Abstract
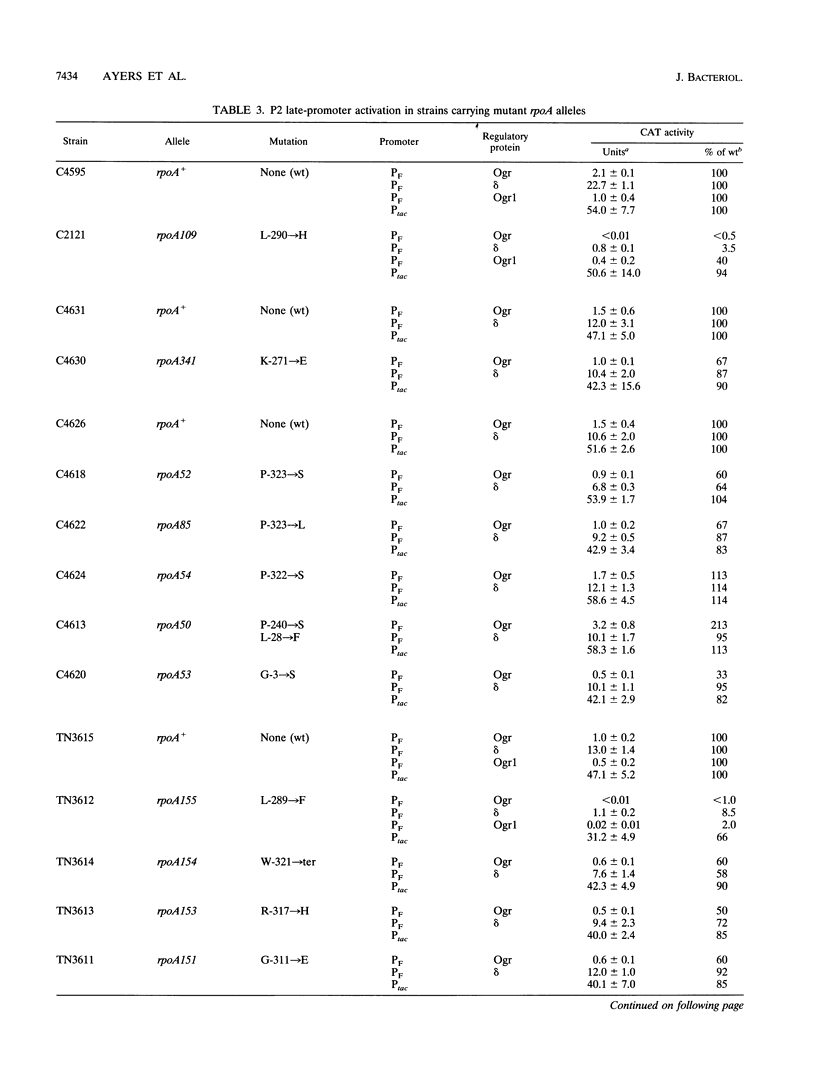
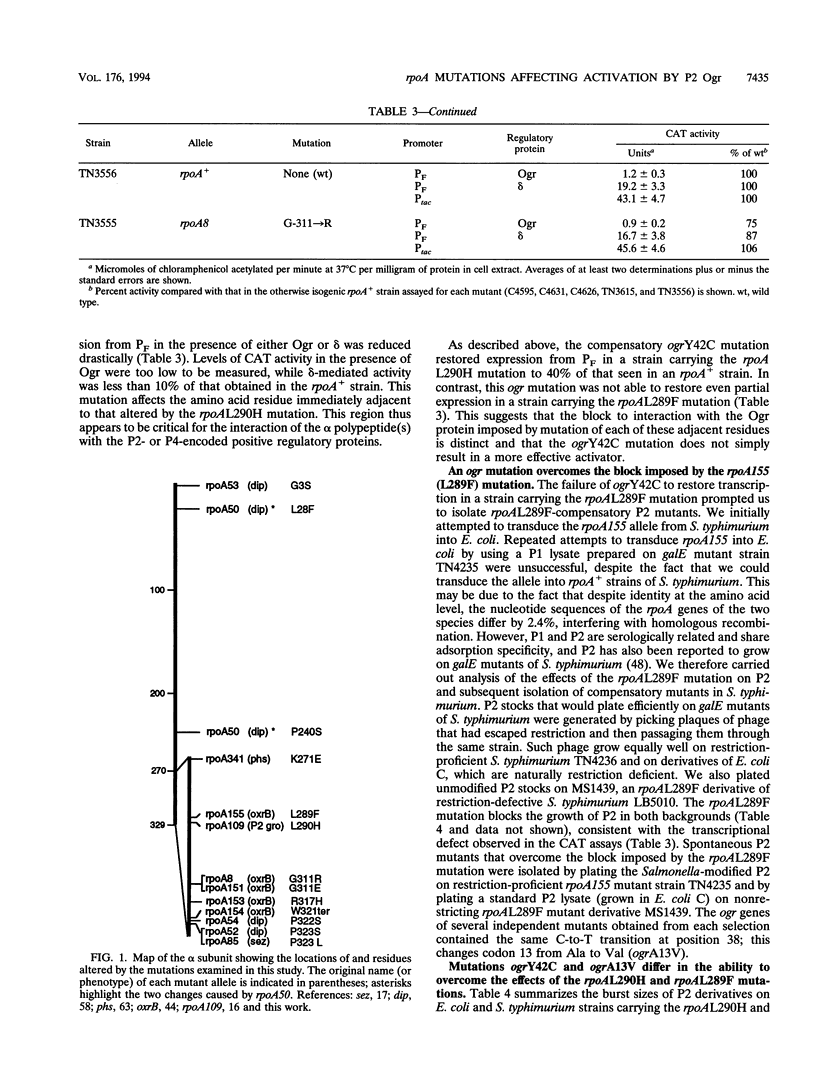
The bacteriophage P2 ogr gene product is a positive regulator of transcription from P2 late promoters. The ogr gene was originally defined by compensatory mutations that overcame the block to P2 growth imposed by a host mutation, rpoA109, in the gene encoding the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. DNA sequence analysis has confirmed that this mutation affects the C-terminal region of the alpha subunit, changing a leucine residue at position 290 to a histidine (rpoAL290H). We have employed a reporter plasmid system to screen other, previously described, rpoA mutants for effects on activation of a P2 late promoter and have identified a second allele, rpoA155, that blocks P2 late transcription. This mutation lies just upstream of rpoAL290H, changing the leucine residue at position 289 to a phenylalanine (rpoAL289F). The effect of the rpoAL289F mutation is not suppressed by the rpoAL290H-compensatory P2 ogr mutation. P2 ogr mutants that overcome the block imposed by rpoAL289F were isolated and characterized. Our results are consistent with a direct interaction between Ogr and the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase and support a model in which transcription factor contact sites within the C terminus of alpha are discrete and tightly clustered.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Garges S. Positive control. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10797–10800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTANI L. E. The effect of the inhibition of protein synthesis on the establishment of lysogeny. Virology. 1957 Aug;4(1):53–71. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barreiro V., Haggård-Ljungquist E. Attachment sites for bacteriophage P2 on the Escherichia coli chromosome: DNA sequences, localization on the physical map, and detection of a P2-like remnant in E. coli K-12 derivatives. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):4086–4093. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.4086-4093.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell A., Gaston K., Williams R., Chapman K., Kolb A., Buc H., Minchin S., Williams J., Busby S. Mutations that alter the ability of the Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein to activate transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7243–7250. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard H. U., Helinski D. R. Use of the lambda phage promoter PL to promote gene expression in hybrid plasmid cloning vehicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:482–492. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkeland N. K., Lindquist B. H. Coliphage P2 late control gene ogr. DNA sequence and product identification. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):487–490. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90170-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullas L. R., Ryu J. I. Salmonella typhimurium LT2 strains which are r- m+ for all three chromosomally located systems of DNA restriction and modification. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):471–474. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.471-474.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Shang C., Ptashne M. A single glutamic acid residue plays a key role in the transcriptional activation function of lambda repressor. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1163–1171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90514-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. E., Calendar R. Bacteriophage P2 late promoters. II. Comparison of the four late promoter sequences. J Mol Biol. 1985 Feb 5;181(3):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90226-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. E., Calendar R. Bacteriophage P2 late promoters. Transcription initiation sites for two late mRNAs. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 15;167(4):773–790. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80110-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. E., Haggård-Ljungquist E., Feiwell R., Calendar R. Regulation of bacteriophage P2 late-gene expression: the ogr gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3238–3242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowl R., Seamans C., Lomedico P., McAndrew S. Versatile expression vectors for high-level synthesis of cloned gene products in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90200-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H. Transcription activation at Class I CAP-dependent promoters. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(5):797–802. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenlauer A. C., Reznikoff W. S. Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein mutants defective in positive control of lac operon transcription. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5024–5029. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5024-5029.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki H., Palm P., Zillig W., Calendar R., Sunshine M. Identification of a mutation within the structural gene for the a subunit of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Apr 23;145(1):19–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00331552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett S., Silhavy T. J. Isolation of mutations in the alpha operon of Escherichia coli that suppress the transcriptional defect conferred by a mutation in the porin regulatory gene envZ. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1379–1385. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1379-1385.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisselsoder J., Mandel M., Calendar R., Chattoraj D. K. In vivo transcription patterns of temperate coliphage P2. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jul 5;77(3):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90447-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giffard P. M., Booth I. R. The rpoA341 allele of Escherichia coli specifically impairs the transcription of a group of positively-regulated operons. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Sep;214(1):148–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00340193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giffard P. M., Rowland G. C., Kroll R. G., Stewart L. M., Bakker E. P., Booth I. R. Phenotypic properties of a unique rpoA mutation (phs) of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):904–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.904-910.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giladi H., Igarashi K., Ishihama A., Oppenheim A. B. Stimulation of the phage lambda pL promoter by integration host factor requires the carboxy terminus of the alpha-subunit of RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):985–990. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90514-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grambow N. J., Birkeland N. K., Anders D. L., Christie G. E. Deletion analysis of a bacteriophage P2 late promoter. Gene. 1990 Oct 30;95(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90407-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Nye J. S., Hochschild A., Ptashne M. Mutant lambda phage repressor with a specific defect in its positive control function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2236–2239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gussin G. N., Olson C., Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Activation defects caused by mutations in Escherichia coli rpoA are promoter specific. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):5156–5160. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.5156-5160.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halling C., Sunshine M. G., Lane K. B., Six E. W., Calendar R. A mutation of the transactivation gene of satellite bacteriophage P4 that suppresses the rpoA109 mutation of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3541–3548. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3541-3548.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. The effect of a lambda repressor mutation on the activation of transcription initiation from the lambda PRM promoter. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):327–333. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90452-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Irwin N., Ptashne M. Repressor structure and the mechanism of positive control. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90451-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Identification of a subunit assembly domain in the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 5;218(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Sequence analysis of two temperature-sensitive mutations in the alpha subunit gene (rpoA) of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):5945–5948. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.5945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Hanamura A., Makino K., Aiba H., Aiba H., Mizuno T., Nakata A., Ishihama A. Functional map of the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: two modes of transcription activation by positive factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8958–8962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Bipartite functional map of the E. coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit: involvement of the C-terminal region in transcription activation by cAMP-CRP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1015–1022. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90553-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A. Protein-protein communication within the transcription apparatus. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2483–2489. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2483-2489.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A. Role of the RNA polymerase alpha subunit in transcription activation. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(22):3283–3288. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A., Shimamoto N., Aiba H., Kawakami K., Nashimoto H., Tsugawa A., Uchida H. Temperature-sensitive mutations in the alpha subunit gene of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 25;137(2):137–150. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90321-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi A. K., Baichwal V., Ames G. F. Rapid polymerase chain reaction amplification using intact bacterial cells. Biotechniques. 1991 Jan;10(1):42, 44-5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. A., Anders D. L., Christie G. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of an amino acid residue in the bacteriophage P2 ogr protein implicated in interaction with Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(22):3313–3320. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Igarashi K., Ishihama A., Lavigne M., Buckle M., Buc H. E. coli RNA polymerase, deleted in the C-terminal part of its alpha-subunit, interacts differently with the cAMP-CRP complex at the lacP1 and at the galP1 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 25;21(2):319–326. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. C., Christie G. E. Purification and properties of the bacteriophage P2 ogr gene product. A prokaryotic zinc-binding transcriptional activator. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7472–7477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel J. A., Calendar R. Control of bacteriophage P2 protein and DNA synthesis. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):305–313. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90170-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., Moyle H., Susskind M. M. Target of the transcriptional activation function of phage lambda cI protein. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):75–77. doi: 10.1126/science.8272867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. C., Squires C. L., Squires C. Antitermination of E. coli rRNA transcription is caused by a control region segment containing lambda nut-like sequences. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):851–860. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl G. On the control of transcription in bacteriophage P2. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):620–633. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo M. J., Bagga D., Miller C. G. Mutations in rpoA affect expression of anaerobically regulated genes in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7511–7518. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7511-7518.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama S., Mizushima S. Novel rpoA mutation that interferes with the function of OmpR and EnvZ, positive regulators of the ompF and ompC genes that code for outer-membrane proteins in Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90489-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornellas E. P., Stocker B. A. Relation of lipopolysaccharide character to P1 sensitivity in Salmonella typhimurium. Virology. 