Abstract
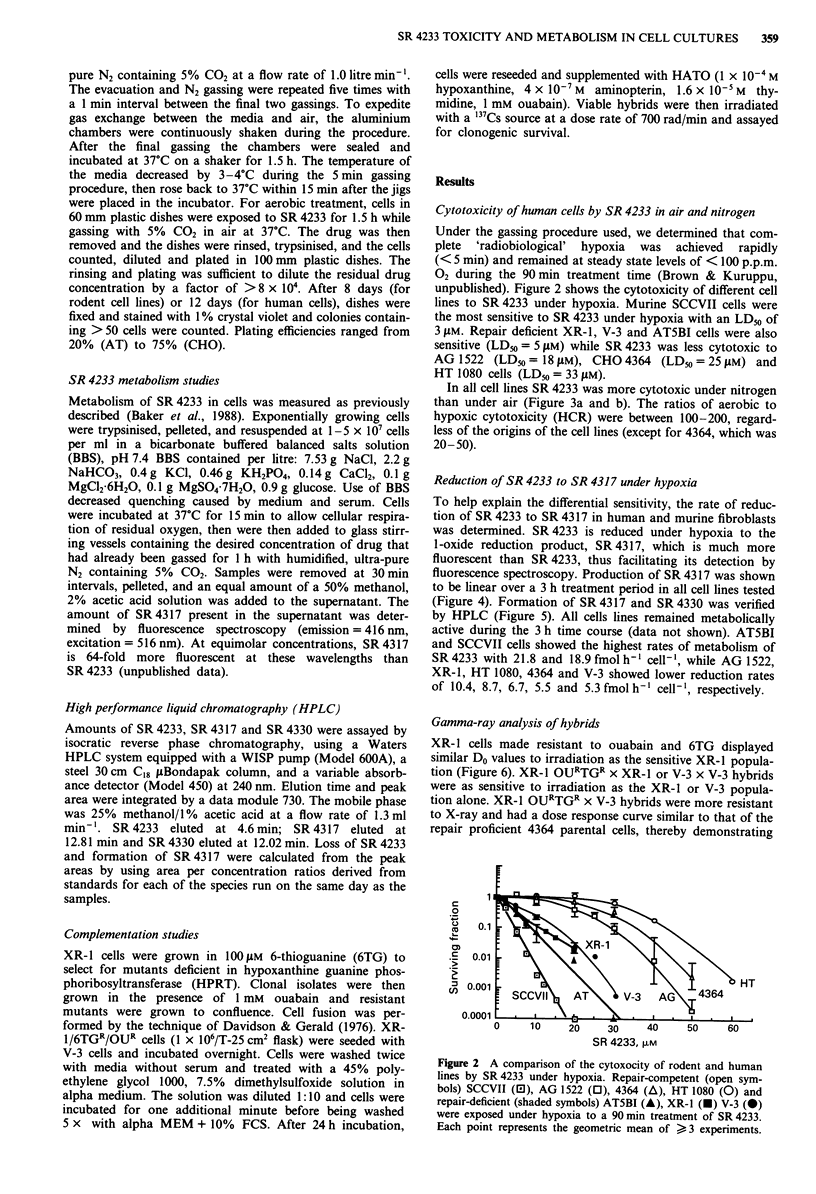
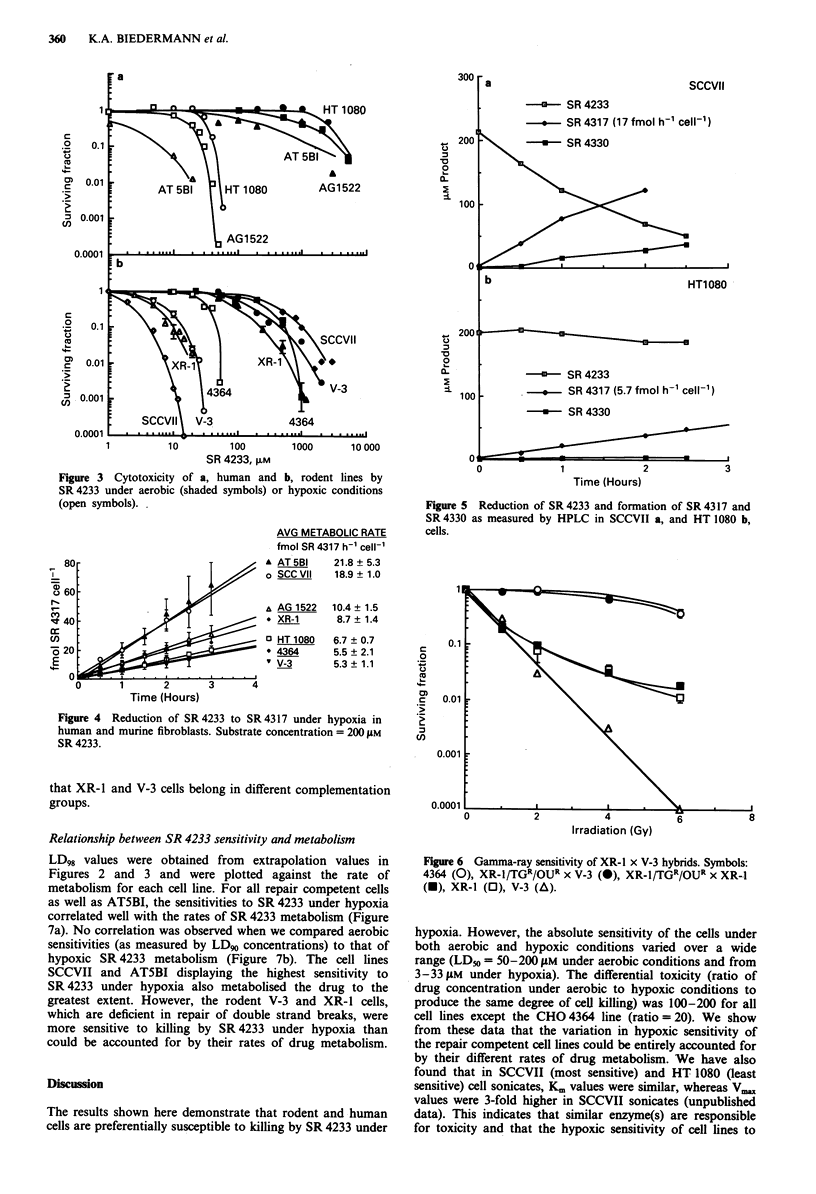
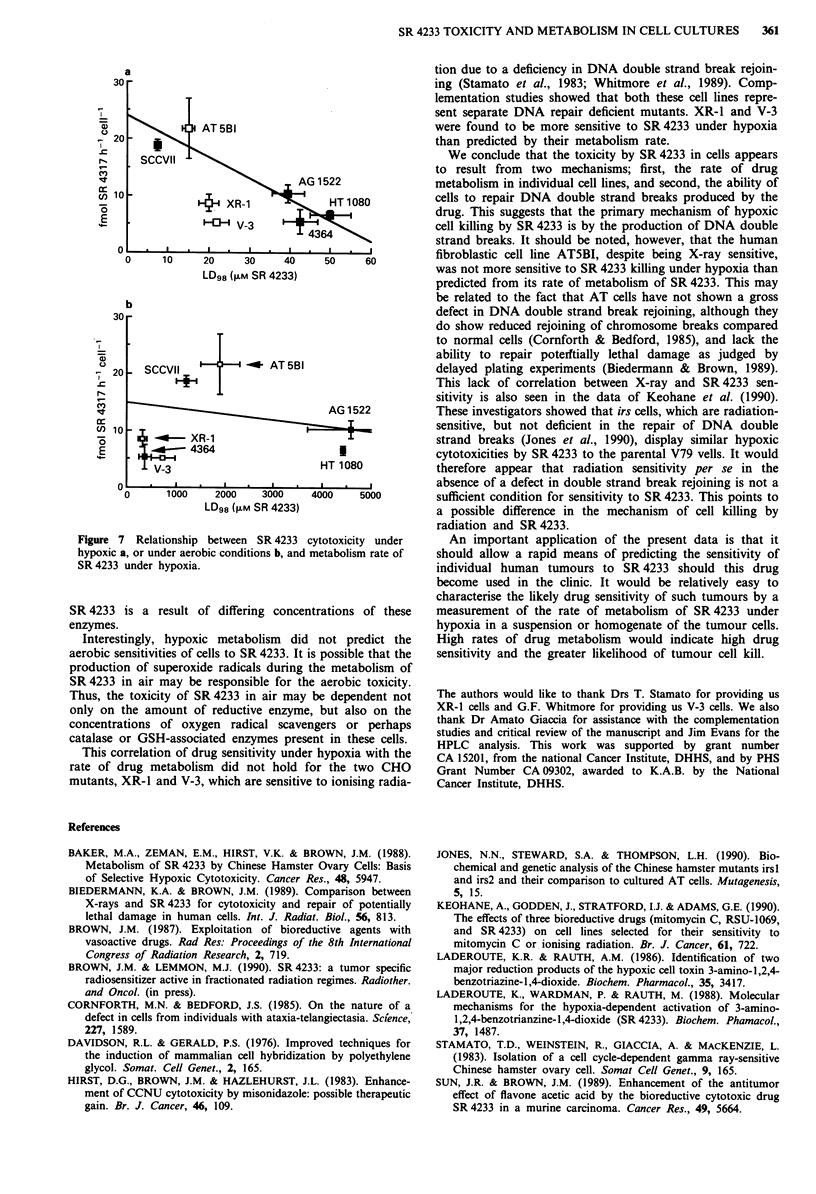
In order to understand in more detail the mechanism underlying the preferential hypoxic cytotoxicity of the benzotriazine N-oxide SR 4233, we have compared the hypoxic cytotoxicity of this drug to the rates of hypoxic metabolism in both DNA double strand break repair-competent and repair-deficient cell cultures. Rodent SCCVII cells and repair deficient, radiation sensitive cells (rodent XR-1, V-3, and human AT5BI) were most sensitive to SR 4233 under hypoxia with a lethal dose needed to kill 50% of cells (LD50) of less than 5 microM. SR 4233 was less cytotoxic to human AG 1522 (LD50 = 18 microM), CHO 4364 (LD50 = 25 microM) and human HT 1080 cells (LD50 = 33 microM). The sensitivities to SR 4233 were found to be inversely proportional to the rates of SR 4233 metabolism in repair-competent cells (R2 = 0.9). However, XR-1 and V-3 cells were more sensitive to SR 4233 than predicted by the metabolism rate. Thus, the toxicity by SR 4233 towards hypoxic cells appears to result from two mechanisms; the rate of drug metabolism and the ability to repair DNA double strand breaks.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker M. A., Zeman E. M., Hirst V. K., Brown J. M. Metabolism of SR 4233 by Chinese hamster ovary cells: basis of selective hypoxic cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. 1988 Nov 1;48(21):5947–5952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedermann K. A., Brown J. M. Comparison between X-rays and SR 4233 for cytotoxicity and repair of potentially lethal damage in human cells. Int J Radiat Biol. 1989 Nov;56(5):813–816. doi: 10.1080/09553008914552091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornforth M. N., Bedford J. S. On the nature of a defect in cells from individuals with ataxia-telangiectasia. Science. 