Abstract
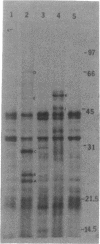
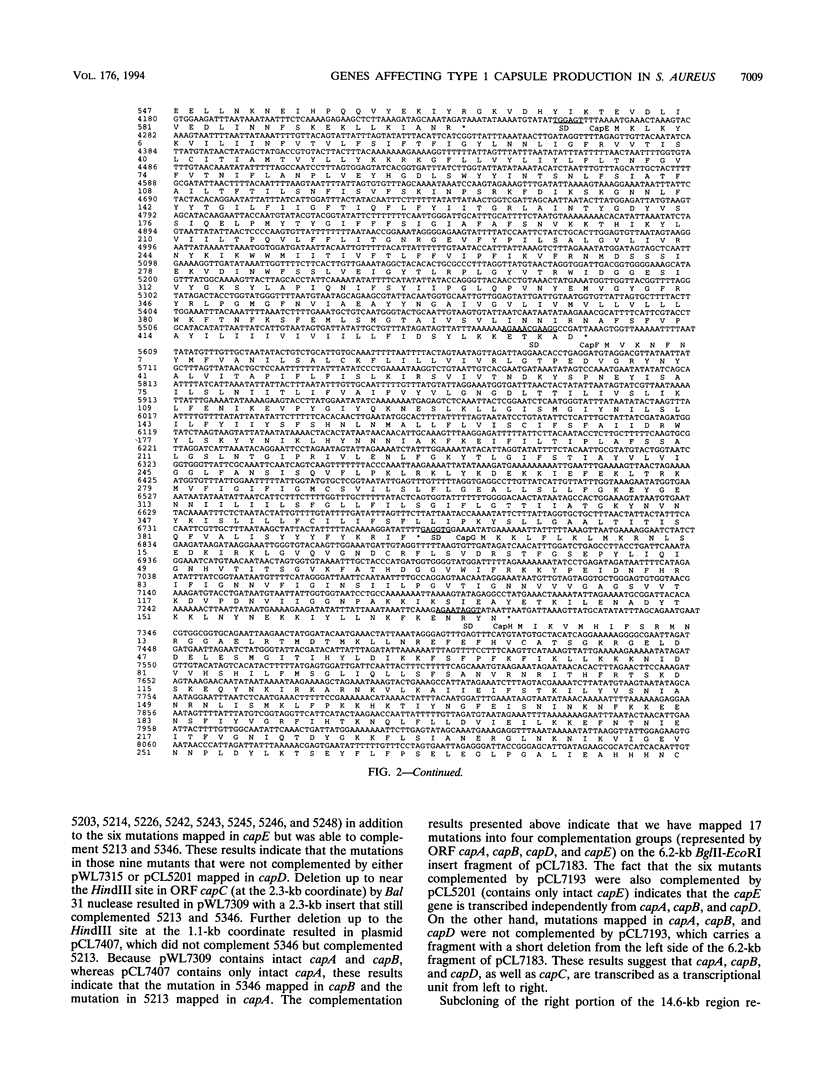
We previously cloned a 19.4-kb DNA region containing a cluster of genes affecting type 1 capsule production from Staphylococcus aureus M. Subcloning experiments showed that these capsule (cap) genes are localized in a 14.6-kb region. Sequencing analysis of the 14.6-kb fragment revealed 13 open reading frames (ORFs). Using complementation tests, we have mapped a collection of Cap- mutations in 10 of the 13 ORFs, indicating that these 10 genes are involved in capsule biosynthesis. The requirement for the remaining three ORFs in the synthesis of the capsule was demonstrated by constructing site-specific mutations corresponding to each of the three ORFs. Using an Escherichia coli S30 in vitro transcription-translation system, we clearly identified 7 of the 13 proteins predicted from the ORFs. Homology search between the predicted proteins and those in the data bank showed very high homology (52.3% identity) between capL and vipA, moderate homology (29% identity) between capI and vipB, and limited homology (21.8% identity) between capM and vipC. The vipA, vipB, and vipC genes have been shown to be involved in the biosynthesis of Salmonella typhi Vi antigen, a homopolymer polysaccharide consisting of N-acetylgalactosamino uronic acid, which is also one of the components of the staphylococcal type 1 capsule. The homology between these sets of genes therefore suggests that capL, capI, and capM may be involved in the biosynthesis of amino sugar, N-acetylgalactosamino uronic acid. In addition, the search showed that CapG aligned well with the consensus sequence of a family of acetyltransferases from various prokaryotic organisms, suggesting that CapG may be an acetyltransferase. Using the isogenic Cap- and Cap+ strains constructed in this study, we have confirmed that type 1 capsule is an important virulence factor in a mouse lethality test.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albus A., Arbeit R. D., Lee J. C. Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus mutants altered in type 5 capsule production. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1008–1014. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1008-1014.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albus A., Fournier J. M., Wolz C., Boutonnier A., Ranke M., Høiby N., Hochkeppel H., Döring G. Staphylococcus aureus capsular types and antibody response to lung infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2505–2509. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2505-2509.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allignet J., Loncle V., Simenel C., Delepierre M., el Solh N. Sequence of a staphylococcal gene, vat, encoding an acetyltransferase inactivating the A-type compounds of virginiamycin-like antibiotics. Gene. 1993 Aug 16;130(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90350-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbeit R. D., Karakawa W. W., Vann W. F., Robbins J. B. Predominance of two newly described capsular polysaccharide types among clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;2(2):85–91. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(84)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddour L. M., Lowrance C., Albus A., Lowrance J. H., Anderson S. K., Lee J. C. Staphylococcus aureus microcapsule expression attenuates bacterial virulence in a rat model of experimental endocarditis. J Infect Dis. 1992 Apr;165(4):749–753. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.4.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastin D. A., Stevenson G., Brown P. K., Haase A., Reeves P. R. Repeat unit polysaccharides of bacteria: a model for polymerization resembling that of ribosomes and fatty acid synthetase, with a novel mechanism for determining chain length. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(5):725–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C. A rapid alkaline extraction method for the isolation of plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:243–255. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downie J. A. The nodL gene from Rhizobium leguminosarum is homologous to the acetyl transferases encoded by lacA and cysE. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1649–1651. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. W., Iandolo J. J. Rapid isolation of DNA from Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):283–285. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.283-285.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göhmann S., Manning P. A., Alpert C. A., Walker M. J., Timmis K. N. Lipopolysaccharide O-antigen biosynthesis in Shigella dysenteriae serotype 1: analysis of the plasmid-carried rfp determinant. Microb Pathog. 1994 Jan;16(1):53–64. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1994.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y., Li N., Yokoyama H., Ezaki T. Complete nucleotide sequence and molecular characterization of ViaB region encoding Vi antigen in Salmonella typhi. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4456–4465. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4456-4465.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochkeppel H. K., Braun D. G., Vischer W., Imm A., Sutter S., Staeubli U., Guggenheim R., Kaplan E. L., Boutonnier A., Fournier J. M. Serotyping and electron microscopy studies of Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates with monoclonal antibodies to capsular polysaccharide types 5 and 8. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):526–530. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.526-530.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Nucleotide sequence and functional map of pC194, a plasmid that specifies inducible chloramphenicol resistance. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):815–825. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.815-825.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Fournier J. M., Vann W. F., Arbeit R., Schneerson R. S., Robbins J. B. Method for the serological typing of the capsular polysaccharides of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Sep;22(3):445–447. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.3.445-447.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Sutton A., Schneerson R., Karpas A., Vann W. F. Capsular antibodies induce type-specific phagocytosis of capsulated Staphylococcus aureus by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1090–1095. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1090-1095.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klena J. D., Ashford R. S., 2nd, Schnaitman C. A. Role of Escherichia coli K-12 rfa genes and the rfp gene of Shigella dysenteriae 1 in generation of lipopolysaccharide core heterogeneity and attachment of O antigen. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(22):7297–7307. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.22.7297-7307.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiswirth B. N., Löfdahl S., Betley M. J., O'Reilly M., Schlievert P. M., Bergdoll M. S., Novick R. P. The toxic shock syndrome exotoxin structural gene is not detectably transmitted by a prophage. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):709–712. doi: 10.1038/305709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Buranen S. L., Ye Z. H. Construction of single-copy integration vectors for Staphylococcus aureus. Gene. 1991 Jul 15;103(1):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90399-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
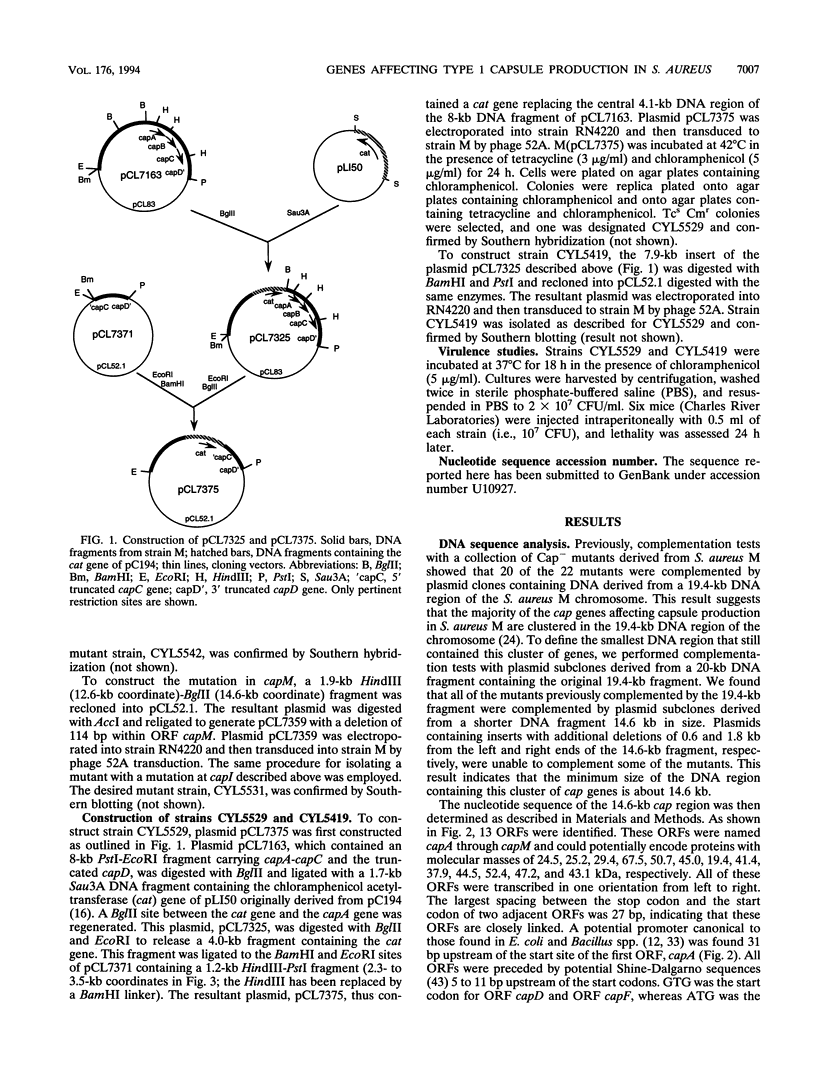
- Lee C. Y. Cloning of genes affecting capsule expression in Staphylococcus aureus strain M. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jun;6(11):1515–1522. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Iandolo J. J. Integration of staphylococcal phage L54a occurs by site-specific recombination: structural analysis of the attachment sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5474–5478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Betley M. J., Hopkins C. A., Perez N. E., Pier G. B. Virulence studies, in mice, of transposon-induced mutants of Staphylococcus aureus differing in capsule size. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):741–750. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire H. G., Müller-Hill B. Nucleotide sequences of the gal E gene and the gal T gene of E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7705–7711. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melly M. A., Duke L. J., Liau D. F., Hash J. H. Biological properties of the encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus M. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):389–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.389-397.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy S. V., Melly M. A., Harris T. M., Hellerqvist C. G., Hash J. H. The repeating sequence of the capsular polysaccharide of Staphylococcus aureus M. Carbohydr Res. 1983 Jun 16;117:113–123. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(83)88080-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent R., Roy P. H. The chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene of Tn2424: a new breed of cat. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):2891–2897. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2891-2897.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Schmeling D., Quie P. G. Influence of encapsulation on staphylococcal opsonization and phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):943–949. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.943-949.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poutrel B., Boutonnier A., Sutra L., Fournier J. M. Prevalence of capsular polysaccharide types 5 and 8 among Staphylococcus aureus isolates from cow, goat, and ewe milk. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jan;26(1):38–40. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.1.38-40.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury S., May T. B., Gill J. F., Singh S. K., Feingold D. S., Chakrabarty A. M. Purification and characterization of guanosine diphospho-D-mannose dehydrogenase. A key enzyme in the biosynthesis of alginate by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9380–9385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. C. A capsulate Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Aug;2(3):253–260. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-3-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Iandolo J. J. Genetics of staphylococcal enterotoxin B in methicillin-resistant isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):902–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.902-911.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Samra Z., Karakawa W. W., Vann W. F., Schneerson R., Malik Z. Encapsulation and capsular types in isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from different sources and relationship to phage types. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):828–834. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.828-834.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennigkeit J., Matzura H. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a chloramphenicol-resistance determinant from Agrobacterium tumefaciens and identification of its gene product. Gene. 1991 Feb 1;98(1):113–116. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90112-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peterson P. K., Nguyen B. Y., Sisson S. P., Kim Y. Opsonization of encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus: the role of specific antibody and complement. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1681–1687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R. F., Kushner S. R. Construction of versatile low-copy-number vectors for cloning, sequencing and gene expression in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1991 Apr;100:195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga R. K., Terpstra P., Hol W. G. Prediction of the occurrence of the ADP-binding beta alpha beta-fold in proteins, using an amino acid sequence fingerprint. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 5;187(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Cryptic peptidoglycan and the antiphagocytic effect of the Staphylococcus aureus capsule: model for the antiphagocytic effect of bacterial cell surface polymers. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):502–508. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.502-508.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu S., Arbeit R. D., Lee J. C. Phagocytic killing of encapsulated and microencapsulated Staphylococcus aureus by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1358–1362. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1358-1362.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye Z. H., Buranen S. L., Lee C. Y. Sequence analysis and comparison of int and xis genes from staphylococcal bacteriophages L54a and phi 11. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2568–2575. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2568-2575.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G. In vitro synthesis of protein in microbial systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:267–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]