1974 Aug;60(2):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90343-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Gosink K. K., Salomon J., Igarashi K., Zou C., Ishihama A., Severinov K., Gourse R. L. A third recognition element in bacterial promoters: DNA binding by the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1407–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.8248780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland G. C., Giffard P. M., Booth I. R. Genetic studies of the phs locus of Escherichia coli, a mutation causing pleiotropic lesions in metabolism and pH homeostasis. FEBS Lett. 1984 Aug 6;173(2):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80794-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland G. C., Giffard P. M., Booth I. R. phs Locus of Escherichia coli, a mutation causing pleiotropic lesions in metabolism, is an rpoA allele. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):972–975. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.972-975.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo F. D., Silhavy T. J. Alpha: the Cinderella subunit of RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14515–14518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakumi K., Igarashi K., Sekiguchi M., Ishihama A. The Ada protein is a class I transcription factor of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(8):2455–2457. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.8.2455-2457.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki I., Bertani G. Growth abnormalities in Hfr derivatives of Escherichia coli strain C. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Sep;40(3):365–376. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-3-365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharif T. R., Igo M. M. Mutations in the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase that affect the regulation of porin gene transcription in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(17):5460–5468. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.17.5460-5468.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:737–755. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Six E. W. The helper dependence of satellite bacteriophage P4: which gene functions of bacteriophage P2 are needed by P4? Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):249–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90422-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slauch J. M., Russo F. D., Silhavy T. J. Suppressor mutations in rpoA suggest that OmpR controls transcription by direct interaction with the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7501–7510. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7501-7510.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slettan A., Gebhardt K., Kristiansen E., Birkeland N. K., Lindqvist B. H. Escherichia coli K-12 and B contain functional bacteriophage P2 ogr genes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):4094–4100. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.4094-4100.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza L., Calendar R., Six E. W., Lindqvist B. H. A transactivation mutant of satellite phage P4. Virology. 1977 Aug;81(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunshine M. G., Sauer B. A bacterial mutation blocking P2 phage late gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2770–2774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao K., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Involvement of the RNA polymerase alpha subunit C-terminal region in co-operative interaction and transcriptional activation with OxyR protein. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(6):859–864. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. S., Glass R. E. Escherichia coli rpoA mutation which impairs transcription of positively regulated systems. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2719–2725. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Bokkelen G. B., Dale E. C., Halling C., Calendar R. Mutational analysis of a bacteriophage P4 late promoter. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):37–45. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.37-45.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y., Zhang X., Ebright R. H. Identification of the activating region of catabolite gene activator protein (CAP): isolation and characterization of mutants of CAP specifically defective in transcription activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6081–6085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zou C., Fujita N., Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Mapping the cAMP receptor protein contact site on the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2599–2605. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