1985 Mar 29;227(4694):1589–1591. doi: 10.1126/science.3975628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L., Gerald P. S. Improved techniques for the induction of mammalian cell hybridization by polyethylene glycol. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 Mar;2(2):165–176. doi: 10.1007/BF01542629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst D. G., Brown J. M., Hazlehurst J. L. Enhancement of CCNU cytotoxicity by misonidazole: possible therapeutic gain. Br J Cancer. 1982 Jul;46(1):109–116. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1982.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. J., Stewart S. A., Thompson L. H. Biochemical and genetic analysis of the Chinese hamster mutants irs1 and irs2 and their comparison to cultured ataxia telangiectasia cells. Mutagenesis. 1990 Jan;5(1):15–23. doi: 10.1093/mutage/5.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keohane A., Godden J., Stratford I. J., Adams G. E. The effects of three bioreductive drugs (mitomycin C, RSU-1069 and SR4233) on cell lines selected for their sensitivity to mitomycin C or ionising radiation. Br J Cancer. 1990 May;61(5):722–726. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laderoute K. R., Rauth A. M. Identification of two major reduction products of the hypoxic cell toxin 3-amino-1,2,4-benzotriazine-1,4-dioxide. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 1;35(19):3417–3420. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90448-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laderoute K., Wardman P., Rauth A. M. Molecular mechanisms for the hypoxia-dependent activation of 3-amino-1,2,4-benzotriazine-1,4-dioxide (SR 4233). Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 15;37(8):1487–1495. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamato T. D., Weinstein R., Giaccia A., Mackenzie L. Isolation of cell cycle-dependent gamma ray-sensitive Chinese hamster ovary cell. Somatic Cell Genet. 