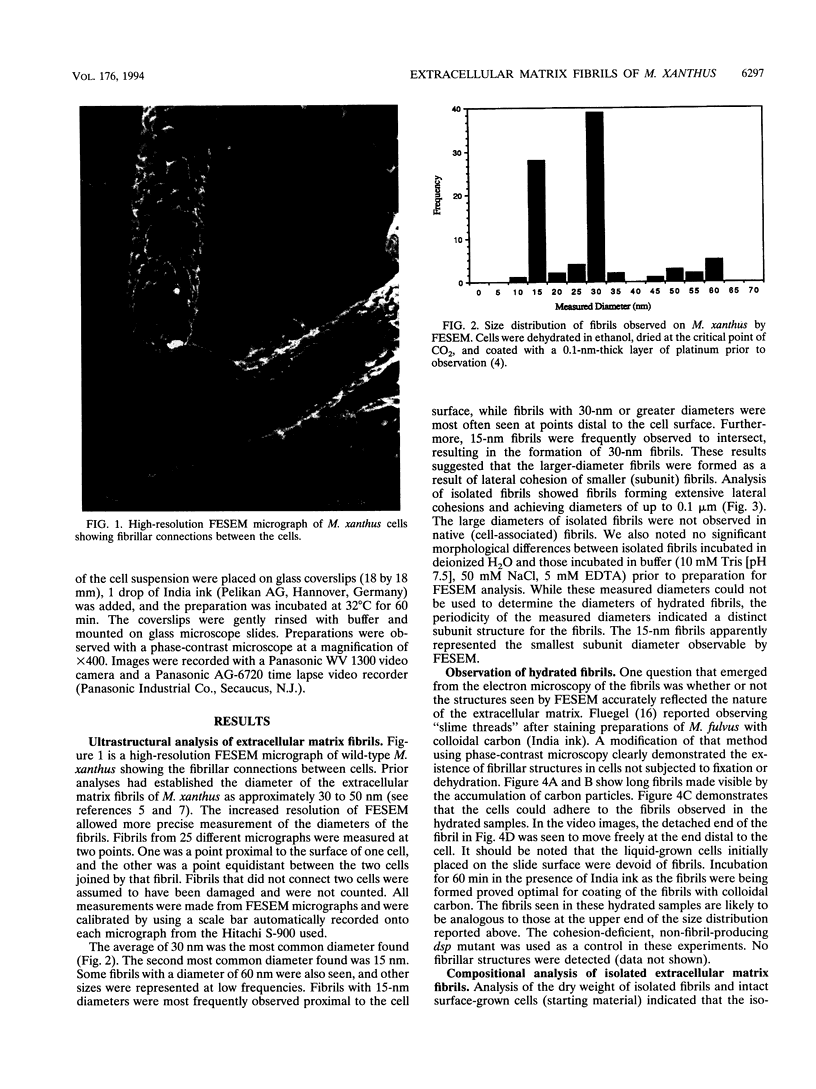



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian M., Dubochet J., Lepault J., McDowall A. W. Cryo-electron microscopy of viruses. Nature. 1984 Mar 1;308(5954):32–36. doi: 10.1038/308032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold J. W., Shimkets L. J. Cell surface properties correlated with cohesion in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5771–5777. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5771-5777.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold J. W., Shimkets L. J. Inhibition of cell-cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus by congo red. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5765–5770. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5765-5770.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behmlander R. M., Dworkin M. Extracellular fibrils and contact-mediated cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7810–7820. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7810-7820.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behmlander R. M., Dworkin M. Integral proteins of the extracellular matrix fibrils of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1994 Oct;176(20):6304–6311. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.20.6304-6311.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Nutrition of Myxococcus xanthus, a fruiting myxobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):763–768. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.763-768.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemans D. L., Chance C. M., Dworkin M. A development-specific protein in Myxococcus xanthus is associated with the extracellular fibrils. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(21):6749–6759. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.21.6749-6759.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Irvin R. T., Cheng K. J. The bacterial glycocalyx in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:299–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dana J. R., Shimkets L. J. Regulation of cohesion-dependent cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3636–3647. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3636-3647.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M., Eide D. Myxococcus xanthus does not respond chemotactically to moderate concentration gradients. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):437–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.437-442.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLUEGEL W. SIMPLE METHOD FOR DEMONSTRATING MYXOBACTERIAL SLIME. J Bacteriol. 1963 May;85:1173–1174. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.5.1173-1174.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen G. R., Dworkin M. Cell-cell interactions in developmental lysis of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1985 Nov;112(1):194–202. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Kaiser D. Cell alignment required in differentiation of Myxococcus xanthus. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):926–928. doi: 10.1126/science.2118274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. F., Shimkets L. J. Effect of dsp mutations on the cell-to-cell transmission of CsgA in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3648–3652. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3648-3652.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCurdy H. D. Studies on the taxonomy of the Myxobacterales. I. Record of Canadian isolates and survey of methods. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Dec;15(12):1453–1461. doi: 10.1139/m69-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Vatter A. E., Baros J., Arnold J. Mechanism of coaggregation between Actinomyces viscosus T14V and Streptococcus sanguis 34. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):978–988. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.978-988.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C., Dworkin M. Effects of glucosamine on lysis, glycerol formation, and sporulation in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7164–7175. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7164-7175.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Correlation of energy-dependent cell cohesion with social motility in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):837–841. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.837-841.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Rafiee H. CsgA, an extracellular protein essential for Myxococcus xanthus development. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5299–5306. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5299-5306.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Role of cell cohesion in Myxococcus xanthus fruiting body formation. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):842–848. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.842-848.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Social and developmental biology of the myxobacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):473–501. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.473-501.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland I. W., Thomson S. Comparison of polysaccharides produced by Myxococcus strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jul;89(1):124–132. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-1-124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]