1983 Mar;9(2):165–173. doi: 10.1007/BF01543175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. R., Brown J. M. Enhancement of the antitumor effect of flavone acetic acid by the bioreductive cytotoxic drug SR 4233 in a murine carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1989 Oct 15;49(20):5664–5670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMLINSON R. H., GRAY L. H. The histological structure of some human lung cancers and the possible implications for radiotherapy. Br J Cancer. 1955 Dec;9(4):539–549. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1955.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock I., Guttman P. Response of Chinese hamster ovary cells to anticancer drugs under aerobic and hypoxic conditions. Br J Cancer. 1981 Feb;43(2):245–248. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1981.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton M. I., Wolf C. R., Workman P. Molecular enzymology of the reductive bioactivation of hypoxic cell cytotoxins. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989 Apr;16(4):983–986. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(89)90900-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitmore G. F., Varghese A. J., Gulyas S. Cell cycle responses of two X-ray sensitive mutants defective in DNA repair. Int J Radiat Biol. 1989 Nov;56(5):657–665. doi: 10.1080/09553008914551881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeman E. M., Brown J. M., Lemmon M. J., Hirst V. K., Lee W. W. SR-4233: a new bioreductive agent with high selective toxicity for hypoxic mammalian cells. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986 Jul;12(7):1239–1242. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(86)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeman E. M., Hirst V. K., Lemmon M. J., Brown J. M. Enhancement of radiation-induced tumor cell killing by the hypoxic cell toxin SR 4233. Radiother Oncol. 1988 Jul;12(3):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0167-8140(88)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


